Professional Documents
Culture Documents
9Bb-4 Adapts For Photosyn
Uploaded by
Umraan AhmadOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
9Bb-4 Adapts For Photosyn
Uploaded by
Umraan AhmadCopyright:
Available Formats
Adaptations for
9Bb-4 photosynthesis
Water is needed to fill up the cells of plants, to help the plants stand up straight. Water also carries
dissolved mineral salts. Roots take in the water. Roots have many branches, which means that
they can hold a plant firmly in the ground. This also gives them a large surface area to take in
water from a large volume of soil quickly. The stem is strong to support the leaves and contains
many hollow tubes to carry the water to the leaves. Leaves have small holes called stomata and
gases move in and out of the leaf through these (e.g. carbon dioxide for photosynthesis). Leaves
have a large surface area to collect lots of light.
1 In the passage, underline three phrases that describe a process for which water is needed.
2 Parts of roots contain root hair tissue. Draw a box around the sentence in the passage that best
describes why.
3 a What is gas exchange?
b In the passage, circle one chemical substance that takes part in gas exchange in a plant.
c In what plant organ does gas exchange mainly occur?
d Give one way in which this organ is adapted for gas exchange.
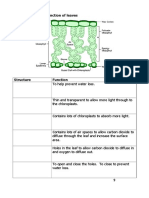
4 a The cells that carry out most photosynthesis are
shown in the drawing. How are they adapted to
their function?
b Apart from their cells, explain one other way in which leaves are adapted for
photosynthesis.
5 Describe the route that water takes into and out of a plant.
I can…
● describe how leaves, roots and stems are adapted for their functions
● explain how substances enter and leave plants.
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015. Copying permitted for
purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free. 15
You might also like
- 9Bb-4 Adapts For PhotosynDocument1 page9Bb-4 Adapts For PhotosynHAMAD NoorNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 - Questions - Summary S2024Document6 pagesLecture 12 - Questions - Summary S2024sydneepnNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes - Plant ScienceDocument8 pagesBiology Notes - Plant Sciencesarah_beck100% (1)
- CAPEc 05Document26 pagesCAPEc 05Isheba Warren100% (2)
- 8.0 Transport in PlantsDocument9 pages8.0 Transport in Plantskhenso sitholeNo ratings yet
- Structureoftheleaf Complete LessonDocument28 pagesStructureoftheleaf Complete Lessonjerylle25No ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument35 pagesTransport in PlantsChantae JulienNo ratings yet
- Bio LabDocument13 pagesBio Labapi-3730385100% (9)
- Midterm Exam in Plant Phy.Document7 pagesMidterm Exam in Plant Phy.Jingjing AguilarNo ratings yet
- 9.1 Plant Structure and Growth: Topic 9: Plant Science (HL)Document6 pages9.1 Plant Structure and Growth: Topic 9: Plant Science (HL)Morgan LockeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Structure and Functions of Leaves Student WorksheetDocument3 pagesLesson 5 Structure and Functions of Leaves Student WorksheetEunice Xiiao Wenn100% (2)
- Topic 8 Revision Notes 2btdx6pDocument4 pagesTopic 8 Revision Notes 2btdx6psalmasomaNo ratings yet
- B5.1 Revision Notes Wk700bDocument3 pagesB5.1 Revision Notes Wk700bmaraamNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plant SDADocument5 pagesTransport in Plant SDAkmakabe78No ratings yet
- Self-Paced Learning Module Gen Bio 1 Week 2Document10 pagesSelf-Paced Learning Module Gen Bio 1 Week 2Ashley Jade DomalantaNo ratings yet
- Answer Key For Class 8 J Biology J Transport in PlantsDocument3 pagesAnswer Key For Class 8 J Biology J Transport in Plantsgea1300015No ratings yet
- Transport in Plants PDFDocument26 pagesTransport in Plants PDFMasOom Si ChuRail100% (2)
- Screenshot 2022-09-30 at 11.20.12 AMDocument23 pagesScreenshot 2022-09-30 at 11.20.12 AMgs6b974fwvNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument20 pagesBiologyAMRA IQBALNo ratings yet
- Plant TransportDocument41 pagesPlant Transportyohoho 87No ratings yet
- Section C: Plant Physiology: Plants and FoodDocument8 pagesSection C: Plant Physiology: Plants and FoodMD MotinNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology 4.2 Plant NutritionDocument14 pagesIGCSE Biology 4.2 Plant NutritionsarNo ratings yet
- 1 TranspirationDocument20 pages1 TranspirationSuriez DoNo ratings yet
- Alexa Riley - Transpiration LabDocument7 pagesAlexa Riley - Transpiration Labapi-553676905No ratings yet
- QUIZ 1 Chapter 2 Leaf StructureDocument2 pagesQUIZ 1 Chapter 2 Leaf StructureoliviaNo ratings yet
- Topic 8 Transport in Plants: 8.1 Vascular Tissue Functions of Xylem & PhloemDocument10 pagesTopic 8 Transport in Plants: 8.1 Vascular Tissue Functions of Xylem & PhloemMuhammad Hassan TariqNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants HandoutDocument5 pagesTransport in Plants HandoutAsawni McDowellNo ratings yet
- The Shoot System II: The Form and Structure of LeavesDocument22 pagesThe Shoot System II: The Form and Structure of LeavesTristan LirioNo ratings yet
- 8.1 - Transport in PlantsDocument9 pages8.1 - Transport in PlantsAvyay TopraniNo ratings yet
- Transport of Materials in Flowering Plants + Trans LocationDocument71 pagesTransport of Materials in Flowering Plants + Trans LocationCarolyn KhooNo ratings yet
- ch7 NotesDocument6 pagesch7 Notesisabella cucumberNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Transport in PlantsDocument3 pagesChapter 8 - Transport in PlantsLeann LeeNo ratings yet
- Biology Questions and Answers Form 2Document41 pagesBiology Questions and Answers Form 2Zubin Jammaa FulaniNo ratings yet
- Adaptations of MangrovesDocument3 pagesAdaptations of MangrovesLeonard LennoxNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument34 pagesTransport in PlantsYagna LallNo ratings yet
- Hortbot Lesson Plan6Document9 pagesHortbot Lesson Plan6BarbyannNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Transport System in PlantsDocument18 pagesForm 3 Transport System in PlantsachikgaiNo ratings yet
- Sugars, Starches and CelluloseDocument4 pagesSugars, Starches and CelluloseCitraNo ratings yet
- Biozone 2 PG 342Document3 pagesBiozone 2 PG 342Ji-Soo KimNo ratings yet
- 28 02 14 The Exchange System in PlantsDocument53 pages28 02 14 The Exchange System in Plantsapi-263322904No ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument20 pagesTransport in PlantsLeon XuNo ratings yet
- GCSE Biology Physiology Part 2 (Transport in Plants)Document3 pagesGCSE Biology Physiology Part 2 (Transport in Plants)Fasih AhmadNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Plants and WaterDocument27 pages4.1 Plants and Waternyanmoemyat2010No ratings yet
- Writtenreport AllauiganxcerenoDocument9 pagesWrittenreport AllauiganxcerenoFerdinand RyanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Nutrition and Gas Exchange in Plants: Learning ObjectivesDocument14 pagesChapter 10 - Nutrition and Gas Exchange in Plants: Learning Objectivesthanks btNo ratings yet
- Alwadi International School Biology Grade-9 6.plant Nutrition NotesDocument50 pagesAlwadi International School Biology Grade-9 6.plant Nutrition NotesMohammed HelmyNo ratings yet
- Biology Written SectionDocument3 pagesBiology Written Sectionsherrypan1213No ratings yet
- Plants (HL)Document25 pagesPlants (HL)Boris-Jeremie-Latyr GueyeNo ratings yet
- Leaf Structure Plant NutritionDocument5 pagesLeaf Structure Plant NutritionShahed Bulbul PaponNo ratings yet
- Part 1 Plant TransportDocument28 pagesPart 1 Plant Transportrawan SaketNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument20 pagesTransport in PlantsForthtNo ratings yet
- Biology Icse CHP 4 Absorption by RootsDocument25 pagesBiology Icse CHP 4 Absorption by RootsAMRA IQBALNo ratings yet
- KSSM Bio F5 C2Document84 pagesKSSM Bio F5 C2Jia XuanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Biology 11Document52 pagesChapter 13 Biology 11ax1leNo ratings yet
- LeavesDocument3 pagesLeavessssfiresssNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In PlantsFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In PlantsNo ratings yet
- How Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersFrom EverandHow Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersNo ratings yet
- Hydroponic Gardening: A Beginner Guide to Learn How to Design and Build Your Own Sustainable Hydroponics System, for Growing Plants and Vegetables at HomeFrom EverandHydroponic Gardening: A Beginner Guide to Learn How to Design and Build Your Own Sustainable Hydroponics System, for Growing Plants and Vegetables at HomeNo ratings yet