Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Effect of PH
Uploaded by
Samvit MahashayOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Effect of PH
Uploaded by
Samvit MahashayCopyright:
Available Formats
Date :
EFFECT OF DIFFERENT pH ON ACTIVITY OF β-AMYLASE ENZYME EXTRACTED FROM
SWEET POTATO
Aim: To study the effect of different pH on the activity of β-amylase enzyme extracted from sweet potato.
Requirements: Sweet potato, funnel, conical flask, cotton, filter paper, plate, distilled water, mortar and
pestle, DNSA reagent, boiling water bath, 0.2% NaCl, different pH of acetate buffer (0.2M) – pH 4.2, 4.6,
4.8, 5.0, 5.2, 5.4, 16 test tubes, 210ml pipettes.
Principle: Activity of β-amylase is analysed by the maltose that is produced by its activity on starch.
Maltose being a reducing sugar, reduces 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid to 3-amino-5-nitro salicylic acid which
is orange brown in colour. The colour intensity is read at 520 nm.
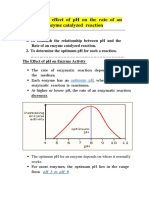
Each enzyme has it's optimum pH at which it shows maximum activity, above or below which the activity
declines. Very high or low pH affects the ionic properties of amino acids at the active site of the enzyme,
thus affecting its activity. Optimum pH is decided by the type of amino acids that make up the active site
of the enzyme.
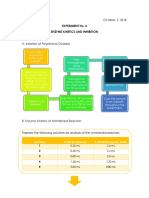
Procedure: Prepare the following set of tubes as shown in the chart.
Calculations: Henderson Hasselbalch equation is used to prepare buffers
pH Volume of CH3COOH (ml) Volume of CH3COONa (ml) Total volume
4.2 0.784 0.216 1.000
4.4 0.696 0.304 1.000
4.6 0.591 0.409 1.000
4.8 0.477 0.523 1.000
5.0 0.365 0.635 1.000
5.2 0.266 0.734 1.000
Observation Table :
pH Acetate 2% 0.2% Instructions Enzyme Instructions Corrected
buffer Starch NaCl Extract Abs (520
(ml) Solution Solution (ml) nm)
(ml) (ml)
Blank 1.0 1.0 1.0 Keep all test 1.0 Keep all tubes at
(D/W) tubes at 37°C (D/W) 37°C for 30
for 5 minutes. minutes. Then
4.2 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 take 1 ml of
reaction mixture
into
4.4 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 corresponding
tubes having 1ml
DNSA reagent.
4.6 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 Keep in a
boiling water
bath for 5
minutes, colour
4.8 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
change occurs.
Cool the test
tubes and add
5.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 8ml d/w. Take
absorbance at
520 nm.
5.2 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
5.4 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
Graph: Plot a graph of Absorbance at 520 nm on Y-axis v/s pH on X-axis
Result: The enzyme β-amylase shows maximum activity at pH .
Thus pH is the optimum pH for β-amylase enzyme activity.
Viva questions :-
Q - What are the examples of enzymes with optimum pH?
Ans -
Enzyme Optimum pH
Lipase (pancreas) 8.0
Lipase (stomach) 4.0-5.0
Lipase (castor oil) 4.7
Pepsin 1.5-1.6
Trypsin 7.8-8.7
Urease 7.0
Invertase 4.5
Maltase 6.1-6.8
Amylase 6.7-7.0
Amylase (malt) 4.6-5.2
Catalase 7.0
Q- Explain the nature of the graph of effect of pH on enzymes?
Ans-The most favorable pH value - the point where the enzyme is most active - is known as the optimum
pH. Extremely high or low pH values generally result in complete loss of activity for most enzymes.
The inflection points on each side of the curve represent the pKa of the critical R-groups in the
enzyme.The inflection points on each side of the curve represent the pKa of the critical R-groups in the
enzyme. http://plantphys.info/plant_physiology/enzymekinetics.shtml
******
You might also like
- The Total Synthesis of Natural ProductsFrom EverandThe Total Synthesis of Natural ProductsJohn ApSimonNo ratings yet
- Compound Forming Extractants, Solvating Solvents and Inert Solvents: Iupac Chemical Data SeriesFrom EverandCompound Forming Extractants, Solvating Solvents and Inert Solvents: Iupac Chemical Data SeriesNo ratings yet
- Production of L-Asparginase From Submerged Fermentation & Solid-State FermentationDocument10 pagesProduction of L-Asparginase From Submerged Fermentation & Solid-State FermentationAnuraj DaheriyaNo ratings yet
- Practical 3Document9 pagesPractical 3ARYSSA BINTI AZRINo ratings yet
- Alkaline Phosphatase Assay Kit InstructionsDocument3 pagesAlkaline Phosphatase Assay Kit InstructionsLinh ĐỗNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Kinetics and Inhibition ExperimentDocument2 pagesEnzyme Kinetics and Inhibition ExperimentAnonymous s2jaDmP5FNo ratings yet
- ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY of NIPA SAP DRAFT 1 PDFDocument13 pagesANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY of NIPA SAP DRAFT 1 PDFnabilaNo ratings yet
- Bio Lab 2Document7 pagesBio Lab 2CassyNo ratings yet
- Determination of Phytase Activity PDFDocument4 pagesDetermination of Phytase Activity PDFrdvemedimNo ratings yet
- LDH OutlineDocument7 pagesLDH OutlinejahnNo ratings yet
- Act 3 Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity PH and Inhibitors PDFDocument3 pagesAct 3 Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity PH and Inhibitors PDFGezem GigantoNo ratings yet
- DOC316.53.01234 9edDocument6 pagesDOC316.53.01234 9edWater QualityNo ratings yet
- Lactase Enzyme SpectrophotometryDocument9 pagesLactase Enzyme SpectrophotometryBenito KameloNo ratings yet
- Lab Practical 2Document4 pagesLab Practical 2asdadadNo ratings yet
- ENCARNACION, Jericho P - AnaChemLab - ExperimentNo11Document6 pagesENCARNACION, Jericho P - AnaChemLab - ExperimentNo11Jericho EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Protein Isolation TechniquesDocument8 pagesProtein Isolation TechniquesIsla CalugayNo ratings yet
- S AzcasDocument8 pagesS Azcasعبدالاعلا نوریNo ratings yet
- HTBC003Document10 pagesHTBC003Amal ..No ratings yet
- Assay of Amylase ActivityDocument17 pagesAssay of Amylase ActivityPeach BabyNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 - Effect of Enzyme Concentration On Enzyme ActivityDocument5 pagesExperiment 4 - Effect of Enzyme Concentration On Enzyme ActivityLinhNguyeNo ratings yet
- SI No.: Scope of The DocumentDocument4 pagesSI No.: Scope of The DocumentGanesh KashinathNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Activities Assay by Chia-Lin ChungDocument4 pagesEnzyme Activities Assay by Chia-Lin ChunghanifahNo ratings yet
- Stool DNA Kit Manual PI27600 7Document7 pagesStool DNA Kit Manual PI27600 7linbert simon callataNo ratings yet
- Experiment 15 Lab ReportDocument7 pagesExperiment 15 Lab Reportapi-480265521No ratings yet
- TFS-Assets_BID_manuals_EEA002-manual-metabolic-finalDocument11 pagesTFS-Assets_BID_manuals_EEA002-manual-metabolic-finaldewiNo ratings yet
- EN12720Document3 pagesEN12720Šetkić SemirNo ratings yet
- W2021 Lab-MF1 Protein Absorbance and ConcentrationDocument7 pagesW2021 Lab-MF1 Protein Absorbance and Concentrationrtm haiderNo ratings yet
- Expt 6 FreportDocument8 pagesExpt 6 Freportapi-3856754No ratings yet
- SGOT ASAT Kit Reitman Frankel MethodDocument3 pagesSGOT ASAT Kit Reitman Frankel MethodShribagla MukhiNo ratings yet
- 261 Labs - U1 - Osmolarity - Lab ReportDocument12 pages261 Labs - U1 - Osmolarity - Lab ReportSummerNo ratings yet
- Acid Phosphatase 21072020Document5 pagesAcid Phosphatase 21072020sanskriti pandeyNo ratings yet
- BCH3110 - Practical Manual - Sem2 20222023 - RevisedDocument31 pagesBCH3110 - Practical Manual - Sem2 20222023 - RevisedMUHAMMAD ARIF ARHAM BIN S.ROSLI / UPMNo ratings yet
- USP-NF 481 Riboflavin AssayDocument8 pagesUSP-NF 481 Riboflavin AssayALEJANDRA JIMENEZNo ratings yet
- Experiment-2: Spectrophotometric Determination of in Tablets by Standard Addition Method OutcomesDocument4 pagesExperiment-2: Spectrophotometric Determination of in Tablets by Standard Addition Method Outcomesbinseung skzNo ratings yet
- MSDS PhenolpthaleinDocument4 pagesMSDS PhenolpthaleinRyan Anthony LualhatiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1: ACIDS, BASES, AND BUFFERS: Post-Lab ActivityDocument4 pagesExperiment 1: ACIDS, BASES, AND BUFFERS: Post-Lab ActivitySam EstanocoNo ratings yet
- Full Complete Lab Presentation (Group 6)Document31 pagesFull Complete Lab Presentation (Group 6)Aneesch PreethaNo ratings yet
- Assess Salivary Amylase Optimal pHDocument1 pageAssess Salivary Amylase Optimal pHSenafoet NuñezNo ratings yet
- Applied Biotechnology CatalogueDocument18 pagesApplied Biotechnology CatalogueMohamed Salem SoltanNo ratings yet
- Lab 4Document3 pagesLab 4Noor JanahiNo ratings yet
- Enzymes LolsDocument38 pagesEnzymes LolsThon JustineNo ratings yet
- Paracetamol TabletasDocument2 pagesParacetamol TabletasHéctor Michel Galindo HernándezNo ratings yet
- METHOD #: 340.3 Title: Analyte: Instrumentation: Storet NoDocument4 pagesMETHOD #: 340.3 Title: Analyte: Instrumentation: Storet NoKarimah SabilaNo ratings yet
- The Effect of pH on Enzyme ActivityDocument12 pagesThe Effect of pH on Enzyme ActivityAb AbNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Vinegar TitrationDocument5 pagesLab Report Vinegar TitrationJessica CumlatNo ratings yet
- AOAC99110Document1 pageAOAC99110Jhon Alexander Rincon ReinaNo ratings yet
- Alkaline Phosphatase KitDocument2 pagesAlkaline Phosphatase KitDinesh SreedharanNo ratings yet
- Materi 9-10 SVP-LVPDocument31 pagesMateri 9-10 SVP-LVPMarvel SitorusNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 3Document12 pagesLab Report 3bpspearman100% (2)
- Dna Genomic Extraction - 230201 - 135014Document8 pagesDna Genomic Extraction - 230201 - 135014AhuyamaNo ratings yet
- Separate Mixture of Benzoic Acid, Naphthalene and AnilineDocument8 pagesSeparate Mixture of Benzoic Acid, Naphthalene and Anilinejarissa bannerNo ratings yet
- OrthophosphateDocument7 pagesOrthophosphateLuong Duc AnhNo ratings yet
- Isolation of Plant Genomic DNA (Draft - 2)Document4 pagesIsolation of Plant Genomic DNA (Draft - 2)Prayash NayakNo ratings yet
- Anas Muaamar Jeff Ludovico BIOL 1406.SL7 EnzymesDocument5 pagesAnas Muaamar Jeff Ludovico BIOL 1406.SL7 Enzymesblackrose0No ratings yet
- USEPA Aminoantipryne Metoda HACHDocument6 pagesUSEPA Aminoantipryne Metoda HACHdark_knight007No ratings yet
- Distillation LabDocument18 pagesDistillation LabWong XimeiNo ratings yet
- Title 3. Principle 4. Materials 5. Procedure 6. Results 7. Graph 8. Deduction 9. DiscussionDocument16 pagesTitle 3. Principle 4. Materials 5. Procedure 6. Results 7. Graph 8. Deduction 9. Discussionkritimahajan1989No ratings yet
- Favorprep DNA Isolation GuideDocument2 pagesFavorprep DNA Isolation GuidewiwienNo ratings yet
- A Note On Quantitative Urobilinogen Determinations: Bernard BalikovDocument5 pagesA Note On Quantitative Urobilinogen Determinations: Bernard BalikovTanveerNo ratings yet
- Effect of Substrate Concentration on α -AmylaseDocument26 pagesEffect of Substrate Concentration on α -Amylasepriyaa100% (5)
- High-Capacity cDNA Reverse Transcription Kits: Product Information SheetDocument2 pagesHigh-Capacity cDNA Reverse Transcription Kits: Product Information SheetHairul IslamNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology 1609322314Document100 pagesBiotechnology 1609322314Abdullah SaeedNo ratings yet
- CHE222 Important Course InformationDocument45 pagesCHE222 Important Course InformationStudent 365No ratings yet
- Senior Dual-Chamber Orifice Fitting - DanielsDocument30 pagesSenior Dual-Chamber Orifice Fitting - DanielsJoseVillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Codeline User Guide E8S SP and E8H SPDocument49 pagesCodeline User Guide E8S SP and E8H SPOsama AhmedNo ratings yet
- Molex ProcessDocument382 pagesMolex Processwriteandrewpaul7707100% (1)
- X2CrNiMoN22-5-3 - 1Document3 pagesX2CrNiMoN22-5-3 - 1Nithin KannanNo ratings yet
- Kinetic molecular model of the three states of matterDocument12 pagesKinetic molecular model of the three states of matterdavid jenil nabuaNo ratings yet
- Mini Project Final ReportDocument37 pagesMini Project Final ReportSamanth Kumar Vasam86% (14)
- Faculty of Science Bachelor of Science (Hons) Chemistry Year 1 Trimester 3 Udec 1224 - Chemistry Laboratory IDocument7 pagesFaculty of Science Bachelor of Science (Hons) Chemistry Year 1 Trimester 3 Udec 1224 - Chemistry Laboratory IOh Zi YiNo ratings yet
- Test For Common GasesDocument2 pagesTest For Common GasesAbigail IsraelNo ratings yet
- CE429 - U09 - Day1 - Wood Connections BackgroundDocument28 pagesCE429 - U09 - Day1 - Wood Connections BackgroundnickNo ratings yet
- PressedDocument102 pagesPressedMalik RizwanNo ratings yet
- Indonesian Journal of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Emilia, Lia Destiarti, AdhitiyawarmanDocument10 pagesIndonesian Journal of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Emilia, Lia Destiarti, Adhitiyawarmanjoenni hansNo ratings yet
- Annealing Oligos - Sigma AldrichDocument2 pagesAnnealing Oligos - Sigma AldrichBenedikt EngelNo ratings yet
- 1112283stock2075 3 17Document5 pages1112283stock2075 3 17cds nepalNo ratings yet
- Sticky Molecules - StudentDocument6 pagesSticky Molecules - StudentVanessa MurphyNo ratings yet
- Science Worksheet Grade 7Document2 pagesScience Worksheet Grade 7Ricky KhoasebNo ratings yet
- Synthesis and Characterization of Oligosalicylaldehyde-Based Epoxy ResinsDocument5 pagesSynthesis and Characterization of Oligosalicylaldehyde-Based Epoxy ResinsFrancesca TeocoliNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Test Questions Humss 1 & Abm 3Document9 pagesUnit 5 - Test Questions Humss 1 & Abm 3Neil GabatoNo ratings yet
- Tank Foundatio PDFDocument10 pagesTank Foundatio PDFnabeel najjarNo ratings yet
- Colorimetric Sensing of Metal Ions by Schiff Base ChemosensorsDocument33 pagesColorimetric Sensing of Metal Ions by Schiff Base ChemosensorsSubhabrata MabhaiNo ratings yet
- Doctor Test PDFDocument2 pagesDoctor Test PDFMugesh Kanna100% (1)
- How Many Water Molecules Does It Take To Dissociate HCL?: Doi: 10.1002/chem.201504016Document7 pagesHow Many Water Molecules Does It Take To Dissociate HCL?: Doi: 10.1002/chem.201504016Exlonk Gil PeláezNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY 6 - Science Education and Indigenous Science and Technology in The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesACTIVITY 6 - Science Education and Indigenous Science and Technology in The PhilippinesSherlyn MamacNo ratings yet
- Honeycomb Wound Filter Cartridge - Data Sheet - IPF NADocument4 pagesHoneycomb Wound Filter Cartridge - Data Sheet - IPF NAAlejandro GilNo ratings yet
- Elongational Flow in Multiple Screw ExtrudersDocument5 pagesElongational Flow in Multiple Screw ExtrudersAmr KamelNo ratings yet
- Brochure Reverlink 07-2015Document9 pagesBrochure Reverlink 07-2015Christophe DuquenneNo ratings yet
- TDS - 2080 - Penguard Midcoat - Euk - GBDocument5 pagesTDS - 2080 - Penguard Midcoat - Euk - GBRifki ArifinNo ratings yet
- FTS - Test-02 (Code-B) - 24-03-2023Document32 pagesFTS - Test-02 (Code-B) - 24-03-2023XembergNo ratings yet