0% found this document useful (0 votes)
138 views1 pageSolving Single-Sided Equations Guide
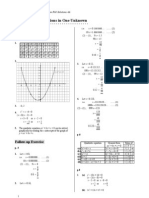
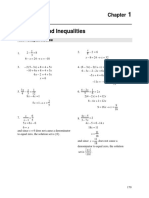
1. The document provides examples of solving single variable equations by isolating the variable on one side of the equation and showing each step.
2. More examples are given with variables isolated using addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
3. Further examples involve combining operations, fractions, decimals, and parentheses.
Uploaded by
vtsarjunaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
138 views1 pageSolving Single-Sided Equations Guide
1. The document provides examples of solving single variable equations by isolating the variable on one side of the equation and showing each step.
2. More examples are given with variables isolated using addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
3. Further examples involve combining operations, fractions, decimals, and parentheses.
Uploaded by
vtsarjunaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd