Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Geometry - Parabola
Uploaded by
Jason CostanzoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Geometry - Parabola
Uploaded by
Jason CostanzoCopyright:
Available Formats
Notes – Parabola
The parabola can be defined as a locus (collection) of points satisfying a geometric property. Most
likely, in your first encounter with a parabola, you learned that the graph of the quadratic function
𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑎𝑥 2 + 𝑏𝑥 + 𝑐
is a parabola that opens upward or downward. The definition given below is more general in that it is
independent of the orientation of the parabola.
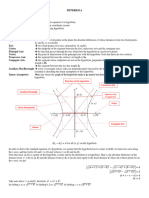
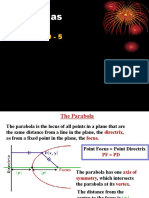
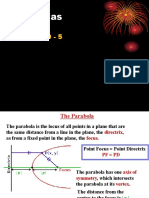
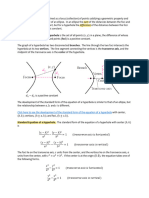
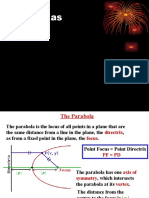
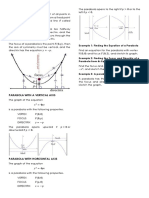
Definition of Parabola. A parabola is the set of all points (𝑥, 𝑦) in a plane that are equidistant from a
fixed line (directrix) and a fixed point (focus) not on the line (directrix).
The midpoint between the focus and the directrix is called the vertex, and the line passing through the
focus and the vertex is called the axis of the parabola. A parabola is symmetric with respect to its axis.
Using this definition of a parabola, one can derive the following form of the equation of a parabola with
vertex at (ℎ, 𝑘) and whose directrix is parallel to the 𝑥-axis or to the 𝑦-axis.
Equation of a Parabola
(𝑥 − ℎ)2 = 4𝑝(𝑦 − 𝑘), 𝑝 ≠ 0 (has a vertical axis and directrix: 𝑦 = 𝑘 − 𝑝)
(𝑦 − 𝑘)2 = 4𝑝(𝑥 − ℎ), 𝑝 ≠ 0 (has a horizontal axis and directrix: 𝑥 = ℎ − 𝑝)
(Click here to see the development of this equation)
The focus lies on the axis 𝑝 units (directed distance) from the vertex. If the vertex is at the origin (0, 0),
the equation takes one of the following forms.
𝑥 2 = 4𝑝𝑦, 𝑝 ≠ 0 (has a vertical axis (𝑦-axis) and directrix: 𝑦 = −𝑝)
𝑦 2 = 4𝑝𝑥, 𝑝 ≠ 0 (has a horizontal axis (𝑥-axis) and directrix: 𝑥 = −𝑝)
You might also like
- Lesson 3 - Parabola 1P PDFDocument17 pagesLesson 3 - Parabola 1P PDFDe Guia, Yuan Loriene NinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Polar CoordinatesDocument29 pagesChapter Two Polar CoordinatesRamez AlaliNo ratings yet
- Q1 W2 PrecalculusDocument11 pagesQ1 W2 PrecalculusArianne MolinaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2. The ParabolaDocument12 pagesLesson 2. The ParabolaAlanbert BangloNo ratings yet
- ParabolaDocument13 pagesParabolaapi-339611548No ratings yet
- MATH 1023 ANALGEOM Lesson 3 - Conic Sections - PARABOLADocument20 pagesMATH 1023 ANALGEOM Lesson 3 - Conic Sections - PARABOLAxandie wayawayNo ratings yet
- MATH161 Conic Sections Part 1 (Parabolas and Circles)Document7 pagesMATH161 Conic Sections Part 1 (Parabolas and Circles)Sakhile GumedeNo ratings yet
- Exponential and Square Transformations (? ? ?, ? 2 )Document4 pagesExponential and Square Transformations (? ? ?, ? 2 )Nithish kumar RajendranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 ConicsDocument10 pagesChapter 4 ConicsSong KimNo ratings yet
- Conic Sections ParabolaDocument32 pagesConic Sections ParabolaPubgm JeroNo ratings yet
- SAT Coordinate GeometryDocument3 pagesSAT Coordinate GeometryΜάριος Α. ΠαππάςNo ratings yet
- Math 11-STEM Pre Cal-Q1-Module 2Document12 pagesMath 11-STEM Pre Cal-Q1-Module 2Thyviel DoeNo ratings yet
- M2 T2 ParabolaDocument6 pagesM2 T2 ParabolaKurianPaulNo ratings yet
- ELECTIVE MATHEMATICS 10 Module 1 Equation of ParabolaDocument20 pagesELECTIVE MATHEMATICS 10 Module 1 Equation of ParabolaFVERON, JESSICA FABELLORENo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Parabolas Week 4Document6 pagesChapter 3 Parabolas Week 4Angelo ResuelloNo ratings yet
- 3 PART I LineDocument11 pages3 PART I Linejayaram1234.hrNo ratings yet
- Conic Sections: ParabolaDocument92 pagesConic Sections: ParabolaJR DevienteNo ratings yet
- Conic SectionsDocument26 pagesConic SectionsljcarbosNo ratings yet
- Coleen ParabolaDocument21 pagesColeen ParabolaHannah Coleen Gonzalo PojolNo ratings yet
- 9.2 - Parabolas 1Document8 pages9.2 - Parabolas 1Jayron GordonNo ratings yet
- 9.2 - Parabolas 1Document8 pages9.2 - Parabolas 1alfred naveaNo ratings yet
- G11 Pre Cal W2 LASDocument12 pagesG11 Pre Cal W2 LASStreaming Lalisa03100% (1)
- Module 5Document11 pagesModule 5Jean LeysonNo ratings yet
- Conics: ParabolaDocument9 pagesConics: Parabolahappygirl833100% (1)
- HyperbolaDocument4 pagesHyperbolaRhasher YbañezNo ratings yet
- Precal Q1 M2 W2Document12 pagesPrecal Q1 M2 W2destroyer kingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document22 pagesChapter 2Eunice SiervoNo ratings yet
- Parabola 10-5 RevDocument8 pagesParabola 10-5 RevZia AdriannaNo ratings yet
- Elective Mathematics 10 Module Tangent Line of 4th QTRDocument14 pagesElective Mathematics 10 Module Tangent Line of 4th QTRMatsuri VirusNo ratings yet
- Parabola Equations - MathBitsNotebook (Geo - CCSS Math) PDFDocument1 pageParabola Equations - MathBitsNotebook (Geo - CCSS Math) PDFRavi KumarNo ratings yet
- Parabola 10-5 RevDocument8 pagesParabola 10-5 RevRhyz Mareschal DongonNo ratings yet
- Parabola 10-5 RevDocument8 pagesParabola 10-5 RevAlejandra PinedaNo ratings yet
- Parabolas: Section 10 - 5Document8 pagesParabolas: Section 10 - 5biboyNo ratings yet
- Parabola 10-5 RevDocument8 pagesParabola 10-5 RevKarissaNo ratings yet
- Unit1 Lesson3-ParabolaDocument45 pagesUnit1 Lesson3-Parabolachristine faith seducoNo ratings yet
- Geometry - HyperbolaDocument2 pagesGeometry - HyperbolaJason CostanzoNo ratings yet
- Axis of SymmetryDocument3 pagesAxis of SymmetryPaula FanaNo ratings yet
- MATH161 Conic Sections Part 2 (Ellipses and Hyperbolas)Document11 pagesMATH161 Conic Sections Part 2 (Ellipses and Hyperbolas)Sakhile GumedeNo ratings yet
- Deped Learning Activity Sheets (Las) Name of Learner: Grade Level: Section: Date: Pre-Calculus Parabola Week No. 2Document5 pagesDeped Learning Activity Sheets (Las) Name of Learner: Grade Level: Section: Date: Pre-Calculus Parabola Week No. 2Evangeline Martinez-FechalinNo ratings yet
- The Parabola - MathematicsDocument12 pagesThe Parabola - Mathematicsolowejohn.2006No ratings yet
- Stem 1 - Pre Calculus: Lesson 3 - Conic Sections - ParabolaDocument12 pagesStem 1 - Pre Calculus: Lesson 3 - Conic Sections - ParabolaMary Jasmine AzulNo ratings yet
- MVC Week 2 LectureDocument13 pagesMVC Week 2 Lecturefaizanmehmood579No ratings yet
- Para BulaDocument23 pagesPara BulaErienne IbanezNo ratings yet
- The Coordinate Plane and GraphingDocument3 pagesThe Coordinate Plane and GraphingAllysa Laas [Basic HS]No ratings yet
- Formula Final Exam MathDocument2 pagesFormula Final Exam MathBetty CooperNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 4 (Lines, Planes and Quadratic Surfaces)Document23 pagesLecture # 4 (Lines, Planes and Quadratic Surfaces)Rakhmeen GulNo ratings yet
- Graphing A Quadratic FunctionDocument4 pagesGraphing A Quadratic FunctionAbo MoussaNo ratings yet
- ParabolaDocument9 pagesParabolaAna Marie ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- ParabolaDocument9 pagesParabolaAna Marie ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- ParabolasDocument1 pageParabolasBata BatutaNo ratings yet
- Functions and InversesDocument32 pagesFunctions and InversesWooNo ratings yet
- Precal SHS 1 - W3Document4 pagesPrecal SHS 1 - W3Chaelin CLNo ratings yet
- The Parabola. by - OpenStaxCollegeDocument35 pagesThe Parabola. by - OpenStaxCollegeJomar SaliNo ratings yet
- Ch1 - Algebraic and Non-Algebraic Functions and Their InverseDocument37 pagesCh1 - Algebraic and Non-Algebraic Functions and Their InverseRafi SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Om 2Document7 pagesOm 2Rennekien MateoNo ratings yet
- Analgeom. Parabola 2Document8 pagesAnalgeom. Parabola 2RiNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Geometry - Reflective SurfacesDocument1 pageGeometry - Reflective SurfacesJason CostanzoNo ratings yet
- M4.3 Fixed Points and IvpDocument1 pageM4.3 Fixed Points and IvpJason CostanzoNo ratings yet
- Geometry - 1 Translation and RotationDocument13 pagesGeometry - 1 Translation and RotationJason CostanzoNo ratings yet
- M2 - Supremum and InfimumDocument2 pagesM2 - Supremum and InfimumJason CostanzoNo ratings yet
- M2 - Review of SequencesDocument1 pageM2 - Review of SequencesJason CostanzoNo ratings yet
- M2 - Onvergence Using The DefinitionDocument3 pagesM2 - Onvergence Using The DefinitionJason CostanzoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Logic, Copi and Cohen: Prentice Hall Elogic This MethodDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Logic, Copi and Cohen: Prentice Hall Elogic This MethodJason CostanzoNo ratings yet
- MAT-315-Official GeometryDocument3 pagesMAT-315-Official GeometryJason CostanzoNo ratings yet
- Major Declaration Form: Issouri Estern Tate NiversityDocument1 pageMajor Declaration Form: Issouri Estern Tate NiversityJason CostanzoNo ratings yet
- Brain NEURO PDFDocument11 pagesBrain NEURO PDFJason Costanzo100% (1)
- Aertsen, J. - Being and One in Duns ScotusDocument19 pagesAertsen, J. - Being and One in Duns ScotusJason CostanzoNo ratings yet