Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Google Secure Ai Framework Summary
Uploaded by
Fadli Fadli0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views1 pageGoogle is introducing the Secure AI Framework (SAIF) to help manage risks as AI advances. SAIF has six core elements: 1) Expand strong security foundations to the AI ecosystem, 2) Extend detection and response to bring AI into an organization's threat universe, 3) Automate defenses to keep pace with existing and new threats, 4) Harmonize platform level controls to ensure consistent security across the organization, 5) Adapt controls to adjust mitigations and create faster feedback loops for AI deployment, and 6) Contextualize AI system risks in surrounding business processes.
Original Description:
Original Title
google_secure_ai_framework_summary
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGoogle is introducing the Secure AI Framework (SAIF) to help manage risks as AI advances. SAIF has six core elements: 1) Expand strong security foundations to the AI ecosystem, 2) Extend detection and response to bring AI into an organization's threat universe, 3) Automate defenses to keep pace with existing and new threats, 4) Harmonize platform level controls to ensure consistent security across the organization, 5) Adapt controls to adjust mitigations and create faster feedback loops for AI deployment, and 6) Contextualize AI system risks in surrounding business processes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views1 pageGoogle Secure Ai Framework Summary
Uploaded by
Fadli FadliGoogle is introducing the Secure AI Framework (SAIF) to help manage risks as AI advances. SAIF has six core elements: 1) Expand strong security foundations to the AI ecosystem, 2) Extend detection and response to bring AI into an organization's threat universe, 3) Automate defenses to keep pace with existing and new threats, 4) Harmonize platform level controls to ensure consistent security across the organization, 5) Adapt controls to adjust mitigations and create faster feedback loops for AI deployment, and 6) Contextualize AI system risks in surrounding business processes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Google’s Secure AI Framework
AI is advancing rapidly, and it’s important that effective risk management strategies evolve along with it. To help achieve this evolution, we’re
introducing the Secure AI Framework (SAIF), a conceptual framework for secure AI systems. SAIF has six core elements:
1. Expand strong security foundations to the AI ecosystem
Leverage secure-by-default infrastructure protections and expertise
built over the last two decades to protect AI systems, applications and
users. At the same time, develop organizational expertise to keep pace
with advances in AI and start to scale and adapt infrastructure
protections in the context of AI and evolving threat models. For
example, injection techniques like SQL injection have existed for some
time, and organizations can adapt mitigations, such as input sanitization
and limiting, to help better defend against prompt injection style attacks.
2. Extend detection and response to bring AI into an organization’s
threat universe
Detect and respond to AI-related cyber incidents in time by extending
threat intelligence and other capabilities. For organizations, this includes
monitoring inputs and outputs of generative AI systems to detect
anomalies, and using threat intelligence to anticipate attacks. This effort
typically requires collaboration with trust and safety, threat intelligence,
and counter abuse teams.
3. Automate defenses to keep pace with existing and new threats
Harness the latest AI innovations to improve the scale and speed of
response efforts to security incidents. Adversaries will likely use AI to
scale their impact, so it is important to use AI and its current and
emerging capabilities to stay nimble and cost effective in protecting
against them.
4. Harmonize platform level controls to ensure consistent security
across the organization
Align control frameworks to support AI risk mitigation and scale
protections across different platforms and tools to ensure that the best
protections are available to all AI applications in a scalable and cost
efficient manner. At Google, this includes extending secure-by-default
protections to AI platforms like Vertex AI and Security AI Workbench, and
building controls and protections into the software development lifecycle.
Capabilities that address general use cases, like Perspective API, can
help the entire organization benefit from state of art protections.
5. Adapt controls to adjust mitigations and create faster feedback
loops for AI deployment
Constantly test implementations through continuous learning and evolve
detection and protections to address the changing threat environment.
This includes techniques like reinforcement learning based on incidents
and user feedback, and involves steps such as updating training data
sets, fine-tuning models to respond strategically to attacks, and allowing
the software that is used to build models to embed further security in
context (e.g. detecting anomalous behavior). Organizations can also
conduct regular Red Team exercises to improve safety assurance for
AI-powered products and capabilities.
6. Contextualize AI system risks in surrounding business processes
Conduct end-to-end risk assessments related to how organizations will
deploy AI. This includes an assessment of the end-to-end business risk,
such as data lineage, validation and operational behavior monitoring for
certain types of applications. In addition, organizations should construct
automated checks to validate AI performance.
You might also like
- 2 6 Risk Management PolicyDocument47 pages2 6 Risk Management PolicyRaja ManiNo ratings yet
- CSP Complete Guide PDFDocument32 pagesCSP Complete Guide PDFttdost100% (1)
- Implementing Generative Ai With Speed and SafetyDocument10 pagesImplementing Generative Ai With Speed and SafetyromainNo ratings yet
- IntercompanyDocument9 pagesIntercompanyMohan BallaNo ratings yet
- Frank Ayirebi ResumeDocument2 pagesFrank Ayirebi Resumedurga prasad ravvaNo ratings yet
- Business Analyst Interview Question AnswersDocument69 pagesBusiness Analyst Interview Question Answersfaisalaziz27No ratings yet
- SANS - 5 Critical ControlsDocument19 pagesSANS - 5 Critical ControlsAni MNo ratings yet
- Technology Security ControlsDocument2 pagesTechnology Security Controlsrenusai chitooriNo ratings yet
- CPQ Solution StudyDocument16 pagesCPQ Solution StudyDemand MetricNo ratings yet
- Secure Controls Framework 2023 4Document280 pagesSecure Controls Framework 2023 4ice1025No ratings yet
- CompTIA CASP+ CAS-004 Exam Guide: A-Z of Advanced Cybersecurity Concepts, Mock Exams, Real-world Scenarios with Expert Tips (English Edition)From EverandCompTIA CASP+ CAS-004 Exam Guide: A-Z of Advanced Cybersecurity Concepts, Mock Exams, Real-world Scenarios with Expert Tips (English Edition)No ratings yet
- AI in Cybersecurity - Report PDFDocument28 pagesAI in Cybersecurity - Report PDFTaniya Faisal100% (1)
- AccentureDocument23 pagesAccentureYusef Shaqeel50% (2)
- Fortinet Enterprise Partner Sales GuideDocument64 pagesFortinet Enterprise Partner Sales GuideFelipe Gabriel Nieto ConchaNo ratings yet
- Securing Artificial Intelligence Systems Tda Cyber SnapshotDocument10 pagesSecuring Artificial Intelligence Systems Tda Cyber SnapshottonykwannNo ratings yet
- Incorporating AI-Driven Strategies in DevSecOps For Robust Cloud SecurityDocument7 pagesIncorporating AI-Driven Strategies in DevSecOps For Robust Cloud SecurityInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Cyber Snapshot Issue 4Document39 pagesCyber Snapshot Issue 4Bekim KrasniqiNo ratings yet
- Snyke Developer Security ToolsDocument12 pagesSnyke Developer Security ToolsMichel ThomasiusNo ratings yet
- Report State of Ai Cyber Security 2024 1714045778Document32 pagesReport State of Ai Cyber Security 2024 1714045778dresses.wearier.0nNo ratings yet
- Breach & Attack Simulation 101: Expert Tips InsideDocument20 pagesBreach & Attack Simulation 101: Expert Tips InsideRikrdo BarcoNo ratings yet
- Comparing A Security Strategic Plan - Edited.editedDocument6 pagesComparing A Security Strategic Plan - Edited.editedPaul WahomeNo ratings yet
- 5 Steps For Moving To Mobile DevSecOpsDocument3 pages5 Steps For Moving To Mobile DevSecOpsdmomentsbymmNo ratings yet
- Seven Ways To Better Connect Your Security Operations CenterDocument18 pagesSeven Ways To Better Connect Your Security Operations CenterBobby bobbinsNo ratings yet
- Ai GovernanceDocument21 pagesAi GovernanceVijay KashettiNo ratings yet
- Drive Intelligent Security With These Six Cisco Secure Application FeaturesDocument10 pagesDrive Intelligent Security With These Six Cisco Secure Application FeaturesfptstopNo ratings yet
- Ibm Appscan Source DatasheetDocument12 pagesIbm Appscan Source DatasheetAnonymous G1iPoNOKNo ratings yet
- Cybersecurity For BusinessesDocument10 pagesCybersecurity For BusinessesNairit MondalNo ratings yet
- Content - Dam - Blackberry Com - Asset - Enterprise - PDF - Evalguide 5 Tips For Evaluating Ai Driven Security SolutionsDocument4 pagesContent - Dam - Blackberry Com - Asset - Enterprise - PDF - Evalguide 5 Tips For Evaluating Ai Driven Security SolutionsCarlos BarrezuetaNo ratings yet
- Application Security With Automated Threat Modeling and Self ProtectionDocument4 pagesApplication Security With Automated Threat Modeling and Self ProtectionRazafindrabeNo ratings yet
- Trustworthy AI: From Principles To PracticesDocument49 pagesTrustworthy AI: From Principles To PracticesNabila HassanNo ratings yet
- Software SecurityDocument4 pagesSoftware Securitykavuru.abhijeetNo ratings yet
- The Continuous Application Security Handbook: Unify Security Strategy Across Development & OperationsDocument32 pagesThe Continuous Application Security Handbook: Unify Security Strategy Across Development & OperationsWijdane AoufiNo ratings yet
- Csi Deploying Ai Systems SecurelyDocument11 pagesCsi Deploying Ai Systems SecurelyJordi Martin14No ratings yet
- Consulting Data Sheet OverviewDocument2 pagesConsulting Data Sheet OverviewtmendisNo ratings yet
- Utilizing Fake InsightsDocument1 pageUtilizing Fake Insightsiansojunior60No ratings yet
- Surya CVDocument4 pagesSurya CVvivekNo ratings yet
- FORTIFY Overview PSVDocument48 pagesFORTIFY Overview PSVminh khangNo ratings yet
- BSIMM V ActivitiesDocument32 pagesBSIMM V ActivitiesmabesninaNo ratings yet
- Ebook Ai Breach ProtectionDocument11 pagesEbook Ai Breach ProtectionDonat KaciNo ratings yet
- Bsa Software Security Framework Web FinalDocument40 pagesBsa Software Security Framework Web Finalcours stockNo ratings yet
- Third Generation Sandboxing Delivers Ai Based Breach PreventionDocument13 pagesThird Generation Sandboxing Delivers Ai Based Breach PreventionDaniel HanganuNo ratings yet
- Security Advisory Issue 3Document8 pagesSecurity Advisory Issue 3Ofrates SiringanNo ratings yet
- Raw 14200 Us enDocument20 pagesRaw 14200 Us enrexiaNo ratings yet
- A Crash Course in Security Management: Learning The Keys To A Better Security PostureDocument22 pagesA Crash Course in Security Management: Learning The Keys To A Better Security PostureSufeeyan AhmedNo ratings yet
- An Outlook On The Status of Security Performance in The Light of IntelligenceDocument7 pagesAn Outlook On The Status of Security Performance in The Light of IntelligenceIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Evaluacion Triptico InglesDocument2 pagesEvaluacion Triptico Inglesever rodriguezNo ratings yet
- ISF Embedding Security Into Agile Development Executive Summary 2023Document2 pagesISF Embedding Security Into Agile Development Executive Summary 2023TNo ratings yet
- FortiGuard Security ServicesDocument8 pagesFortiGuard Security Servicesdoris marcaNo ratings yet
- Application Security ArchitectureDocument20 pagesApplication Security ArchitectureManish WaliaNo ratings yet
- Evaluator 039 S Guide Nextgen Siem 38720Document20 pagesEvaluator 039 S Guide Nextgen Siem 38720Kat singhNo ratings yet
- Transparency in AIDocument31 pagesTransparency in AISuvadeep DasNo ratings yet
- Protect and Defend Your Systems With Cysa+!: Skills You'Ll Master When You Earn Your Cysa+ CertificationDocument1 pageProtect and Defend Your Systems With Cysa+!: Skills You'Ll Master When You Earn Your Cysa+ CertificationJemar DouglasNo ratings yet
- Reaserch Paper On EA SecurityDocument4 pagesReaserch Paper On EA Securityrachna rathoreNo ratings yet
- NTT Data Ai Governance v04Document23 pagesNTT Data Ai Governance v04radhikaseelam1No ratings yet
- Cisco Technical Security Assessment AagDocument3 pagesCisco Technical Security Assessment Aaglakbabi1035No ratings yet
- C2M2 Implementation GuideDocument13 pagesC2M2 Implementation GuideKPNo ratings yet
- Top Security Orchestration Use CasesDocument17 pagesTop Security Orchestration Use CasesocallagdNo ratings yet
- Bsa Framework Secure Software Update 2020Document44 pagesBsa Framework Secure Software Update 2020Sameh MohamedNo ratings yet
- Nomios - The Rise of AI in CybersecurityDocument13 pagesNomios - The Rise of AI in CybersecurityNico MorarNo ratings yet
- Security Validation Datasheet enDocument3 pagesSecurity Validation Datasheet enjaimeguzmanrodriguez8No ratings yet
- Tripwire Executives Guide To The Cis Controls PDFDocument19 pagesTripwire Executives Guide To The Cis Controls PDFcheenuNo ratings yet
- Eb Transforming AppsecDocument9 pagesEb Transforming AppsecKate RichNo ratings yet
- The Ciso'S Guide To Modern Appsec: Bsimm11 DigestDocument9 pagesThe Ciso'S Guide To Modern Appsec: Bsimm11 Digestep230842No ratings yet
- Top 6 Technology Trends That Affect Software Security: 1. Everything Is MobileDocument5 pagesTop 6 Technology Trends That Affect Software Security: 1. Everything Is MobileShreya KasturiaNo ratings yet
- IBM Security Resilient Security Orchestration, Automation and Response (SOAR) Platform Privacy Add-OnDocument7 pagesIBM Security Resilient Security Orchestration, Automation and Response (SOAR) Platform Privacy Add-OnTan DoNo ratings yet
- Head of Information SecurityDocument2 pagesHead of Information SecurityazzuNo ratings yet
- Course Outline MM-II 2016Document13 pagesCourse Outline MM-II 2016Akansha BansalNo ratings yet
- As of July 13, 2010: Appendix B Codes For Specific Disciplines Under Major DisciplinesDocument40 pagesAs of July 13, 2010: Appendix B Codes For Specific Disciplines Under Major Disciplineskirk jason silvanoNo ratings yet
- CFO Chief Financial Officer in Chicago IL Resume Philip GrybasDocument3 pagesCFO Chief Financial Officer in Chicago IL Resume Philip GrybasPhilipGrybasNo ratings yet
- BA 5017 Managerial Behaviour and Effectiveness: Dr.K.Ravi Kumar ProfessorDocument18 pagesBA 5017 Managerial Behaviour and Effectiveness: Dr.K.Ravi Kumar Professorrakum81No ratings yet
- SAP Certified Consultant ListDocument64 pagesSAP Certified Consultant ListPhani PrakashNo ratings yet
- MM - 1550 - 4118 - 1 - Buyer Seller Relationship - Lecture # 4Document43 pagesMM - 1550 - 4118 - 1 - Buyer Seller Relationship - Lecture # 4ain khanNo ratings yet
- Flexible Budgets and Overhead Analysis: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument78 pagesFlexible Budgets and Overhead Analysis: Mcgraw-Hill/Irwinsaka haiNo ratings yet
- Adidas (Latest) 1Document21 pagesAdidas (Latest) 1Jalila Abd. MuktiNo ratings yet
- Example Answers For Assignment On Small Business EnterpriseDocument6 pagesExample Answers For Assignment On Small Business EnterpriseHND Assignment Help100% (1)
- Handout - CHAPTER 2Document15 pagesHandout - CHAPTER 2Merveille SadyNo ratings yet
- VP Finance Controller in Philadelphia PA Resume William SteeleDocument2 pagesVP Finance Controller in Philadelphia PA Resume William SteeleWilliamSteeleNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategy Analysis ProjectDocument4 pagesMarketing Strategy Analysis Projectnavimala85No ratings yet
- 90over100 Quiz 2 Risk ManagementDocument12 pages90over100 Quiz 2 Risk ManagementKenneth EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Rizal Technological University: Boni Ave., Mandaluyong City College of Business and Entrepreneurial TechnologyDocument5 pagesRizal Technological University: Boni Ave., Mandaluyong City College of Business and Entrepreneurial TechnologyAndrew Miguel SantosNo ratings yet
- Motorbus CompanyDocument2 pagesMotorbus CompanyJerome KengNo ratings yet
- Study On Inventory Management in Bhandary Powerlines LTDDocument11 pagesStudy On Inventory Management in Bhandary Powerlines LTDRajendraNo ratings yet
- The Field of Strategy in Search of A Walking Stick PDFDocument13 pagesThe Field of Strategy in Search of A Walking Stick PDFdlanorxNo ratings yet
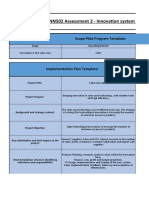
- BSBINN502 Assessment 2 - Innovation System Pilot ProjectDocument5 pagesBSBINN502 Assessment 2 - Innovation System Pilot ProjectIvson SilvaNo ratings yet
- Essay BreakevenDocument7 pagesEssay BreakevenDulcee HnzNo ratings yet
- Brochure ICCIBM 2022Document10 pagesBrochure ICCIBM 2022gourickgNo ratings yet
- Asif Rehman: Assistant Professor Bahria UniversityDocument12 pagesAsif Rehman: Assistant Professor Bahria UniversityAliRazaNo ratings yet
- CM121.COA (IL-I) Question CMA May-2023 Exam.Document7 pagesCM121.COA (IL-I) Question CMA May-2023 Exam.Md FahadNo ratings yet
- An Evaluation of Demand and Capacity Planning Processes - A Qualitative Case Study On Completely-Knocked-Down Vehicles at Mercedes-Benz CarsDocument276 pagesAn Evaluation of Demand and Capacity Planning Processes - A Qualitative Case Study On Completely-Knocked-Down Vehicles at Mercedes-Benz Carsmiracle ndeuleNo ratings yet
- University of MaurtiusDocument6 pagesUniversity of MaurtiusAtish KissoonNo ratings yet