Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Add1 Bivariate Analysis
Uploaded by
ara.vcnt16Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Add1 Bivariate Analysis
Uploaded by
ara.vcnt16Copyright:
Available Formats
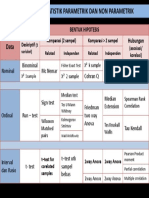
ADDITIONAL #1: BIVARIATE ANALYSIS
RECAP ON THE TYPE OF DATA CONTINUOUS DICHOTOMOUS Student’s t-
(DU) test
• Ordinal CONTINUOUS DICHOTOMOUS Paired t-test
• Nominal (DP)
• Continuous CONTINUOUS NOMINAL ANOVA (F-
test)
• Dichotomous
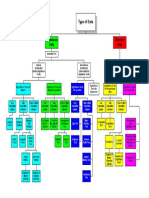
RECAP ON THE PARAMETRIC AND NON- ORDINAL & OTHER TYPE DATA (VICE VERSA)
PARAMETRIC
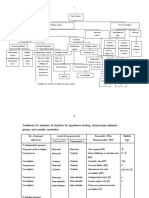
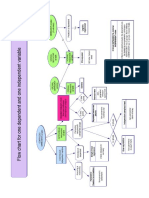
Choice of Appropriate Statistical Significance Test
Parametric tests of Nonparametric tests of
in Bivariate Analysis (Analysis of One Independent
means medians
1-sample sign, Variable and One Dependent Variable)
1-sample t-test
1-sample wilcoxon First Variable Second Appropriate
2-sample t-test Mann-Whitney test Variable Test/s
One-Way ANOVA Kruskal-Wallis
ORDINAL ORDINAL Spearman
correlation
coefficient
PARAMETRIC (rho); Kendall
Sample size correlation
Parametric analyses requirements for coefficient (tau)
nonnormal data ORDINAL DICHOTOMOUS Mann-Whitney
(DU) U test
1-sample t-test Greater than 20
ORDINAL DICHOTOMOUS Wilcoxon
2-sample t-test Each group should have
(DP) matched-pairs
more than 15 observations
signed-ranks
One-Way ANOVA For 2-9 groups, each
test
group should have more
ORDINAL NOMINAL Kruskal-Wallis
than 15 observations
test
For 10-12 groups, each
group should have more
than 20 observations
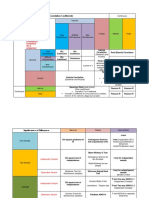
DICHOTOMOUS, NOMINAL & OTHER TYPE
DATA (OR VICE VERSA)
CONTINUOUS & OTHER TYPE DATA (VICE
First Variable Second Appropriate
VERSA) Variable Test/s
Choice of Appropriate Statistical Significance Test DICHOTOMOU DICHOTOMOUS Spearman
(DU) correlation
in Bivariate Analysis (Analysis of One Independent coefficient
Variable and One Dependent Variable) (rho); Kendall
correlation
First Variable Second Appropriate coefficient
Variable Test/s (tau)
CONTINUOUS CONTINUOUS Pearson DICHOTOMOU DICHOTOMOUS Mann-Whitney
correlation (DP) U test
coefficient (r); DICHOTOMOU NOMINAL Wilcoxon
linear matched-pairs
regression signed-ranks
CONTINUOUS ORDINAL Group the test
continuous NOMINAL NOMINAL Kruskal-Wallis
variable and test
calculate
Spearman
correlation
coefficient
(rho)†
VARIABLE’S INTERPRETATION • Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-ranks test
• Kruskal-Wallis test
NOMINAL (CATEGORICAL) [=/≠]
• Gender
• McNemar chi-square test
• Race • Chi-square test
• Ethnicity • t-test
• Hobbies • ANOVA (F-test)
• Occupation
• Color PEARSON’S CORRELATION COEFFICIENT
• Brand Name
• Preffered type of chocolate Pearson’s correlation coefficient is the test
• Cities statistics that measures the statistical relationship,
MODE AND PERCENTAGE or association, between two continuous variables.
• Pie Graph and Bar Graph
ASSUMPTIONS:
ORDINAL (=/≠) (</>) • Independent of case
• Sequence • Linear relationship
• Rankings • Homoscedasticity
• Order
• Satisfaction PROPERTIES:
• Happiness
• Awareness • Limit
• Likert Scale • Pure number
• Net Promoter Score (NPS) • Symmetric
• Bipolar Matrix Table
MEAN, MEDIAN, MODE, AND PERCENTAGE DEGREE OF CORRELATION:
• Bar Graph
• Perfect
INTERVAL (=/≠) (</>) (+/-) • High degree
• Temperature • Moderate degree
• Dates • Low degree
MEAN, MEDIAN, AND STANDARD DEVIATION • No correlation
• Pie Graph and Bar Graph
LINEAR REGRESSION
RATIO (=/≠) (</>) (+/-) (x/÷) Linear regression is a basic and commonly used
• Annual Income type of predictive analysis. The overall idea of
• IQ Test regression is to examine two things:
• Age
• Number of family member • Does a set of predictor variables do a good
• Length job in predicting an outcome (dependent)
• Weight variable?
MEAN, MEDIAN, AND STANDARD DEVIATION • Which variables are significant predictors of
• Line Graph and Bar Graph the outcome variable, and in what way do
they–indicated by the magnitude and sign of
APPROPRIATE TEST OR TESTS OF the beta estimates–impact the outcome
SIGNIFICANCE variable?
• Pearson correlation coefficient
• Linear regression
• Spearman correlation coefficient (rho)
• Kendall correlation coefficient (tau)
• Mann-Whitney U test
TYPE OF LINEAR REGREESION KENDALL CORRELATION COEFFICIENT
(TAU)
• Simple linear regression
o 1 dependent variable (interval or ratio), • Kendall's tau-b (τb) correlation coefficient
1 independent variable (interval or (Kendall's tau-b, for short) is a nonparametric
ratio or dichotomous) measure of the strength and direction of
• Multiple linear regression association that exists between two variables
o 1 dependent variable (interval or measured on at least an ordinal scale.
ratio) , 2+ independent variables MANN- WHITNEY U TEST
(interval or ratio or dichotomous)
• Logistic regression • The Mann-Whitney U test is used to compare
o 1 dependent variable (dichotomous), differences between two independent groups
2+ independent variable(s) (interval or when the dependent variable is either ordinal
ratio or dichotomous) or continuous, but not normally distributed.
• Ordinal regression
WILCOXON MATCHED- PAIRS SIGNED-
o 1 dependent variable (ordinal), 1+
RANKS TEST
independent variable(s) (nominal or
dichotomous) • The Wilcoxon signed-rank test is the
• Multinomial regression nonparametric test equivalent to the
o 1 dependent variable (nominal), 1+ dependent t-test.
independent variable(s) (interval or • As the Wilcoxon signed-rank test does not
ratio or dichotomous) assume normality in the data, it can be used
• Discriminant analysis when this assumption has been violated and
o 1 dependent variable (nominal), 1+ the use of the dependent t-test is
independent variable(s) (interval or inappropriate.
ratio) • It is used to compare two sets of scores that
come from the same participants.
SPEARMAN CORRELATION COEFFICIENT
(RHO) KRUSKAL- WALLIS TEST
• The Spearman rank- order correlation • The Kruskal-Wallis H test (sometimes also
coefficient (Spearman’s correlation, for short) called the "one-way ANOVA on ranks") is a
is a nonparametric measure of the strength rank-based nonparametric test that can be
and direction of association that exists used to determine if there are statistically
between two variables measured on at least significant differences between two or more
an ordinal scale. groups of an independent variable on a
continuous or ordinal dependent variable.
Figure Verbal Interpretation
• It is considered the nonparametric alternative
.00 - .19 Very Weak
to the one-way ANOVA, and an extension of
.20 - .39 Weak
the Mann-Whitney U test to allow the
.40 - .59 Moderate
.60 - .79 Strong comparison of more than two independent
.80 - 1.0 Very Strong groups.
MCNEMAR CHI-SQUARE TEST
• Interpretation is similar to that of Pearsons,
e.g. the closer is to the stronger the • The McNemar test is used to determine if
monotonic relationship. there are differences on a dichotomous
• Correlation is an effect size and so we can dependent variable between two related
verbally describe the strength of the groups.
correlation using the following guide for the
absolute value of rs:
• It can be considered to be similar to the
paired-samples t- test, but for a dichotomous
rather than a continuous dependent variable.
However, unlike the paired-samples t-test, it
can be conceptualized to be testing two
different properties of a repeated measure
dichotomous variable, as is explained below.
CHI-SQUARE TEST
• The Chi Square statistic is commonly used for
testing relationships between categorical
variables.
• The null hypothesis of the Chi-Square test is
that no relationship exists on the categorical
variables in the population; they are
independent.
T-TEST
A t-test is a statistical test that is used to compare
the means of two groups.
TYPE OF T-TEST
One-sample, two-sample, or paired t-test?
• Paired t-test.
• Two-sample t-test (a.k.a. independent t- test).
• One-sample t-test.
One-tailed or two-tailed t-test?
• Two-tailed t-test.
• One-tailed t-test.
ANOVA (F- TEST)
• The F-test is most often used when
comparing statistical models that have been
fitted to a data set, in order to identify the
model that best fits the population from which
the data were sampled.
• ANOVA is a particular form of statistical
hypothesis testing heavily used in the analysis
of experimental data.
• ANOVA is used in the analysis of comparative
experiments —those in which only the
difference in outcomes is of interest.
• The statistical significance of the experiment
is determined by a ratio of two variances.
You might also like
- Nolan S.A. - Heinzen, T. E. Statistics For Behavioral Sciences 2nd EditionDocument710 pagesNolan S.A. - Heinzen, T. E. Statistics For Behavioral Sciences 2nd Editionsam100% (1)
- Formula Cheat Sheet CreDocument40 pagesFormula Cheat Sheet CreKabala Usman100% (3)
- 5 WAIS-IV Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale 4th EditionDocument1 page5 WAIS-IV Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale 4th EditionVINEET GAIROLANo ratings yet
- Choosing the right statistical testDocument1 pageChoosing the right statistical testد.شيماءسعيدNo ratings yet
- Choice of Statistical Method Flow DiagramDocument1 pageChoice of Statistical Method Flow DiagramAhmed Adel RagabNo ratings yet
- Psychological StatisticsDocument95 pagesPsychological StatisticsShang0% (1)
- Marketing ResearchDocument2 pagesMarketing ResearchKarin OneNo ratings yet
- Penggunaan Statistik Parametrik Dan Non Parametrik: Jenis DataDocument1 pagePenggunaan Statistik Parametrik Dan Non Parametrik: Jenis DataHerriNo ratings yet
- Critical Appraisal Kuantitatif 2021Document34 pagesCritical Appraisal Kuantitatif 2021Adang MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Skala Ukur: Binominal MC Nemar X K Sample Contigency Coefficient C Cohran QDocument2 pagesSkala Ukur: Binominal MC Nemar X K Sample Contigency Coefficient C Cohran QAINUL MARDIA OKTIARANo ratings yet
- Data Analysis Comparison Between Groups Test of Correlation Interval/ratio Nominal/ Ordinal Orinal/interval/ Ratio NominalDocument2 pagesData Analysis Comparison Between Groups Test of Correlation Interval/ratio Nominal/ Ordinal Orinal/interval/ Ratio NominalEka FitrianiNo ratings yet
- Data AnalisisDocument2 pagesData AnalisisGilang apria ajiNo ratings yet
- Statistical techniques and tests classified by variables and scalesDocument5 pagesStatistical techniques and tests classified by variables and scalesethachappunkNo ratings yet
- Week 4 VariousTestMethodsDocument20 pagesWeek 4 VariousTestMethodsSilvestar MežnarićNo ratings yet
- Q Statistik Parametrik Statistik Non Parametrik Pengujian Spss Pengujian SpssDocument1 pageQ Statistik Parametrik Statistik Non Parametrik Pengujian Spss Pengujian SpssnizanzizahNo ratings yet
- Week 5 RiskRateChisquaretestsDocument18 pagesWeek 5 RiskRateChisquaretestsSilvestar MežnarićNo ratings yet
- 3 Analisis DataDocument26 pages3 Analisis DataImelia AgustinNo ratings yet
- Parametric Versus Non Parametric StatisticsDocument19 pagesParametric Versus Non Parametric Statisticsمهنوش جوادی پورفرNo ratings yet
- Choosing The Right Statistical Test: SourceDocument4 pagesChoosing The Right Statistical Test: SourceSaiNo ratings yet
- Peta StatistikDocument1 pagePeta StatistikfuadNo ratings yet
- Which Statistical Tests To UseDocument1 pageWhich Statistical Tests To UsePam FajardoNo ratings yet
- Data AnalysisDocument83 pagesData AnalysisLantana MedikaNo ratings yet
- Flow-Chart For Popularly Used Statistical TestsDocument1 pageFlow-Chart For Popularly Used Statistical TestsMohammad HeidariNo ratings yet
- Chisquare GonzalesDocument32 pagesChisquare GonzalesJ-Roe ArdemilNo ratings yet
- Test of Difference Correlational SP EsDocument6 pagesTest of Difference Correlational SP EsLampano AngelineNo ratings yet
- 4 Unit III Statistical TestsDocument9 pages4 Unit III Statistical TestsashuNo ratings yet
- SiegelDocument1 pageSiegelasmita sainiNo ratings yet
- 1 Parametrik Dan NonparametrikDocument14 pages1 Parametrik Dan Nonparametrik3rlangNo ratings yet
- Guide in Choosing Appropriate Statistical ToolDocument8 pagesGuide in Choosing Appropriate Statistical ToolAmiDacunoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-1Document27 pagesChapter 2-1EdgarNo ratings yet
- Depedpang 1Document127 pagesDepedpang 1Bayoyong NhsNo ratings yet
- Correlation Coefficients and Statistical Tests for Nominal, Ordinal and Continuous DataDocument2 pagesCorrelation Coefficients and Statistical Tests for Nominal, Ordinal and Continuous DataNeil Isaac Perez100% (1)
- Lecture 5 Inferential StatDocument58 pagesLecture 5 Inferential StatChristian SaladagaNo ratings yet
- Ingilizce Biyoistatistik Komite3 1Document215 pagesIngilizce Biyoistatistik Komite3 1Erdem AltunNo ratings yet
- What Statistic To UseDocument11 pagesWhat Statistic To UseA. Jean DemetrioNo ratings yet
- FEM 3004 - Lab Revision - para Vs Non-ParaDocument12 pagesFEM 3004 - Lab Revision - para Vs Non-ParaAINA NADHIRAH BINTI A ROZEY / UPMNo ratings yet
- Choose Statistical TestDocument2 pagesChoose Statistical Testtulkas72No ratings yet
- Rumus-Rumus Uji Statistik: Pedoman Memilih Uji KorelasiDocument1 pageRumus-Rumus Uji Statistik: Pedoman Memilih Uji KorelasiDevita AnnidaNo ratings yet
- Transprs Statistik 2Document1 pageTransprs Statistik 2MADU BASUKINo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - How To Choose A Statistical TestDocument18 pagesLecture 4 - How To Choose A Statistical TestLucasAzevedoNo ratings yet
- Summary of Statistical Tests: TABLE 6.4Document50 pagesSummary of Statistical Tests: TABLE 6.4Henry BarberenaNo ratings yet
- Choosing A Statistical Test PDFDocument5 pagesChoosing A Statistical Test PDFmpc.9315970No ratings yet
- Statistical TestsDocument32 pagesStatistical TestsAnurag MunshiNo ratings yet
- Which Statistical Tests To UseDocument2 pagesWhich Statistical Tests To Useian1231No ratings yet
- GURATDocument3 pagesGURATJoemar SubongNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Test Decision TreeDocument1 pageHypothesis Test Decision TreeIoan Mihai ArmăşelNo ratings yet
- What Test Flowchart and TableDocument2 pagesWhat Test Flowchart and TableiyerpadmaNo ratings yet
- Chap10 ReviewerDocument3 pagesChap10 ReviewerYhel TrinidadNo ratings yet
- STA 2020 Non ParametricsDocument38 pagesSTA 2020 Non ParametricsAmelie GriffithNo ratings yet
- Relationship Different Between Set of Data: (Between or Within Group(s) )Document1 pageRelationship Different Between Set of Data: (Between or Within Group(s) )Moazim Bin MohamedNo ratings yet
- Choosing Correct Statistical TestsDocument3 pagesChoosing Correct Statistical TestsMAILNPN4U0% (1)
- How To Select A Test ?Document11 pagesHow To Select A Test ?Triando ErsandiNo ratings yet
- Parametric Vs Non Parametric TestDocument4 pagesParametric Vs Non Parametric TestRitvik ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter36a (Compatibility Mode)Document65 pagesChapter36a (Compatibility Mode)billasylverine81No ratings yet
- Choosing A Statistical TestDocument2 pagesChoosing A Statistical TestWifi Sa bahayNo ratings yet
- How to choose the right statistical testDocument2 pagesHow to choose the right statistical testN RoNo ratings yet
- Basic Statistical Test Flow Chart Geo 441: Quantitative Methods Group Comparison and AssociationDocument2 pagesBasic Statistical Test Flow Chart Geo 441: Quantitative Methods Group Comparison and AssociationKomal AlamNo ratings yet
- Overview - of - Statistical - Tests 2Document1 pageOverview - of - Statistical - Tests 2CarlosNo ratings yet
- A Handbook of Statistics and Quantitative Analysis for Educational LeadershipFrom EverandA Handbook of Statistics and Quantitative Analysis for Educational LeadershipNo ratings yet
- The Application of Mathematical Statistics to Chemical AnalysisFrom EverandThe Application of Mathematical Statistics to Chemical AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Group 1Document13 pagesGroup 1Noreen DaquipilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 TDocument25 pagesChapter 19 TVISITACION ALFADNo ratings yet
- SMU Research on Grade 11 Students' Practice of CHSF GoalsDocument1 pageSMU Research on Grade 11 Students' Practice of CHSF Goalsanon_696745452No ratings yet
- Research Methodology Solved Mcqs Set 16Document6 pagesResearch Methodology Solved Mcqs Set 16Alok ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- 2-2nd Part Inform Manage PDFDocument33 pages2-2nd Part Inform Manage PDFjykaNo ratings yet
- Research Project On Time Management SystemsDocument60 pagesResearch Project On Time Management Systemsapi-378192367No ratings yet
- Guidance Center: Philippine School DohaDocument4 pagesGuidance Center: Philippine School DohacaparasangelamNo ratings yet
- Marketing: Isa 2 Market Research Group 4Document27 pagesMarketing: Isa 2 Market Research Group 4moqimNo ratings yet
- T-Test Analysis: Comparing Life Satisfaction and Science KnowledgeDocument9 pagesT-Test Analysis: Comparing Life Satisfaction and Science KnowledgeMas KudinNo ratings yet
- Sat Course NoteDocument2 pagesSat Course Notenikes 1No ratings yet
- Art (Cohen, 1962) The Statistical Power of Abnormal-Social Psychological Research - A ReviewDocument9 pagesArt (Cohen, 1962) The Statistical Power of Abnormal-Social Psychological Research - A ReviewIsmael NeuNo ratings yet
- Makalah ExperimentalDocument13 pagesMakalah ExperimentalNurjannah AnwarNo ratings yet
- Biometry Final 1999 KeyDocument12 pagesBiometry Final 1999 Keyallbayrakg1No ratings yet
- Mid Assessment Phil Iri Oral Reading Class Scoring Template Filipino EnglishDocument3 pagesMid Assessment Phil Iri Oral Reading Class Scoring Template Filipino EnglishGlaze BoncalesNo ratings yet
- BA BBA Economics IV SEM IV-12Document4 pagesBA BBA Economics IV SEM IV-12krish bhatiaNo ratings yet
- Critical AppraisalDocument71 pagesCritical Appraisaloddone_outNo ratings yet
- Aptitude Personality Practice TestsDocument5 pagesAptitude Personality Practice Testsmita000No ratings yet
- Quasi-Experimental Design (Pre-Test and Post-Test Studies) in Prehospital and Disaster ResearchDocument2 pagesQuasi-Experimental Design (Pre-Test and Post-Test Studies) in Prehospital and Disaster ResearchNino AlicNo ratings yet
- BQ Questionnaire Assesses Pain DimensionsDocument7 pagesBQ Questionnaire Assesses Pain Dimensionsi pentungNo ratings yet
- Ch-4 QuestionnaireDocument18 pagesCh-4 QuestionnaireTanvir IslamNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3: Research MethodologyDocument10 pagesCHAPTER 3: Research Methodologysaksham sharmaNo ratings yet
- Prem Mann, Introductory Statistics, 7/EDocument30 pagesPrem Mann, Introductory Statistics, 7/EZihad hasanNo ratings yet
- Oxford University Press - Online Resource Centre - Multiple Choice Questions7Document4 pagesOxford University Press - Online Resource Centre - Multiple Choice Questions7pink1231No ratings yet
- 05 MQA Pre-Test & Post Test Analysis With SAMPLE COMPUTATIONSDocument5 pages05 MQA Pre-Test & Post Test Analysis With SAMPLE COMPUTATIONSDvy D. VargasNo ratings yet
- Lem4 - 500x200 - Garnet EspDocument276 pagesLem4 - 500x200 - Garnet Esphannah goldNo ratings yet