Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CSTP 1 CTP Continuum Blank
Uploaded by
api-7018359490 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views7 pagesOriginal Title
cstp 1 ctp continuum blank
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views7 pagesCSTP 1 CTP Continuum Blank
Uploaded by
api-701835949Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
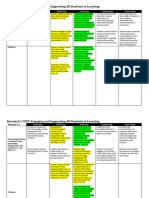
Standard 1 CSTP: Engaging and Supporting All Students in Learning
Element 1.1 Emerging Exploring Applying Integrating Innovating
Learns about students Gathers additional Uses data from a variety of formal and Uses data from Uses comprehensive
through data provided data to learn about informal sources to learn about multiple measures to knowledge of students
by the school and/or individual students. students and guide selection of make adjustments to to make ongoing
assessments. instructional strategies to meet diverse instruction and meet adjustments and
learning needs. individual identified accommodations in
learning needs. instruction.
Using knowledge Students engage in learning through the
of students to use of adjustments in instruction to
engage them in Some students may Students engage in meet their needs. Students actively Students take
learning engage in learning single lessons or utilize a variety of ownership of their
using instructional sequence of lessons instructional strategies learning by choosing
strategies focused on that include some and technologies in from a wide range of
the class as a whole. adjustments based on learning that ensure methods to further
assessments equitable access to the their learning that are
9/25/23
curriculum. responsive to their
learning needs.
Incorporating real-life :
connections into the
curriculum is a
powerful way to
engage students and
demonstrate the
relevance of
mathematical concepts.
Here are a few ways
real-life connections
can be evidenced in my
class:
-If students are
Evidence engaged in activities
that require them to
apply mathematical
concepts to solve real-
world problems, such
as calculating areas of
spaces for interior
design or using algebra
to manage personal
finances, it
demonstrates a
connection between
math and everyday life.
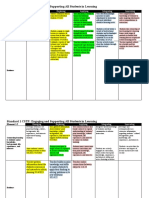
Standard 1 CSTP: Engaging and Supporting All Students in Learning
Element 1.2 Emerging Exploring Applying Integrating Innovating
Develops awareness of Uses gathered Uses school resources and Integrates broad Develops and
prior knowledge, culture, information about family contacts to expand knowledge of students systematically uses
backgrounds, life students’ prior understanding of and their communities to extensive information
experiences, and interests knowledge, cultural students’ prior inform instruction. regarding students’
represented among backgrounds, life knowledge, cultural cultural backgrounds,
students. experiences, and interest backgrounds, life prior knowledge, life
Connecting learning
to support student experiences, and interests experiences, and
to students’ prior
learning. to connect to student interests.
knowledge, 9/25/2023
learning.7/16/23
backgrounds, life
experiences, and
Some students connect Students participate in Students make Students are actively Students can articulate
interests
learning activities to their single lessons or connections between engaged in curriculum, the relevance and impact
own lives. sequences of lessons curriculum, and their which relates their prior of lessons on their lives
related to their interests prior knowledge, knowledge, experiences, and society.
and experiences. backgrounds, life and interests within and
experiences, and across learning activities.
interests.
Encourage students to
share their experiences
and apply their cultural
perspectives in problem-
solving or discussions,
fostering an inclusive
classroom environment.
Implement hands-on
activities that engage
students in collaborative
group projects where
they can bring their
unique perspectives to
Evidence
solve algebraic problems
or explore mathematical
concepts within the
context of their
backgrounds.
Modify teaching
approaches and learning
materials based on
students’ responses and
feedback, ensuring that
the learning environment
remains inclusive and
accommodating of their
Standard 1 CSTP: Engaging and Supporting All Students in Learning
diverse backgrounds and
experiences.
Standard 1 CSTP: Engaging and Supporting All Students in Learning
Element 1.3 Emerging Exploring Applying Integrating Innovating
Uses real-life connections Explore using additional Integrates connections Integrates connections to Engages student in
during instruction as real-life connections to from subject matter to meaningful, real-life actively making
identified to curriculum. subject matter in single meaningful, real-life contexts in planning connections to relevant,
lessons or sequence of contexts, including those subject matter instruction meaningful, and real-life
lessons to support specific to students’ and is responsive during contexts throughout
understanding. family and community. instruction to engage subject matter
Connecting subject students in relating to instruction.
matter to 9/25/2023 subject matter.
meaningful, real-life
contexts Some students relate Students make use of Students utilize real-life Students actively engage Students routinely
subject matter to real-life. real-life connections connections regularly to in making and using real- integrate subject matter
provided in single lessons develop understandings life connections to subject into their own thinking
or sequence of lessons to of subject matter. matter to extend their and make relevant
support understanding of understanding. applications of subject
subject matter. matter during learning
activities.
A series of lessons on
geometry and spatial
reasoning. Incorporates
real-life connections by
using examples from
urban planning and
design. Present
architectural blueprints,
city maps, and
construction layouts,
demonstrating how
geometry concepts are
Evidence utilized in real-world
applications.
Standard 1 CSTP: Engaging and Supporting All Students in Learning
Element 1.4 Emerging Exploring Applying Integrating Innovating
Uses instructional Explores additional Utilizes a variety of Creates, adapts, and Refines the flexible use of
strategies, resources, and instructional strategies, strategies including integrates a broad range an extensive repertoire of
technologies as provided resources, and culturally responsive of strategies, resources, strategies, resources, and
by school and/or district. technologies in single pedagogy, resources, and and technologies into technologies to meet
lessons or sequence of technologies during instruction designed to students’ diverse learning
Using a variety of lessons to meet students’ ongoing instruction to meet students’ diverse needs.
instructional diverse learning needs. meet students’ diverse learning needs.
strategies, resources, learning needs.
and technologies to
meet students’ Some students participate Students participate in Students participate in Students actively engage Students take
diverse learning in instructional strategies, single lessons or instruction using in instruction and make responsibilities for using
needs using resources and sequence of lessons strategies, resources, and use of a variety of a wide range of strategies,
technologies provided. related to their interests technologies matched to targeted strategies, resources, and
and experiences. their learning needs. resources, and technologies that
technologies to meet their successfully advance their
9/25/2023
individual students learning.
needs.
Students participate in
the lesson using these
resources and
technologies. They solve
problems on tablets or
laptops using math
software, engaging with
interactive activities that
allow them to manipulate
shapes, plot graphs, or
solve equations in a
digital format. This
Evidence approach not only
enhances their
understanding of math
concepts but also makes
learning more dynamic
and enjoyable.
Standard 1 CSTP: Engaging and Supporting All Students in Learning
Element 1.5 Emerging Exploring Applying Integrating Innovating
Asks questions that focus Includes questions in Guide students to think Supports students to Facilitates systematic
on factual knowledge and single lessons or a critically through use of initiate critical thinking opportunities for student
comprehension. sequence of lessons that questioning strategies, through independently to apply critical thinking
require students to recall, posing/solving problems, developing questions, by designing structured
interpret, and think and reflection on issues in posing problems and inquiries into complex
critically. content. reflecting on multiple problems.
Promoting critical
perspectives.
thinking though 9/25/2023
inquiry, problem
Some students respond to Students respond to Students respond to Students pose problems Students pose and
solving, and
questions regarding facts varied questions or tasks questions and problems and construct questions answer a wide-range of
reflection
and comprehension. designed to promote posed by the teacher and of their own to support complex questions and
comprehension and begin to pose and solve inquiries into content. problems, reflect, and
critical thinking in single problems of their own communicate
lessons or a sequence of related to the content. understandings based on
lessons. in depth analysis of
content learning.
Some students respond
by providing definitions
and explanations based
on their understanding of
the facts and
comprehension of the
material. They might
articulate the steps to
solve a basic linear
equation, identify
variables, or describe the
purpose of algebraic
equations in problem-
Evidence solving.
This approach helps
gauge the students' grasp
of the foundational
knowledge required for
the lesson. It also
encourages active
participation and allows
students to demonstrate
their understanding of
the factual information
and the basic principles of
algebraic equations.
Standard 1 CSTP: Engaging and Supporting All Students in Learning
Element 1.6 Emerging Exploring Applying Integrating Innovating
Implements lessons Seeks to clarify Makes ongoing Adjusts strategies during Makes adjustments to
following curriculum instruction and learning adjustments to instruction based on the extend learning
guidelines. activities to support instruction based on ongoing monitoring of opportunities and
student understanding. observation of student individual student needs provide assistance to
engagement and regular for assistance, support, or students in mastering the
Monitoring student 9/25/2023 checks for understanding. challenge. concepts flexibly and
learning and effectively.
adjusting instruction
while teaching. Some students receive Students receive Students successfully Students are able to Students monitor their
individual assistance assistance individually or participate and stay articulate their level of progress in learning and
during instruction. in small groups during engaged in learning understanding and use provide information to
instruction. activities. teacher guidance to meet teacher that informs
their needs during adjustments in
instruction. instruction.
Provide individualized
assistance to these
students while the rest of
the class is engaged in the
lesson. For instance, if a
group of students is
having difficulty grasping
the concept of fractions,
the teacher offers
additional explanations,
personalized examples, or
extra practice problems
Evidence to reinforce
understanding.
You might also like
- cstp1 2009Document7 pagescstp1 2009api-557045107No ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Morales 9Document6 pagesCSTP 1 Morales 9api-706935007No ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Cortez 5Document6 pagesCSTP 1 Cortez 5api-510049480No ratings yet
- Kami Export - cstp1 - Engaging and Supporting All Students in LearningDocument9 pagesKami Export - cstp1 - Engaging and Supporting All Students in Learningapi-557217564No ratings yet
- 1 CSTP Harnetiaux 9Document9 pages1 CSTP Harnetiaux 9api-703176754No ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Sarmiento 4Document7 pagesCSTP 1 Sarmiento 4api-468338109No ratings yet
- Emerging Exploring Applying Integrating Innovating: Element 1.1Document9 pagesEmerging Exploring Applying Integrating Innovating: Element 1.1Lola JonesNo ratings yet
- CSTP 1 AlvaradoDocument7 pagesCSTP 1 Alvaradoapi-679251480No ratings yet
- Standard 1 CSTPDocument9 pagesStandard 1 CSTPapi-622432874No ratings yet
- CSTP 1Document6 pagesCSTP 1api-557064190No ratings yet
- CSTP 1Document7 pagesCSTP 1api-643035312No ratings yet
- cstp1 2009Document11 pagescstp1 2009api-483535623No ratings yet
- CSTP Semester 4Document41 pagesCSTP Semester 4api-464335930No ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Cardenas 9Document7 pagesCSTP 1 Cardenas 9api-431761955No ratings yet
- cstp1 2009Document6 pagescstp1 2009api-635814181No ratings yet
- cstp1 Kapp 04Document8 pagescstp1 Kapp 04api-621763585No ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Parsons Mara 9Document24 pagesCSTP 1 Parsons Mara 9api-705466847No ratings yet
- cstp1 Nguyen 071323Document7 pagescstp1 Nguyen 071323api-621911859No ratings yet
- CSTP 1Document4 pagesCSTP 1api-701835949No ratings yet
- CSTP 1-6 Ehlers 7Document39 pagesCSTP 1-6 Ehlers 7api-622333255No ratings yet
- CSTP 2 Parsons MaraDocument44 pagesCSTP 2 Parsons Maraapi-705466847No ratings yet
- CSTP 1-6 Anderson 0925Document46 pagesCSTP 1-6 Anderson 0925api-636976481No ratings yet
- CSTPDocument39 pagesCSTPapi-621911859No ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Welch 5 1 22Document9 pagesCSTP 1 Welch 5 1 22api-556922417No ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Paniagua 9Document8 pagesCSTP 1 Paniagua 9api-703694794No ratings yet
- cstp1 2009Document6 pagescstp1 2009gayle CervantesNo ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Lynch 10.23.22Document8 pagesCSTP 1 Lynch 10.23.22Jill LNo ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Hamilton 9Document7 pagesCSTP 1 Hamilton 9api-431552136No ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Johnson 9Document6 pagesCSTP 1 Johnson 9api-701823031No ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Salamone 9.18.22Document6 pagesCSTP 1 Salamone 9.18.22Taylor SalamoneNo ratings yet
- Karli Keller cstp1 2009 1Document7 pagesKarli Keller cstp1 2009 1api-637097800No ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Basani 4Document10 pagesCSTP 1 Basani 4api-518571218No ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Smith 9Document7 pagesCSTP 1 Smith 9api-701691719No ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Stack 9Document6 pagesCSTP 1 Stack 9api-528653613No ratings yet
- cstp1 2023Document7 pagescstp1 2023api-679038994No ratings yet
- Standard 1 CSTP: Engaging and Supporting All Students in LearningDocument7 pagesStandard 1 CSTP: Engaging and Supporting All Students in LearningKaitlyn AprilNo ratings yet
- CSTP J Galindo 7 16 22 1Document7 pagesCSTP J Galindo 7 16 22 1api-622411184No ratings yet
- Cstps Churchill 0522Document41 pagesCstps Churchill 0522api-572990955No ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Anderson 12Document10 pagesCSTP 1 Anderson 12api-636976481No ratings yet
- CSTP 1 WhyteDocument6 pagesCSTP 1 Whyteapi-529397255No ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Lee 7Document6 pagesCSTP 1 Lee 7api-679039283No ratings yet
- CTSP 1 Martin 11Document6 pagesCTSP 1 Martin 11api-484707727No ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Romo 04Document6 pagesCSTP 1 Romo 04api-468055323No ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Steiss 7Document8 pagesCSTP 1 Steiss 7api-678983495No ratings yet
- CSTP 9 25 22 Mary ArmasDocument55 pagesCSTP 9 25 22 Mary Armasapi-637047815No ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Knepper 9Document8 pagesCSTP 1 Knepper 9api-635789824No ratings yet
- CTSP 1 Butterbrodt 7Document6 pagesCTSP 1 Butterbrodt 7api-679216509No ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Naamani 9 21 19Document6 pagesCSTP 1 Naamani 9 21 19api-483582055No ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Sammy 5Document6 pagesCSTP 1 Sammy 5api-432388156No ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Eanes 7Document7 pagesCSTP 1 Eanes 7api-621917909No ratings yet
- CSTPDocument24 pagesCSTPapi-701572518No ratings yet
- CSTP Bauman 9.12.23Document7 pagesCSTP Bauman 9.12.23michelle BaumanNo ratings yet
- CSTP 1 Thomas 4Document6 pagesCSTP 1 Thomas 4api-571036019No ratings yet
- Mastering the Art of Teaching: A Comprehensive Guide to Becoming an Exceptional EducatorFrom EverandMastering the Art of Teaching: A Comprehensive Guide to Becoming an Exceptional EducatorNo ratings yet
- Connecting Readers to Multiple Perspectives: Using Culturally Relevant Pedagogy in a Multicultural ClassroomFrom EverandConnecting Readers to Multiple Perspectives: Using Culturally Relevant Pedagogy in a Multicultural ClassroomNo ratings yet
- Classroom-Ready Resources for Student-Centered Learning: Basic Teaching Strategies for Fostering Student Ownership, Agency, and Engagement in K–6 ClassroomsFrom EverandClassroom-Ready Resources for Student-Centered Learning: Basic Teaching Strategies for Fostering Student Ownership, Agency, and Engagement in K–6 ClassroomsNo ratings yet
- Connected Science: Strategies for Integrative Learning in CollegeFrom EverandConnected Science: Strategies for Integrative Learning in CollegeTricia A. FerrettNo ratings yet
- Teacher Guide for A Girl Called Echo: Learning About the History and Culture of the Métis Nation in Grades 6–8From EverandTeacher Guide for A Girl Called Echo: Learning About the History and Culture of the Métis Nation in Grades 6–8No ratings yet
- Resource Teachers: A Changing Role in the Three-Block Model of Universal Design for LearningFrom EverandResource Teachers: A Changing Role in the Three-Block Model of Universal Design for LearningNo ratings yet
- Narrative End of Year Report Card Comments: Created by Ed-Spread's Report Card Comment GeneratorDocument4 pagesNarrative End of Year Report Card Comments: Created by Ed-Spread's Report Card Comment GeneratorSouthNo ratings yet
- Final Reaction Paper: Asawakowitkorn)Document3 pagesFinal Reaction Paper: Asawakowitkorn)Wasit ASawaNo ratings yet
- Hmec5313 - V2 Counseling and Guiding Children in Early Childhood EducationDocument13 pagesHmec5313 - V2 Counseling and Guiding Children in Early Childhood EducationTutor EvonNo ratings yet
- Fostering Metacognition To SupportDocument7 pagesFostering Metacognition To SupportAnabel Espitia CamposNo ratings yet
- Student Perceptions of Academic Integrity: A Qualitative Study of Understanding, Consequences, and ImpactDocument19 pagesStudent Perceptions of Academic Integrity: A Qualitative Study of Understanding, Consequences, and ImpactUsama SyedNo ratings yet
- 19 Cost Engineer Interview Questions (With Example Answers)Document19 pages19 Cost Engineer Interview Questions (With Example Answers)Rahul JangirNo ratings yet
- Critical ReadingDocument16 pagesCritical ReadingAlain DaccacheNo ratings yet
- Property Law Course Manual Fall 2023Document16 pagesProperty Law Course Manual Fall 2023Aastha JainNo ratings yet
- Assistance Country ManagerDocument3 pagesAssistance Country Managerwinniet_nNo ratings yet
- HB Technology Scope SequenceDocument4 pagesHB Technology Scope Sequenceapi-256818695No ratings yet
- Patricio Abinales Philosopher Info PaperDocument8 pagesPatricio Abinales Philosopher Info Paperkenta AdachiNo ratings yet
- School Grade Level ONE Teacher Subject ENGLISH Week Week 3 Quarter Fourth QuarterDocument4 pagesSchool Grade Level ONE Teacher Subject ENGLISH Week Week 3 Quarter Fourth QuarterEvan Maagad LutchaNo ratings yet
- January 2020 Mark SchemeDocument16 pagesJanuary 2020 Mark SchemeSumbal MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Placement Opportunity - MyCaptainDocument2 pagesPlacement Opportunity - MyCaptainShikhar chauhanNo ratings yet
- Jan Faye (Auth.) - The Nature of Scientific Thinking - On Interpretation, Explanation, and Understanding-Palgrave Macmillan UK (2014)Document347 pagesJan Faye (Auth.) - The Nature of Scientific Thinking - On Interpretation, Explanation, and Understanding-Palgrave Macmillan UK (2014)maricelly gomez100% (1)
- Body Paragraphs Lesson GoodrellDocument3 pagesBody Paragraphs Lesson Goodrellleahjones73No ratings yet
- 0096 Primary Maths Stage 2 Scheme of Work - tcm142-594956Document96 pages0096 Primary Maths Stage 2 Scheme of Work - tcm142-594956Tatenda HapazariNo ratings yet
- Integrated ModelDocument1 pageIntegrated Modelapi-256532643No ratings yet
- DLLEYAAADocument5 pagesDLLEYAAAfor everNo ratings yet
- Preamble General Agric SyllabusDocument72 pagesPreamble General Agric SyllabusDaniel AnsonNo ratings yet
- Ubd Lesson Plans and MaterialsDocument27 pagesUbd Lesson Plans and Materialsapi-349579702No ratings yet
- 10 Characteristics of Successful SalespeopleDocument11 pages10 Characteristics of Successful SalespeopleDean BacicNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7Document5 pagesLesson 7api-359979131No ratings yet
- Listening StrategicsDocument24 pagesListening StrategicsKaren Cecilia RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Music Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesMusic Lesson Planapi-663007399No ratings yet
- AQA A Level Business Unit Assessment Unit 3.4 SampleDocument22 pagesAQA A Level Business Unit Assessment Unit 3.4 SampleAejaz MohamedNo ratings yet
- Cassandra Lia Edma310 At1Document2 pagesCassandra Lia Edma310 At1api-357921202No ratings yet
- MYP Spanish 3 IB Unit Planner - Cuban RevolutionDocument4 pagesMYP Spanish 3 IB Unit Planner - Cuban RevolutionColin Krysl100% (1)
- Bridges Page 2 in Mathematics Kindergarten Family Overview Unit 4Document1 pageBridges Page 2 in Mathematics Kindergarten Family Overview Unit 4api-292285340No ratings yet
- Chat GPTDocument8 pagesChat GPTMohuddin MemonNo ratings yet