Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Simplex Transmission Mode?: Computer Networking
What Is Simplex Transmission Mode?: Computer Networking
Uploaded by
Debabrata DuttaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is Simplex Transmission Mode?: Computer Networking
What Is Simplex Transmission Mode?: Computer Networking
Uploaded by
Debabrata DuttaCopyright:
Available Formats
Computer Networking
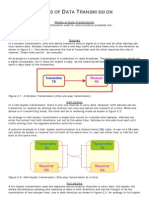
Full-Duplex mode has double bandwidth as compared to the half-duplex. The capacity
of the channel is divided between the two directions of communication. This mode is
used when communication in both directions is required simultaneously.
For Example, a Telephone Network, in which both the persons can talk and listen to
each other simultaneously.
Following are the advantages of using a full-duplex transmission mode:
1. The two-way communication can be carried out simultaneously in both
directions.
2. It is the fastest mode of communication between devices.
Following are the disadvantages of using a half-duplex transmission mode:
1. The capacity of the communication channel is divided into two parts. Also, no
dedicated path exists for data transfer.
2. It has improper channel bandwidth utilization as there exist two separate paths
for two communicating devices.
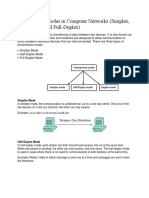
What is Simplex Transmission Mode?
In this mode, we have unidirectional communication- meaning it’s a one-way street.
Out of the two connecting devices, only one is capable of transmission- the other one
is only capable of receiving. The simplex mode can always utilize a channel’s entire
capacity for sending the data in a single direction.
For Example – Traditional monitors and keyboards use the Simplex transmission
mode. In this case, the monitor can only generate the output, and the keyboard can
only introduce an input in the system.
What is Half Duplex Transmission Mode?
In this mode, every station can both- receive and transmit data- but not at the very
same moment. When one of the devices sends information, the other one can only
then receive it. It also happens vice versa because the transmission is not
unidirectional. The half-duplex mode comes into play in those cases where we don’t
need the transmission in both directions at the same moment.
For Example – A walkie-talkie uses the Half-Duplex Transmission Mode. Here, we
send messages in both directions, but the transmission still occurs in one direction at
a time.
What is Full Duplex Transmission Mode?
Compiled By Dr. Debabrata Dutta Session 2023 2024 Page 8
Computer Networking
In this mode, both the stations have the ability to both receive and transmit data
simultaneously. The signals that go in one direction in a Full-Duplex mode share the
link’s capacity with the signals that go in the other direction. Such kind of sharing can
occur in two alternative ways:
The transmission link must have two transmission paths that are physically separate-
one of them for receiving and the other one for sending.
The link can divide the capacity between the signals that travel in either of the
directions.
The Full-Duplex communication mode comes into play when one requires a
continuous connection in both directions all the time. However, it needs to divide the
channel’s capacity between both these directions.
For Example – Telephone networks that establish communication between two people
via a telephone line use the Full Duplex method. Here, the individuals can listen as
well as talk at the very same time.
Difference Between Simplex, Half Duplex, and Full Duplex Transmission Modes
Simplex Transmission Half Duplex Full Duplex
Parameters
Mode Transmission Mode Transmission Mode
It is a mode of It is a mode of
transmission in which It is a mode of transmission in which
the flow of data is transmission in which the flow of data is bi-
unidirectional. It the flow of data is bi- directional. But here,
means that the directional but only in the devices can send as
participant can do one direction at a time. well as receive data
Definition
only one task at a It means that the simultaneously at the
time in a single receiver can receive as same time. It means
direction. The receiver well as send data but that the receiver can
can only receive data can perform only one of receive as well as send
and not send it (and these tasks at a time. data at the very same
vice versa). time with no hitch.
The Full-Duplex Mode
As already mentioned The Half-Duplex Mode
supports a BiDirectional
above, the Simplex supports a
flow of data in both
Flow of Data Mode supports a BiDirectional flow of
directions at the same
UniDirectional flow of data but in one
time (simultaneous
data. direction at a time.
flow).
The sender can only A device can both send Both the devices or end
send data. But there’s and receive data. But it stations in the
Sender and no option to receive it cannot perform both transmission can act as
Receiver (and vice versa). Thus, the processes together- senders as well as
the transmission only one thing is receivers. The
involves one station as possible at a time. This transmission also occurs
Compiled By Dr. Debabrata Dutta Session 2023 2024 Page 9
You might also like
- Lab Packet Tracer Voip Plus: TopologyDocument4 pagesLab Packet Tracer Voip Plus: TopologyFernando FigueredoNo ratings yet
- Data Transmission Modes and FormsDocument3 pagesData Transmission Modes and FormsRepunzel Raaj0% (1)
- History and Evolution of Information Transmission TechniquesDocument18 pagesHistory and Evolution of Information Transmission Techniquespaola lancheros0% (1)
- Nso User Guide-5.3 PDFDocument178 pagesNso User Guide-5.3 PDFAla JebnounNo ratings yet
- HD IP Camera User Manual - V1.1Document49 pagesHD IP Camera User Manual - V1.1A.Sina. DidebanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document15 pagesUnit 1jkashish04No ratings yet
- Intrudaction Communication SystemDocument15 pagesIntrudaction Communication System47b363575eNo ratings yet
- Transmission ModesDocument15 pagesTransmission ModesBlendie Quiban Jr.No ratings yet
- Computer Network Notes Unit-2Document19 pagesComputer Network Notes Unit-2Medhanshu KaushikNo ratings yet
- Transmission Modes - Lec3Document20 pagesTransmission Modes - Lec3Heba FarhatNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization and ArchitectureDocument22 pagesComputer Organization and ArchitectureasratNo ratings yet
- Networking (Mcan 204) Unit 1Document51 pagesNetworking (Mcan 204) Unit 1mohinibhimtay1289No ratings yet
- Simplex Half and Full DuplexDocument4 pagesSimplex Half and Full DuplexM.E. Sarwar LemonNo ratings yet
- Works Across Apps and Sites: Simplex, Half-Duplex, And, Full-Duplex ExplainedDocument3 pagesWorks Across Apps and Sites: Simplex, Half-Duplex, And, Full-Duplex Explainedoluwatosin PereiraNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Simplex, Half Duplex and Full Duplex Transmission ModesDocument5 pagesDifference Between Simplex, Half Duplex and Full Duplex Transmission ModesNafisa IslamNo ratings yet
- Computer Network Tut DocumentationDocument2 pagesComputer Network Tut Documentationgowilaf601No ratings yet
- Transmission Modes in Computer Networks (Simplex, Half-Duplex and Full-Duplex) - GeeksforGeeksDocument2 pagesTransmission Modes in Computer Networks (Simplex, Half-Duplex and Full-Duplex) - GeeksforGeeksBhageerathi SahuNo ratings yet
- Transmission ModesDocument5 pagesTransmission ModesMuneeza AlizaNo ratings yet
- Transmission Modes in Computer Networks: Simplex ModeDocument2 pagesTransmission Modes in Computer Networks: Simplex ModeJawad SandhuNo ratings yet
- Differentiate Simplex, Half-Duplex, and Full-Duplex Transmission ModesDocument2 pagesDifferentiate Simplex, Half-Duplex, and Full-Duplex Transmission ModesAdelfa Mae BerdonNo ratings yet
- 1 Transmission ModeDocument12 pages1 Transmission Modechabdulmanan8953No ratings yet
- Modes of Data Transfer in Computer: Bca 5 SemDocument14 pagesModes of Data Transfer in Computer: Bca 5 SemDr. M. Karthigai Pandian Asso Prof ICENo ratings yet
- Transmission Modes of CommunicationDocument2 pagesTransmission Modes of CommunicationLalith KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Transmission Modes in Computer NetworksDocument2 pagesTransmission Modes in Computer Networkstrevor100% (1)
- Simplex Vs Half Duplex Vs Full DuplexDocument1 pageSimplex Vs Half Duplex Vs Full DuplexNur SyahirahNo ratings yet
- Basis For ComparisonDocument1 pageBasis For ComparisonNur SyahirahNo ratings yet
- Data TransmissionDocument11 pagesData TransmissionDr. Muhammad SafdarNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkingDocument2 pagesComputer NetworkingDebabrata DuttaNo ratings yet
- CN 234567832Document243 pagesCN 234567832TanvirNo ratings yet
- CN Unit 1Document29 pagesCN Unit 1Harish NarayananNo ratings yet
- LO 2 Slide 1Document23 pagesLO 2 Slide 1biruk mollaNo ratings yet
- 3 - Transmission ModesDocument10 pages3 - Transmission ModesUmaa OhriNo ratings yet
- Types of Transmission ModesDocument2 pagesTypes of Transmission ModesMega TronNo ratings yet
- Network DuplexingDocument15 pagesNetwork DuplexingLouie AngelesNo ratings yet
- Presentation 3Document47 pagesPresentation 3AyanNo ratings yet
- 02 - Modes of Data TransmissionDocument2 pages02 - Modes of Data TransmissionOmer107100% (1)
- CN Unit1Document47 pagesCN Unit1uppiliraja4440No ratings yet
- CN-lecture2 Network Arch and Tran ModeDocument7 pagesCN-lecture2 Network Arch and Tran ModeⲤʟᴏᴡɴᴛᴇʀ ᏀᴇɪꜱᴛNo ratings yet
- CS8591 - CN Unit 1 PDFDocument44 pagesCS8591 - CN Unit 1 PDFMsd70% (1)
- cs3591 CN Unit 1Document45 pagescs3591 CN Unit 1spartansheikNo ratings yet
- Transmission Modes in Computer NetworksDocument8 pagesTransmission Modes in Computer Networksvishnu neupaneNo ratings yet
- Communication ChannelsDocument9 pagesCommunication Channelsmohammed aliNo ratings yet
- Cs8591 - CN Unit 1Document44 pagesCs8591 - CN Unit 1E L A N G ONo ratings yet
- FIT Lecture Data CommunicationDocument33 pagesFIT Lecture Data Communicationsyed abuzarNo ratings yet
- CN Unit 2Document39 pagesCN Unit 2Tarun SinghNo ratings yet
- Data TransmissionDocument13 pagesData TransmissionShubhamKumar100% (1)
- Data FlowDocument9 pagesData Flowjakatoh804No ratings yet
- Mod - Computer - 10Document3 pagesMod - Computer - 10Mauro ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument239 pagesComputer NetworksDev RanaNo ratings yet
- Cs8591-Computer Networks-1593855642-Cs8591 CN PDFDocument239 pagesCs8591-Computer Networks-1593855642-Cs8591 CN PDFDark TurboNo ratings yet
- CS8591 - CN Unit 1Document44 pagesCS8591 - CN Unit 1Vishnu priyaNo ratings yet
- Data TransmissionDocument13 pagesData TransmissionShaikh Mohammed LoveNo ratings yet
- 03 Simplex Half Duplex, DuplexDocument1 page03 Simplex Half Duplex, DuplexWafula DerrickNo ratings yet
- Data TransmissionDocument14 pagesData TransmissionPankaj Kumar100% (1)
- F3 Computer Science-Data TransmissionDocument15 pagesF3 Computer Science-Data TransmissionIss MeNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and Computer NetworkingDocument44 pagesData Communication and Computer Networkingeskedar assefaNo ratings yet
- 1.what Are The Different Modes of Communication?explain in BriefDocument3 pages1.what Are The Different Modes of Communication?explain in Briefmieb svxsNo ratings yet
- Simplex, Half-Duplex & Duplex Communication Channels: Networks and Communications Bscs 2Document6 pagesSimplex, Half-Duplex & Duplex Communication Channels: Networks and Communications Bscs 2JAYROLD LLAVANNo ratings yet
- ICT PresentationDocument13 pagesICT Presentationsaiflaghari04No ratings yet
- Data CommmDocument11 pagesData CommmMiraculous MiracleNo ratings yet
- ComputerDocument7 pagesComputerSushil KaphleNo ratings yet
- Compare Between Simplex, Half Duplex, and Full-Duplex ModeDocument1 pageCompare Between Simplex, Half Duplex, and Full-Duplex ModeNatha lieNo ratings yet
- ACE Workbook v2.0Document81 pagesACE Workbook v2.0tarantula_22No ratings yet
- FortiAnalyzer 7.2.1 Administration GuideDocument398 pagesFortiAnalyzer 7.2.1 Administration Guidelahidu lakshanNo ratings yet
- Glossario TelecomDocument31 pagesGlossario Telecomarh91No ratings yet
- DWDM-April2011 Question PapersDocument3 pagesDWDM-April2011 Question PapersRaja VeerlaNo ratings yet
- BelView NMS User Guide 5 3Document285 pagesBelView NMS User Guide 5 3michael dejeneNo ratings yet
- What Is It?: WAN OptimizationDocument4 pagesWhat Is It?: WAN OptimizationAjitNo ratings yet
- Atm ProjectDocument18 pagesAtm Projectsujit_ranjanNo ratings yet
- Share 'CSS NCII Institutional Assessment Task - Docx'Document1 pageShare 'CSS NCII Institutional Assessment Task - Docx'jonathan labajoNo ratings yet
- 07Document15 pages07vinodNo ratings yet
- 3) Infrastructure Level Threats and VulnerabilitiesDocument33 pages3) Infrastructure Level Threats and VulnerabilitiesBhanu NaikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document14 pagesChapter 10abishekNo ratings yet
- ATAK Change Log CIV 4.0Document19 pagesATAK Change Log CIV 4.0foxbat1988No ratings yet
- Individual Control Home Automation System PDFDocument72 pagesIndividual Control Home Automation System PDFعلي ناصرNo ratings yet
- IGNOU STUDENT ZONE - Discussion Board: Download Solved Assignment of BCS-056Document4 pagesIGNOU STUDENT ZONE - Discussion Board: Download Solved Assignment of BCS-056Jayakrishna IJNo ratings yet
- CSIT 413 - Session 1Document53 pagesCSIT 413 - Session 1Ferdinand KatsrikuNo ratings yet
- Protect Kids Using Parental Control For Internet AccessDocument2 pagesProtect Kids Using Parental Control For Internet AccessVishal SunilNo ratings yet
- Tropos Product Line Overview: Tropos Mesh Routers Software VDocument2 pagesTropos Product Line Overview: Tropos Mesh Routers Software VfathiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Xinu and Kernel Programming: Bina Ramamurthy Bina@Buffalo - EduDocument40 pagesIntroduction To Xinu and Kernel Programming: Bina Ramamurthy Bina@Buffalo - Edudsangria119No ratings yet
- ProtonodeDocument36 pagesProtonodeWilliamAlfonsoSanchezPaezNo ratings yet
- Router 6000 Ericsson 6273Document2 pagesRouter 6000 Ericsson 6273Zoumana KaridioulaNo ratings yet
- NFV and MEC - DifferencesDocument3 pagesNFV and MEC - DifferencesAjay VachhaniNo ratings yet
- TwinCAT EC Diag Eng 21Document105 pagesTwinCAT EC Diag Eng 21SenderTC100% (2)
- Proliant Dl380P Gen8 SFF Proliant Dl380P Gen8 8LffDocument2 pagesProliant Dl380P Gen8 SFF Proliant Dl380P Gen8 8Lffkalin3169899No ratings yet
- Bridging: Bridged Interface To An External RouterDocument16 pagesBridging: Bridged Interface To An External RoutersureshccnaNo ratings yet
- Iotivity - Connecting Things in Iot: Ashok SubashDocument48 pagesIotivity - Connecting Things in Iot: Ashok SubashVishal RathodNo ratings yet
- Wonderware - InTouch Access Anywhere Admin Manual 2013Document58 pagesWonderware - InTouch Access Anywhere Admin Manual 2013efNo ratings yet