Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cost Benifit Analysis
Uploaded by
Ava Das0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageCost Benifit Analysis
Uploaded by
Ava DasCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
The following information pertains to questions 81 and 82. Petro Ltd.
refines raw oil into several different
products and in one month produces 50,000 units of Product A and 40,000 units of Product B. Each unit
of A can be sold for $14 and each unit of B can be sold for $20. The monthly joint costs are $600,000. All
units produced are sold, and there is no beginning inventory. 81. Using the sales value at split-off
method, what are the joint allocation costs for Product B (rounded to the nearest thousand)? a)
$280,000 b) $353,000 c) $320,000 d) $267,000 82. Using the physical measure method, what are the
joint allocation costs for Product A (rounded to the nearest thousand)? a) $333,000 b) $267,000 c)
$280,000 d) $353,000 2013 Sample Entrance Examination CMA Canada Page 31 83. A company has the
following unit production data for June: Work-in-process inventory, June 1 118,000 Started in production
254,500 Completed production 251,500 Work-in-process inventory, June 30 111,950 The company
expects normal spoilage of 2% of completed goods. What is the abnormal spoilage for June? a) 5,030 b)
3,000 c) 4,020 d) 9,050 84. (-) For a manufacturing company, which of the following statements is true?
a) Wages paid to manufacturing labour are period costs. b) Salaries paid to the sales manager are
product costs. c) Wages paid to the receptionist in the human resources office are period costs. d)
Stationery and supplies used by the bookkeeping clerk in the accounting office are product costs. 85. A
company has the following quarterly sales information: Q1 (Actual) Q2 (Budgeted) Cash sales $150,000
$175,000 Credit sales $325,000 $330,000 60% of credit sales are collected in the quarter of the sale, and
remaining credit sales are collected in the quarter after that. The company expects 3% of credit sales to
be uncollectable. What is the budgeted cash received in Q2? a) $318,160 b) $503,000 c) $367,060 d)
$493,160 2013 Sample Entrance Examination CMA Canada Page 32 The following information pertains to
questions 86 and 87. Liza’s Flowers had the following unit sales results for February: Budgeted Sales
Budgeted Contribution Margin Actual Sales Actual Contribution Margin Roses 5,500 $1.25 6,500 $1.15
Tulips 6,500 $0.75 6,000 $0.80 86. What is the favourable sales-volume variance for roses? a) $1,250 b)
$1,150 c) $550 d) $650 87. What is the favourable sales-mix variance (rounded to the nearest dollar)? a)
$123 b) $250 c) $385 d) $500 ------------------------------------ 88. Glory Ltd. sells tires. In March it sold 5,000
tires and had an inventory of 3,500 tires on March 1. For April, budgeted sales are 5,250 tires and
budgeted ending inventory is 3,000 tires. If there were 3,300 tires in inventory on March 31, how many
tires should Glory purchase in April? a) 4,950 b) 8,250 c) 4,450 d) 1,750 89. If total sales volume variance
is $2,100 unfavourable, total sales mix variance is $900 favourable, and market share variance is $500
favourable, then the market size variance is a) $2,500 unfavourable. b) $1,700 unfavourable. c) $700
unfavourable. d) $3,500 unfavourable. 2013 Sample Entrance Examination CMA Canada Page 33 90. XY
Manufacturing Ltd. had the following inventory data for July, Year 14: July 1 July 31 Direct materials
$140,000 $135,000 Work-in-process $40,000 $42,000 Finished goods $65,000 $70,000 Actual costs
incurred in July include direct materials purchases of $100,000, direct labour of $250,000 and
manufacturing overhead of $125,000. What is the cost of goods manufactured for July using absorption
costing? a) $478,000 b) $480,000 c) $473,000 d) $355,000 91. DHC Ltd. produces X, Y and Z through a
joint production process. It can further refine all of Product X into X-Plus. The following information is
available: i) Selling price per unit of X-Plus ii) Cost of the additional refining to produce X-Plus iii) Joint
costs to produce X iv) Selling price of X Which of the above information is relevant to the decision to
further refine Product X? a) i) only b) i) and ii) only c) iii) and iv) only d) i), ii) and iv) only 92. A company is
considering the following projects: J M V Annual after-tax cash inflows $950,000 $1,000,000 $1,100,000
Initial project cost $5,000,000 $5,000,000 $5,000,000 Cost of capital 7% 10% 12% Project life 7 years 8
years 7 years Based only on profitability index, which project(s) should the company invest in? a) Only J
b) Only M c) Only V d) All three projects
You might also like
- Chapters 6-12 Managerial Accounting ProblemsDocument7 pagesChapters 6-12 Managerial Accounting ProblemsVivek BhattNo ratings yet
- CMA-self Exam QuestionDocument1 pageCMA-self Exam QuestionAva DasNo ratings yet
- Addtional Exercises - 6Document18 pagesAddtional Exercises - 6Gega XachidENo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Answer On The Scantron Provided ONLYDocument10 pagesMultiple Choice Answer On The Scantron Provided ONLYGiovana Marie Balasquide100% (1)
- Practice FinalDocument13 pagesPractice FinalngStephanie26No ratings yet
- Sampleexam 2 BDocument13 pagesSampleexam 2 Btrs1234No ratings yet
- Study Guide For Mgr. Exam 2Document10 pagesStudy Guide For Mgr. Exam 2Skirmante ZalysNo ratings yet
- Cost-Volume - Profit Analysis Multiple QuestionsDocument3 pagesCost-Volume - Profit Analysis Multiple QuestionsRose Jean Raniel Oropa0% (1)
- NameDocument13 pagesNameNitinNo ratings yet
- TT08Document8 pagesTT0822002837No ratings yet
- ACCT_322_absorp_var_and_bgt (1)Document3 pagesACCT_322_absorp_var_and_bgt (1)gurnoorkaurgilllNo ratings yet
- ACG 201 Quiz Chapter 5 Multiple ChoiceDocument2 pagesACG 201 Quiz Chapter 5 Multiple Choiceqwerty17327No ratings yet
- Budgeting and Variance Analysis QuestionsDocument13 pagesBudgeting and Variance Analysis QuestionsAli Rizwan100% (1)
- Answers Chapter 5 Quiz.s13Document2 pagesAnswers Chapter 5 Quiz.s13Jalen RoseNo ratings yet
- Extra Exam 3 Review ProblemsDocument17 pagesExtra Exam 3 Review ProblemsEmily Archie0% (1)
- Fa Ii. ObjDocument5 pagesFa Ii. ObjSonia ShamsNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems For Midterm - Spring 2017Document6 pagesPractice Problems For Midterm - Spring 2017Derny FleurimaNo ratings yet
- Midterm 1+ 2 (T NG H P)Document13 pagesMidterm 1+ 2 (T NG H P)Shen NPTDNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting SeatworkDocument2 pagesCost Accounting SeatworkLorena TuazonNo ratings yet
- Answers Chapter 5 Quiz.s13Document3 pagesAnswers Chapter 5 Quiz.s13Aurcus JumskieNo ratings yet
- Kuis UTS Genap 21-22 ACCDocument3 pagesKuis UTS Genap 21-22 ACCNatasya FlorenciaNo ratings yet
- Test 2 Sample Questions With Correct AnswersDocument8 pagesTest 2 Sample Questions With Correct AnswersBayoumy ElyanNo ratings yet
- Adoption of variable costing for managerial decision makingDocument6 pagesAdoption of variable costing for managerial decision makingFabian NonesNo ratings yet
- Accounting Quiz Chpts 7-9 Night ClassDocument9 pagesAccounting Quiz Chpts 7-9 Night ClassZeren BegumNo ratings yet
- 3. If the critical path is longer than 60 days, what is the least amount that Dr. Watage can spend and still achieve the schedule objective? How can he prove to the Pathminder Fund that this is the minimum cost alternative?Document2 pages3. If the critical path is longer than 60 days, what is the least amount that Dr. Watage can spend and still achieve the schedule objective? How can he prove to the Pathminder Fund that this is the minimum cost alternative?Jonathan Altamirano Burgos0% (1)
- Production, Materials & Overhead BudgetsDocument11 pagesProduction, Materials & Overhead BudgetsEaint Nadi SoeNo ratings yet
- Brewer, Introduction To Managerial Accounting, 3/eDocument11 pagesBrewer, Introduction To Managerial Accounting, 3/eJoe BlackNo ratings yet
- Exam 7Document15 pagesExam 7mohit verrmaNo ratings yet
- Cost Classification Practice ProblemsDocument4 pagesCost Classification Practice ProblemsSandra TanNo ratings yet
- SchedDocument6 pagesSchedprettyNo ratings yet
- Latihan Chapter 3 CVPDocument9 pagesLatihan Chapter 3 CVPS AdemNo ratings yet
- MAS, CVP Analysis, MultichoiceDocument3 pagesMAS, CVP Analysis, MultichoiceChristopher PriceNo ratings yet
- Inventory Costing MethodsDocument4 pagesInventory Costing MethodsIzzahIkramIllahiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 QuestionsDocument8 pagesChapter 6 QuestionsJanelle Joyce Maranan DipasupilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 Test Bank Cost AccDocument5 pagesChapter 01 Test Bank Cost AccNada AlhenyNo ratings yet
- Strat Cost ActivityDocument2 pagesStrat Cost ActivityManuelAngeloBernalNo ratings yet
- Exam 3 Review ProblemsDocument8 pagesExam 3 Review ProblemsEmily ArchieNo ratings yet
- Cost FM Sample PaperDocument6 pagesCost FM Sample PapercacmacsNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting and Cost Concepts ChapterDocument14 pagesManagerial Accounting and Cost Concepts ChapterHardly Dare GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Week #2 ACCT 3039 Worksheet Jan 2021Document6 pagesWeek #2 ACCT 3039 Worksheet Jan 2021Priscella LlewellynNo ratings yet
- DocxDocument6 pagesDocxMico Duñas CruzNo ratings yet
- Quiz CH 9-11 SchoologyDocument8 pagesQuiz CH 9-11 SchoologyperasadanpemerhatiNo ratings yet
- CVP Analysis of Billings CompanyDocument3 pagesCVP Analysis of Billings CompanyAhmed El Khateeb100% (1)
- Cost and Management AccountingDocument6 pagesCost and Management AccountingTIMOREGHNo ratings yet
- Sample MAS 3rd Evals KEY Set BDocument13 pagesSample MAS 3rd Evals KEY Set BJoanna MNo ratings yet
- UNIVERSIDAD DE MANILA MIDTERM EXAMDocument6 pagesUNIVERSIDAD DE MANILA MIDTERM EXAMShiela Mae Pon AnNo ratings yet
- Acc 640Document9 pagesAcc 640Terence NgNo ratings yet
- ZoroDocument11 pagesZoroDrinNo ratings yet
- 8508 QuestionsDocument3 pages8508 QuestionsHassan MalikNo ratings yet
- Test2 ReviewDocument14 pagesTest2 ReviewalolhasNo ratings yet
- Long Test 2 Set BDocument2 pagesLong Test 2 Set BMonica ReyesNo ratings yet
- Homework CVP & BEDocument11 pagesHomework CVP & BEYamato De Jesus NakazawaNo ratings yet
- Islamic Univ. of Gaza Advanced Managerial Accounting Final Exam Break-Even AnalysisDocument3 pagesIslamic Univ. of Gaza Advanced Managerial Accounting Final Exam Break-Even AnalysisRabah ElmasriNo ratings yet
- Cost and Management Accounting -II - Work SheetDocument7 pagesCost and Management Accounting -II - Work SheetBeamlak WegayehuNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Examination MC (Q)Document9 pagesPreliminary Examination MC (Q)Vanessa HaliliNo ratings yet
- Accounting 561Document10 pagesAccounting 561enesworldNo ratings yet
- Computerised Accounting Practice Set Using MYOB AccountRight - Advanced Level: Australian EditionFrom EverandComputerised Accounting Practice Set Using MYOB AccountRight - Advanced Level: Australian EditionNo ratings yet
- Drycleaning Plant Revenues World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryFrom EverandDrycleaning Plant Revenues World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Analysis of Tax Administration in Asia and the Pacific—Sixth EditionFrom EverandA Comparative Analysis of Tax Administration in Asia and the Pacific—Sixth EditionNo ratings yet
- CFP Exam Calculation Workbook: 400+ Calculations to Prepare for the CFP Exam (2018 Edition)From EverandCFP Exam Calculation Workbook: 400+ Calculations to Prepare for the CFP Exam (2018 Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Prime CostDocument1 pagePrime CostAva DasNo ratings yet
- Absorpstion Vs ProcessDocument1 pageAbsorpstion Vs ProcessAva DasNo ratings yet
- Period CoseDocument1 pagePeriod CoseAva DasNo ratings yet
- Prime CostDocument1 pagePrime CostAva DasNo ratings yet
- Pricing Strategy To The Product Life Cycle StageDocument9 pagesPricing Strategy To The Product Life Cycle StageAva DasNo ratings yet
- Bookshelf OnlineDocument1 pageBookshelf OnlineAva DasNo ratings yet
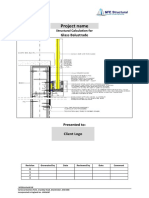
- Project Name: Glass BalustradeDocument11 pagesProject Name: Glass BalustradeNp Pw100% (1)
- Menomonee Falls Express News 091413Document32 pagesMenomonee Falls Express News 091413Hometown Publications - Express NewsNo ratings yet
- A Teacher Education ModelDocument128 pagesA Teacher Education ModelMelinda LabianoNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor 8086 Memory and ArchitectureDocument13 pagesMicroprocessor 8086 Memory and ArchitecturehrrameshhrNo ratings yet
- Bus Crash LawsuitDocument7 pagesBus Crash LawsuitNewsTeam20No ratings yet
- Hydrogen Plant For The New MillenniumDocument21 pagesHydrogen Plant For The New Millenniumapi-3799861100% (2)
- Framing MMT - Modern Money NetworkDocument23 pagesFraming MMT - Modern Money NetworkUmkc Economists86% (7)
- Altracs: A Superior Thread-Former For Light AlloysDocument8 pagesAltracs: A Superior Thread-Former For Light AlloysSquidwardNo ratings yet
- Dialogic DSI Signaling Servers: SIU Mode User ManualDocument304 pagesDialogic DSI Signaling Servers: SIU Mode User ManualAdiansyah Rama67% (3)
- BROC Mackam Dab en v1.0Document2 pagesBROC Mackam Dab en v1.0jangri1098No ratings yet
- Thermodynamics d201Document185 pagesThermodynamics d201Rentu PhiliposeNo ratings yet
- Sensory Marketing: How Toothpaste Brands Appeal to the SensesDocument17 pagesSensory Marketing: How Toothpaste Brands Appeal to the SensesNavodi RathnasingheNo ratings yet
- Bloodborne Pathogens Program: Western Oklahoma State College Employee Training HandbookDocument35 pagesBloodborne Pathogens Program: Western Oklahoma State College Employee Training HandbookKashaNo ratings yet
- New Product Introduction Process: August 16, 2016Document30 pagesNew Product Introduction Process: August 16, 2016JuliaChenNo ratings yet
- Copyblogger Content Marketing Research 2 PDFDocument44 pagesCopyblogger Content Marketing Research 2 PDFvonnig100% (1)
- Rate of Grease Penetration of Flexible Barrier Materials (Rapid Method)Document3 pagesRate of Grease Penetration of Flexible Barrier Materials (Rapid Method)DanZel Dan100% (1)
- 2021 Subsector OutlooksDocument24 pages2021 Subsector OutlooksHungNo ratings yet
- 11 Ways To Encourage Stakeholder Participation:: Writing Good Consultation QuestionsDocument1 page11 Ways To Encourage Stakeholder Participation:: Writing Good Consultation QuestionsLuz Alinsunurin DulogNo ratings yet
- No or Islamic Bank OurStory EnglishDocument45 pagesNo or Islamic Bank OurStory EnglishTalib ZaidiNo ratings yet
- 2015 Idmp Employee Intentions Final PDFDocument19 pages2015 Idmp Employee Intentions Final PDFAstridNo ratings yet
- Haukongo Nursing 2020Document86 pagesHaukongo Nursing 2020Vicky Torina ShilohNo ratings yet
- RCT Methodology ChecklistDocument6 pagesRCT Methodology ChecklistSyahidatul Kautsar NajibNo ratings yet
- The Difficult Patient' As Perceived by Family Physicians: Dov Steinmetz and Hava TabenkinDocument6 pagesThe Difficult Patient' As Perceived by Family Physicians: Dov Steinmetz and Hava TabenkinRomulo Vincent PerezNo ratings yet
- Vargas V YapticoDocument4 pagesVargas V YapticoWilfredo Guerrero IIINo ratings yet
- OPTION STRATEGIES PAYOFF CALCULATOR v2Document9 pagesOPTION STRATEGIES PAYOFF CALCULATOR v2Jay KewatNo ratings yet
- Cameron VBR-II (Variable Bore Ram) PackerDocument2 pagesCameron VBR-II (Variable Bore Ram) Packerjuan olarteNo ratings yet
- Engg Maths Sem 3 Curve FittingDocument13 pagesEngg Maths Sem 3 Curve FittingRonak Raju ParmarNo ratings yet
- Azbil - SS2 DEO412 0010 02Document12 pagesAzbil - SS2 DEO412 0010 02Magoroku D. YudhoNo ratings yet
- Meita Juniar - 41921200002 - Teknik Sipil Reg b2 Uas English For EngineerDocument18 pagesMeita Juniar - 41921200002 - Teknik Sipil Reg b2 Uas English For EngineerREG.B/41921200002/MEITA JUNIARNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Design RulesDocument19 pagesModule 3 - Design RulesSamNo ratings yet