0% found this document useful (0 votes)
383 views10 pagesAI Project Cycle
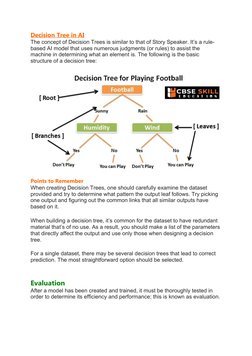
The document outlines the stages of the AI project cycle, beginning with problem scoping. It discusses identifying the problem, stakeholders, objectives, and constraints. Next it covers data acquisition, which involves collecting structured and unstructured data from sources like surveys, cameras, APIs and sensors. It then discusses data exploration using visualization techniques to understand trends. The modeling stage involves different AI approaches like rule-based, machine learning and deep learning. It provides examples of decision tree models. Finally, it states that after model creation, evaluation is needed to determine its performance.
Uploaded by
ipscr.mansiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
383 views10 pagesAI Project Cycle
The document outlines the stages of the AI project cycle, beginning with problem scoping. It discusses identifying the problem, stakeholders, objectives, and constraints. Next it covers data acquisition, which involves collecting structured and unstructured data from sources like surveys, cameras, APIs and sensors. It then discusses data exploration using visualization techniques to understand trends. The modeling stage involves different AI approaches like rule-based, machine learning and deep learning. It provides examples of decision tree models. Finally, it states that after model creation, evaluation is needed to determine its performance.
Uploaded by
ipscr.mansiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- AI Project Cycle: Describes the stages involved in an AI project cycle with emphasis on problem scoping and data acquisition.
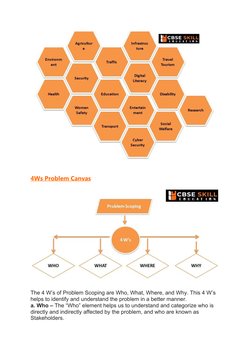
- 4Ws Problem Canvas: Focuses on four main dimensions of problem analysis: Who, What, Where, and Why.
- Data Acquisition: Provides methods for data collection and processing, emphasizing structured and unstructured data.
- Data Exploration: Discusses techniques for understanding data using visualization and statistical tools.
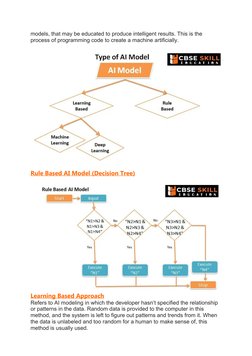
- Modelling: Covers AI modeling techniques including rule-based approaches and deep learning models.
- Evaluation: Discusses the importance of evaluating AI models to determine their efficacy and performance.