0% found this document useful (0 votes)
739 views14 pagesGRADE-10 Trigonometry
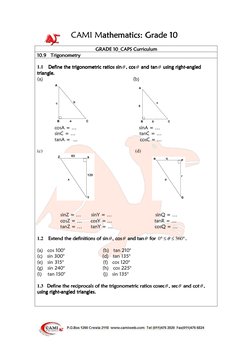
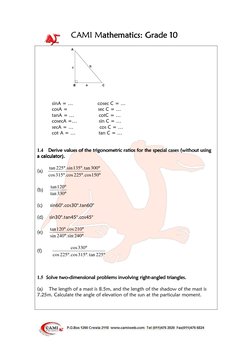
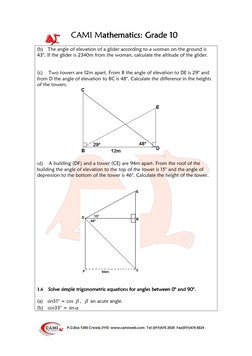
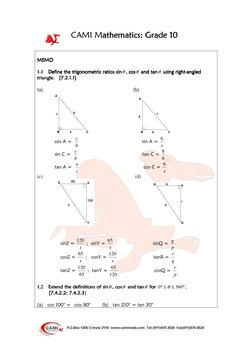
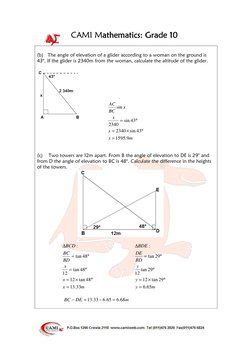
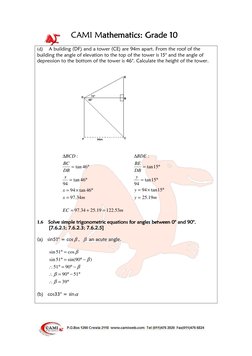
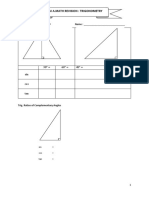
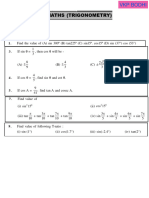
This document provides definitions and examples for trigonometric ratios (sine, cosine, tangent) using right triangles. It defines trig ratios for angles between 0 and 360 degrees, and for their reciprocals (cosecant, secant, cotangent). Examples derive specific trig ratio values and solve right triangle problems, including finding angles of elevation from shadows, altitude from distance and elevation angle, and differences in tower heights.
Uploaded by
julianqophisoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
739 views14 pagesGRADE-10 Trigonometry
This document provides definitions and examples for trigonometric ratios (sine, cosine, tangent) using right triangles. It defines trig ratios for angles between 0 and 360 degrees, and for their reciprocals (cosecant, secant, cotangent). Examples derive specific trig ratio values and solve right triangle problems, including finding angles of elevation from shadows, altitude from distance and elevation angle, and differences in tower heights.
Uploaded by
julianqophisoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Trigonometric Definitions and Problems
- Memo/Answers