Professional Documents
Culture Documents
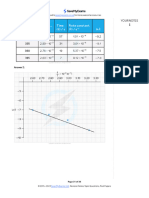
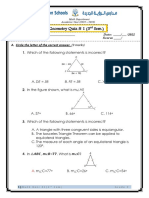
3.coordinate Geometry
Uploaded by
RS JOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3.coordinate Geometry
Uploaded by
RS JCopyright:
Available Formats
CIE IGCSE Maths Revision Notes savemyexams.co.
uk
YOUR NOTES
3. Coordinate Geometry ⬇
CONTENTS
3.1 Coordinate Geometry
3.1.1 Coordinates
3.1.2 Straight Lines – Finding Equations
3.1.3 Straight Lines – Drawing Graphs
3.1.4 Perpendicular Lines
3.1 COORDINATE GEOMETRY
3.1.1 COORDINATES
What are coordinates?
When we want to plot a point on a graph we need to know where to put it
If the horizontal axis is labelled x and the vertical axis is labelled y, then the x and y
coordinates are how far we go along the x and y axes to plot the point
What can we do with coordinates?
If we have two points with coordinates (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) then we should be able to find
the gradient of the line through them
the midpoint of the two points
the distance between the two points
Don’t get fazed by the horrid notation (x1, y1) – this is just “point 1” and the other is “point 2”
so we put the little numbers (subscripts) in so that we know which coordinate we are
referring to. In questions there’ll be lots of nice numbers
Here’s how we do each of those:
© copyright Save My Exams
CIE IGCSE Maths Resources Page 1
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE IGCSE Maths Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
3. Coordinate Geometry ⬇
You should also know that three points A, B and C lie on the same STRAIGHT LINE if AB and
AC (or BC) have the same gradient
Exam Tip
If in doubt, SKETCH IT!
A quick, reasonably accurate sketch can make things a lot clearer.
Worked Example
© copyright Save My Exams
CIE IGCSE Maths Resources Page 2
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE IGCSE Maths Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
3. Coordinate Geometry ⬇
© copyright Save My Exams
CIE IGCSE Maths Resources Page 3
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE IGCSE Maths Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
3. Coordinate Geometry ⬇
3.1.2 STRAIGHT LINES - FINDING EQUATIONS
Why do we want to know about straight lines and their equations?
Straight Line Graphs (Linear Graphs) have lots of uses in mathematics – one use is in
navigation
We may want to know the equation of a straight line so we can program it into a computer
that will plot the line on a screen, along with several others, to make shapes and graphics
How do we find the equation of a straight line?
The general EQUATION of a straight line is y = mx + c
where m is the gradient
c is the y-axis intercept
To find the EQUATION of a straight line you need TWO things:
the gradient, m
any point on the line
You might find these things from a graph, another equation or two points
You may be asked to give the equation in the form ax + by + c = 0
(especially if m is a fraction)
If in doubt, SKETCH IT!
© copyright Save My Exams
CIE IGCSE Maths Resources Page 4
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE IGCSE Maths Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
3. Coordinate Geometry ⬇
Worked Example
© copyright Save My Exams
CIE IGCSE Maths Resources Page 5
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE IGCSE Maths Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
3. Coordinate Geometry ⬇
© copyright Save My Exams
CIE IGCSE Maths Resources Page 6
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE IGCSE Maths Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
3. Coordinate Geometry ⬇
3.1.3 STRAIGHT LINES - DRAWING GRAPHS
How do we draw the graph of a straight line from an equation?
Before you start trying to draw a straight line, make sure you understand how to find the
equation of a straight line – that will help you understand this
How we draw a straight line depends on what form the equation is given in
There are two main forms you might see:
y = mx + c and ax + by = c
Different ways of drawing the graph of a straight line:
1. From the form y = mx + c
(you might be able to rearrange to this form easily)
plot c on the y-axis
go 1 across, m up (and repeat until you can draw the line)
2. From ax + by = c
put x = 0 to find y-axis intercept
put y = 0 to find x-axis intercept
(You may prefer to rearrange to y = mx + c and use above method)
Exam Tip
It might be easier just to plot ANY two points on the line (a third one as a
check is not a bad idea either) or use the TABLE function on your calculator.
© copyright Save My Exams
CIE IGCSE Maths Resources Page 7
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE IGCSE Maths Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
3. Coordinate Geometry ⬇
Worked Example
© copyright Save My Exams
CIE IGCSE Maths Resources Page 8
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE IGCSE Maths Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
3. Coordinate Geometry ⬇
3.1.4 PERPENDICULAR LINES
What are perpendicular lines?
You should already know that PARALLEL lines have equal gradients
PERPENDICULAR LINES do meet each other and where they do the two lines form a right
angle – ie they meet at 90°
What’s the deal with perpendicular gradients (and lines)?
Before you start trying to work with perpendicular gradients and lines, make sure you
understand how to find the equation of a straight line – that will help you do the sorts of
questions you will meet
Gradients m1 and m2 are PERPENDICULAR if m1 × m2 = -1
We can use m2 = -1 ÷ m2 to find a perpendicular gradient
(This is called the NEGATIVE RECIPROCAL)
If in doubt, SKETCH IT!
Worked Example
© copyright Save My Exams
CIE IGCSE Maths Resources Page 9
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE IGCSE Maths Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
3. Coordinate Geometry ⬇
© copyright Save My Exams
CIE IGCSE Maths Resources Page 10
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
You might also like
- Third Space Learning Angle Rules GCSE WorksheetDocument15 pagesThird Space Learning Angle Rules GCSE WorksheetZoonieFRNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IGCSE Maths Edexcel IGCSE Maths 2.1.1 Expanding One Bracket SaveMyExamsDocument77 pagesEdexcel IGCSE Maths Edexcel IGCSE Maths 2.1.1 Expanding One Bracket SaveMyExamsAsma ElassarNo ratings yet
- Venture Mathematics Worksheets: Bk. A: Algebra and Arithmetic: Blackline masters for higher ability classes aged 11-16From EverandVenture Mathematics Worksheets: Bk. A: Algebra and Arithmetic: Blackline masters for higher ability classes aged 11-16No ratings yet
- Multiplying Monomials With Polynomials Worksheet PDFDocument4 pagesMultiplying Monomials With Polynomials Worksheet PDFDesiree HernandezNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Maths Specimen Paper 1Document11 pagesYear 9 Maths Specimen Paper 1Aarti MahtaniNo ratings yet
- Godel's Incompleteness Theorem: by Dale MyersDocument9 pagesGodel's Incompleteness Theorem: by Dale MyersgodardoNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra ProblemsDocument5 pagesLinear Algebra Problemssmithap_ullalNo ratings yet
- Third Space Learning Corresponding Angles GCSE WorksheetDocument16 pagesThird Space Learning Corresponding Angles GCSE WorksheetGaurav MittalNo ratings yet
- Applied and Computational Linear Algebra A First Course Charles L. ByrneDocument469 pagesApplied and Computational Linear Algebra A First Course Charles L. ByrneAshoka VanjareNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document130 pagesChapter 9Andy ChauNo ratings yet
- Congruence and Similarity HardDocument3 pagesCongruence and Similarity Hardpoonam.upadhyayNo ratings yet
- Functions2121Document97 pagesFunctions2121Safety KingNo ratings yet
- Sine Rule, Cosine Rule, Area of Any Triangle QPDocument7 pagesSine Rule, Cosine Rule, Area of Any Triangle QPSaba AnjumNo ratings yet
- 2.13 Linear Graphs QP Very HardDocument7 pages2.13 Linear Graphs QP Very HardLyShan TanNo ratings yet
- Third Space Learnisyng Circle Theorems GCSE WorksheetDocument22 pagesThird Space Learnisyng Circle Theorems GCSE Worksheetanomad153No ratings yet
- FunctionsDocument153 pagesFunctionsSafety KingNo ratings yet
- Trigo IgcseDocument8 pagesTrigo IgcseAurna BanerjeeChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Save My Exams Mechanics 3Document28 pagesSave My Exams Mechanics 3ezzahjvNo ratings yet
- Geometry - Trigonometry111Document105 pagesGeometry - Trigonometry111Safety KingNo ratings yet
- AS Maths CIE: 2. Kinematics (Straight Line Motion)Document28 pagesAS Maths CIE: 2. Kinematics (Straight Line Motion)pparinooshmsh8484No ratings yet
- Parallel Lines (H)Document4 pagesParallel Lines (H)Souvik GhoshNo ratings yet
- 4K5s3KJh 40xtq XDocument23 pages4K5s3KJh 40xtq Xmohamed rahilNo ratings yet
- Sine Rule, Cosine RuleDocument8 pagesSine Rule, Cosine RuleAurna BanerjeeChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- B. Collecting Like TermsDocument3 pagesB. Collecting Like Termswaleedkhan567799No ratings yet
- Grade 6 Maths Study Pack 2 FractionsDocument6 pagesGrade 6 Maths Study Pack 2 FractionsMy LêNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Making Scale Drawings Using The Parallel Method: Student OutcomesDocument15 pagesLesson 3: Making Scale Drawings Using The Parallel Method: Student OutcomesCrisanto Paulo Bernardo CatapNo ratings yet
- Differentiation Very HardDocument5 pagesDifferentiation Very Hardabdullahthaher04No ratings yet
- CrossProductFormulaConcept, ImportantPoints, Examples 1710827282774Document7 pagesCrossProductFormulaConcept, ImportantPoints, Examples 1710827282774pearl ikebuakuNo ratings yet
- B. Collecting Like TermsDocument3 pagesB. Collecting Like Termswaleedkhan567799No ratings yet
- riFHM ITwjvHsxNHDocument8 pagesriFHM ITwjvHsxNHAshraf HosamNo ratings yet
- Circle Theorems Third Space Learning GCSE WorksheetDocument18 pagesCircle Theorems Third Space Learning GCSE WorksheetZoonieFR0% (1)
- Module 4 HMWRK Lesson 7Document2 pagesModule 4 HMWRK Lesson 7ReekhaNo ratings yet
- Third Space Learning Perpendicular Bisectors GCSE Worksheet 1Document14 pagesThird Space Learning Perpendicular Bisectors GCSE Worksheet 1charvisan098No ratings yet
- 10.trigonometry MS P4Document169 pages10.trigonometry MS P4LingNo ratings yet
- Factorising & Expanding - Easy 2Document11 pagesFactorising & Expanding - Easy 2Thu Thuy NguyenNo ratings yet
- SME Area and Perimeter H and VHDocument35 pagesSME Area and Perimeter H and VHvenusNo ratings yet
- Example 1:: Support Session 09/11/22 - ParametricsDocument1 pageExample 1:: Support Session 09/11/22 - ParametricsEmilly BaileyNo ratings yet
- Maths IGSCE NOTES geOMETRYDocument40 pagesMaths IGSCE NOTES geOMETRYAli OpNo ratings yet
- 3e Nick Mcivor Core Maths PresentationDocument47 pages3e Nick Mcivor Core Maths PresentationSally WangNo ratings yet
- A Quadratic Function Through Three PointsDocument1 pageA Quadratic Function Through Three PointsEnes VranaNo ratings yet
- SME Chemistry Topic 16 NotesDocument6 pagesSME Chemistry Topic 16 Notesdnam7736No ratings yet
- GCSE Maths Revision Straight Line Graphs QuestionsDocument5 pagesGCSE Maths Revision Straight Line Graphs QuestionsarumugamNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 10 Maths Question Paper Solution 2020Document32 pagesICSE Class 10 Maths Question Paper Solution 2020Harshu KNo ratings yet
- 3D Trigonometry - Worksheet: Skill Group A - Visualising Lines in 3DDocument20 pages3D Trigonometry - Worksheet: Skill Group A - Visualising Lines in 3DMaier SheikhNo ratings yet
- Linear Functions Ii: Headstart MathematicsDocument11 pagesLinear Functions Ii: Headstart MathematicsIshaan IngrejiNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Polar Coordinates: Question PaperDocument7 pages7.1 Polar Coordinates: Question PaperKrishnendu SahaNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 MathematicsDocument11 pagesGrade 8 Mathematicsmoona imranNo ratings yet
- 2021 P2 Maths Bite Sized Assessment 3 ACSJDocument11 pages2021 P2 Maths Bite Sized Assessment 3 ACSJFattah Morris MarudyNo ratings yet
- Congruency and Similarity Part 1Document6 pagesCongruency and Similarity Part 1shadowosNo ratings yet
- Third Space Learning Plans and Elevations GCSE WorksheetDocument18 pagesThird Space Learning Plans and Elevations GCSE WorksheetAbdallah ElmenawyNo ratings yet
- 1.measurement &uncertaintiesDocument47 pages1.measurement &uncertaintiesArrush AhujaNo ratings yet
- Uere 9 Hu 2 TS2 LT QMKDocument18 pagesUere 9 Hu 2 TS2 LT QMKshishir jhaNo ratings yet
- Solutions 32 3Document13 pagesSolutions 32 3Smpnsatubontang KaltimNo ratings yet
- Erocido Feb14 LPDocument6 pagesErocido Feb14 LPjohnnen.magtolisNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Formula (H) : Name: Total MarksDocument2 pagesQuadratic Formula (H) : Name: Total MarksMinh NgoNo ratings yet
- Geometry m2 Topic B Lesson 8 TeacherDocument15 pagesGeometry m2 Topic B Lesson 8 TeacherDanny Riel BarachinaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 22: Congruence Criteria For Triangles-SAS: Student OutcomesDocument13 pagesLesson 22: Congruence Criteria For Triangles-SAS: Student OutcomesJae selliNo ratings yet
- Linear Equalities and InequalitiesDocument5 pagesLinear Equalities and Inequalitieshtetaunglynn.bwNo ratings yet
- G9 GEometryMidTerm ExamDocument5 pagesG9 GEometryMidTerm Examomama_thNo ratings yet
- Lesson 22: Congruence Criteria For Triangles-SAS: Student OutcomesDocument10 pagesLesson 22: Congruence Criteria For Triangles-SAS: Student OutcomesPERLA Casiano OrtizNo ratings yet
- Basic Proportionality Theorem & Similar TrianglesDocument1 pageBasic Proportionality Theorem & Similar TrianglesdwdadNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Maths - Number - Questions (Ch1)Document16 pagesYear 10 Maths - Number - Questions (Ch1)Shashmini Vibhawari GamageNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - Google SearchDocument1 pageMathematics - Google Searchurassaya sperbundNo ratings yet
- U3 e KC NVyb XEq JPG 4Document7 pagesU3 e KC NVyb XEq JPG 4Jade DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Geometric vs. ArithmeticDocument2 pagesGeometric vs. ArithmeticEmmadell LelisNo ratings yet
- Simplifying ExpressionsDocument3 pagesSimplifying ExpressionsUmm ArafaNo ratings yet
- Risk Review 2021 AraDocument97 pagesRisk Review 2021 AraRS JNo ratings yet
- Diploma FullStack Software Development Specialization Europe Brochure-1Document19 pagesDiploma FullStack Software Development Specialization Europe Brochure-1RS JNo ratings yet
- Day+01 +Unit+030+Knowledge+OverviewDocument82 pagesDay+01 +Unit+030+Knowledge+OverviewRS JNo ratings yet
- Onsite Course PacketDocument9 pagesOnsite Course PacketRS JNo ratings yet
- 616d97f4ee41ee7aa48cabcb - Software Development Bootcamp SyllabusDocument8 pages616d97f4ee41ee7aa48cabcb - Software Development Bootcamp SyllabusRS JNo ratings yet
- Full-Stack Scientific PythonDocument3 pagesFull-Stack Scientific PythonRS JNo ratings yet
- Automating Teacher Work? A History of The Politics of Automation and Artificial Intelligence in EducationDocument19 pagesAutomating Teacher Work? A History of The Politics of Automation and Artificial Intelligence in EducationMazi PrimaNo ratings yet
- Diploma FullStack Software Development Specialization Uk Brochure-1Document19 pagesDiploma FullStack Software Development Specialization Uk Brochure-1RS JNo ratings yet
- Regulation 3 AwardsDocument8 pagesRegulation 3 AwardsRS JNo ratings yet
- Security Advisory Services Brochure For CandidatesDocument8 pagesSecurity Advisory Services Brochure For CandidatesRS JNo ratings yet
- Task 1 - Creating An Answer FileDocument40 pagesTask 1 - Creating An Answer FileRS JNo ratings yet
- Paper DetailsDocument2 pagesPaper DetailsRS JNo ratings yet
- Task A - Administer UserprofilesDocument21 pagesTask A - Administer UserprofilesRS JNo ratings yet
- Reasoning Book PDFDocument182 pagesReasoning Book PDFSurendraNo ratings yet
- Paper1 Details ZoologyDocument2 pagesPaper1 Details ZoologyRS JNo ratings yet
- Paper5 Details PhysicsDocument2 pagesPaper5 Details PhysicsRS JNo ratings yet
- Ur DadDocument40 pagesUr DadRizan RazakNo ratings yet
- 1.8 Revision Guide Thermodynamics AqaDocument8 pages1.8 Revision Guide Thermodynamics AqaRabia RafiqueNo ratings yet
- 3.16 Revision Guide Chromatography AqaDocument3 pages3.16 Revision Guide Chromatography AqaRS JNo ratings yet
- A Level Biology 2019 2020Document27 pagesA Level Biology 2019 2020RS JNo ratings yet
- Biorevise Notes MAINDocument34 pagesBiorevise Notes MAINRS JNo ratings yet
- Aqa Y2 P2 Jun 19 MSDocument19 pagesAqa Y2 P2 Jun 19 MSestee.onyeNo ratings yet
- June 2017 QPDocument36 pagesJune 2017 QPAnanda PillayNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Revision Guide Calculations AqaDocument14 pages1.2 Revision Guide Calculations AqaRS JNo ratings yet
- 3.14 Revision Guide Organic Synthesis AqaDocument7 pages3.14 Revision Guide Organic Synthesis AqaRutba SafdarNo ratings yet
- 3.9 Revision Guide Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives AqaDocument8 pages3.9 Revision Guide Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives AqaRS JNo ratings yet
- 1.9 Revision Guide Rate Equations AqaDocument8 pages1.9 Revision Guide Rate Equations AqaRS JNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Revision Guide Equilibria AQADocument7 pages1.6 Revision Guide Equilibria AQAAreeba EjazNo ratings yet
- 1.10 Partial Pressures and KP: Mole FractionDocument3 pages1.10 Partial Pressures and KP: Mole Fractionbazel mukuzeNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Revision Guide Bonding AqaDocument8 pages1.3 Revision Guide Bonding AqaRS JNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Polynomials & WorksheetDocument10 pagesCBSE Class 10 Polynomials & WorksheetVINOTHKANNA DEVANo ratings yet
- Segment Tree. (E Maxx)Document24 pagesSegment Tree. (E Maxx)ShubhamNo ratings yet
- The Center Graph of A Group: P. Balakrishnan, M. Sattanathan, R. KalaDocument8 pagesThe Center Graph of A Group: P. Balakrishnan, M. Sattanathan, R. KalasattanathanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 4Document13 pagesMathematics 4Suman KarthikNo ratings yet
- Stress RecoveryDocument6 pagesStress RecoveryVipin NairNo ratings yet
- Calculus Final Term Exam Spring 2020 CS 27062020 125626amDocument2 pagesCalculus Final Term Exam Spring 2020 CS 27062020 125626amFadi KhanNo ratings yet
- ECEN 615 Methods of Electric Power Systems Analysis: Lecture 19: Equivalents, Voltage StabilityDocument35 pagesECEN 615 Methods of Electric Power Systems Analysis: Lecture 19: Equivalents, Voltage StabilityMohamed ShamseldeinNo ratings yet
- Week5Lecture2 PDFDocument17 pagesWeek5Lecture2 PDFjayroldparcedeNo ratings yet
- Actual and Approximate TimeDocument2 pagesActual and Approximate TimeAriane Malou GorreonNo ratings yet
- Non-Linear Curve Fit ProofDocument5 pagesNon-Linear Curve Fit ProofAhmadMoaazNo ratings yet
- Book Review H Dym and H P McKean Fourier Series AnDocument6 pagesBook Review H Dym and H P McKean Fourier Series AnGuillermo Manuel DiazNo ratings yet
- TM15Document3 pagesTM15Evripidis ThemelisNo ratings yet
- 3 orDocument68 pages3 orYuri BrasilkaNo ratings yet
- 3.6 Iterative Methods For Solving Linear SystemsDocument35 pages3.6 Iterative Methods For Solving Linear SystemsAbdulaziz H. Al-MutairiNo ratings yet
- 2.3 ALGEBRA-Simultaneous EquationsDocument11 pages2.3 ALGEBRA-Simultaneous EquationsAmana IBNo ratings yet
- Table of Useful IntegralsDocument6 pagesTable of Useful IntegralsAjdin PalavrićNo ratings yet
- There Are Some Laws of Indices Which Are As FollowsDocument50 pagesThere Are Some Laws of Indices Which Are As FollowsAnimeNo ratings yet
- KAUST CS204 Fall2022 Lecture8 AnalysisRecursiveDocument42 pagesKAUST CS204 Fall2022 Lecture8 AnalysisRecursivereema alnafisiNo ratings yet
- Relations and Functions Class 12 Notes Maths Chapter 1 - Learn CBSEDocument2 pagesRelations and Functions Class 12 Notes Maths Chapter 1 - Learn CBSETanmay ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Cedram: Éric Gourgoulhon and Marco ManciniDocument58 pagesCedram: Éric Gourgoulhon and Marco ManciniM Sohaib M HanifNo ratings yet
- M Etodos de F Isica Te Orica II - CF367 Lista de Exerc Icios IDocument1 pageM Etodos de F Isica Te Orica II - CF367 Lista de Exerc Icios IFernando Bazílio de LimaNo ratings yet
- Sequencing Problems - Operation Research CalculatorDocument2 pagesSequencing Problems - Operation Research Calculatormks5071No ratings yet
- scws1 6224Document36 pagesscws1 6224Naeem AhmedNo ratings yet
- Aops Community 2020 Isl: Imo Shortlist 2020Document6 pagesAops Community 2020 Isl: Imo Shortlist 2020Andrej BorovicNo ratings yet