Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mind Map
Uploaded by
Jennifer GonzálezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mind Map
Uploaded by
Jennifer GonzálezCopyright:
Available Formats
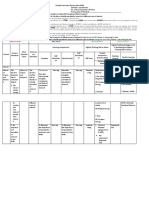
Sources: Tests measure general ability to use specific skills.
Testing can identify the areas where she needs targeted instruction and help
Tools:
-Scholastic Reading Inventory (SRI)
-Woodcock Reading Mastery Test (WRMT -III)
-Gray Oral Reading Test (GORT ? 5)
-Comprehensive Test of Phonological Processing
-Test of Word reading Efficiency (TOWRE ? 2)
-Rapid Automatized Naming Tasks
-Test of Early Reading Ability (TERA ? 3) Sources: Diagnostic measures for determining a child ?
s gross motors skills, fine manipulative skills and hearing, sight speech and language abilitie
Tests for reading, writing & math
-Wide Range Achievement Test 4
-Scholastic Reading Inventory (SRI)
-Woodcock Reading Mastery Test (WRMT -III)
-Gray Oral Reading Test (GORT ? 5) Skill evaluation Tools: Full physical test Evaluation as part of the process of gathering the evidence.
-Comprehensive Test of Phonological Processing
-Test of Word reading Efficiency (TOWRE ? 2)
-Rapid Automatized Naming Tasks
-Test of Early Reading Ability (TERA ? 3) People involved: Speech pathologist Pediatrician Specialist
-Wide Range Achievement Test 4
Sources: Daily, weekly & monthly observational records that show a child ?
s performance
People involved: Psychologists specialized in applying this type of test
Tools:
Sources: Standardized tests that assess the intellectual capacity of the child Observational Classwork Homework
records Tests
Participation Observing all of th
Tools:
WISC ? RM
Intellectual areas
K ? ABC People involved: Anyone who works with the child
Raven's progressive matrices test
Sources: Folder of assignments Portfolio
People involved: Psychologist Evaluator Parents Draft
The evaluation process and its tools
Sources: test batteries whose objective is to collect medical, adaptive, cognitive, perceptive- motor, and sociocultural information. Samples of student work Tools: Test Homework Projects
Tools: System of Multicultural and Pluralistic Assessment (SOMPA) adapted in Mexico. Motor development References:
People involved: teachers
Learning Disabilities Association of America. (n.d.). Symptoms of
learning disabilities. Retrieved June 15, 2012, from
https://ldaamerica.org/symptoms-of- learning-disabilities/
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. (n.d.). Dyslexia
information page. Retrieved March 6, 2017, from
People involved:Physical therapy specialist or neurodevelopmental specialist https://www.ninds.nih.gov/Disorders/All- Disorders/Dyslexia- Sources: Teacher?s interview, who he/she interacts with, work with...
Information-Page#disorders- r1
SEP. ?La integración educativa en el aula regular. Principios,
finalidades y estrategias?: 2009. Recuperado de:
https://anahuac.brightspace.com/d2l/le/lessons/965112/topics/9560493
Source Caring for Your School-Age Child: Ages 5 to 12 (Copyright
Sources: Evaluates the child's performance in roles outside of school. 2004 American Academy of Pediatrics) School Tools: Interview Observation Interaction
Tools: Adaptive Behavior Inventory for Children (ABIC) adapted in Mexico. Aspects of adaptation & social intersection People involved: Teacher Classmates
People involved: Psychologist Social worker Sources: Fill out checklists.
Answer questions Participate in an interview. Write a report addressing a child?s strengths, challenges, and development (or lack thereof) over time
Sources: Projective tests to know the structure of the person, discover their emotions and internal "conflicts" that the child can project in their responses.
Developmental & social history Tools: Questionnaires Interviews Observation
Tools:House, Tree, Person (HTP) Human figure
Incomplete Sacks sentences Children Apperception Test (CAT) Emotional aspects
People involved: Teacher
Parents Pediatricians School specialists
People involved: Psychologist
You might also like
- Edes 6359 - Informal Formal TestsDocument3 pagesEdes 6359 - Informal Formal Testsapi-457414554No ratings yet
- Week 1-2 Ch. 1. PPT Language TestingDocument15 pagesWeek 1-2 Ch. 1. PPT Language TestingWaad MajidNo ratings yet
- Language Testing and Assessment, 2018-2019Document79 pagesLanguage Testing and Assessment, 2018-2019Jasmin CadirNo ratings yet
- Assessment of LanguageDocument28 pagesAssessment of LanguagePallaviKulshrestha100% (1)
- Appropriateness of Assessment Methods Assessment Instruments AppropriatenessDocument3 pagesAppropriateness of Assessment Methods Assessment Instruments AppropriatenessJaysonNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Basic Language and Learning Skills - Revised (ABLLS-R)Document2 pagesAssessment of Basic Language and Learning Skills - Revised (ABLLS-R)Medi Cal75% (4)
- 2012 MUBALAGTAS Assessment of Learning - CONTENT UPDATE - 1 PDFDocument20 pages2012 MUBALAGTAS Assessment of Learning - CONTENT UPDATE - 1 PDFJP MRNNo ratings yet
- Lecturer: Dr. Jan Mujiyanto M.Hum. Teguh Ardianto Mat Ibnu Setyono UNNES, September 11, 2012Document21 pagesLecturer: Dr. Jan Mujiyanto M.Hum. Teguh Ardianto Mat Ibnu Setyono UNNES, September 11, 2012Diego MelgarNo ratings yet
- PP Kel 1Document14 pagesPP Kel 1m naufalNo ratings yet
- Secondary AssessmentsDocument12 pagesSecondary Assessmentsapi-338389967No ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument16 pagesAssessmentyina fabiola castro ochoaNo ratings yet
- Course Profile: I. General InformationDocument7 pagesCourse Profile: I. General InformationEmail KoreaNo ratings yet
- EDUC3 Module 3Document23 pagesEDUC3 Module 3Dahlia GalimbaNo ratings yet
- Approaches To Language TestingDocument46 pagesApproaches To Language TestingranggaNo ratings yet
- 15 Assessments For Struggling ReadersDocument9 pages15 Assessments For Struggling Readersapi-509847207No ratings yet
- Week 2Document12 pagesWeek 2Dewo MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Fidp - PriiDocument19 pagesFidp - PriiSirJo Rios NillosNo ratings yet
- Assessment CompilationDocument17 pagesAssessment CompilationArjie ConsignaNo ratings yet
- Testing, Assessing, and TeachingDocument25 pagesTesting, Assessing, and TeachingAudyNo ratings yet
- My Dashboard: Course Syllabus For Assessment of Learning 1Document6 pagesMy Dashboard: Course Syllabus For Assessment of Learning 1Jonalyn ObinaNo ratings yet
- FS 5 Episode 5Document5 pagesFS 5 Episode 5CezLuzarraga80% (5)
- Course Syllabus For Assessment of Learning 1Document6 pagesCourse Syllabus For Assessment of Learning 1Jonalyn ObinaNo ratings yet
- Individual VS Group Test: Understanding the DifferencesDocument29 pagesIndividual VS Group Test: Understanding the DifferencesScritte SNo ratings yet
- Teaching Listening Comprehension: Unit 5Document31 pagesTeaching Listening Comprehension: Unit 5Inés Amaya DíazNo ratings yet
- Achievement Test Proficiency TestDocument3 pagesAchievement Test Proficiency TestGenesis Angelo100% (1)
- Study and Thinking SkillsDocument23 pagesStudy and Thinking SkillsRyan Cornista100% (1)
- Assessment1 Reading 3 2020Document16 pagesAssessment1 Reading 3 2020MjimenaNo ratings yet
- Psychological Tests ExplainedDocument53 pagesPsychological Tests Explainedbest select servicesNo ratings yet
- Formative AssessmentDocument5 pagesFormative AssessmentHa Nhi TranNo ratings yet
- Listening CoursebookDocument121 pagesListening CoursebookYến VõNo ratings yet
- Criterian and Norm Referenced TestDocument6 pagesCriterian and Norm Referenced TestNawal100% (1)
- Language Assessment MethodsDocument4 pagesLanguage Assessment MethodsBunga RefiraNo ratings yet
- Language Testing. Oxford. Oxford University Press)Document6 pagesLanguage Testing. Oxford. Oxford University Press)Vanessa StoievaNo ratings yet
- Assesment of Learning1Document16 pagesAssesment of Learning1S on the GoNo ratings yet
- Language Testing: Approaches and Techniques: Eng204 February13, 2021 Reporter #1 Gaverell M. CarialDocument7 pagesLanguage Testing: Approaches and Techniques: Eng204 February13, 2021 Reporter #1 Gaverell M. CarialKemberly Semaña PentonNo ratings yet
- Tests Used in Neuropsychological ExamsDocument7 pagesTests Used in Neuropsychological ExamsHanan Ahmed100% (1)
- Tecnicas Unit 6Document15 pagesTecnicas Unit 6cyber holicNo ratings yet
- Approaches to Language Testing يوغللا رابتخلاا قرطDocument8 pagesApproaches to Language Testing يوغللا رابتخلاا قرطLeoDavidNo ratings yet
- IDEAL List of Tools and AssessmentsDocument10 pagesIDEAL List of Tools and AssessmentsAbeliz Durant MunizNo ratings yet
- Basic Considerations in Test Design and Uses of Language TestsDocument2 pagesBasic Considerations in Test Design and Uses of Language TestsPrilia Dwiher FitrianaNo ratings yet
- Assessing Listening and Speaking Skills. ERIC DigestDocument7 pagesAssessing Listening and Speaking Skills. ERIC DigestDini HaryantiNo ratings yet
- ها أشنو خاصك تراجع لإجتياز إمتحان تعليم - تخصص اللغة الإنجليزيةDocument1 pageها أشنو خاصك تراجع لإجتياز إمتحان تعليم - تخصص اللغة الإنجليزيةandresNo ratings yet
- Test Types and DistinctionDocument16 pagesTest Types and Distinctionharoldgalang026No ratings yet
- Language Testing & Development: April 22,2017 Psychology Laboratory (1:00-5:00)Document20 pagesLanguage Testing & Development: April 22,2017 Psychology Laboratory (1:00-5:00)Phee May DielNo ratings yet
- Psychological Assessment GuideDocument63 pagesPsychological Assessment Guidelailani daya100% (19)
- Actionplan-On-Catch-Up-Friday-Reading-1 (2) 2Document10 pagesActionplan-On-Catch-Up-Friday-Reading-1 (2) 2Katreen FelipeNo ratings yet
- Teaching II ConceptsDocument4 pagesTeaching II Conceptsemilioortegam ONo ratings yet
- 07.17 PA Refresher Course Notes-RevisedDocument6 pages07.17 PA Refresher Course Notes-RevisedJesusa Angelika IlustreNo ratings yet
- DLL-Q3-W5 - Mam LouDocument4 pagesDLL-Q3-W5 - Mam LouChello Ann Pelaez AsuncionNo ratings yet
- CEFRDocument10 pagesCEFRHabieburRohmanNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Evaluation Learning 1 - Content OnlyDocument32 pagesAssessment and Evaluation Learning 1 - Content Onlymarvin moscaNo ratings yet
- Chapter III ContentDocument9 pagesChapter III ContentMaryjoy PaladanNo ratings yet
- Advanced Assessment in Language TeachingDocument28 pagesAdvanced Assessment in Language Teachingmasha revaNo ratings yet
- ENg 204 1st Report CARIALDocument5 pagesENg 204 1st Report CARIALCristine G. LagangNo ratings yet
- SYLLABUS III - 2024 ENGLISHDocument10 pagesSYLLABUS III - 2024 ENGLISHAbigail Bravo de RuedaNo ratings yet
- 1 Testing, Assessing and TeachingDocument22 pages1 Testing, Assessing and TeachingToriq Abdul HafizNo ratings yet
- Is the Answer Reasonable?, Grade 4: The Test ConnectionFrom EverandIs the Answer Reasonable?, Grade 4: The Test ConnectionNo ratings yet
- Ms Shared 230822 200352Document1 pageMs Shared 230822 200352Jennifer GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Swot Water Satellite MDocument2 pagesSwot Water Satellite MJennifer GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Cover Letter PDFDocument1 pageCover Letter PDFJennifer GonzálezNo ratings yet
- La Bikina Viola 1Document1 pageLa Bikina Viola 1Jennifer GonzálezNo ratings yet
- La Bikina Viola 2Document1 pageLa Bikina Viola 2Jennifer GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Listening Requests U4L2Document2 pagesListening Requests U4L2Jennifer GonzálezNo ratings yet
- SanCoP7 AgendaDocument2 pagesSanCoP7 AgendaNicolaGreeneNo ratings yet
- 85 HP John Deere 4045DFM50 Marine Diesel EngineDocument2 pages85 HP John Deere 4045DFM50 Marine Diesel EngineDAVIDNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Ukuran Potongan Kopra Dalam Proses Pengeringan: Effect of The Copra Cut Size in The Drying ProcessDocument5 pagesPengaruh Ukuran Potongan Kopra Dalam Proses Pengeringan: Effect of The Copra Cut Size in The Drying ProcessAlexia Desi Ratnasari Loi 1841100210No ratings yet
- En JV Catalogue 2Document56 pagesEn JV Catalogue 2Yudhi Tri IndrawanNo ratings yet
- Synovial Joints StructureDocument20 pagesSynovial Joints StructureJayricDepalobosNo ratings yet
- MFT28 - Greg Plitt's 4-Week Military Fitness Trainer by MET-RxDocument7 pagesMFT28 - Greg Plitt's 4-Week Military Fitness Trainer by MET-RxRayNo ratings yet
- M&SDocument39 pagesM&Sgo.pushp70910% (1)
- Gaggia Cadorna Milk Full Instruction ManualDocument76 pagesGaggia Cadorna Milk Full Instruction ManualKanen Coffee, LLC.No ratings yet
- Implementation of Swachh Bharat in MysoreDocument13 pagesImplementation of Swachh Bharat in MysoreDipyaman ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Symbol High Low R5 R4 R3 R2: DailyDocument8 pagesSymbol High Low R5 R4 R3 R2: Daily257597 rmp.mech.16No ratings yet
- Rational Choice TheoryDocument6 pagesRational Choice TheoryMaria Theresa HerbolingoNo ratings yet
- Modified Pfirrmann Grading System For Lumbar Intervertebral Disc DegenerationDocument6 pagesModified Pfirrmann Grading System For Lumbar Intervertebral Disc DegenerationZack StylesNo ratings yet
- Trangia Worksheet IntroDocument2 pagesTrangia Worksheet Introjames.mccooeyNo ratings yet
- Presentation on Chancroid: Bacterial STI Causes Painful Genital UlcersDocument12 pagesPresentation on Chancroid: Bacterial STI Causes Painful Genital UlcersBikash Sah0% (1)
- MMDST PDFDocument50 pagesMMDST PDFChristopher OlipasNo ratings yet
- Fermentation Technology for Food Preservation and ProcessingDocument47 pagesFermentation Technology for Food Preservation and ProcessingAhmad Syamil Muhamad ZinNo ratings yet
- Revised Provisional Selection List 30122022 1Document150 pagesRevised Provisional Selection List 30122022 1onlinetrash45No ratings yet
- Paragenesis of OlivineDocument18 pagesParagenesis of OlivineSyed Zaman100% (2)
- Operator Manual For Respons920 With ISE - v2016.02Document358 pagesOperator Manual For Respons920 With ISE - v2016.02Juan Pablo CondoriNo ratings yet
- API 578 Mock QuestionDocument4 pagesAPI 578 Mock QuestionsheikmoinNo ratings yet
- Impact of Excessive Mobile Phone Usage On Human JCSB 1000235Document5 pagesImpact of Excessive Mobile Phone Usage On Human JCSB 1000235nidNo ratings yet
- Scope Management Plan TemplateDocument10 pagesScope Management Plan TemplateAlessandro Rota100% (1)
- C612Document5 pagesC612dinhtung2210100% (1)
- Make Every Day Count: George Eliot's inspirational poemDocument3 pagesMake Every Day Count: George Eliot's inspirational poemRUTUJA KALENo ratings yet
- Type 3730-1 Electropneumatic PositionerDocument112 pagesType 3730-1 Electropneumatic PositionerDaniel ReyNo ratings yet
- Logiqids Sample Paper KG FinalDocument15 pagesLogiqids Sample Paper KG FinalShenbaga Devi PadmanabanNo ratings yet
- Business Plan Hair DyeDocument12 pagesBusiness Plan Hair Dyercool_rahul0039341No ratings yet
- Sprocket Asa 180Document1 pageSprocket Asa 180jhampolrosalesNo ratings yet
- Envl 4300 Lab3Document9 pagesEnvl 4300 Lab3api-662867343No ratings yet
- REBA Employee Assessment Worksheet: A. Neck, Trunk and Leg AnalysisDocument1 pageREBA Employee Assessment Worksheet: A. Neck, Trunk and Leg AnalysisAgni JayantiNo ratings yet