0% found this document useful (0 votes)
60 views1 pageMass Transfer in Food Drying Processes
This document contains two mass transfer tutorial problems:
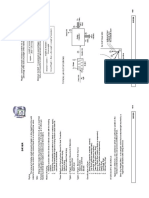
1) A bed of saturated wood pulp is dried by dry air flow. The evaporative flux 1m from the bed edge and radiant power needed to maintain 330K pulp temperature are calculated.
2) A food drying process requires an evaporation rate between 16-18x10-3 kg/s. The food is dried by radiant heating at 330K. Air flow speed required over the bed to guarantee the evaporation rate is determined for fully dry and 50% RH inlet air.
Uploaded by
219016536Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
60 views1 pageMass Transfer in Food Drying Processes
This document contains two mass transfer tutorial problems:
1) A bed of saturated wood pulp is dried by dry air flow. The evaporative flux 1m from the bed edge and radiant power needed to maintain 330K pulp temperature are calculated.
2) A food drying process requires an evaporation rate between 16-18x10-3 kg/s. The food is dried by radiant heating at 330K. Air flow speed required over the bed to guarantee the evaporation rate is determined for fully dry and 50% RH inlet air.
Uploaded by
219016536Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd