Professional Documents
Culture Documents
7 Inventorycost Flow
Uploaded by
arnoldmanullang3Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
7 Inventorycost Flow
Uploaded by
arnoldmanullang3Copyright:
Available Formats
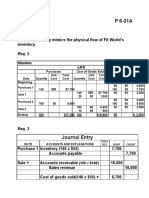
PR 7-1A FIFO perpetual inventory OBJ.
2, 3
The beginning inventory at RTE Office Supplies and data on purchases and sales for a three-month
period ending August 31, 2014, are as follows:
number Per
Transactio
Date n of Units Unit Total
June 1 inventory 500 $30.00 $15,000
1
0 Purchase 1,500 34.00 51,000
2
8 sale 750 50.00 37,500
3
0 sale 250 52.00 13,000
July 5 sale 100 $55.00 $ 5,500
1
0 Purchase 3,600 35.00 126,000
1
6 sale 1,800 56.00 100,800
2
8 sale 1,700 60.00 102,000
Aug. 5 Purchase 3,000 35.80 107,400
1
4 sale 2,000 60.00 120,000
2
5 Purchase 500 36.00 18,000
3
0 sale 1,750 60.00 105,000
Instructions
1. Record the inventory, purchases, and cost of merchandise sold data in a perpetual inventory
record similar to the one illustrated in Exhibit 3, using the first-in, first-out method.
2. Determine the total sales and the total cost of merchandise sold for the period. Journalize the
entries in the sales and cost of merchandise sold accounts. Assume that all sales were on
account.
3. Determine the gross profit from sales for the period.
4. Determine the ending inventory cost as of August 31, 2014.
5. Based upon the preceding data, would you expect the inventory using the last-in, first-out
method to be higher or lower?
PR 7-2A LIFO perpetual inventory OBJ. 2, 3
The beginning inventory at RTE Office Supplies and data on purchases and sales for a three-month
period are shown in Problem 7-1A.
Instructions
1. Record the inventory, purchases, and cost of merchandise sold data in a perpetual inventory record
similar to the one illustrated in Exhibit 4, using the last-in, first-out method.
2. Determine the total sales, the total cost of merchandise sold, and the gross profit from sales for the
period.
3. Determine the ending inventory cost as of August 31, 2014.
You might also like
- FX Option Performance: An Analysis of the Value Delivered by FX Options since the Start of the MarketFrom EverandFX Option Performance: An Analysis of the Value Delivered by FX Options since the Start of the MarketNo ratings yet
- (02D) Inventories Assignment 02 ANSWER KEYDocument9 pages(02D) Inventories Assignment 02 ANSWER KEYGabriel Adrian ObungenNo ratings yet
- Quiz - Inventories CostingDocument1 pageQuiz - Inventories CostingAna Mae Hernandez67% (3)
- Assignment 1Document1 pageAssignment 1Tausif IlyasNo ratings yet
- Aging Accounts Receivable and Calculating Doubtful Accounts ExpenseDocument7 pagesAging Accounts Receivable and Calculating Doubtful Accounts Expenselala gasNo ratings yet
- Ain20190418028 ModifiedDocument5 pagesAin20190418028 ModifiedNiomi GolraiNo ratings yet
- Miljane Perdizo - Inventory QuizDocument3 pagesMiljane Perdizo - Inventory Quizmiljane perdizoNo ratings yet
- IFM - Intro to Financial Accounting Tutorial QuestionsDocument5 pagesIFM - Intro to Financial Accounting Tutorial QuestionsPatric CletusNo ratings yet
- Bank Reconciliation SpreadsheetDocument7 pagesBank Reconciliation Spreadsheetcrisjay ramosNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Answers and Solutions - Assignment On Materials and LaborDocument8 pages4.2 Answers and Solutions - Assignment On Materials and LaborRoselyn LumbaoNo ratings yet
- Exercises 1-4Document4 pagesExercises 1-4Dayana MasturaNo ratings yet
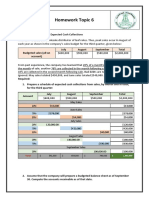
- Homework Topic 6: EXERCISE 8-1 Schedule of Expected Cash CollectionsDocument3 pagesHomework Topic 6: EXERCISE 8-1 Schedule of Expected Cash CollectionskhetamNo ratings yet
- Jimbob Co.'s January Income StatementDocument24 pagesJimbob Co.'s January Income StatementAlyannaNo ratings yet
- Cost & Management Accounting: Material Costing Lecture-8 Mian Ahmad Farhan (ACA)Document21 pagesCost & Management Accounting: Material Costing Lecture-8 Mian Ahmad Farhan (ACA)AnsariRiaz100% (1)
- 2.3inventory - Cost Flow MethodsDocument12 pages2.3inventory - Cost Flow Methodsnermeen alaaeldeinMNo ratings yet
- Jawaban & Latihan UAS AKDAS 1Document15 pagesJawaban & Latihan UAS AKDAS 1Cindy Tri WidiaNo ratings yet
- Group Work - Inventory Cost Flow and LCNRV: AnswerDocument5 pagesGroup Work - Inventory Cost Flow and LCNRV: AnswerKawhileonard LeonardNo ratings yet
- Master Budgeting: June July August September October Third QuarterDocument10 pagesMaster Budgeting: June July August September October Third QuarterЭниЭ.No ratings yet
- Assigment Costing (Ceria Co.)Document4 pagesAssigment Costing (Ceria Co.)Aien NaNo ratings yet
- Sales, Costs, Inventory TrackingDocument34 pagesSales, Costs, Inventory TrackingGenie MaeNo ratings yet
- Ass6 7Document1 pageAss6 7Kath LeynesNo ratings yet
- Exercise Chap 8Document6 pagesExercise Chap 8hangbg2k3No ratings yet
- Master Budgeting (Sample Problems With Answers)Document11 pagesMaster Budgeting (Sample Problems With Answers)Jonalyn TaboNo ratings yet
- Asistensi 2Document2 pagesAsistensi 2CatherineNo ratings yet
- LESSON 7.3Document2 pagesLESSON 7.3crisjay ramosNo ratings yet
- Budgeting - Planning: A325 Discussion - March 19, 2012Document8 pagesBudgeting - Planning: A325 Discussion - March 19, 2012alfaNo ratings yet
- Class Activity CH 6Document4 pagesClass Activity CH 6Sana BatoolNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Inventories Practice QuestionsDocument20 pagesChapter 6 - Inventories Practice Questionssami javaidNo ratings yet
- Rheyna Suryadana - GLSDocument4 pagesRheyna Suryadana - GLSNatasha HerlianaNo ratings yet
- ACC 102.Exercise1.Inventory Cost Flow and LCNRVDocument5 pagesACC 102.Exercise1.Inventory Cost Flow and LCNRVMa. Lou Erika BALITENo ratings yet
- Tanggal Pembelian Penjualan Persediaan Unit Harga/unit Total Unit Harga Total UnitDocument10 pagesTanggal Pembelian Penjualan Persediaan Unit Harga/unit Total Unit Harga Total UnitDeny WilyartaNo ratings yet
- Inventories - ProblemDocument17 pagesInventories - ProblemIris Mnemosyne100% (4)
- Group 2Document51 pagesGroup 2snehaghagNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Accounting For Merchandising OperationDocument48 pagesChapter 5 Accounting For Merchandising OperationMahmud Al HasanNo ratings yet
- Inventory Valuation Work Sheet 2023Document5 pagesInventory Valuation Work Sheet 2023Risha OsfordNo ratings yet
- Inventory Valuation PDFDocument29 pagesInventory Valuation PDFReverie Sevilla78% (9)
- Inventory Valuation C10Document5 pagesInventory Valuation C10music niNo ratings yet
- Master BudgetDocument12 pagesMaster Budgetshi shiiisshhNo ratings yet
- Proj 2Document15 pagesProj 2Shahan AsifNo ratings yet
- AP 5905Q InventoriesDocument3 pagesAP 5905Q Inventoriesaldrin elsisuraNo ratings yet
- CH 7 Exhibit 13, 14 Q 23-25Document4 pagesCH 7 Exhibit 13, 14 Q 23-25ЭниЭ.No ratings yet
- Write Down of Inventory To Net Realizable Value3Document4 pagesWrite Down of Inventory To Net Realizable Value3CJ alandy100% (1)
- 24 Inventories HWDocument4 pages24 Inventories HWSandeep JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Accounting & Financial ReportingDocument9 pagesAccounting & Financial ReportingAhmad ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Expected Sales in Units Unit Sales Price Total SalesDocument17 pagesExpected Sales in Units Unit Sales Price Total SalesFadly David WaasNo ratings yet
- Group Managerial AccountingDocument9 pagesGroup Managerial AccountingSlamet SalimNo ratings yet
- Local Media3459558769538041028Document22 pagesLocal Media3459558769538041028Princes Ann MarcianoNo ratings yet
- (USD $ Millions) : Operating Cash FlowDocument5 pages(USD $ Millions) : Operating Cash Flowsunit dasNo ratings yet
- Tute 3b PDFDocument7 pagesTute 3b PDFChin Hung YauNo ratings yet
- Assessment 2 2024 FAR - 1Document6 pagesAssessment 2 2024 FAR - 1ARBYLESA JUNIONo ratings yet
- Industrial SendasDocument1 pageIndustrial SendasA Chris M'GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Boomstick Corp quarterly budgets and financial statementsDocument14 pagesBoomstick Corp quarterly budgets and financial statementsDivya GoyalNo ratings yet
- Merchandising Solutions WorksheetDocument10 pagesMerchandising Solutions WorksheetChakShaniqueNo ratings yet
- GSLC Case Study Master Budget AnalysisDocument3 pagesGSLC Case Study Master Budget AnalysisNatasha HerlianaNo ratings yet
- Ipil Grocery T AccountsDocument5 pagesIpil Grocery T AccountsJelaina Alimansa100% (1)
- Problem 1Document3 pagesProblem 1Zyrah Manalo50% (2)
- Sales, Expenses and Cash Flow AnalysisDocument6 pagesSales, Expenses and Cash Flow AnalysisRUPIKA R GNo ratings yet
- Group Assignment Business Valuation and AnalysisDocument8 pagesGroup Assignment Business Valuation and Analysischarlesmicky82No ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Inventory Cost FlowDocument6 pagesChapter 11 - Inventory Cost FlowLorence IbañezNo ratings yet
- Principles of Accounts SBADocument24 pagesPrinciples of Accounts SBAmatthew WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Understanding Depreciation Expense and MethodsDocument52 pagesUnderstanding Depreciation Expense and MethodsPiyush Malhotra50% (2)
- WACC - WorksheetDocument4 pagesWACC - Worksheetvwfn8f7xmtNo ratings yet
- ch08 SolDocument18 pagesch08 SolJohn Nigz Payee50% (2)
- Dissolution of Partnership - Question 1Document16 pagesDissolution of Partnership - Question 1anthony hoNo ratings yet
- 502C - Cost AccountingDocument38 pages502C - Cost AccountingMuhammad Arslan Usman100% (1)
- AccountsDocument16 pagesAccountskeshavkaushik182008No ratings yet
- The Nature and Scope of Cost & Management AccountingDocument17 pagesThe Nature and Scope of Cost & Management Accountingfreshkidjay100% (5)
- Engineering Economy by Group ActivityDocument1 pageEngineering Economy by Group ActivityMj MallongaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Financial Statements: Dr. Charles Suresh DavidDocument19 pagesUnderstanding Financial Statements: Dr. Charles Suresh DavidS.Abinith NarayananNo ratings yet
- Education - BE SMART Tutorial CenterDocument14 pagesEducation - BE SMART Tutorial CenterMishell Valerie Ferido100% (1)
- Statement of Financial Position LessonDocument6 pagesStatement of Financial Position LessonJoana Jean SuymanNo ratings yet
- Internal ReconstructionDocument15 pagesInternal Reconstructionramu varmaNo ratings yet
- Sports Equipment Retail Business Plan (Sunny)Document15 pagesSports Equipment Retail Business Plan (Sunny)mattogillNo ratings yet
- Accountants of ProfessionalsDocument13 pagesAccountants of ProfessionalsSangram JadhavNo ratings yet
- Elnet TechnologDocument10 pagesElnet TechnologankiosaNo ratings yet
- Auditors Report Financial Statement 2022Document99 pagesAuditors Report Financial Statement 2022jakariakhan736901No ratings yet
- Nintendo Profile Model TemplateDocument2 pagesNintendo Profile Model TemplateHunter Hearst LevesqueNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement of Analysis Horizontal and VerticalDocument7 pagesFinancial Statement of Analysis Horizontal and VerticalALYSSA MARIE NAVARRANo ratings yet
- Inventory Management TechniquesDocument41 pagesInventory Management TechniquesElizabeth HdzNo ratings yet
- Class-12-Accountancy-Part-2-Chapter-6 SolutionsDocument41 pagesClass-12-Accountancy-Part-2-Chapter-6 Solutionssugapratha lingamNo ratings yet
- M & M Appliance Center January 2008 Income StatementDocument1 pageM & M Appliance Center January 2008 Income StatementsppNo ratings yet
- FABM Week 6 - Financial RatioDocument35 pagesFABM Week 6 - Financial Ratiovmin친구No ratings yet
- Exercise 1-10: Weygandt, Kieso, Kimmel, Trenholm, Kinnear Accounting Principles, Fifth Canadian EditionDocument5 pagesExercise 1-10: Weygandt, Kieso, Kimmel, Trenholm, Kinnear Accounting Principles, Fifth Canadian EditionjorwitzNo ratings yet
- Worksheet To Principle of Acc. II. AregaDocument4 pagesWorksheet To Principle of Acc. II. AregaEtiel Films / ኢትኤል ፊልሞች100% (3)
- Adeola Company ProfileDocument90 pagesAdeola Company ProfileRichard WakoriNo ratings yet
- Uniform Format of Accounts - SummaryDocument8 pagesUniform Format of Accounts - SummaryGotta Patti House100% (1)
- June 2019Document182 pagesJune 2019shankar k.c.No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document2 pagesChapter 4Jao FloresNo ratings yet
- Economic Value AddedDocument14 pagesEconomic Value Addedmanish singh rana0% (1)
- WTB - Applied AuditingDocument24 pagesWTB - Applied AuditingWaye EdnilaoNo ratings yet