Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HMI Stands For Human Interface
Uploaded by
Kao SophearakOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HMI Stands For Human Interface
Uploaded by
Kao SophearakCopyright:
Available Formats
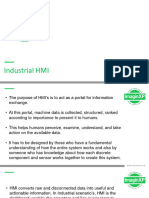
MI stands for Human-Machine Interface.
It is a technology that allows humans to
interact with machines, devices, or systems. The primary purpose of an HMI is to provide
a user-friendly interface that enables effective control and monitoring of machines or
processes. In industrial contexts, HMIs are commonly used to interact with
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and other automation systems.
Key features of HMIs include:
1. Graphical User Interface (GUI): HMIs typically use graphical elements, such as
icons, buttons, and screens, to present information in a visually intuitive manner.
This makes it easier for operators and users to understand and control the
system.
2. Touchscreens and Input Devices: Many modern HMIs utilize touchscreens as
the primary input method. However, other input devices like keyboards, mice, or
physical buttons may also be used, depending on the application.
3. Real-time Monitoring: HMIs provide real-time feedback on the status of
machines or processes. Operators can monitor parameters, view trends, and
receive alerts or alarms if something goes wrong.
4. Control Functionality: In addition to monitoring, HMIs often allow users to
control machines or processes directly. This can include starting and stopping
processes, adjusting setpoints, and performing other control functions.
5. Data Visualization: HMIs can display various types of data in a visual format,
including charts, graphs, and diagrams. This helps operators quickly grasp the
current state of the system.
6. Alarm and Event Handling: HMIs are equipped to handle alarms and events by
providing visual and audible alerts to operators. This helps in quickly identifying
and addressing issues in the system.
7. Communication: HMIs often support communication with other devices, such as
PLCs, sensors, and other control systems. This allows for seamless integration into
larger industrial automation systems.
HMIs are used in a wide range of applications, including manufacturing, process control,
utilities, transportation, and more. They play a crucial role in improving the efficiency,
safety, and operability of complex systems by providing a user-friendly interface for
human interaction.
You might also like
- HMI Seminar ReportDocument30 pagesHMI Seminar ReportNitinSharma67% (3)
- Human Machine InterfaceDocument11 pagesHuman Machine InterfacenazeerplcNo ratings yet
- HMIDocument1 pageHMIk.sophearakNo ratings yet
- Data RecipesDocument3 pagesData RecipesAyush SinghNo ratings yet
- PLC / Scada / Hmi Controllers:: Name: Muhammad Zunair Comsats University Date: 28-October-2018Document13 pagesPLC / Scada / Hmi Controllers:: Name: Muhammad Zunair Comsats University Date: 28-October-2018Arul NNo ratings yet
- Human-Machine-InterfaceDocument64 pagesHuman-Machine-InterfaceDipak K01No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 HMIDocument5 pagesChapter 4 HMIHarshal VaidyaNo ratings yet
- Human Machine InterfaceDocument13 pagesHuman Machine InterfaceBruce LambNo ratings yet
- HMI Systems Design ConsiderationsDocument16 pagesHMI Systems Design ConsiderationsAlberto Hai Re100% (1)
- 03 L3 PPT HciDocument13 pages03 L3 PPT HciakshaykgodaraNo ratings yet
- Human Machine Interface: Group MembersDocument5 pagesHuman Machine Interface: Group MembersFaizan MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Hmi and ScadaDocument26 pagesHmi and Scadaburningsun6991No ratings yet
- Development of The Automatic Control System Based On Human Machine InterfaceDocument4 pagesDevelopment of The Automatic Control System Based On Human Machine Interfaceemmak2097No ratings yet
- H Man/Compu Rin: Te TerfaceDocument9 pagesH Man/Compu Rin: Te TerfaceFernando RomeroNo ratings yet
- AI HMI AnsverDocument1 pageAI HMI AnsvervsimovicNo ratings yet
- Hmi - Unit 1Document10 pagesHmi - Unit 1HarshNo ratings yet
- Human Machine InterfaceDocument5 pagesHuman Machine Interfaceibrahimkhleifat0% (1)
- Instrumentation NutshellDocument3 pagesInstrumentation NutshellGrace Ann AbanteNo ratings yet
- Industrial Machines Pitch DeckDocument8 pagesIndustrial Machines Pitch Deckart estacioNo ratings yet
- 16 Why HMIs Make SenseDocument2 pages16 Why HMIs Make SenseAmmar IshaquiNo ratings yet
- AutomationDocument2 pagesAutomationupendra35No ratings yet
- DESAIN DAN SIMULASI SISTEM HMI (Human Machine Interface) Berbasis Citect Scada Pada Konveyor Proses Di IndustriDocument10 pagesDESAIN DAN SIMULASI SISTEM HMI (Human Machine Interface) Berbasis Citect Scada Pada Konveyor Proses Di IndustriAlexa RyieNo ratings yet
- User Interface: This Article Has Multiple Issues. Please HelpDocument7 pagesUser Interface: This Article Has Multiple Issues. Please HelpKrishna KumarNo ratings yet
- HMI ToDocument3 pagesHMI ToPatrick torresNo ratings yet
- NoscriptDocument1 pageNoscriptEvaNo ratings yet
- Article Importance of Automation PLCDocument4 pagesArticle Importance of Automation PLCWilliam Steven Triana GarciaNo ratings yet
- Industrial AutomationDocument8 pagesIndustrial AutomationNidhin PalliyaliNo ratings yet
- Applications of PLC & HMIDocument5 pagesApplications of PLC & HMIAviral RawatNo ratings yet
- PIN Experion HMIDocument5 pagesPIN Experion HMIAvinash ChoudhariNo ratings yet
- PLC Notes 1Document18 pagesPLC Notes 1Om SaiNo ratings yet
- Industrial Automation - Lecture 1Document56 pagesIndustrial Automation - Lecture 1Elly TongsNo ratings yet
- Automation NotesDocument2 pagesAutomation NotesamritnashuNo ratings yet
- Uk 3Document27 pagesUk 3imstudent40No ratings yet
- Developing A Human Machine Interface (Hmi) For Industrial Automated Systems Using Siemens Simatic Wincc Flexible Advanced SoftwareDocument11 pagesDeveloping A Human Machine Interface (Hmi) For Industrial Automated Systems Using Siemens Simatic Wincc Flexible Advanced SoftwareZeph DugangNo ratings yet
- Industrial Automation: Vignan's LARA Institute of Technology & ScienceDocument26 pagesIndustrial Automation: Vignan's LARA Institute of Technology & ScienceHarsha VardhanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document34 pagesUnit 3Mohammad MunniNo ratings yet
- 09 PDFDocument9 pages09 PDFpkj009No ratings yet
- Scada PLC HmiDocument4 pagesScada PLC HmiM. S. ChikkamaniNo ratings yet
- Scada System: Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) Is A Control System ArchitectureDocument10 pagesScada System: Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) Is A Control System Architecturerashid sattarNo ratings yet
- Understanding HMI Scada System Security GapsDocument8 pagesUnderstanding HMI Scada System Security GapsejgawlikNo ratings yet
- PLCDocument1 pagePLCk.sophearakNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Industrial Automation by Jatin Kundara, EI & CE Branch From Govt - Engg College, AjmerDocument41 pagesProject Report On Industrial Automation by Jatin Kundara, EI & CE Branch From Govt - Engg College, AjmerjatinkundaraNo ratings yet
- Design Considerations For Effective: Human Machine Interface SystemsDocument19 pagesDesign Considerations For Effective: Human Machine Interface Systemssilvana_bgNo ratings yet
- ScadaDocument10 pagesScadarashid sattarNo ratings yet
- Embedded Operating Systems For Real-Time Applications: AbstractDocument14 pagesEmbedded Operating Systems For Real-Time Applications: AbstractKunal KucheriaNo ratings yet
- Information Technology IDocument43 pagesInformation Technology Inerurkar_tusharNo ratings yet
- Chapter - I Operating System: Functions of OSDocument7 pagesChapter - I Operating System: Functions of OSAR Ananth Rohith BhatNo ratings yet
- Industrial Automation ReadingDocument33 pagesIndustrial Automation Readingsaurabhrai85No ratings yet
- Automation and RoboticsDocument184 pagesAutomation and RoboticsPrasannaa AundhkarNo ratings yet
- User Interface - Definition From AnswersDocument3 pagesUser Interface - Definition From AnswersMuhammad Siddig HassanNo ratings yet
- OM With TQM (Process TechnologyDocument3 pagesOM With TQM (Process TechnologyMellanie SerranoNo ratings yet
- SCADA Stands For Supervisory Control and Data AcquisitionDocument1 pageSCADA Stands For Supervisory Control and Data AcquisitionKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- Explaining HMI - SCADA - PLCDocument7 pagesExplaining HMI - SCADA - PLCRALPH JULES SARAUSNo ratings yet
- Foundation University: Syed Shahabal Shah Hamdani F171-BCSE050Document7 pagesFoundation University: Syed Shahabal Shah Hamdani F171-BCSE050Shahab HamdaniNo ratings yet
- Foundation University: Syed Shahabal Shah Hamdani F171-BCSE050Document7 pagesFoundation University: Syed Shahabal Shah Hamdani F171-BCSE050Shahab HamdaniNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 2: Name:-Harsh Mendapara Batch: - A2 Roll No: - 31 Subject: - HMI (Human Machine Interaction)Document6 pagesExperiment No 2: Name:-Harsh Mendapara Batch: - A2 Roll No: - 31 Subject: - HMI (Human Machine Interaction)Harsh MendaparaNo ratings yet
- Power MetersDocument2 pagesPower MetersKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- IOS Download: Search"V-BOX" in App Store To DownloadDocument1 pageIOS Download: Search"V-BOX" in App Store To DownloadKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- In Second GradeDocument2 pagesIn Second GradeKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- Maths For Grade 7Document1 pageMaths For Grade 7Kao SophearakNo ratings yet
- Maths Grade 1Document1 pageMaths Grade 1Kao SophearakNo ratings yet
- Math Grade 3Document1 pageMath Grade 3Kao SophearakNo ratings yet
- Link For AgricultureDocument1 pageLink For AgricultureKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- LX3V-2RS485-BD 1Document8 pagesLX3V-2RS485-BD 1Marko GavrilovicNo ratings yet
- Quotation: Phase 7 Underground Option I MDB Panel 400ADocument1 pageQuotation: Phase 7 Underground Option I MDB Panel 400AKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- SCADA Stands For Supervisory Control and Data AcquisitionDocument1 pageSCADA Stands For Supervisory Control and Data AcquisitionKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- Phase 6 OverheadDocument1 pagePhase 6 OverheadKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- Machine ListDocument7 pagesMachine ListKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- MV ProjectDocument8 pagesMV ProjectKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- Hello We Want To LearnDocument1 pageHello We Want To LearnKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- Alend Trading & Engineer Solution: NTS@A4Document1 pageAlend Trading & Engineer Solution: NTS@A4Kao SophearakNo ratings yet
- Quotation: Phase 6 Underground Option I MDB Panel 400ADocument1 pageQuotation: Phase 6 Underground Option I MDB Panel 400AKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- Quotation: Phase 7 Overhead Option I MDB Panel 400ADocument1 pageQuotation: Phase 7 Overhead Option I MDB Panel 400AKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- Alend Trading & Engineer Solution: I MDB 800A Abb 1 SETDocument2 pagesAlend Trading & Engineer Solution: I MDB 800A Abb 1 SETKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- Control and Disconnection: Compact Ns630Bna To 1600na Switch-DisconnectorsDocument2 pagesControl and Disconnection: Compact Ns630Bna To 1600na Switch-DisconnectorsKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- Singsong 240 TPD Tapioca Starch 1year Spareparts List (Electric Department) 2019Document2 pagesSingsong 240 TPD Tapioca Starch 1year Spareparts List (Electric Department) 2019Kao SophearakNo ratings yet
- Machine List Version 2 04 06 2019Document24 pagesMachine List Version 2 04 06 2019Kao SophearakNo ratings yet
- IN OUT PLCDocument1 pageIN OUT PLCKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document21 pagesBook 1Kao SophearakNo ratings yet
- Singsong industial Co.,Ltd: Assembled the main switch cabinet (ตู ้เมนไฟฟ้า)Document3 pagesSingsong industial Co.,Ltd: Assembled the main switch cabinet (ตู ้เมนไฟฟ้า)Kao SophearakNo ratings yet
- 78.milk &pet FA SystemDocument3 pages78.milk &pet FA SystemKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- Transformer Technical Specification: Rated Voltage Ratio (Primary / Secondary)Document3 pagesTransformer Technical Specification: Rated Voltage Ratio (Primary / Secondary)Kao SophearakNo ratings yet
- Mr. Socheat Rice MillDocument1 pageMr. Socheat Rice MillKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- LS Bus Duct System: WWW - Lsis.bizDocument48 pagesLS Bus Duct System: WWW - Lsis.bizKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- 5 6325585094329237555Document1 page5 6325585094329237555Kao SophearakNo ratings yet
- 78.milk &pet - PaDocument2 pages78.milk &pet - PaKao SophearakNo ratings yet