Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Law of Supply
Uploaded by
py8337Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Law of Supply
Uploaded by
py8337Copyright:
Available Formats
Law of Supply
The law of supply is a microeconomic law. It states that, all other factors
being equal, as the price of a good or service increases, the quantity of
that good or service that suppliers offer will increase, and vice versa.
In plain terms, this law means that as the price of an item goes up,
suppliers will attempt to maximize their profits by increasing the number of
that item that they sell.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
The law of supply says that a higher price will lead producers to
supply a higher quantity to the market.
Because businesses seek to increase revenue, when they expect to
receive a higher price for something, they will produce more of it.
Meanwhile, if prices fall, suppliers are disincentivized from producing
as much.
Supply in a market can be depicted as an upward-sloping supply
curve that shows how the quantity supplied will respond to various
prices over a period of time.
Together with demand, the law of supply forms half of the law of
supply and demand.
Understanding the Law of Supply
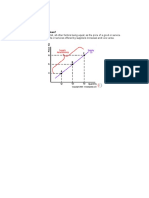
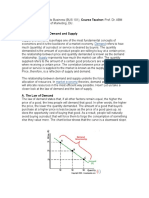
The chart below depicts the law of supply using a supply curve, which is
upward sloping. A, B, and C are points on the supply curve. Each point on
the curve reflects a direct correlation between quantity supplied (Q) and
price (P). So, at point A, the quantity supplied will be Q1 and the price will
be P1, and so on.
The supply curve is upward sloping because, over time, suppliers can
choose how much of their goods to produce and later bring to market. At
any given point in time, however, the supply that sellers bring to market is
fixed, and sellers simply face a decision to either sell or withhold their
stock from a sale; consumer demand sets the price, and sellers can only
charge what the market will bear.
If consumer demand rises over time, the price will rise, and suppliers can
choose to devote new resources to production (or new suppliers can enter
the market), which increases the quantity supplied. Demand ultimately sets
the price in a competitive market; supplier response to the price they can
expect to receive sets the quantity supplied.
The law of supply is one of the most fundamental concepts in economics.
It works with the law of demand to explain how market economies allocate
resources and determine the prices of goods and services.
Examples of the Law of Supply
The law of supply summarizes the effect price changes have on producer
behavior. For example, a business will make more video game systems if
the price of those systems increases. The opposite is true if the price of
video game systems decreases. The company might supply 1 million
systems if the price is $200 each, but if the price increases to $300, they
might supply 1.5 million systems.
Factors Affect Supply
Supply is influenced by prices and consumer demand. The number of
suppliers available, the level of competition, the state of technology, and
the presence of government support or restriction will play important roles.
For certain products like agricultural commodities, supply is also impacted
by factors such as weather and crop yields.
You might also like
- The Law of SupplyDocument6 pagesThe Law of SupplyAngelenemae MohamadNo ratings yet
- A level Economics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA level Economics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Health Economics SupplyDocument7 pagesHealth Economics SupplyPao C EspiNo ratings yet
- Accounting, Maths and Computing Principles for Business Studies V11From EverandAccounting, Maths and Computing Principles for Business Studies V11No ratings yet
- Managerial EconomicsDocument24 pagesManagerial EconomicsRudydanvinz BernardoNo ratings yet
- Law of Demand: Key PointsDocument7 pagesLaw of Demand: Key PointsFalah SohailNo ratings yet
- Law of Supply and DemandDocument6 pagesLaw of Supply and DemandArchill YapparconNo ratings yet
- Economic Theory 1Document16 pagesEconomic Theory 1Dyepoy Figs VjoucherNo ratings yet
- Law of Supply and DemandDocument49 pagesLaw of Supply and DemandArvi Kyle Grospe PunzalanNo ratings yet
- Eco GTUDocument12 pagesEco GTUnicholas_sudanNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Supply & Market EquilibriumDocument14 pagesModule 4 - Supply & Market EquilibriumMarjon DimafilisNo ratings yet
- Group2 Demand and SupplyDocument20 pagesGroup2 Demand and SupplySeth DivinagraciaNo ratings yet
- Economics Word File Roll No 381 To 390Document19 pagesEconomics Word File Roll No 381 To 390Spandan ThakkarNo ratings yet
- All About Supply, Demand, Elasticity, UtilityDocument11 pagesAll About Supply, Demand, Elasticity, Utilityantara nodiNo ratings yet
- Economics Basics - Supply and Demand - InvestopediaDocument5 pagesEconomics Basics - Supply and Demand - Investopediaddeww100% (1)
- Determinants of Demand Followings Are The Determinants or DemandDocument8 pagesDeterminants of Demand Followings Are The Determinants or DemandSherazButtNo ratings yet
- Laws of Demand and Supply: Submitted By: Bipul Deka Roll No: 05 B.Pharm 4 YearDocument7 pagesLaws of Demand and Supply: Submitted By: Bipul Deka Roll No: 05 B.Pharm 4 YearLulu BritanniaNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument53 pagesAssignmentSamyuktha SaminathanNo ratings yet
- Economics ReviewerDocument15 pagesEconomics ReviewerPatriciaNo ratings yet
- Demand and Supply Law of DiminishingDocument6 pagesDemand and Supply Law of DiminishinggralenekovaNo ratings yet
- Supply and Demand Is Perhaps One of The Most Fundamental Concepts of Economics and It Is The Backbone of A Market EconomyDocument6 pagesSupply and Demand Is Perhaps One of The Most Fundamental Concepts of Economics and It Is The Backbone of A Market EconomySheikh MohsinNo ratings yet
- Market Market Demand Market Supply EquilibriumDocument10 pagesMarket Market Demand Market Supply EquilibriumPrincess Kyle Abella AlotaNo ratings yet
- Supply and DemandDocument3 pagesSupply and DemandSulaiman KhanNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument9 pagesUntitledgeofreyNo ratings yet
- Supply and Demand Is Perhaps One of The Most Fundamental Concepts of Economics and It Is The Backbone of A Market EconomyDocument7 pagesSupply and Demand Is Perhaps One of The Most Fundamental Concepts of Economics and It Is The Backbone of A Market EconomyJed FarrellNo ratings yet
- 3 Demand ForecastingDocument8 pages3 Demand ForecastingShanmukh GollapudiNo ratings yet
- Supply and DemandDocument8 pagesSupply and Demandabhi1910100% (1)
- Applied Economics Week 3 (Market Demand - Supply Equilibrium)Document59 pagesApplied Economics Week 3 (Market Demand - Supply Equilibrium)ALCondezEdquibanEbuenNo ratings yet
- 3 Law of Supply and Price EqualibriumDocument22 pages3 Law of Supply and Price EqualibriumAkshay BNo ratings yet
- Economics NotesDocument13 pagesEconomics Noteskarankumar67656No ratings yet
- Theory of Supply and Demand: Unraveling Market Dynamics: IntroductionDocument4 pagesTheory of Supply and Demand: Unraveling Market Dynamics: IntroductionSharan RarhiNo ratings yet
- Economics Basics: Supply and DemandDocument8 pagesEconomics Basics: Supply and Demandrizqi febriyantiNo ratings yet
- Demand & SupplyDocument6 pagesDemand & SupplySoham GuhaNo ratings yet
- Basic Economic Concepts and TerminologyDocument11 pagesBasic Economic Concepts and TerminologyAbdul QuorishyNo ratings yet
- Law of Supply and DemandDocument4 pagesLaw of Supply and DemandSteven MoisesNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics READING WEEK 2Document3 pagesApplied Economics READING WEEK 2jeanaguilos2023No ratings yet
- Supply and DemandDocument16 pagesSupply and DemandMartin JanuaryNo ratings yet
- Elements of Demand and SupplyDocument24 pagesElements of Demand and SupplyAnn Michelle Tarrobago100% (1)
- EconomicsDocument11 pagesEconomics41Sudipta BeraNo ratings yet
- Economics BasicsDocument17 pagesEconomics BasicsmdsalmanarNo ratings yet
- Law of Supply and DemandDocument2 pagesLaw of Supply and DemandLhoy Guisihan Asoy Idulsa100% (1)
- Demand and SupplyDocument6 pagesDemand and Supplybotnarumaria22No ratings yet
- ECN1014 Lecture SlidesDocument48 pagesECN1014 Lecture SlidesDanes WaranNo ratings yet
- Supply and DemandDocument1 pageSupply and DemandSherwin Gabriel RodenasNo ratings yet
- Basic Analysis of Demand and Supply 1Document6 pagesBasic Analysis of Demand and Supply 1Jasmine GarciaNo ratings yet
- Law of SupplyDocument15 pagesLaw of SupplyZahid RaihanNo ratings yet
- Sambheet Pal - Essay AssignmentDocument10 pagesSambheet Pal - Essay AssignmentNIKITA AGARWALLANo ratings yet
- Law of Supply ContentDocument2 pagesLaw of Supply ContentMARK VIDALNo ratings yet
- Economics BasicsDocument9 pagesEconomics BasicsGermaine CasiñoNo ratings yet
- Economics Basic3 Supply DemandDocument6 pagesEconomics Basic3 Supply Demandwaluyo2010No ratings yet
- Part 1: Introduction To Economics Chapter # 1: Micro EconomicsDocument24 pagesPart 1: Introduction To Economics Chapter # 1: Micro EconomicsjavedNo ratings yet
- Bs-It 5 Semester: Topic: Supply Teacher Name: Fizza ShaukatDocument10 pagesBs-It 5 Semester: Topic: Supply Teacher Name: Fizza Shaukatwarda abbasNo ratings yet
- The Basic Analysis of Demand and SupplyDocument44 pagesThe Basic Analysis of Demand and SupplyGillian Louise SaquianNo ratings yet
- Demand Supply: A. The Law of DemandDocument4 pagesDemand Supply: A. The Law of DemandJoshua KeanuNo ratings yet
- Market Forces:: MonopolyDocument5 pagesMarket Forces:: Monopolymaryam gullNo ratings yet
- Economics Basics-Demand & SupplyDocument8 pagesEconomics Basics-Demand & SupplyNahiyan Islam ApuNo ratings yet
- Demand and Supply Lecture NotesDocument6 pagesDemand and Supply Lecture NotesСтанислав Филин100% (2)
- Suply Demand CurvesDocument7 pagesSuply Demand CurvesonkaliyaNo ratings yet
- Law of Supply and DemandDocument18 pagesLaw of Supply and DemandArnee Pantajo80% (5)
- MwigaDocument89 pagesMwigamichael richardNo ratings yet
- MarchDocument214 pagesMarchbhargavtangudu117No ratings yet
- Final Chapter 6 Financial PlanDocument26 pagesFinal Chapter 6 Financial Planangelo felizardoNo ratings yet
- Project Management Manual Part II RequirementsDocument120 pagesProject Management Manual Part II RequirementsKyawt Kay Khine Oo100% (1)
- Business-Plan ENTREPDocument3 pagesBusiness-Plan ENTREPGlen Ruzzel ElleveraNo ratings yet
- Audit Work Program TemplateDocument64 pagesAudit Work Program TemplateleonciongNo ratings yet
- Ramada Case Study Final ProjectDocument17 pagesRamada Case Study Final ProjectHamnaNo ratings yet
- Kenya Energy SituationDocument162 pagesKenya Energy SituationArudo Elly OkaraNo ratings yet
- PPT1-The Innovation Imperative, and Social InnovationsDocument35 pagesPPT1-The Innovation Imperative, and Social InnovationsIqbal Kharisma83% (6)
- SchoolCafe - HouseholdLetterDocument1 pageSchoolCafe - HouseholdLetterDinora Grimaldo SanchezNo ratings yet
- Product Concept: Apple Co. Is A Well-Known Company For Its Gadgets andDocument4 pagesProduct Concept: Apple Co. Is A Well-Known Company For Its Gadgets andcarloNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document3 pagesTutorial 1Chun Yeen NgaiNo ratings yet
- Wintershall DeaDocument11 pagesWintershall Dearadoslav micicNo ratings yet
- All Sbi Branches Ifsc CodeDocument4,315 pagesAll Sbi Branches Ifsc CodeMadhan Gopal75% (12)
- Modern Office & Its FunctionsDocument14 pagesModern Office & Its FunctionsYash SharmaNo ratings yet
- SimhaDocument14 pagesSimhaArunachalam ANo ratings yet
- Cash BudgetDocument8 pagesCash BudgetKei CambaNo ratings yet
- Active Agency September 2022Document8 pagesActive Agency September 2022Karthik ShankarNo ratings yet
- Lit266 Bli Heal Abut Options FinalDocument2 pagesLit266 Bli Heal Abut Options FinalJean-Christophe PopeNo ratings yet
- Axe Effect PresentationDocument17 pagesAxe Effect PresentationAmey SankheNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Environmental Turbulence On Organizational Learning PDFDocument12 pagesThe Impact of Environmental Turbulence On Organizational Learning PDFSuharli MarbunNo ratings yet
- Abbot Photocopier & Net Cafe: (Business Plan) History and BackgroundDocument9 pagesAbbot Photocopier & Net Cafe: (Business Plan) History and Backgroundirfan99651No ratings yet
- Bản Dịch MarDocument5 pagesBản Dịch MarHùng ThanhNo ratings yet
- System Test Cases TemplateDocument12 pagesSystem Test Cases TemplatetrajarameshNo ratings yet
- Masterclass Brochure 2023Document10 pagesMasterclass Brochure 2023Nuhu Dan-azumi MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Marginal CostingDocument36 pagesChapter 5 Marginal CostingSuku Thomas SamuelNo ratings yet
- Resume TKTI Modul 1 Cobit 2019 - Framework MethodologyDocument23 pagesResume TKTI Modul 1 Cobit 2019 - Framework MethodologyShiryu XavierNo ratings yet
- Hamleys RILPR12082008Document3 pagesHamleys RILPR12082008Sudip GuptaNo ratings yet
- Name: Tamzid Ahmed Anik ID:1911031 Code: HRM 370 Submitted To: Dr. SHIBLY KHAN Date: 5 July, 2022Document8 pagesName: Tamzid Ahmed Anik ID:1911031 Code: HRM 370 Submitted To: Dr. SHIBLY KHAN Date: 5 July, 2022Tamzid Ahmed AnikNo ratings yet
- Central Pollution Control Board Guidelines For Poultry Farms in Haryana - Naresh KadyanDocument6 pagesCentral Pollution Control Board Guidelines For Poultry Farms in Haryana - Naresh KadyanNaresh Kadyan100% (3)