Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 Lymphatic System PDF Notes by Noteskarts
Uploaded by
Filmy LandOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 Lymphatic System PDF Notes by Noteskarts
Uploaded by
Filmy LandCopyright:
Available Formats
Noteskarts
Subscribe Our YouTube Channel For Video Classes
Human Anatomy And Physiology Chapter – 6
Lymphatic System
Lymph and lymphatic system, composition, function and its
formation.
Structure and functions of spleen and lymph node.
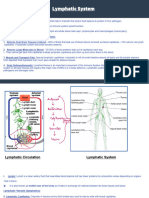
Lymphatic system
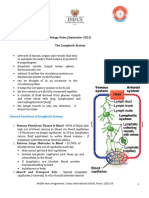
Lymphatic system is a closed system of lymph channels or
lymph vessels through which the lymph flows. It arises from the tissue
spaces and allows the lymph flow towards the blood.
Lymphatic system works as one way system because lymphatic vessels
are more porous and allows the fluid to move into the lymph capillaries
and not allows in the opposite direction.
Lymphatic system participate in our immunity system and prevent
against any infections or disease because it contains the lymphocytes
cell and other antibodies molecules.
Lymph-
Lymph is a clear to white fluid formed from intestinal fluid and flow in
the lymphatic system. About 120ml of lymph flows into blood per hour.
Out of this, about 100ml/hour flow through thoracic duct and 20ml/hour
flow through the right lymphatic duct.
Visit Our Website For Notes www.noteskarts.com
Noteskarts
Subscribe Our YouTube Channel For Video Classes
Composition of Lymph-
It is formed by 96% water and 4% solids. Some blood cell are also
present in lymph. Solid substances present in the form of--
Organic substances- proteins, lipids, aminoacids, carbohydrates,
enzymes, clotting factors
Inorganic substances- Na+,Ca+2,Cl-, HCO3-
Cellular compounds- Macrophages,monocytes,plasma cells.
Formation of Lymph-
When the blood passes through blood capillaries in the tissue to venous
end of capillaries from the arterial end. Then major part of fluid flow
and small amount of fluid passes into lymph capillaries, which have
more permeability than blood capillaries.
Factor responsible for lymph formation-
Interstitial fluid pressure.
Blood capillaries pressure.
Permeability of lymph capillaries.
Function activities of tissue.
Functions of lymph-
Lymph contains the lymphocytes and macrophages and other
phagocytosis cell which helps in removing the bacteria, foreign
bodies and helps in the immunity.
Lymph is rich source of protein and minerals so it helps in the
redistribution of fluid in the body parts.
Lymph flow is responsible for the maintence of structural and
functional integrity of tissue. Obstruction to lymph flow affects
Visit Our Website For Notes www.noteskarts.com
Noteskarts
Subscribe Our YouTube Channel For Video Classes
various tissue, particularly myocardium, nephrons, and hepatic
cells.
Spleen
Introduction - Spleen is highly vascular lymphoid organ present in the
body. It is situated in left hypochondriac region that is upper left part of
the abdomen, behind the stomach and just below the diaphragm.
The spleen is part of our lymphatic system, which fights against the
infection and keeps your body fluids in balance.
Structure of Spleen-
It is the similar structure to lymph node and covered by an outer serous
coat and an inner fibromuscular capsule. From the capsule, trabeculae
and trabecular network arises.
The parenchyma of spleen is divided into red pulp and white pulp.
Red pulp- Red pulp consists of venous sinus and cord of structures such
as blood cells, macrophages and mesenchymal cells.
White pulp- The structure of white pulp is similar to that of lymphoid
tissue. It has a central artery, which is surrounded by splenic corpuscles
or Malpighian corpuscles. These corpuscles are formed by lymphatic
sheath containing lymphocytes and Macrophages.
Functions of Spleen-
Spleen play an important role in the hematopoietic function in
embryo.
Spleen are also called graveyard of RBCs because it participate in
the destruction of RBCs and other old blood cells.
Visit Our Website For Notes www.noteskarts.com
Noteskarts
Subscribe Our YouTube Channel For Video Classes
Spleen stored the large amount of RBCs so it act as reservoir
function. The RBCs are released from spleen into circulation
during the emergency conditions like hypoxia and hemorrhage.
It plays important role in the defense mechanism. The microphages
in splenic pulp destroy the microbes and other foreign bodies by
phagocytosis.
It is also participate in the the excretory process and helps in the
ions balance.
Lymph nodes-
Lymph nodes are small glandular structures located in the course
of lymph vessels. The lymph nodes are also called lymph glands or
lymphatic nodes.
Lymph node receives lymph by one or two lymphatic vessels
called afferent vessels.
Lymph nodes are present along the course of lymphatic vessels in
axilla, elbow, knee, and groin. Lymph nodes are also present in
certain points in abdomen, thorax, and neck, where many lymph
vessels join.
Structure Of Lymph Nodes.
Lymph nodes are generally bean in shaped. Each lymph nodes
constitutes masses of lymphatic tissue, covered by a dense connective
tissue capsule. The structures are arranged in three layers namely cortex,
paracortex and medulla.
Cortex- Cortex of lymph consists of the lymphoid follicles. During any
antigens entry follicles starts proliferation and distribute to different
Visit Our Website For Notes www.noteskarts.com
Noteskarts
Subscribe Our YouTube Channel For Video Classes
different area where cause the infection. Cortex also contain some B
lymphoid cell and macrophages which also participate against infection.
Paracortex- paracortex is in between the cortex and medulla. Paracortex
contain T lymphocytes.
Medulla- Medulla contains B and T lymphocytes and macrophages.
Blood vessels of lymph node pass through medulla.
Functions of lymph nodes-
✓ When lymph passes through the lymph nodes, it is filtered that is the
water and electrolytes are removed. But, the proteins and lipids are
retained in the lymph.
✓Bacteria and other toxic substances are destroyed by macrophages of
lymph nodes are called barriers.
Visit Our Website For Notes www.noteskarts.com
Noteskarts
Subscribe Our YouTube Channel For Video Classes
Visit Our Website For Notes www.noteskarts.com
You might also like
- Lymphatic SystemDocument5 pagesLymphatic SystemCurex QANo ratings yet
- UNIT 5 Lymphatic SystemDocument84 pagesUNIT 5 Lymphatic SystemChandan ShahNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System NotesDocument7 pagesLymphatic System NotesNahid ParveenNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Lymphatic SystemDocument86 pagesAnatomy of The Lymphatic Systemahmed elsebaeyNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System: Prof. Shekhar TeliDocument19 pagesLymphatic System: Prof. Shekhar TeliShekhar TeliNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument30 pagesLymphatic SystemDARSHAN BhirudNo ratings yet
- Self Test 2Document5 pagesSelf Test 2202310446No ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument13 pagesLymphatic SystemMaxwell C Jay KafwaniNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic TissueDocument50 pagesLymphatic TissueRukshan RanatungaNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System OrgansDocument6 pagesLymphatic System OrgansАнна КатраженкоNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Lymphatic System: 3D4MedicalDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Lymphatic System: 3D4MedicalLalajimNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System: Lymph Glands and Its Function, Spleen-Structure and FunctionsDocument7 pagesLymphatic System: Lymph Glands and Its Function, Spleen-Structure and FunctionsSalini DasNo ratings yet
- HUMR+248 the+Lymphatic+System Part+I MoodleDocument37 pagesHUMR+248 the+Lymphatic+System Part+I MoodleNadia SolohNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic SystemDocument23 pagesThe Lymphatic SystemMERIDIAN SEESNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Lymphatic and Immune SystemsDocument8 pagesAnatomy of The Lymphatic and Immune SystemsAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Lymphatic SystemDocument2 pagesFunctions of The Lymphatic SystemSpamie FabulaNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic SystemDocument6 pagesThe Lymphatic SystemcrtgyhujikNo ratings yet
- (S.C. Rastogi) Essentials of Animal Physiology, 4t (BookSee - Org) 239Document1 page(S.C. Rastogi) Essentials of Animal Physiology, 4t (BookSee - Org) 239Indah Rizka AprilianiNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic SystemDocument17 pagesThe Lymphatic SystemIzza Javaid100% (1)
- 1.4 The Lymphatic System: Prepared By: Ling Mei TengDocument15 pages1.4 The Lymphatic System: Prepared By: Ling Mei TengJuliet LingNo ratings yet
- 12SUMMARYLYMPHATICSYSTEMDocument20 pages12SUMMARYLYMPHATICSYSTEMArvenBitasNo ratings yet
- Leq-1 Perin PDFDocument5 pagesLeq-1 Perin PDFBhavya PatelNo ratings yet
- Lymph Nodes of Head and Neck RegionDocument65 pagesLymph Nodes of Head and Neck RegionpreyasjoshiNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument28 pagesLymphatic Systemdeepika kushwahNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument4 pagesLymphatic System1445800No ratings yet
- Lymphatics and BloodDocument9 pagesLymphatics and BloodIchokwu VivianNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System: Carlo Cabra Impal, RMTDocument14 pagesLymphatic System: Carlo Cabra Impal, RMTDarlene Claire MamintodNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System For Medical StudentsDocument18 pagesLymphatic System For Medical StudentsTriza JeremiahNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 2nd-U-2 Lymphatic SystemDocument52 pagesAnatomy 2nd-U-2 Lymphatic Systemsinte beyuNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic System and Immunity by Navarro and Orjalo BS Psy 3 1Document27 pagesThe Lymphatic System and Immunity by Navarro and Orjalo BS Psy 3 1markNo ratings yet
- Reticuloendothelial SystemDocument26 pagesReticuloendothelial SystemNashreen QtqtNo ratings yet
- Lymphatics BD BloodDocument10 pagesLymphatics BD BloodIchokwu VivianNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesLymphatic System Anatomy and PhysiologyElyka Alivan Valdez Polonio100% (1)
- Unit-IXLymphatic System Anatomy and Physiology.Document9 pagesUnit-IXLymphatic System Anatomy and Physiology.Rao Asad MubeenNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument15 pagesLymphatic Systemkumaryogesh9934No ratings yet
- VIIII Lymphatic SystemDocument23 pagesVIIII Lymphatic SystemHannah DiñosoNo ratings yet
- Assignment#4: Submitted To: Maam Arooj Ameer HamzaDocument9 pagesAssignment#4: Submitted To: Maam Arooj Ameer HamzaHamza MalikNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic & Body DefensesDocument11 pagesLymphatic & Body DefensesJeah LourraineNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System-Unit 6Document44 pagesLymphatic System-Unit 6Marife AquinoNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Sistem Limfatik (Dr. Diah)Document45 pagesAnatomi Sistem Limfatik (Dr. Diah)Arie Krisnayanti Ida AyuNo ratings yet
- Lymph SystemDocument7 pagesLymph SystemghaiathNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Lymph SystemDocument7 pagesPhysiology of Lymph SystemMwangi NyawiraNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument13 pagesLymphatic SystemAlyssa Mae AzarconNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument13 pagesLymphatic SystemCharli ParachinniNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument3 pagesLymphatic SystemRenjyl Gay DeguinionNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Lymphatic SystemDocument16 pagesUnit 5 Lymphatic SystemChandan ShahNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic SystemDocument16 pagesThe Lymphatic SystemColeen Joyce NeyraNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System (Anaphy)Document27 pagesLymphatic System (Anaphy)Ryan RanasNo ratings yet
- 4 19 Lymphmatic SystemDocument10 pages4 19 Lymphmatic SystemJohn Lawrence Ybanez100% (1)
- The Lymphatic SystemDocument7 pagesThe Lymphatic SystemPreeti ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System and ImmunityDocument22 pagesLymphatic System and ImmunityBae SeulgeyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Lymphatic SystemDocument76 pagesAnatomy of The Lymphatic SystemManisha RaoNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System TransDocument17 pagesLymphatic System TransRheeanne AmilasanNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument17 pagesLymphatic SystemxoxoNo ratings yet
- The Anatomy of The Immune System (Lymphatic SystemDocument4 pagesThe Anatomy of The Immune System (Lymphatic SystemMohammed R.HusseinNo ratings yet
- Biology - MYP 3 - 15th SeptDocument14 pagesBiology - MYP 3 - 15th Septarchit.kulkarni7756No ratings yet
- ملزمه الانسجه الجهاز اللمفاويDocument31 pagesملزمه الانسجه الجهاز اللمفاويليث علي احمد حريفشNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument44 pagesLymphatic SystemZeyNo ratings yet
- Llymphatic SystemDocument14 pagesLlymphatic SystemfauziharunNo ratings yet
- 1 &2. Acute Inflammation..Document140 pages1 &2. Acute Inflammation..Asmara SyedNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Chapter 36: Digestive Systems & NutritionDocument24 pagesAP Biology Chapter 36: Digestive Systems & Nutritionderekg608No ratings yet
- BIBLIOGRAFIE Neural Conduction Synaptic TransmisionDocument16 pagesBIBLIOGRAFIE Neural Conduction Synaptic TransmisionMirela GiurgeaNo ratings yet
- Science - Cell SpecializationDocument4 pagesScience - Cell SpecializationAvila VarshiniNo ratings yet
- Autotrophic Nutrition Heterotrophic NutritionDocument1 pageAutotrophic Nutrition Heterotrophic NutritionAditya KediaNo ratings yet
- SB7.1p HormonesDocument9 pagesSB7.1p HormonesHisokagenNo ratings yet
- The CerebellumDocument3 pagesThe CerebellumХина КападиаNo ratings yet
- Module01 AnOverviewofClinicalLaboratoryHemtologyDocument52 pagesModule01 AnOverviewofClinicalLaboratoryHemtologyKoarie Frae ZuleNo ratings yet
- Journal of Pediatric Surgery Case Reports: Wandering Mesenteric CystDocument4 pagesJournal of Pediatric Surgery Case Reports: Wandering Mesenteric CysthilalNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Apheresis Operator Competency Aug06Document43 pagesTherapeutic Apheresis Operator Competency Aug06Jose Gregorio Riobueno BolivarNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Mind MapDocument1 pageNervous System Mind MapAra Malagón González100% (1)
- Cell AnalogyDocument11 pagesCell AnalogyMikaella Jayne CatanaoanNo ratings yet
- Cardiorespiratory SystemDocument15 pagesCardiorespiratory SystemDafchen Villarin MahasolNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Cell, Organ, CycleDocument56 pagesReproductive Cell, Organ, CycleAjay MeghanathiNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Terminology and OrientationDocument18 pagesAnatomical Terminology and OrientationTuong KhueNo ratings yet
- 23 Soft Tissue TumorsDocument115 pages23 Soft Tissue TumorsorliandoNo ratings yet
- Group 3 BB CrossmatchingDocument34 pagesGroup 3 BB CrossmatchingKhalid SeliaNo ratings yet
- Sensory and Motor Nerve EndingsDocument42 pagesSensory and Motor Nerve EndingsMark GanirNo ratings yet
- C40 - RATNA UMI AZIZAH - G41172240 - Prak 2Document3 pagesC40 - RATNA UMI AZIZAH - G41172240 - Prak 2Ratna Umi AzizahNo ratings yet
- S8 - End-of-Unit 1 TestDocument2 pagesS8 - End-of-Unit 1 TestWilliam Anthony56% (9)
- Transfusion Related Immunomodulation (Trim) : By/ Aymen OmerDocument14 pagesTransfusion Related Immunomodulation (Trim) : By/ Aymen OmeraymenNo ratings yet
- Extracellular VesicleDocument14 pagesExtracellular VesicleLucas Monteiro LopesNo ratings yet
- Ceva NecropsyDocument18 pagesCeva NecropsyNanda Ayu Cindy KashiwabaraNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For Class 11 Biology - Cell The Unit of LifeDocument7 pagesImportant Questions For Class 11 Biology - Cell The Unit of LifeAli WarisNo ratings yet
- Worksheet For Kinder - q1w6Document20 pagesWorksheet For Kinder - q1w6lccyu9No ratings yet
- CBC Normal Ranges (Infant)Document2 pagesCBC Normal Ranges (Infant)haris hussainNo ratings yet
- Diseases: Soekimin Dept. of Anatomical Patology Universitas Sumatera Utara MedanDocument124 pagesDiseases: Soekimin Dept. of Anatomical Patology Universitas Sumatera Utara MedanZayadhaHazriniNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET 10.1 The Importance of Transport SystemDocument2 pagesWORKSHEET 10.1 The Importance of Transport SystemAzim Azimah0% (1)
- Anatomy & Physiology of Endocrine SystemDocument34 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of Endocrine SystemUzma Khan100% (1)
- Anatomy & Physiology of SwallowingDocument6 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of Swallowingbagir_dm10No ratings yet