Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Page 1
Uploaded by
sumitchauhan100000Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Page 1
Uploaded by
sumitchauhan100000Copyright:
Available Formats
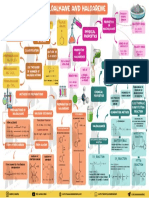
INTRODUCTION
❖ Milk
Milk is a white liquid food produced by the mammary glands of mammals. It is the
primary source of nutrition for young mammals (including breastfed human infants)
before they are able to digest solid food. Immune factors and immune-modulating components
in milk contribute to milk immunity. Early-lactation milk, which is called colostrum,
contains antibodies that strengthen the immune system and thus reduce the risk of many
diseases. Milk contains many nutrients, including protein and lactose.
As an agricultural product, dairy milk is collected from farm animals. In 2011, dairy farms
produced around 730 million tonnes (800 million short tons) of milk from 260 million dairy
cows. India is the world's largest producer of milk and the leading exporter of skimmed milk
powder, but it exports few other milk products. Because there is an ever-increasing demand
for dairy products in India, it could eventually become a net importer of dairy products. New
Zealand, Germany, and the Netherlands are the largest exporters of milk products. The US
Centres for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that children over the age of 12
months should have two servings of dairy milk products a day.
More than six billion people worldwide consume milk and milk products, and between 750
and 900 million people live in dairy-farming households.
Composition
Milk contains several different carbohydrates, including lactose, glucose, galactose, and other
oligosaccharides. The lactose gives milk its sweet taste and contributes approximately 40% of
the calories in whole cow's milk's.
A glass of cow milk
You might also like
- What is Milk and its Nutritional BenefitsDocument1 pageWhat is Milk and its Nutritional Benefitsmegawhat115No ratings yet
- Milk: Nature's Primary Nutrition for Young MammalsDocument1 pageMilk: Nature's Primary Nutrition for Young MammalsSaleh RehmanNo ratings yet
- Nutrients in Milk and Global Dairy ProductionDocument1 pageNutrients in Milk and Global Dairy ProductionjadgugNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document4 pagesPresentation 1Daniel PetrovNo ratings yet
- Nutrient Food Mammary Glands Mammals Infant Humans Btaastfed Digest Lactation Colostrum Antibodies Protein Lactose Extracted From Farm Animals Dairy Farms Tonnes India Skimmed MilkDocument1 pageNutrient Food Mammary Glands Mammals Infant Humans Btaastfed Digest Lactation Colostrum Antibodies Protein Lactose Extracted From Farm Animals Dairy Farms Tonnes India Skimmed MilkjadgugNo ratings yet
- Cow's Milk Nutrition and ProductionDocument149 pagesCow's Milk Nutrition and Productionritz dayaoNo ratings yet
- Nutrient Food Mammary Glands Mammals Infant Humans Btaastfed Digest Lactation Colostrum Antibodies 78otein LactoseDocument1 pageNutrient Food Mammary Glands Mammals Infant Humans Btaastfed Digest Lactation Colostrum Antibodies 78otein LactosejadgugNo ratings yet
- Article About MilkDocument3 pagesArticle About MilkMohammad 08No ratings yet
- ChemDocument10 pagesChemthirumalaivasan GNo ratings yet
- Components of Breast MilkDocument2 pagesComponents of Breast MilkAlya Putri KhairaniNo ratings yet
- Tugas ASIDocument20 pagesTugas ASIMia Mia MiaNo ratings yet
- Breast FeedingDocument17 pagesBreast FeedingАйгуль ТугелбаеваNo ratings yet
- Interesting Milk FactsDocument2 pagesInteresting Milk FactsGomatheeswariNo ratings yet
- MilkDocument2 pagesMilkthivanaNo ratings yet
- Short Note On MilkDocument5 pagesShort Note On MilkTasin RahmanNo ratings yet
- HND 403 - Nutrition During LactationDocument23 pagesHND 403 - Nutrition During LactationDanish KhanNo ratings yet
- Lactose Intolerance: A Review On Increasing Maldigestion and Milk Intolerance, Its Applications and SourcesDocument2 pagesLactose Intolerance: A Review On Increasing Maldigestion and Milk Intolerance, Its Applications and SourcesPiyush MannNo ratings yet
- Refuting Anti-Milk Propaganda Why Dairy Products Are The Healthiest Foods For Most PeopleFrom EverandRefuting Anti-Milk Propaganda Why Dairy Products Are The Healthiest Foods For Most PeopleRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- LPT 311 1Document207 pagesLPT 311 1Sanjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Project of Milk (Tests)Document18 pagesProject of Milk (Tests)Mohammad Sabir HussainNo ratings yet
- Human Breast MilkDocument14 pagesHuman Breast MilkJoel SantosNo ratings yet
- Breast Feeding PhtecDocument13 pagesBreast Feeding PhtecAfolabi Horlarmilekan AbdulbasitNo ratings yet
- Breastfeeding Benefits of ColostrumDocument5 pagesBreastfeeding Benefits of ColostrumbalaNo ratings yet
- Lec 5Document69 pagesLec 5mdtajim011No ratings yet
- Aavin Milk ProjectDocument3 pagesAavin Milk ProjectEDU TECHNo ratings yet
- Dairy productDocument9 pagesDairy producthoangngominh169No ratings yet
- Flavoured Milk Market ReportDocument12 pagesFlavoured Milk Market ReportKaren NoronhaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 - Lactation: Current Breast-Feeding RatesDocument5 pagesLecture 9 - Lactation: Current Breast-Feeding Ratesrachel oNo ratings yet
- Sweetened Condensed Milk Nutrition InformationDocument9 pagesSweetened Condensed Milk Nutrition InformationRobert Magana100% (1)
- Milk Proteins Good & BadDocument3 pagesMilk Proteins Good & BadJose PalomarNo ratings yet
- LPT 311 PDFDocument190 pagesLPT 311 PDFIbad Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Dairy Farming Nutrition GuideDocument3 pagesDairy Farming Nutrition Guidevector dairyNo ratings yet
- Bone HealthDocument21 pagesBone Healthvivekpandeyd2No ratings yet
- 3401 Review On Goat Milk Composition and Its Nutritive ValueDocument10 pages3401 Review On Goat Milk Composition and Its Nutritive ValueRed DiggerNo ratings yet
- Whey in Animal Nutrition - A Valuable Ingredient EWPA BrochureDocument20 pagesWhey in Animal Nutrition - A Valuable Ingredient EWPA BrochureachihaiaNo ratings yet
- Chandra Nabil Alfaridzi - 23010121140266 - English Writing ADocument4 pagesChandra Nabil Alfaridzi - 23010121140266 - English Writing AChandra NabilNo ratings yet
- Dairy Manual - Milk Quality PDFDocument52 pagesDairy Manual - Milk Quality PDFMarko MalambugiNo ratings yet
- Goat Milk, A Divine Superfood!Document3 pagesGoat Milk, A Divine Superfood!S. Zook, MS, PhD100% (6)
- Milk Nutrition and Health FactsDocument34 pagesMilk Nutrition and Health FactsPeter NjalaNo ratings yet
- Essential Infant Nutrition: Benefits of Exclusive BreastfeedingDocument11 pagesEssential Infant Nutrition: Benefits of Exclusive BreastfeedingRosa PalconitNo ratings yet
- Benifits of Cow MilkDocument2 pagesBenifits of Cow MilkAli ZafarNo ratings yet
- DairyProducts - Lab 3 - WordDocument3 pagesDairyProducts - Lab 3 - WordsyafNo ratings yet
- Understanding Milk: Types, Benefits and UsesDocument16 pagesUnderstanding Milk: Types, Benefits and Usesskills provider technological institue incNo ratings yet
- Breast Feeding and Its AdvantagesDocument45 pagesBreast Feeding and Its AdvantagesRajeev NepalNo ratings yet
- Exclusive BreastfeedingDocument6 pagesExclusive BreastfeedingDezttie IdEss Ndess100% (1)
- Facts About Milk 2Document15 pagesFacts About Milk 2hanisah ahmad jaafarNo ratings yet
- Cattle/ Cow: Edible By-Products Are Things We Can EatDocument15 pagesCattle/ Cow: Edible By-Products Are Things We Can EatShane Marie MacaraegNo ratings yet
- What Is Milk?: Milk and Milk ProductsDocument8 pagesWhat Is Milk?: Milk and Milk ProductsErole MissionNo ratings yet
- PLAGIARISM SCAN REPORTDocument2 pagesPLAGIARISM SCAN REPORTBhavin MehtaNo ratings yet
- Milk Production from CowsDocument16 pagesMilk Production from CowsSmaranda CerbuNo ratings yet
- Nutrition 2nd Yr RevisedaDocument90 pagesNutrition 2nd Yr Revisedaapi-3748748No ratings yet
- Project Management ReportDocument12 pagesProject Management ReportGaurav VermaNo ratings yet
- Milk Intake For Holistic HealthDocument6 pagesMilk Intake For Holistic HealthNishita SuratkalNo ratings yet
- Bio Inv - ProjectDocument12 pagesBio Inv - ProjectnoobNo ratings yet
- 2breastfeeding and Lactation ManagementDocument21 pages2breastfeeding and Lactation ManagementSid Flavier100% (1)
- Pediatrics Dr. Haydar 1-Oct-06 Lec: - 2Document4 pagesPediatrics Dr. Haydar 1-Oct-06 Lec: - 2api-3829364No ratings yet
- Milk ProductsDocument16 pagesMilk ProductsTeodora AncaNo ratings yet
- The Oat Milk Cookbook: More than 100 Delicious, Dairy-free Vegan RecipesFrom EverandThe Oat Milk Cookbook: More than 100 Delicious, Dairy-free Vegan RecipesNo ratings yet
- Saurabhdubey 123Document10 pagesSaurabhdubey 123sumitchauhan100000No ratings yet
- Page 2Document1 pagePage 2sumitchauhan100000No ratings yet
- Chem ProjectDocument14 pagesChem ProjectArjun Singh Rawat100% (2)
- C10 Haloakanes & HaloarenesDocument1 pageC10 Haloakanes & HaloarenesMiroNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument30 pagesFinalsumitchauhan100000No ratings yet
- General Organic ChemistryDocument46 pagesGeneral Organic ChemistryAbijasree BijukumarNo ratings yet
- Solutions PYQDocument13 pagesSolutions PYQTanmay SharmaNo ratings yet
- S-Block Class 11Document27 pagesS-Block Class 11sumitchauhan100000No ratings yet