Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lymphatic System Diseases
Uploaded by
RJ San JuanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lymphatic System Diseases
Uploaded by
RJ San JuanCopyright:
Available Formats
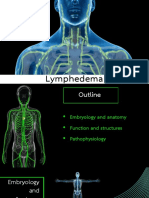
Lymphatic System Diseases and Disorders: The lymphatic system, like other parts of the body, is susceptible to a variety
of diseases and disorders. A number of bacteria and other infectious agents can cause inflammations of the lymph vessels (lymphangitis) or the lymph nodes (lymphadenitis). Lymphedema is a disorder wherein there is an obstruction of the lymph vessels, as caused by scar tissue or tumor cells. The obstruction can cause accumulation of fluid and protein within the affected tissue as a result tissue becomes swollen. Hodgkin's disease is a malignant tumor of the lymph nodes. The lymphatic system may also spread malignant cells from cancerous organs to healthy ones.
Lymphedema: One of the most prevalent lymphatic disorder is lymphatic insufficiency, or lymphedema which occurs due to an accumulation of lymphatic fluid in the interstitial tissue. This results in swelling in the arms, legs and sometimes in other parts of the body. The severity of this disorder varies from extremely mild complications to a disfiguring, painful and cellulite infections deep in skin. If not treated, the skin eventually becomes fibrotic (thickening of the skin and subcutaneous tissues) with loss of normal structure, functionality and mobility. The two types of lymphedema are:
Primary Lymphedema: It is an inherited condition that occurs due to impaired or missing lymphatic vessels. It affects from one to as many as four limbs and even other body parts, including internal organs. It can exhibit at birth, develop with the onset of puberty or occur in adulthood, with no apparent causes. Secondary Lymphedema: The disorder is basically acquired regional lymphatic insufficiency which occurs due to any trauma, infection or surgery that disrupts the lymphatic vessels or results in the loss of lymph nodes.
Filariasis: Filariasis is another lymphatic system disorder that occurs from a parasitic-caused infection causing lymphatic insufficiency, and in some cases predisposes elephantiasis (thickening of the skin and underlying tissues especially in the legs, male genitals and female breasts).
Lymphoma: Lymphoma is a medical term used for a group of cancers that originate in the lymphatic system. Lymphomas usually begin with malignant transformation of the lymphocytes (white blood cells) in lymph nodes or bunch of lymphatic tissue in organs like the stomach or intestines. Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma are two major categories in Lymphoma, characterized by enlargement of lymph nodes, usually present in the neck. Symptoms of lymphoma mainly include chronic fatigue, weak immune function, weight loss, night sweats and pain after drinking alcohol. Lymphadenopathy: Lymphadenopathy is a lymphatic disorder in which the lymph nodes become swollen or enlarged, due an infection. For example, swollen lymph nodes in the neck may occur as a result of a throat infection. Lymphadenitis: Also known as adenitis, Lymphadenitis is an inflammation of the lymph node due to a bacterial infection of the tissue in the node causing swelling, reddening, and tenderness of the skin overlying the lymph node. Splenomegaly: Splenomegaly or enlarged spleen is another lymphatic system disorder, that develops due to a viral infection like mononucleosis. Tonsillitis: Of many other lymphatic system disorders, tonsillitis is another disease caused by an infection of the tonsils, the lymphoid tissues present in the back of the mouth at the top of the throat. These lymphoid tissues help filter out bacteria and when infected, they become swollen and inflamed, leading to a sore throat, fever, and difficulty and pain while swallowing. HIV/AIDS and inflammatory and auto-immune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosis (SLE), scleroderma, Wegener's granulomatosis, etc., are directly impacted by the lymphatic system. Hence, lymphatic insufficiency of the internal organs and unhealthy lifestyles can eventually lead to any of the aforementioned lymphatic system diseases.
You might also like
- Cellulitis: Current Insights Into Pathophysiology and Clinical ManagementDocument13 pagesCellulitis: Current Insights Into Pathophysiology and Clinical Managementtucto849915No ratings yet
- LymphedemaDocument3 pagesLymphedemaFirtanty Tasya Andriami SyahputriNo ratings yet
- Investigations of LymphaticsDocument26 pagesInvestigations of LymphaticsManoj B MyatherNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic System HandoutDocument2 pagesThe Lymphatic System HandoutbernachurchNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic TissueDocument50 pagesLymphatic TissueRukshan RanatungaNo ratings yet
- Agranulocytosis, A Simple Guide to The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandAgranulocytosis, A Simple Guide to The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Virus-Induced T1 Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms and Future ResearchDocument46 pagesVirus-Induced T1 Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms and Future ResearchamyNo ratings yet
- Analyzing and Defining Medical TermsDocument7 pagesAnalyzing and Defining Medical Termsmarcus colgroveNo ratings yet
- Immunologic and Allergic DiseaseDocument49 pagesImmunologic and Allergic DiseaseFidz LiankoNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Diseases and Disorders Sourcebook, Fifth EditionFrom EverandGastrointestinal Diseases and Disorders Sourcebook, Fifth EditionNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide To Anal Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide To Anal Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- CellulitisDocument3 pagesCellulitisAllen MallariNo ratings yet
- Health, Stress, and CopingDocument43 pagesHealth, Stress, and CopingKar Gayee100% (1)
- DeVry HIT 111 All Discussions - LatestDocument11 pagesDeVry HIT 111 All Discussions - Latestshonwilllen0% (1)
- Anti-Microbial Therapy Final With AlarmsDocument245 pagesAnti-Microbial Therapy Final With AlarmsMahmoud Ahmed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- LymphomaDocument5 pagesLymphomaBlossom Wawa IINo ratings yet
- Studies on Hepatitis Viruses: Life Cycle, Structure, Functions, and InhibitionFrom EverandStudies on Hepatitis Viruses: Life Cycle, Structure, Functions, and InhibitionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Cancer Prevention - The Causes and Prevention of Cancer Volume 1 (Cancer Prevention-Cancer Causes) (PDFDrive) PDFDocument338 pagesCancer Prevention - The Causes and Prevention of Cancer Volume 1 (Cancer Prevention-Cancer Causes) (PDFDrive) PDFtheresaNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune Disorders - AgungDocument40 pagesAutoimmune Disorders - AgungalgutNo ratings yet
- Natthaphong Jirojananukul's Lymphedema ReviewDocument26 pagesNatthaphong Jirojananukul's Lymphedema ReviewPuthiput ChotsutaworakulNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Insufficiency and Addison's DiseaseDocument8 pagesAdrenal Insufficiency and Addison's DiseaseyancefinceNo ratings yet
- Immunology in the Twentieth Century: From Basic Science to Clinical ApplicationFrom EverandImmunology in the Twentieth Century: From Basic Science to Clinical ApplicationNo ratings yet
- I Got the Flu! What is Influenza? - Biology Book for Kids | Children's Diseases BooksFrom EverandI Got the Flu! What is Influenza? - Biology Book for Kids | Children's Diseases BooksNo ratings yet
- Expectorants and Antitussives-Dr - Jibachha Sah, M.V.SC, LecturerDocument26 pagesExpectorants and Antitussives-Dr - Jibachha Sah, M.V.SC, Lecturerjibachha sahNo ratings yet
- Marfan's Syndrome Diagnosis Using Ghent CriteriaDocument4 pagesMarfan's Syndrome Diagnosis Using Ghent CriteriaAldi SetyoNo ratings yet
- Hereditary Spherocytosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHereditary Spherocytosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis in The Emergency DepartmentDocument19 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis in The Emergency DepartmentMichael NovilloNo ratings yet
- Cystic FibrosisDocument2 pagesCystic Fibrosisthatkid94No ratings yet
- Section 3: Nomenclature of TumorDocument71 pagesSection 3: Nomenclature of TumorIsuri GanNo ratings yet
- Adjuvant breast cancer therapy agentsDocument3 pagesAdjuvant breast cancer therapy agentsGem BulaongNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune DiseasesDocument41 pagesAutoimmune DiseasesGanesh V GaonkarNo ratings yet
- 4 Circulation Disorders PDFDocument69 pages4 Circulation Disorders PDFSetiawan SukmadjaNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic Infections in HumansFrom EverandAnaerobic Infections in HumansSydney FinegoldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Man Meets Microbes: An Introduction to Medical MicrobiologyFrom EverandMan Meets Microbes: An Introduction to Medical MicrobiologyNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid Arthritis "An Autoimmune Mystery"Document23 pagesRheumatoid Arthritis "An Autoimmune Mystery"Manisanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Peptic UlcerDocument31 pagesPeptic UlcerHarpal Bajwa0% (1)
- Diagnostic Common Nutrient Deficiency SymptomsDocument3 pagesDiagnostic Common Nutrient Deficiency SymptomsdelacruzjobyNo ratings yet
- Heart DiseaseDocument38 pagesHeart DiseaseDr.Sunil KumarNo ratings yet
- Hiv Treatment: IC2 Haemato-Lymphoid and Tropical Medicine HLTM Dr. Eoghan de Barra 2014Document55 pagesHiv Treatment: IC2 Haemato-Lymphoid and Tropical Medicine HLTM Dr. Eoghan de Barra 2014Faiq Syukri Bin SaparudinNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle and Prevention of Ascaris Lumbricoides InfectionDocument6 pagesLife Cycle and Prevention of Ascaris Lumbricoides InfectionPika PearlasNo ratings yet
- Client 1Document4 pagesClient 1api-238798073No ratings yet
- Vitamin D Deficiency Causes Rickets Skeletal DisorderDocument3 pagesVitamin D Deficiency Causes Rickets Skeletal DisorderLoverMind CabaronNo ratings yet
- The Information About EDSDocument3 pagesThe Information About EDSAmber100% (1)
- Reactive ArthritisDocument3 pagesReactive ArthritisMohammadAbuelhaijaNo ratings yet
- Nature of DiseaseDocument14 pagesNature of DiseaseLambo Ignacio Queen Quin100% (1)
- HiperkalemiaDocument41 pagesHiperkalemiaJansonNo ratings yet
- Corneal Foreign BodiesDocument9 pagesCorneal Foreign BodiesAfria TikaNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction MIDocument23 pagesMyocardial Infarction MIأبو محمدNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune DiseasesDocument125 pagesAutoimmune DiseasesJustin Ahorro-DionisioNo ratings yet
- Seminar 4Document49 pagesSeminar 4Yamuna SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- ARVs (Antiretroviral) TherapyDocument4 pagesARVs (Antiretroviral) TherapyAnonymous dVoPOXLOaENo ratings yet
- Understanding Alcoholism: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Alcoholism: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentKaren JulaoNo ratings yet
- Scabies and PediculosisDocument35 pagesScabies and PediculosisleenaloveuNo ratings yet
- Water An Electrolyte Metabolism and Their DisordersDocument60 pagesWater An Electrolyte Metabolism and Their DisordersAbigail AdegbuluNo ratings yet
- Acute Radiation CerebroVascular SyndromeDocument15 pagesAcute Radiation CerebroVascular SyndromeDmitri PopovNo ratings yet
- Immune Disorders, Vaccines, Covid-19 and Drug Reactions DiscussedDocument73 pagesImmune Disorders, Vaccines, Covid-19 and Drug Reactions DiscussedErum JanNo ratings yet
- Von Willebrand DiseaseDocument63 pagesVon Willebrand Diseasesaad awanNo ratings yet
- Cystic FibrosisDocument3 pagesCystic FibrosissakthiprimeNo ratings yet
- Adult Health Nursing MCQsDocument18 pagesAdult Health Nursing MCQsarshi khanNo ratings yet
- Assessing the spine, hands, muscles and jointsDocument2 pagesAssessing the spine, hands, muscles and jointskrull243No ratings yet
- Body Revolution Syllabus DraftDocument4 pagesBody Revolution Syllabus Draftapi-508557357No ratings yet
- Republic Act No 11332Document6 pagesRepublic Act No 11332AnnyleneMauricioNo ratings yet
- The EMBO Journal - 2023 - Konaka - Secretion of Mitochondrial DNA Via Exosomes Promotes Inflammation in Beh Et S SyndromeDocument27 pagesThe EMBO Journal - 2023 - Konaka - Secretion of Mitochondrial DNA Via Exosomes Promotes Inflammation in Beh Et S Syndromerifqi fathulNo ratings yet
- Capsaicina Tópica en El Tratamiento Del Dolor Neuropático: RevisiónDocument13 pagesCapsaicina Tópica en El Tratamiento Del Dolor Neuropático: RevisiónJAVIER RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Field Attachment GracieDocument14 pagesField Attachment GracieHSFXHFHXNo ratings yet
- NCM 105A Nutrition and Diet Therapy Laboratory Laboratory Exercise No. 8 Macronutrients - FatsDocument6 pagesNCM 105A Nutrition and Diet Therapy Laboratory Laboratory Exercise No. 8 Macronutrients - Fatsann campos67% (3)
- 2008, Editrice Kurtis: Square-Stepping Exercise Versus Strength and Balance Training For Fall Risk FactorsDocument6 pages2008, Editrice Kurtis: Square-Stepping Exercise Versus Strength and Balance Training For Fall Risk Factorsnandhini raguNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument1 pageReportSrinivasateja ReddyNo ratings yet
- T Cells & Autoimmunity, s3Document21 pagesT Cells & Autoimmunity, s3LiaAriestaNo ratings yet
- A Review On Nasal Drug Delivery System and Its Contribution in TherapeuticDocument6 pagesA Review On Nasal Drug Delivery System and Its Contribution in Therapeuticedgar palominoNo ratings yet
- Effectofberberineon GiardiasisDocument5 pagesEffectofberberineon GiardiasisSummiNo ratings yet
- GUIDE TO CLINICAL USES OF SPACE MAINTAINERSDocument6 pagesGUIDE TO CLINICAL USES OF SPACE MAINTAINERSKhalid AhmedNo ratings yet
- Utility Arches in Orthodontics Case Reports PDFDocument5 pagesUtility Arches in Orthodontics Case Reports PDFbelwin athickal92No ratings yet
- Beauty Nail CareDocument48 pagesBeauty Nail CareRoden Son75% (4)
- TLE - Beauty Care Nail Care Services Quarter 1: Self Learning Module 1 Nail StructureDocument7 pagesTLE - Beauty Care Nail Care Services Quarter 1: Self Learning Module 1 Nail StructureChoy Choy BokyaNo ratings yet
- Capillary Fragility/ Resistance Test: Tourniquet or Rumpel-Leede or Hess TestDocument4 pagesCapillary Fragility/ Resistance Test: Tourniquet or Rumpel-Leede or Hess TestGerly MaglangitNo ratings yet
- Activity-Accomplishment Report On 44th Anniversary CelebrationDocument3 pagesActivity-Accomplishment Report On 44th Anniversary CelebrationjohnNo ratings yet
- Assay The Activity of Alkaline Phosphatase: (Disodium Phenyl Phosphate Method)Document14 pagesAssay The Activity of Alkaline Phosphatase: (Disodium Phenyl Phosphate Method)AllyNo ratings yet
- Yatharth Jain - The Black Death MagazineDocument7 pagesYatharth Jain - The Black Death MagazineYatharth JainNo ratings yet
- Acute Infections During PregnancyDocument63 pagesAcute Infections During PregnancyHussein AliNo ratings yet
- YDS İlgisiz Cümle Soru TipiDocument9 pagesYDS İlgisiz Cümle Soru TipiAhmet GürkanNo ratings yet
- WHO - Weekly Epidemiological Update On COVID-19 - 22 February 2022Document26 pagesWHO - Weekly Epidemiological Update On COVID-19 - 22 February 2022Adam ForgieNo ratings yet
- 808nm Vs 904nm - 41598 - 2019 - Article - 44141Document14 pages808nm Vs 904nm - 41598 - 2019 - Article - 44141Gino DammiuncrodinoNo ratings yet
- US Trade Deficit Rises Amid Record Drop in Exports: QuotesDocument28 pagesUS Trade Deficit Rises Amid Record Drop in Exports: QuotesjayNo ratings yet
- Effects of common illegal drugsDocument4 pagesEffects of common illegal drugsKaren DacasinNo ratings yet
- Medical ReportDocument2 pagesMedical ReportOussama SissaouiNo ratings yet
- CBLM - Swine FinalDocument127 pagesCBLM - Swine FinalMarwin NavarreteNo ratings yet
- Training Design for Hypertension Online CourseDocument13 pagesTraining Design for Hypertension Online CourseRuth Mary PadaNo ratings yet