Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Maternal Last Topic (Jam)
Uploaded by
Jamilah BanglanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Maternal Last Topic (Jam)
Uploaded by
Jamilah BanglanCopyright:
Available Formats
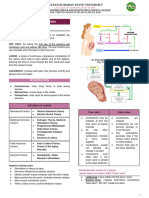
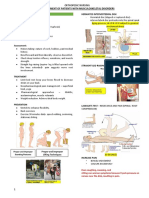
METHODS TO DETERMINE FETAL POSITION, PRESENTATION, AND LIE: - Activity: Continue to walk
• Leopold’s maneuvers – combined abdominal inspection and 2. Active phase – 40 to 60s, 4-7cm, 3 hrs nullipra, 2 hrs multipara,
palpation 3-5mins
• Vaginal Examination 3. Transition – contractions reach peak, 60-90s, 8-10cm, 2-3mins
• Auscultation of fetal heart tones - Identified by slight slowing rate of cervical dilation
• Ultrasound - Irresistible urge to push occurs
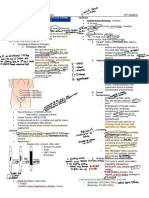
Powers of Labor SECOND STAGE
• Powers of labor – second important requirement for a - Full dilation and cervical effacement
successful labor - Perineum bulge and tense
- Force supplied by fundus, implemented by uterine - Anus everted and stool may expel
contractions (a natural process that causes cervical - Crowning – opening is slit like, oval, then circular
dilation) THIRD STAGE
• Uterine contraction – primary power in labor - Begins birth of infant and ends with delivery of
- Mark of effective uterine contraction: rhythmicity placenta
and progressive lengthening and intensity - After birth, uterus can be palpated as firm round
- HOW UTERINE CONTRACTION CAUSE PAIN: cervical mass
stretching during dilation - After rest, organ assumes DISCOID SHAPE
- PHASES: - Two Phase:
1) Increment ▪ PLACENTAL SEPARATION
2) Acme (Peak) Signs are: Lengthening of umbilical cord,
3) Decrement Sudden gush of vaginal blood, change in
• Duration – length of time a contraction lasts, increment to shape of uterus, firm contraction, and
decrement appearance of placenta at vaginal
• Frequency – time interval between beginning of one opening.
contraction to beginning of next contraction ▪ PLACENTAL EXPULSION
• Interval of Rest– time from end of one contraction to the start Placenta is delivered by either: natural
of next contraction bearing down of mother or Crede’s
Maneuver (gentle pressure on uterine
• Intensity – the strength or a contraction at acne.
fundus)
- MILD If uterine wall can be indented easily
- STRONG INTENSITY if cannot be indented
PLACENTAL PRESENTATION
• RULES OF PALPATION OF UTERINE CONTRACTIONS:
✓ Schultze – placenta separate first at center and tends to fold like
- Use FINGERTIPS not the palmar surface
umbrella, appears shiny and glistening
- Place fingertips LIGHTLY and not firmly
✓ Duncan – raw, red, irregular
- Uterotubal junction – where pacemaker sites are
✓ Normal blood loss: 300-500ml
found
• Physiologic retraction ring – separation or differentiation of the
MATERNAL AND FETAL RESPONSES TO LABOR
active, shorter but thicker upper uterine segment from the
lower segment
PHYSIOLOGIC EFFECT ON WOMAN
• Pathologic retraction ring or Bandl’s ring – danger sign that
• INCREASE – hemopoietic, respiration, temperature, neurologic
signifies impending rupture of lower segment
and sensory
• Effacement – shortening and thinning of cervical canal
• DECREASE – cardiac output, blood pressure, fluid balance,
- Primipara: effacement before dilation
urinary, muscuskeletal
- Multipara: dilation before effacement
PSYCHOLOGICAL EFFECT ON WOMAN
• Dilatation – enlargement or widening of cervical canal
• Fatigue, Fear, Cultural influences
1 finger 1.25cm
MATERNAL DANGER SIGNS
2 fingers 3cm
• Abnormal pulse, Inadequate or prolonged contraction,
3 fingers 4.5cm
pathologic retraction ring, Abnormal lower abdominal contour,
4 fingers 5.5cm
increasing apprehension
5 fingers 7cm
6 fingers 8.5cm FETAL DANGER SIGNS
7 fingers 9.5cm • High or Low Fetal Heart Rate, Meconium Staining, Hyperactivity,
Fully dilated 10cm Oxygen Saturation
COLOR OF AMNIOTIC FLUID
• Psyche – refers to psychological state or feelings that woman • Yellow stained – blood incompatibility
bring into labor • Bilirubin stained – breakdown of RBC
• Green fluid – meconium stained
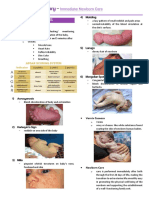
STAGES OF LABOR: Get FHR every 30mins beginning of labor, 15mins active labor, and 5 mins
1. First stage of labor begins when uterine contraction, frequency, 2nd stage of labor
and intensity result in effacement and dilation of cervix. VAGINAL EXAMINATION – necessary to determine extent of cervical
- Completed when cervix reaches 10cm effacement and dilatation
2. The second stage involve descent of fetus and eventual PERINEAL SKIN PREP – systematic aseptic perineal prior to delivery
expulsion from vagina
3. The third stage involves delivery of placenta
4. Fourth stage – first 1-4 hrs after birth of placenta. Close
maternal observation needed.
PHASES OF FIRST STAGE OF LABOR:
1. Latent Phase – begins onset of regularly perceived uterine
contraction and ends when rapid dilation begins.
- 20 to 40s , 0 to 3cm, 6 hrs in nullipara, 4-5 in
multipara, 5-8mins, analgesia should NOT be given
- If phase is prolonged, cephalopelvic disproportion
occurs.
You might also like
- The Basics: A Comprehensive Outline of Nursing School ContentFrom EverandThe Basics: A Comprehensive Outline of Nursing School ContentRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Canada Gateway MCC Qe Questions 1Document100 pagesCanada Gateway MCC Qe Questions 1Kak KfgaNo ratings yet
- Cervical Changes During Menstrual Cycle (Photos)Document9 pagesCervical Changes During Menstrual Cycle (Photos)divyanshu kumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 - Labor and Birth: Ob LectureDocument15 pagesChapter 15 - Labor and Birth: Ob LectureMARIA PEARLITA TANNo ratings yet
- Stages of LaborDocument23 pagesStages of LaborPortia Dulce Toquero100% (5)
- ANC OB and GYN HISTORY Taking SampleDocument43 pagesANC OB and GYN HISTORY Taking SampleGebremichael Reta100% (3)
- CMCALEC Lesson9MDocument14 pagesCMCALEC Lesson9Mluisgregory113No ratings yet
- 1 Unit 31 Intro and Components-of-Labor - 231115 - 191959Document150 pages1 Unit 31 Intro and Components-of-Labor - 231115 - 191959Mariah Angela PonceNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Labor + InfertilityDocument12 pagesAbnormal Labor + InfertilityKristine VanzuelaNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Labor and Infertility 2016 PDFDocument12 pagesAbnormal Labor and Infertility 2016 PDFLarissa TacalanNo ratings yet
- MCN Rle MidtermDocument17 pagesMCN Rle MidtermKaela ChoiNo ratings yet
- Signs of LaborDocument5 pagesSigns of Labormarianne_07No ratings yet
- CN DystociaDocument7 pagesCN DystociaAlbert Francis BialaNo ratings yet
- Pemicu 2 Repro RakaDocument106 pagesPemicu 2 Repro RakaHaraka NabdaNo ratings yet
- Stages of LaborDocument4 pagesStages of LaborAizy BastionNo ratings yet
- 1.1.unit 3.care of A Woman During Intrapartum PeriodDocument188 pages1.1.unit 3.care of A Woman During Intrapartum PeriodBabyjane BalagonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Abrubtio PlacentaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Abrubtio PlacentaLei Ortega0% (1)
- Labor and DeliveryDocument6 pagesLabor and Deliveryjenryl91% (11)
- Normal Labor and DeliveryDocument29 pagesNormal Labor and DeliveryManish ShahNo ratings yet
- INTRAPARTUMDocument174 pagesINTRAPARTUMRUSTOM JAKENo ratings yet
- The Stages of LaborDocument18 pagesThe Stages of LaborLYRA GUEVARRANo ratings yet
- DR NotesDocument3 pagesDR Notesnoreen ellie100% (2)
- Intrapartum CareDocument6 pagesIntrapartum CareKATE LAWRENCE BITANTOSNo ratings yet
- Nursing NotesDocument16 pagesNursing NotesChelzie LasernaNo ratings yet
- THE 3F Intra Partal CareDocument7 pagesTHE 3F Intra Partal Care1B - Zafra, RamoneNo ratings yet
- 3F Intranatal NotesDocument5 pages3F Intranatal NotesAlyssa Claire TumulakNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Nursing (Complications After Birth)Document4 pagesMaternal and Child Nursing (Complications After Birth)PAULINE BERNICE BAGUIONo ratings yet
- Normal LabourDocument88 pagesNormal LabourDebayan KhanNo ratings yet
- Labor & DeliveryDocument19 pagesLabor & Deliveryahmed shorshNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment LectureDocument48 pagesHealth Assessment LectureJade Buri100% (1)
- DystociaDocument6 pagesDystociasarguss14100% (2)
- Mechanisms of LaborDocument4 pagesMechanisms of LaborIrish Paulene NiroNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 - SL - Mat - 1Document100 pagesNCM 107 - SL - Mat - 1marilexdomagsangNo ratings yet
- The Abdomen: E Sther Sunday C. Faller, RMT, MDDocument7 pagesThe Abdomen: E Sther Sunday C. Faller, RMT, MDMarimiel PagulayanNo ratings yet
- Ob FinalDocument5 pagesOb Finalsofiapanlilio32No ratings yet
- NOTES ON OB NursingDocument19 pagesNOTES ON OB NursingElizabeth Idanan100% (1)
- Stages of LaborDocument66 pagesStages of LaborRuth RallosNo ratings yet
- Intrapartal - Theories of LaborDocument21 pagesIntrapartal - Theories of LaborJan Oliver YaresNo ratings yet
- PREGNANCYDocument4 pagesPREGNANCYShaileeNo ratings yet
- PregnancyDocument4 pagesPregnancyShaileeNo ratings yet
- 1 - Dystocia - Doc GuzmanDocument7 pages1 - Dystocia - Doc Guzmand99452727No ratings yet
- Semis - MCN RLEDocument12 pagesSemis - MCN RLEKorean GirlNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Normal LabourDocument41 pagesPhysiology of Normal LabourEric Mayo Dagradi KabatNo ratings yet
- High Risk Labor and DeliveryDocument5 pagesHigh Risk Labor and DeliveryCarl John ManaloNo ratings yet
- The Powers of LaborDocument12 pagesThe Powers of LaborElinor Faith V. Retita-CoronadoNo ratings yet
- First Stage Second Stage Third Stage I. The Powers: A. Physiology of LaborDocument4 pagesFirst Stage Second Stage Third Stage I. The Powers: A. Physiology of LaborfinellajanNo ratings yet
- RECAP - ColoredDocument8 pagesRECAP - Coloredreminder to be happyNo ratings yet
- 2 Unit 31 Stages-of-Labor - 231115 - 192051Document131 pages2 Unit 31 Stages-of-Labor - 231115 - 192051Mariah Angela PonceNo ratings yet
- Intrapartum 11: The Stages of LaborDocument9 pagesIntrapartum 11: The Stages of LaborJane MartinNo ratings yet
- 1 Labor and Delivery ProcessDocument13 pages1 Labor and Delivery ProcessBardiaga JmayNo ratings yet
- NCA - 2.5 - Postpartum Complications-Labordo-saldana-serrano-sabejon-sarsozaDocument7 pagesNCA - 2.5 - Postpartum Complications-Labordo-saldana-serrano-sabejon-sarsozaFranz Earl Niño AlbesaNo ratings yet
- MCN - Notes (1) PREWLIMDocument3 pagesMCN - Notes (1) PREWLIMvanessaNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 Problems With Power DraftDocument3 pagesNCM 109 Problems With Power DraftJP Porras Ali100% (1)
- Newborn NotesDocument3 pagesNewborn NotesSharlotte EbayNo ratings yet
- 4 Immediate Newborn Care TransesDocument9 pages4 Immediate Newborn Care TransesKeana DacayanaNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Management of Musculoskeltal Disorders PDFDocument2 pages3.2 Management of Musculoskeltal Disorders PDFDiana CalderonNo ratings yet
- Complications of Intrapartum and Post PartumDocument8 pagesComplications of Intrapartum and Post PartumMikasa AckermanNo ratings yet
- mh6zxph8r - 11 STAGES - OF - LABORDocument25 pagesmh6zxph8r - 11 STAGES - OF - LABORHecy CristoNo ratings yet
- PediaDocument52 pagesPediakayperez100% (1)
- Intrapartum Bsn2 UslDocument15 pagesIntrapartum Bsn2 UslAlessandra CruzNo ratings yet
- Regaining Bladder Control: For Incontinence on Exertion or Following Pelvic SurgeryFrom EverandRegaining Bladder Control: For Incontinence on Exertion or Following Pelvic SurgeryNo ratings yet
- Observations on Abortion: Containing an account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes which produced it, and the method of preventing or treating itFrom EverandObservations on Abortion: Containing an account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes which produced it, and the method of preventing or treating itNo ratings yet
- Vulvitis, Vaginitis, Bartholin's Cyst and CervicitisDocument56 pagesVulvitis, Vaginitis, Bartholin's Cyst and CervicitisSushma Thakuri100% (1)
- MiscarriageDocument38 pagesMiscarriagezianab aliNo ratings yet
- AMC OBS & GYNAC 2005 To 2009Document22 pagesAMC OBS & GYNAC 2005 To 2009Vidarshi Supushpa KithminiNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument6 pagesDocumentkrishcelNo ratings yet
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument55 pagesEctopic PregnancyDr-Saja O. DmourNo ratings yet
- B Ingg - SalinDocument12 pagesB Ingg - SalinBuat AplodNo ratings yet
- Management of LabourDocument16 pagesManagement of LabourAlbert MusinguziNo ratings yet
- MRCOG Part 1 Pastpapers Recall - (2005-2010)Document220 pagesMRCOG Part 1 Pastpapers Recall - (2005-2010)VINOD GUPTANo ratings yet
- Repeat Breeding in Cattle and BuffaloesDocument34 pagesRepeat Breeding in Cattle and BuffaloesGovind Narayan Purohit100% (2)
- Thin PrepDocument4 pagesThin PrepkookroachNo ratings yet
- Pelvic ExamDocument6 pagesPelvic ExamJaigurudev Ashi SanskarNo ratings yet
- PARTOGRAPHDocument2 pagesPARTOGRAPHHERRERA, ANGELANo ratings yet
- Uttar Basti - B S Prasad-KLEU's Shri BMK Ayurveda MahavidyalayaDocument30 pagesUttar Basti - B S Prasad-KLEU's Shri BMK Ayurveda Mahavidyalayagraspayurveda100% (2)
- Maternal AnatomyDocument60 pagesMaternal AnatomyRaraNo ratings yet
- Ekstirpasi Myoma Geburt + Kuretase HP GynDocument22 pagesEkstirpasi Myoma Geburt + Kuretase HP GynpraburastraNo ratings yet
- Biology AssignmentDocument21 pagesBiology AssignmentKenardNo ratings yet
- Family PlanningDocument8 pagesFamily PlanningAnonymous h2EnKyDbNo ratings yet
- Abortion 1Document46 pagesAbortion 1Nikhil TyagiNo ratings yet
- AbortionDocument32 pagesAbortionKirandeep ParmarNo ratings yet
- Dsfasdfsadf PDFDocument246 pagesDsfasdfsadf PDFrpascua123No ratings yet
- Obsandgyne Tables 200pagesDocument221 pagesObsandgyne Tables 200pagesRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- When Is A Cow in Estrus Clinical and Practical AspectsDocument18 pagesWhen Is A Cow in Estrus Clinical and Practical AspectsZavala H Irving100% (1)
- Genitalia AssessmentDocument99 pagesGenitalia AssessmentGloriaCoronado75% (8)
- Brachy Catalog RAD10536C August2021Document164 pagesBrachy Catalog RAD10536C August2021Richar Pinedo CadilloNo ratings yet
- 2011 IFCPC Nomenclature: Accepted in Rio World Congress, July 5, 2011Document3 pages2011 IFCPC Nomenclature: Accepted in Rio World Congress, July 5, 2011ginecologiahigasmNo ratings yet
- XaxaxDocument3 pagesXaxaxDarren BalbasNo ratings yet
- Gyne & Obes. Step.1st BitsDocument70 pagesGyne & Obes. Step.1st BitsSkyNo ratings yet