0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views34 pagesL15 ImageRestroration
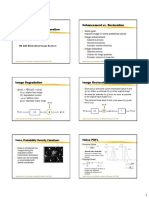
This document summarizes image restoration techniques. It discusses how images can become degraded by blurring from cameras, environments, or devices, as well as noise. Common degradation types include optical blur, motion blur, quantization, and noise. The goal of image restoration is to remove distortions and recover the original image using knowledge of the degradation process. Key steps involve modeling the degradation, applying the inverse process, and evaluating restoration quality. Common restoration techniques for noise removal include mean, median, and alpha trimmed filters.
Uploaded by
tirumareddybhavyaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views34 pagesL15 ImageRestroration
This document summarizes image restoration techniques. It discusses how images can become degraded by blurring from cameras, environments, or devices, as well as noise. Common degradation types include optical blur, motion blur, quantization, and noise. The goal of image restoration is to remove distortions and recover the original image using knowledge of the degradation process. Key steps involve modeling the degradation, applying the inverse process, and evaluating restoration quality. Common restoration techniques for noise removal include mean, median, and alpha trimmed filters.
Uploaded by
tirumareddybhavyaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd