0% found this document useful (0 votes)
303 views7 pagesSAT Math Formulas - Worthington Prep
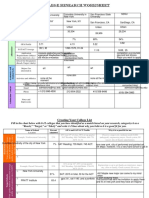
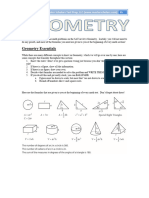
The document provides formulas and definitions for various topics that may appear on the SAT Math exam, including:
- Lines and linear equations with formulas for slope, standard form, point-slope form, and parallel/perpendicular lines
- Simple and compound interest formulas
- Distance, rate, and midpoint formulas
- Mean, median, mode, and standard deviation formulas for statistics
- Exponent rules, factoring, and the quadratic formula
- Formulas for perimeter, area, and the Pythagorean theorem for triangles
- Trigonometry definitions and the SOHCAHTOA mnemonic
- Circle formulas including circumference, area, and properties of tangents/chords/arcs
- Complex number notation
Uploaded by
ashrafshehab695Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
303 views7 pagesSAT Math Formulas - Worthington Prep
The document provides formulas and definitions for various topics that may appear on the SAT Math exam, including:
- Lines and linear equations with formulas for slope, standard form, point-slope form, and parallel/perpendicular lines
- Simple and compound interest formulas
- Distance, rate, and midpoint formulas
- Mean, median, mode, and standard deviation formulas for statistics
- Exponent rules, factoring, and the quadratic formula
- Formulas for perimeter, area, and the Pythagorean theorem for triangles
- Trigonometry definitions and the SOHCAHTOA mnemonic
- Circle formulas including circumference, area, and properties of tangents/chords/arcs
- Complex number notation
Uploaded by
ashrafshehab695Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd