Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 14 Summary Sheet
Uploaded by
jordanleewyngaard60 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views3 pagesThe document defines key terms related to waves and optics, including:
- Superposition and interference of waves
- Constructive and destructive interference
- Standing waves, nodes, and anti-nodes
- Reflection, refraction, and the law of reflection
- Index of refraction and Snell's law
- Critical angle and total internal reflection
It also provides comprehension questions to test understanding of these concepts.
Original Description:
st
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document defines key terms related to waves and optics, including:
- Superposition and interference of waves
- Constructive and destructive interference
- Standing waves, nodes, and anti-nodes
- Reflection, refraction, and the law of reflection
- Index of refraction and Snell's law
- Critical angle and total internal reflection
It also provides comprehension questions to test understanding of these concepts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views3 pagesUnit 14 Summary Sheet
Uploaded by
jordanleewyngaard6The document defines key terms related to waves and optics, including:
- Superposition and interference of waves
- Constructive and destructive interference
- Standing waves, nodes, and anti-nodes
- Reflection, refraction, and the law of reflection
- Index of refraction and Snell's law
- Critical angle and total internal reflection
It also provides comprehension questions to test understanding of these concepts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
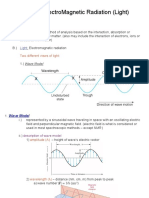
Unit 15 Summary Sheet
Term Definition Student Notes
Superposition When two or more waves traveling
through a medium meet at a point
they will interfere with each other.
This is superposition.
Constructive Interference When two waves superimpose and
the resultant wave is additive
(larger) this is constructive
interference.
Destructive Interference When two waves superimpose and
the resultant wave cancelled this is
destructive interference.
Standing Waves Standing Waves can occur when a
wave reflects between two
boundaries.
Nodes Fixed points in standing waves are
called nodes.
Anti-nodes Points where a standing wave is at
its amplitude are called anti-nodes.
Wave boundaries Wave boundaries can be fixed or
free. Fixed boundaries cause a
wave 180o reflection. Free
boundaries do not have any
reflection.
Harmonic Series Music Strings can only resonate at certain
frequencies.
Law of Reflection Reflection happens when a wave or
particle reaches a boundary between
two different media (materials) and
returns into the original medium.
Specular Reflection Specular Reflection occurs at mirror
like surfaces.
Diffuse Reflection Uneven surfaces will reflect, this
reflection is called a diffuse
reflection, and does not result in a
clear image.
Index of Refraction The index of refraction of a material
is the ration of the speed of light in
a vacuum to the speed of light
through the material.
Refraction Refraction describes the change of
direction of a wave as it moves from
one medium to another. It happens
when a wave reaches a boundary
between two different media and
passes through into the new
medium.
Law of Refraction or “Snell’s The law of refraction, or “Snell’s
Law” Law,” in equation form is
Where n1 is the refractive index for
the incident ray and n2 is the
refractive index for the refracted
ray.
Critical Angle When the refracted angle equals 90o,
the incident angle is called the
critical angle, θc.
Total Internal Reflection If the incident angle is greater than
the critical angle, all the light is
reflected. This is called total internal
reflection.
Comprehension Set #1
1) Can you see interference if there is only one wave?
a) Yes b) No
2) Can standing waves can have any wavelength?
a) Yes b) No
3) Draw the result of the superposition of the
following two waves.
Example - Set #2
The speed of a wave on a particular string is 24 m/s. If the string is 6.0 m long, at what frequencies is it able
to resonate? Draw a picture of the string for the first three resonance frequencies.
Comprehension Set #3
1) Diffuse reflection results in clear images.
a) True b) False
2) If an incident ray hits the following mirrored surface, and what
angle to the surface will the ray be reflected off the mirror?
a) 41o b) 45o c) 49o
3) If light moves from ethanol (n=1.361) to air (n = 1.000) at an angle of 22o? What is the angle of
refraction?
a)31o b) 22o c) 51o
4) In question 3 above, if the angle of incidence was 70o, will some the light refract into the air, or will it
undergo total internal reflection?
You might also like
- Tesla's Golden Ratios 3-6-9Document24 pagesTesla's Golden Ratios 3-6-9Branko R Babic100% (6)
- CSEC-revision-physics (Notes)Document8 pagesCSEC-revision-physics (Notes)gNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument24 pagesWavesHarveen Kaur AnandNo ratings yet
- Effect of Music On Plants - An OverviewDocument5 pagesEffect of Music On Plants - An OverviewAkshay RamrekhaNo ratings yet
- Waves Revision Notes (IGCSE PHYSICS)Document12 pagesWaves Revision Notes (IGCSE PHYSICS)Khushi MehtaNo ratings yet
- How Do Waves Behave? How Are They Measured? Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandHow Do Waves Behave? How Are They Measured? Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Irish Flute Design OptimizationDocument75 pagesIrish Flute Design OptimizationFernando PerezNo ratings yet
- Room AcousticsDocument52 pagesRoom AcousticsDavezel ZerxNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Properties of Waves Including Light and Sound: What Is Wave Motion?Document11 pagesTopic 3 Properties of Waves Including Light and Sound: What Is Wave Motion?PichakornNo ratings yet
- At 1.1 - Optical Properties of Radio WavesDocument3 pagesAt 1.1 - Optical Properties of Radio WavesSam PunoNo ratings yet
- Properties of WaveDocument61 pagesProperties of WavePASSAWAT BOONCHITSIRIKULNo ratings yet
- CIVL1180 - 18sep2023Document20 pagesCIVL1180 - 18sep2023jv5gfmjd4xNo ratings yet
- Science NotesDocument3 pagesScience Noteswemedo7083No ratings yet
- Wave OpticsDocument6 pagesWave Opticsaayushfreefire18No ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument13 pagesPhysicskeosotepyNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Wave Behavior: Marquez Heron Dondre SaveryDocument10 pagesPresentation On Wave Behavior: Marquez Heron Dondre SaveryMARQUEZ HERONNo ratings yet
- 8 HuygenPrincipleDocument15 pages8 HuygenPrincipleShaina Joice PortugalNo ratings yet
- Waves pdf100Document15 pagesWaves pdf100Levente SusztarNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Wave Behavior: Marquez Heron Dondre SaveryDocument10 pagesPresentation On Wave Behavior: Marquez Heron Dondre SaveryMARQUEZ HERONNo ratings yet
- Ok 4Document25 pagesOk 4mnaqash272000No ratings yet
- Chapter 25 - Instruments For Optical SpecDocument12 pagesChapter 25 - Instruments For Optical SpecS. MartinezNo ratings yet
- Su1c2 by Adel KhamisDocument12 pagesSu1c2 by Adel KhamisAdel KhamisNo ratings yet
- Interference and RefractionDocument17 pagesInterference and RefractiontyeNo ratings yet
- Reflection and RefracionDocument21 pagesReflection and RefracionJames Yuri ArcaNo ratings yet
- Physics Light Reflection and RefractionDocument5 pagesPhysics Light Reflection and RefractionVj RanchesNo ratings yet
- Wave Optics: IntroductionDocument15 pagesWave Optics: IntroductionChandra sekharNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22.1 4Document34 pagesChapter 22.1 4Richard Renz VillafuerteNo ratings yet
- Dutch Physicist Christian Huygens Captured This Propagation Mechanism MATHEMATICALLYDocument16 pagesDutch Physicist Christian Huygens Captured This Propagation Mechanism MATHEMATICALLYAijaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument8 pagesPhysicsYen AduanaNo ratings yet
- Articulo IeeeDocument5 pagesArticulo IeeeFajardo Acosta Julian CamiloNo ratings yet
- GenPhysics2 - Q2 Module 4Document18 pagesGenPhysics2 - Q2 Module 4Jasmin SorianoNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة العاشرة فيزياءDocument7 pagesالمحاضرة العاشرة فيزياءm26292391No ratings yet
- Double Slit Project 6Document26 pagesDouble Slit Project 6mnaqash272000No ratings yet
- Ch-10 Wave OpticsDocument34 pagesCh-10 Wave Opticstessa mariaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Optical Fiber Waveguides Ray Theory Part - 1Document9 pagesLecture 4 - Optical Fiber Waveguides Ray Theory Part - 1samarthNo ratings yet
- General Wave Properties - Free Exam AcademyDocument10 pagesGeneral Wave Properties - Free Exam AcademysinojiayogNo ratings yet
- Phys201: Diffraction and InterferenceDocument86 pagesPhys201: Diffraction and InterferenceassefaNo ratings yet
- Waves at Boundaries: Reflection & Refraction For Stationary WavesDocument17 pagesWaves at Boundaries: Reflection & Refraction For Stationary WavesNisha PeaceNo ratings yet
- DiffractionDocument9 pagesDiffractionmaheshNo ratings yet
- Light EditedDocument41 pagesLight Editedmarc daniel ortizNo ratings yet
- Waves and Types-SummaryDocument3 pagesWaves and Types-SummaryLuz Vargas EstremorNo ratings yet
- Reflection of Light On Curved MirrorDocument5 pagesReflection of Light On Curved MirrorgamahimeNo ratings yet
- 10-7 Waves Webquest: Site 1: Characteristics of WavesDocument5 pages10-7 Waves Webquest: Site 1: Characteristics of WavesTangyNo ratings yet
- 421 821 Chapter 6Document17 pages421 821 Chapter 6April Mergelle LapuzNo ratings yet
- 2 Sound Wave - USDocument29 pages2 Sound Wave - USCharlotte gamingNo ratings yet
- Clem Waves Lesson02 PresentationDocument29 pagesClem Waves Lesson02 PresentationAldiona DaulleNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5.2 LightDocument11 pagesLesson 5.2 LightRais RahimiNo ratings yet
- Lecturer: Tristan O'Hanlon Room: 303-618 T.ohanlon@auckland - Ac.nzDocument32 pagesLecturer: Tristan O'Hanlon Room: 303-618 T.ohanlon@auckland - Ac.nzrobbie_delavega7000No ratings yet
- InterferenceDocument4 pagesInterferenceSGNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 Powerpoint PSDocument46 pagesChapter 17 Powerpoint PSJohn Lloyd AlarconNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5-6Document20 pagesChapter 5-6Hnin Yu Yu AungNo ratings yet
- HSC Physics Module 3: Waves & ThermodynamicsDocument30 pagesHSC Physics Module 3: Waves & ThermodynamicswillNo ratings yet
- Interefenrece in Thin Films Session 1 (Huygenes Wave Theory and Optical Path Difference)Document6 pagesInterefenrece in Thin Films Session 1 (Huygenes Wave Theory and Optical Path Difference)Sanjiv BadheNo ratings yet
- Reflection, Refraction, and DiffractionDocument18 pagesReflection, Refraction, and DiffractionImmanuel Suman ShijuNo ratings yet
- Refraction of LightDocument11 pagesRefraction of Lightshamitmajor100% (1)
- 4 RefractionDocument18 pages4 RefractionJulie heleneNo ratings yet
- Physics Light Reflection and Refraction 1Document5 pagesPhysics Light Reflection and Refraction 1Vj RanchesNo ratings yet
- Waves at Media Boundaries: Free-End Re EctionsDocument7 pagesWaves at Media Boundaries: Free-End Re EctionsRobloxGirl BiancaNo ratings yet
- Project File PhysicsDocument14 pagesProject File PhysicsVedika SinghNo ratings yet
- 2 Wave NatureDocument38 pages2 Wave NatureJulie heleneNo ratings yet
- General Physics2 Lesson 7 PDFDocument3 pagesGeneral Physics2 Lesson 7 PDFJohn Renzo MolinarNo ratings yet
- Physics Mcqs Practice Test PDFDocument23 pagesPhysics Mcqs Practice Test PDF03145565327No ratings yet
- Diffraction and InterferenceDocument40 pagesDiffraction and InterferenceUnexpected TheoryNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS II Unit 1 Oscillations - 1Document90 pagesPHYSICS II Unit 1 Oscillations - 1dharanishlokNo ratings yet
- Most Important 11 Class QuestionsDocument4 pagesMost Important 11 Class QuestionsHimanshu Bhandari100% (2)
- Standing Waves: By: Tocke Chantal AndréaDocument14 pagesStanding Waves: By: Tocke Chantal AndréaChantal Tocke100% (1)
- Omosefe Osakue Physics Coursework 2Document9 pagesOmosefe Osakue Physics Coursework 2Micah TamunoNo ratings yet
- Notes For Lecture #16: Electromagnetic Waves and ConductorsDocument8 pagesNotes For Lecture #16: Electromagnetic Waves and ConductorsJoanna Modupeh HodasiNo ratings yet
- Standing Waves On A StringDocument6 pagesStanding Waves On A StringamirpouyanNo ratings yet
- Physics: Chapter: MagnetismDocument17 pagesPhysics: Chapter: MagnetismkushalNo ratings yet
- Soal Dan Jawaban Sound WaveDocument15 pagesSoal Dan Jawaban Sound WaveshintatrimayangsariNo ratings yet
- Wave QuestionsDocument11 pagesWave Questionsabh_omegaNo ratings yet
- PH 116 MasterDocument53 pagesPH 116 MasterMarkNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument12 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelredwanNo ratings yet
- Definitions - Topic 3 Waves - AQA Physics A-LevelDocument2 pagesDefinitions - Topic 3 Waves - AQA Physics A-LevelKavay KapoorNo ratings yet
- The Physics of MusicDocument13 pagesThe Physics of MusicKavithira DevarajanNo ratings yet
- Iahr 2006 2 PDFDocument15 pagesIahr 2006 2 PDFRabei RomulusNo ratings yet
- CLIP Wave2 PARDocument5 pagesCLIP Wave2 PARPushpanjay KumarNo ratings yet
- SOS - Synth Secrets - Whats in A Sound-1Document3 pagesSOS - Synth Secrets - Whats in A Sound-1seekerbythenetNo ratings yet
- Manual AT-3200D Kit Entrenamiento de Antenas PDFDocument135 pagesManual AT-3200D Kit Entrenamiento de Antenas PDFAndrea SanchezNo ratings yet
- Laser Cavity: (Type Here)Document42 pagesLaser Cavity: (Type Here)hamza tariqNo ratings yet
- Sound Wave English 2CyesgNDocument46 pagesSound Wave English 2CyesgNShrutiNo ratings yet
- On Sound: Phys130, A04 Dr. Robert MacdonaldDocument24 pagesOn Sound: Phys130, A04 Dr. Robert MacdonaldAlinaBogoiNo ratings yet
- Super PositionDocument5 pagesSuper PositionAmirMozammelNo ratings yet
- IB Physics 2025 SyllabusDocument27 pagesIB Physics 2025 Syllabusmastering.alevels.physicsNo ratings yet
- 9-11 6B Uwi Labs 2016 - 17Document9 pages9-11 6B Uwi Labs 2016 - 17Zaire GrahamNo ratings yet