Professional Documents
Culture Documents
X
X
Uploaded by
Valentina Cardenas0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views7 pagesOriginal Title
x
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views7 pagesX
X
Uploaded by
Valentina CardenasCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
° °
I
cugcrcnc=cs — CHSCCHCHAC=CCH,
(a) Protection of carbonyl group
|
CHCCH,CH,C=cii HOCH:CH.OH ae walewoaca
st teme
S-Hexyn-2-one Acetal of reactant (80%)
(b) Alkylation of alkyne
b> san (y ou, Lo
HyC’ ‘CH,CH,C=CH H,C’ ‘CH,CH,C=C: jC’ CH,CH»C=CCH;
Acetal of product (78%)
(c) Removal of the protecting group by hydrolysis UP 105 +
dO °
HC’ “CH,CH;C=CCH, 22+ CHyCCHjCH;C=CCH
Base de Schiff
N-substituted = Water
imine
i
CH + CH,NH, —> € \-cr-sers
Benzaldehyde Methylamine —_-N-Benzylidenemethylamine (70%)
(0 + (CH3)2CHCH2NH, —> (scree
Cyclohexanone Isobutylamine N-Cyclohexylideneisobutylamine (79%)
i
Mex 08 diethyl ether
b+
Grignard reagent
acts as a nucleophile
toward carbon dioxide
Hydration of an Aldehyde or Ketone in Basic Solution we
Overall reaction:
\
=0: + HO: == ‘C—OH
é f
Aldehyde Water Geminal
or ketone diol
STEP 1: Nucleophilic addition of hydroxide ion to the carbonyl group.
R RR
H6r ac) 22 “tor
KX ug:
Hydroxide Aldehyde Alkoxide ion
or ketone intermediate
STEP 2: Proton transfer from water to the intermediate formed in step 1.
RR RR
Ne S-F6u = \t-0-H + 70H
HO: HO:
’ .
Reaccion aldol
0
I
2CH,CH,CH,CH “ORES, HCH CRACK
Butanal
Las condensaciones con aldehidos aromaticos se ven favorecidas por el aumento de la
conjugacién, estas reacciones se conocen como condensaciones de Claisen-Schmidt
i » enol he
(CH3);CCCH;CH; _— (CH sOOGH—CHCHCH,
CH,
2.2-Dimethyl-3-pentanone Sydroy.224imety
a halogenacion de compuestos carbonilicos
O° °°
Reaccion de Wittig
RA
Ye’ + HPO
R _A
bo + Cane
x
ete lide Aline oxide
(0 + (C.H.)P—CH, 2S (ct, + (CH)P—O-
phosphorane (86%) oxide
Oxidacion de Baeyer-Villiger 7
vo i q
RCR’ + R'COOH —> RCOR’ + R'COH
Ketone _Peroxy acid Ester__ Carboxylic acid
°
I
catdoon i
con, SS (oben,
(Cyclohexy! methy! ketone Cyelohexyl acetate (67%)
—CHs —CH.R —CHR2 —CR3
Metiyt Primary Secondary Tertiary
alkyl allyl alkyl
Reaccion del haloformo
La halogenacién de compuestos carbonilicos también puede hacerse en medio basico, en
este caso suele usarse exceso de halégeno y el compuesto formado es cloroformo,
bromoformo o yodoformo dependiendo de cual halégeno se use.
oO Oo
RACER = act
x
Aldehyde or ketone Halo aldehyde or ketone
Adicidn de Michael cit
CH, ° LG
° I gy, Row CCC
+ H.C=CHCCHs Sina?
‘oO O
2-Methyl-13- ‘Methyl vinyl 2-Methyl-2-(3'-oxobutyl)-
‘cyclohexanedione ‘ketone 1,3-cyclohexanedione
Este producto puede reaccionar intramolecularmente mediante una condensacién aldolica.
Cuando esto sucede, el producto formado es ciclico y hablamos de una reaccién llamada
Robinson annulation.
Robinson Annula .
E cts CH CH
ine CO = CB,
‘oO
2-Methyl-2-(3'-oxobutyD- Intramolecular aldol addition
1,3-cyclohexanedione product; not isolated
Uplos anc =
Reaccion de Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky eS
RCCOH + Bh ™% R,CCOH + HBr
| |
Br
HE
«Bromo Hydrogen
carboxvlic acid ‘bromide
1HyCH,CH,CO3H “> CHLCHIAHOO ne CHLCHRHICO
Br on
Botanoic 2-Bromobetancic ‘2-Hydronybutancic
acid acid 77%), acid (69%)
(CHi):CHCHCOnH ex? (CHa) CHEHCORH gh (CHa) CHCHCOat
Br NH)
3-Methylbutanoic 2-Bromo-3-methylbutanoic 2-Amino-3-methylbutanoic
acid acid (88%) acid (48%)
Descarboxilacién
RCO > RH + CO;
Cloruros de dcido
1 f
RCOH + SOCl —> RCCl + SO, + HCl
Casborstic Thionyl Acyl Sulfur. Hydrogen
chloride chloride dioxide chloride
Oo oO
I ll
(CH3),CHCOH 2s (CH),CHCCL
2-Methylpropanoic acid 2-Methylpropanoyl chloride (90%)
Name of reagent ‘Type of product Example
9 NOH
H.NOH Hydroxylamine Oxime cnycH.t amt, cHsct.te
Heptanal Heptane! oxime (81-93%)
NNNHC.Hs
hawks atrinin Pitas (don sts 7) i
Acetophenone
‘Acetophenone
‘phenyinydrazone (87-91%)
9
nnd
(CH2)oCHs
2.Dodecanone.
‘semicarbazone (93%)
°
HaNNHENH, ‘Semicarbazide ‘Semicarbazone CHSCICH.ISCHs surnla,
2.badecanone
Reacci6n de Horner-Emmons
9°
0° we HR?
base / solvent Re Rib re| RY OR I + RB
0-110°C a RoR! RO
NaH, KH,
KHMDS, NaHMDS Atkene
LHMDS, KOFBu
R' = aryl, alkyl; R? = alkyl, aryl, COR, COR, CN, SOR ‘= __Homer-Wittig reaction
R! = O-aryl, O-alky, NRp; R? = aryl, alkenyl, COR, COZR, CN, SO;R ‘=> Wadsworth-Emmons reaction
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5810)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (843)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (346)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Actividad en ClaseDocument1 pageActividad en ClaseValentina CardenasNo ratings yet
- Fenomeno y Contexto LucidsparkDocument1 pageFenomeno y Contexto LucidsparkValentina CardenasNo ratings yet
- Interacciones Ejemplarizantes-2Document1 pageInteracciones Ejemplarizantes-2Valentina CardenasNo ratings yet
- Manifiesto 1 - Plan de Texto (230829)Document3 pagesManifiesto 1 - Plan de Texto (230829)Valentina CardenasNo ratings yet
- Informe P3Document3 pagesInforme P3Valentina CardenasNo ratings yet
- Wat 2 Cardenas Ochoa Valentina - ENGLISH 9-2Document4 pagesWat 2 Cardenas Ochoa Valentina - ENGLISH 9-2Valentina CardenasNo ratings yet
- Informe P3 Físico-2Document14 pagesInforme P3 Físico-2Valentina CardenasNo ratings yet
- Analisis de Caso - Valentina CardenasDocument2 pagesAnalisis de Caso - Valentina CardenasValentina CardenasNo ratings yet
- Tabla Plan de Texto, Segunda EntregaDocument8 pagesTabla Plan de Texto, Segunda EntregaValentina CardenasNo ratings yet
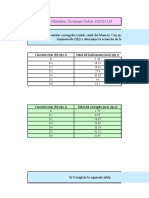
- Tarea 2. Valentina Cardenas Ochoa 202023129: Concentración (M) (Eje X) Señal Del Instrumento (Ma) (Eje Y)Document9 pagesTarea 2. Valentina Cardenas Ochoa 202023129: Concentración (M) (Eje X) Señal Del Instrumento (Ma) (Eje Y)Valentina CardenasNo ratings yet
- Manifiesto 2 - Guia (230829)Document3 pagesManifiesto 2 - Guia (230829)Valentina CardenasNo ratings yet
- 5 Laboratorio Ag2Document13 pages5 Laboratorio Ag2Valentina CardenasNo ratings yet
- TablaPlandetexto DlloHumano2023 1-2Document7 pagesTablaPlandetexto DlloHumano2023 1-2Valentina CardenasNo ratings yet
- 5 Laboratorio Ag3Document13 pages5 Laboratorio Ag3Valentina CardenasNo ratings yet
- IntroduccionDocument7 pagesIntroduccionValentina CardenasNo ratings yet
- Tesis PDFDocument1 pageTesis PDFValentina CardenasNo ratings yet
- 5 Laboratorio AgDocument13 pages5 Laboratorio AgValentina CardenasNo ratings yet
- TopicDocument2 pagesTopicValentina CardenasNo ratings yet
- Taller 3 FinalDocument2 pagesTaller 3 FinalValentina CardenasNo ratings yet
- Arte RomanoDocument2 pagesArte RomanoValentina CardenasNo ratings yet
- Ejercicio Analisis 1Document2 pagesEjercicio Analisis 1Valentina CardenasNo ratings yet
- La CabezaDocument2 pagesLa CabezaValentina CardenasNo ratings yet
- Cuerpo Opinion EssaysDocument3 pagesCuerpo Opinion EssaysValentina CardenasNo ratings yet
- Evaluación Estadística de Indicadores Ácido BaseDocument4 pagesEvaluación Estadística de Indicadores Ácido BaseValentina CardenasNo ratings yet
- Block Pattern Point-by-Point PatternDocument5 pagesBlock Pattern Point-by-Point PatternValentina CardenasNo ratings yet
- Informe Prática 2-421804Document3 pagesInforme Prática 2-421804Valentina CardenasNo ratings yet
- Análisis de Una Mezcla de Carbonato y BicarbonatoDocument4 pagesAnálisis de Una Mezcla de Carbonato y BicarbonatoValentina CardenasNo ratings yet