Professional Documents
Culture Documents
INFLAMMATION
INFLAMMATION
Uploaded by
Portgas D AceOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
INFLAMMATION
INFLAMMATION
Uploaded by
Portgas D AceCopyright:
Available Formats
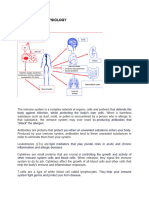
Inflammation is the body's defense against pathogens.
When inflammation occurs without
pathogens, it leads to inflammatory diseases like psoriasis and Crohn's disease. It's crucial
for medical professionals to know about inflammation to treat these diseases.
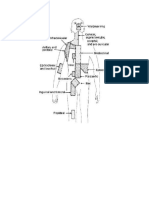
Signs of inflammation include redness, swelling, pain, heat, and loss of function. This
happens due to the body reacting to the foreign invaders. Vasodilation is the initial step in
this process. When pathogens are being destroyed, mast cells release histamine. This
increases blood flow and causes redness, swelling, and heat. Histamine also helps immune
cells reach the infection site.
Cytokines are chemicals that can cause inflammation. Chemokines, like interleukin-8 (IL-8),
make cells move. Macrophages can recognize and respond to foreign and damaged
molecules. Once activated, they release substances to boost the defense and eat the
pathogen. Once inside, the pathogen is destroyed using a process called the respiratory
burst.
Neutrophils contain harmful substances that destroy bacteria. But they can also harm our
tissue, causing pain and dysfunction. The respiratory burst, which involves various chemical
reactions, is vital to kill pathogens but can also harm our cells.
Psoriasis is an inflammatory disease that causes skin issues. Its exact cause is unknown but
involves an overactive immune response. Understanding inflammation is crucial when
treating such diseases because some treatments, like NSAIDs, can make the problem
worse.
You might also like
- How The Immune System WorksDocument13 pagesHow The Immune System Worksnishant nagyan100% (2)
- Drugs Acting On The Immune System: Retchel-Elly D. Dapli-AnDocument60 pagesDrugs Acting On The Immune System: Retchel-Elly D. Dapli-AnJoshua MendozaNo ratings yet
- What Is Immunity?Document37 pagesWhat Is Immunity?heer100% (1)
- 1 The Immune SystemDocument25 pages1 The Immune SystemTumabangNo ratings yet
- Skenario IDocument12 pagesSkenario IRajasa FathahilllahNo ratings yet
- Defence Against Microorganisms: Gopika Suresh - Ims20121Document2 pagesDefence Against Microorganisms: Gopika Suresh - Ims20121Gopika SureshNo ratings yet
- InflammationDocument3 pagesInflammationsitapuNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease: An Introduction Prepared By: Amelia F. Nacario RN, MANDocument69 pagesCommunicable Disease: An Introduction Prepared By: Amelia F. Nacario RN, MANAmelia Filio NacarioNo ratings yet
- Acute InflammationDocument10 pagesAcute InflammationLydia Angel HartonoNo ratings yet
- The Immune System: ST ND RD STDocument1 pageThe Immune System: ST ND RD STamar lalNo ratings yet
- 3.inflammation ProcessDocument13 pages3.inflammation ProcessGerald Limo Arap ChebiiNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY of ALLERGIC REACTIONDocument2 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY of ALLERGIC REACTIONAlkiana SalardaNo ratings yet
- The Inflammatory ResponseDocument3 pagesThe Inflammatory ResponserifatafrozemahimahiNo ratings yet
- What Is The Immune SystemDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Immune Systemkitkat22phNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Immune SystemDocument9 pagesOverview of The Immune SystemAyadi P. AkinwandeNo ratings yet
- Thanavala 2-23-17 Mir 508 Adv Immunol Yt Inflammation 2017Document27 pagesThanavala 2-23-17 Mir 508 Adv Immunol Yt Inflammation 2017kaoutherboublatNo ratings yet
- InflammationDefinition, Symptoms, Treatment,&FactsBritannica 1710882912933Document6 pagesInflammationDefinition, Symptoms, Treatment,&FactsBritannica 1710882912933muhellen8No ratings yet
- Patophysiology Oral Q 1Document134 pagesPatophysiology Oral Q 1TijanaNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument7 pagesLymphatic SystemChloe Gabrielle LlamasNo ratings yet
- RubellaDocument4 pagesRubellatulpe6459No ratings yet
- The Immune SystemDocument33 pagesThe Immune SystemKayla Denize GerardinoNo ratings yet
- L.5 Immune System StrengtheningDocument72 pagesL.5 Immune System StrengtheningMunira SulimanNo ratings yet
- DR Lens Sand CMO Arthritis and Auto-ImmuneDocument24 pagesDR Lens Sand CMO Arthritis and Auto-ImmunepaulxeNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic SystemDocument6 pagesThe Lymphatic SystemErica SharonNo ratings yet
- The Immune SysDocument2 pagesThe Immune SysOmar AlotaibiNo ratings yet
- Immunology: Ectoparasites (I.e. Bed Bugs, Louse, Mites, Ticks and Fleas) Attach Themselves ToDocument18 pagesImmunology: Ectoparasites (I.e. Bed Bugs, Louse, Mites, Ticks and Fleas) Attach Themselves ToPrince RichardsNo ratings yet
- Immunity SystemDocument4 pagesImmunity Systemsanti_1976No ratings yet
- Immune SystemDocument1 pageImmune SystemMargie FernandoNo ratings yet
- Immunology: Ectoparasites (I.e. Bed Bugs, Louse, Mites, Ticks and Fleas) Attach Themselves ToDocument18 pagesImmunology: Ectoparasites (I.e. Bed Bugs, Louse, Mites, Ticks and Fleas) Attach Themselves ToTamicka BonnickNo ratings yet
- Immune System: Presented By: John Ray Dela Crruz Carmela Magadia Nicolle MarantalDocument14 pagesImmune System: Presented By: John Ray Dela Crruz Carmela Magadia Nicolle Marantaljasper oliverosNo ratings yet
- Source:Immunology Eight Edition David MaleDocument3 pagesSource:Immunology Eight Edition David MaleAzzahra FadhlilaNo ratings yet
- IVMS - General Pathology, Inflammation NotesDocument19 pagesIVMS - General Pathology, Inflammation NotesMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.No ratings yet
- Memory For Most Previously Encountered Antigens So That A Second Encounter Prompts An Even MoreDocument2 pagesMemory For Most Previously Encountered Antigens So That A Second Encounter Prompts An Even MoreAmarissa A. TsabitaNo ratings yet
- Yr 10 Yearly Science NotesDocument51 pagesYr 10 Yearly Science NotesMarisa Alves100% (1)
- Research Newsletter-Spring/Summer 2007: Two Faces of InflammationDocument5 pagesResearch Newsletter-Spring/Summer 2007: Two Faces of InflammationNirwana Hana's BellaNo ratings yet
- Immunlogical DisorderDocument36 pagesImmunlogical DisorderSameen NasirNo ratings yet
- I Nflammation-1Document35 pagesI Nflammation-1Ogunsusi DamilolaNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension Worksheet The Immune SystemDocument2 pagesReading Comprehension Worksheet The Immune SystemMohammad ShahidNo ratings yet
- The Role of The Immune SystemDocument4 pagesThe Role of The Immune SystemMahandar OadNo ratings yet
- Non Specific HostDocument46 pagesNon Specific HostAdrian BautistaNo ratings yet
- 11.the Human Immune SystemDocument32 pages11.the Human Immune Systemمحمد عدلي عدلانNo ratings yet
- VCE Biology Unit 3 Summaries - Immune SystemDocument7 pagesVCE Biology Unit 3 Summaries - Immune SystemDJTofiNo ratings yet
- Inflammation Is Part of The Complex Biological Response of Vascular Tissues To Harmful StimuliDocument2 pagesInflammation Is Part of The Complex Biological Response of Vascular Tissues To Harmful StimuliGabitza GabiNo ratings yet
- Saint Joseph Convent School English Program Health Grade 11 Name: - Wachiraporn Uaramnueyporn - Class: - G11/2 - No. - 17Document2 pagesSaint Joseph Convent School English Program Health Grade 11 Name: - Wachiraporn Uaramnueyporn - Class: - G11/2 - No. - 17Wachiraporn UaramnueypornNo ratings yet
- UddayDocument21 pagesUddayJune DumdumayaNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic InflammationDocument13 pagesAcute and Chronic InflammationReymond MagnoNo ratings yet
- The Immune System: Abraham Ponce March 26, 2020 Biology ClassDocument3 pagesThe Immune System: Abraham Ponce March 26, 2020 Biology ClassAbrahamNo ratings yet
- A LEVEL TRANSPORT NOTES 2020 New - 41Document1 pageA LEVEL TRANSPORT NOTES 2020 New - 41Natamba BrianNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 1Document11 pagesBiology Unit 1VinnyNo ratings yet
- Mimiproject Anti InfiamationDocument69 pagesMimiproject Anti Infiamationmukeshcilaveni18No ratings yet
- Bazele PatologieiDocument36 pagesBazele PatologieigeorgemihailNo ratings yet
- Immune System Student Reading PagesDocument37 pagesImmune System Student Reading PagesMariel VillamorNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Health ScienceDocument12 pagesFaculty of Health ScienceAbdirahman YazinNo ratings yet
- A Review On Vyadhikshamatva W.S.R Immunity: Sharma Brahmananad Adlakha Manoj Kumar Ritu Kapoor Sharma Radhy ShamDocument11 pagesA Review On Vyadhikshamatva W.S.R Immunity: Sharma Brahmananad Adlakha Manoj Kumar Ritu Kapoor Sharma Radhy ShamNupur SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Immune SystemDocument4 pagesImmune SystemDaniel PancuNo ratings yet
- Unit 23Document16 pagesUnit 23m a zargarNo ratings yet
- Cell and Tissues of Immune System by Ali AfzalDocument11 pagesCell and Tissues of Immune System by Ali AfzalAli AfzalNo ratings yet
- Immune SystemDocument2 pagesImmune SystemSoleil MaxwellNo ratings yet
- Lu 2021Document14 pagesLu 2021Portgas D AceNo ratings yet
- Narksri 2021Document28 pagesNarksri 2021Portgas D AceNo ratings yet
- Cao Points Charts 2020Document161 pagesCao Points Charts 2020Portgas D AceNo ratings yet
- The Scientific Method Past Exam Questions Higher Level Section A QuestionsDocument3 pagesThe Scientific Method Past Exam Questions Higher Level Section A QuestionsPortgas D AceNo ratings yet