Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Handouts 02a Market
Uploaded by
gugercin80Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Handouts 02a Market
Uploaded by
gugercin80Copyright:
Available Formats
dr Adrian Solek, Department of Microeconomics, Cracow University of Economics
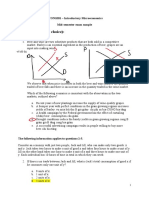
1. Analyze the graph below and fill in the blanks: D S P Q #
g) Hamburgers become more popular.
h) Scientific research proves that eating
beef can be hazardous.
i) Forage for cows gets more expensive.
j) Lower tariffs increase the inflow of
beef from abroad.
k) The price of pork falls.
l) Many butcheries go bankrupt.
a) If buyers want to purchase 2 units of the good, the highest
price they want to pay is $____ per unit.
b) At the price $16, buyers want to purchase ____ units. 1 2
c) The lowest price that would induce sellers to offer 4 units
of the good in the market equals $____ per unit.
d) At the price equal to $12 sellers offer ____ units.
e) At the price equal to $____ per unit the quantity demanded
of the good is equal to the quantity supplied, and at this
price ____ units are exchanged between buyers and sellers.
f) For the quantity equal to 8 units the highest price acceptable
for buyers is $____ and the lowest price acceptable for
sellers is $____.
3 4
g) At the price of $20, there is a _________ in this market; its
size is equal to _____ units. 4. The demand and supply functions for three goods have been
h) If the price is $12, there is a ________ equal to _____ units. estimated. Find the equilibrium price and quantity in each mar-
ket. What is the suppliers’ revenue from sales? How much will
2. Determine whether each of the following factors has a direct the buyers spend on the goods?
influence on demand or supply of a consumer good in the market: a) demand: Q = –2P + 40, supply: Q = 4P – 20;
a) the price of substitutes, e) the price of raw materials, b) demand: P = –0.1Q + 11, supply: P = 0.2Q + 2;
b) buyers’ tastes, f) buyers’ incomes, c) demand: P = 0.04Q2 – 3.2Q + 66,
c) the productivity of g) the technology of production, supply: P = 0.04Q2 + 0.8Q + 6, for 0 ≤ Q ≤ 40.
workers, h) the number of buyers,
d) the price of comple- i) the costs of production, 5. Suppose a severe drought hit the sugarcane crop. Predict
mentary goods, j) the number of sellers. how it would affect the equilibrium price and quantity on the mar-
kets of: sugarcane, sugar and honey. For the three markets
3. What will be the effect of the following events on the demand draw supply and demand curves to illustrate your answers.
for beef or the supply of beef in the national market? (a shift to What happened with: demand, supply, quantity demanded and
the left, right or no shift) Will the equilibrium price and quantity quantity supplied in the markets of the 3 goods? Indicate the
rise or fall? (Assume typical slopes of demand and supply curves). changes in the table below.
Indicate the number (#) of the graph corresponding to each event.
sugarcane sugar honey
effect on:
event #
D S P Q
a) More people become vegetarian.
b) Profits of butcheries decrease.
c) Strikes in butcheries.
d) Consumers expect the price of beef
to rise soon.
e) Inflation rate increases, causing real quantity quantity
good demand supply price
incomes of consumers to drop. demanded supplied
f) A new technology is implemented, sugarcane
allowing to produce beef in a lab, sugar
using stem cells, at a low cost. honey
6. Let’s assume coffee and tea are substitutes for consumers. c) The government buys excess milk that has not been pur-
What happens in the markets of coffee and tea, when changes chased by consumers. The size of the intervention storage
of labour regulations in South America (such as an increase in is ____ thousand litres and the government expenditure on
wages) raise the costs of production and decrease the crop of milk is ____ thousand zł.
coffee? Which curves, if any, shift: demand or supply? Is it a d) If the price floor were 1.75 zł, _____ thousand litres would
change of demand, quantity demanded, supply or quantity sup- be sold at the price of ____ zł. Would the intervention stor-
plied? Draw demand and supply curves in the two markets. age be necessary in such a case? ______
before the changes after the changes 10. The demand for wheat is: QD = –0.5P + 1200 and the supply:
market of:
P Q P Q QS = 2P – 300 (in tons).
coffee 20 50 30 30 a) Calculate the price of wheat in a free market and how many
tons will be purchased. P = _____, Q = _____
tea 10 40 15 50
b) As incomes of farmers are considered insufficient, the gov-
coffee tea ernment set a price floor for wheat equal to $700 in order
to support wheat producers. Find the quantity demanded
and the quantity supplied at this price: QD = _____, QS =
= _____. What will be the effect of such an intervention?
______________ Calculate its size: _____
c) Doctors published results of research saying that wheat
bread is very good for health. As a result the demand curve
shifted to the right and is given by: QD = –0.5P + 1700. Find
the new equilibrium point. P1 = _____, Q1 = _____
d) Is it necessary to maintain the price floor in the market
7. In summer people buy more apples and also spend more time
now? Explain. __________________________________
in holiday resorts than during winter. Why does the price of apples
fall in summer but the accommodation rates in the resorts go up?
11. In a certain city the demand and supply curves in the market
of commercial space rental are: QD = –30P + 250,000 and
8. Which of the following events might cause an increase in price
QS = 20P – 100,000, respectively (quantities in m2).
in the real estate market?
a) Find the equilibrium price and quantity.
a) investments in the construction industry decreased,
b) The local authorities set a price ceiling of 6500 zł per 1 m2.
b) it is easier to get a housing loan in a bank,
What will be the effect of such an intervention and how big
c) buyers expect the prices of houses will fall soon,
will it be?
d) interest rates on housing loans in banks increase,
c) In the long run the price ceiling will cause the supply to
e) construction materials get more expensive.
change. Will it rise or fall and why?
d) The new supply curve is: Q = 20P – 110,000. What hap-
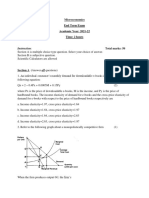
9. The graph shows the milk market (quantity is measured in
pens in the market now?
thousands of litres daily, price – in złotys per litre).
12. Predict effects of the following events in the market of private
universities and show them in graphs:
a) setting a price ceiling for tuition fees below the equilibrium
level,
b) increasing costs of employing professors,
c) reduction of income tax for students enrolled in private uni-
versities,
d) government subsidies for private universities.
price in zł/l
a) b)
c) d)
quantity in thousands of litres
a) In a free market the price of milk is ____ zł, the quantity
actually sold and bought is ____ thousand litres, and the
buyers’ expenditure on milk is ____ thousand zł.
b) The government introduced a price floor at 2.50 zł to pro-
tect the interests of ___________. At this price the quantity
demanded is ____ thousand litres, the quantity supplied is
____ thousand litres, and ____ thousand litres will actually
be sold. © Adrian Solek
You might also like
- Httpslearn Eu Central 1 Prod Fleet02 Xythos - Content.blackboardcdn - Com63ce84988f7ea231535x Blackboard S3 Bucket Learn Eu CeDocument10 pagesHttpslearn Eu Central 1 Prod Fleet02 Xythos - Content.blackboardcdn - Com63ce84988f7ea231535x Blackboard S3 Bucket Learn Eu CeAbdullah AlaamNo ratings yet
- The Economic Theory of Price Indices: Two Essays on the Effects of Taste, Quality, and Technological ChangeFrom EverandThe Economic Theory of Price Indices: Two Essays on the Effects of Taste, Quality, and Technological ChangeNo ratings yet
- UNIT II Exercises SolutionsDocument8 pagesUNIT II Exercises Solutionsvajra1 1999No ratings yet
- HW3Document2 pagesHW3Nakshatra SharmaNo ratings yet
- Mid-Sem Exam SampleDocument5 pagesMid-Sem Exam SampleMinh NgọcNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Questions On Qualitative and Quantitative Demand and Supply AnalysisDocument5 pagesTutorial Questions On Qualitative and Quantitative Demand and Supply AnalysisWise TetteyNo ratings yet
- Midterm1 2019 FormaDocument10 pagesMidterm1 2019 FormaJaures AyumbaNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument69 pagesEconomicsNikithaNo ratings yet
- ECON 201 - Problem Set 1Document5 pagesECON 201 - Problem Set 1KemalNo ratings yet
- Ugbs 201 T1Document5 pagesUgbs 201 T1richmannkansahNo ratings yet
- Mid-Sem Exam SampleDocument4 pagesMid-Sem Exam Samplephuong linh nguyenNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions ECONOMICSDocument3 pagesMultiple Choice Questions ECONOMICSubaidNo ratings yet
- Solution Excel 2DDocument6 pagesSolution Excel 2DSooHan MoonNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document3 pagesAssignment 3bluestacks3874No ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document3 pagesTutorial 5YejiNo ratings yet
- Homework For Exam Preparation - 1Document2 pagesHomework For Exam Preparation - 1Abc AbcNo ratings yet
- CH 4 3 Market System Demand SupplyDocument9 pagesCH 4 3 Market System Demand SupplyCollin LemireNo ratings yet
- Econs Past QuaestionsDocument50 pagesEcons Past QuaestionsYaw AcheampongNo ratings yet
- Imi611s - Intermediate Microeconomics - 2ND Opp - July 2019Document5 pagesImi611s - Intermediate Microeconomics - 2ND Opp - July 2019Smart Academic solutionsNo ratings yet
- Answer-Assignment Two, Essentials-Spring 2023Document4 pagesAnswer-Assignment Two, Essentials-Spring 2023Mostafa ElzanklonyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document5 pagesChapter 2Anh Thu VuNo ratings yet
- ME CH 2 Tutorial ProblemsDocument4 pagesME CH 2 Tutorial ProblemsTabassum AkhtarNo ratings yet
- 45c44f532fd2e65ebbdbe19228c548b8Document13 pages45c44f532fd2e65ebbdbe19228c548b8xinyiNo ratings yet
- Quiz DemandSupply (2019)Document4 pagesQuiz DemandSupply (2019)Trúc Duyên Huỳnh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- CA2 Indicative SolutionsDocument4 pagesCA2 Indicative SolutionsAkshat AnandNo ratings yet
- Document 1Document7 pagesDocument 1madihaadnan1No ratings yet
- Exercises Lecture 2Document13 pagesExercises Lecture 2Bus. Man - 2008-2011100% (1)
- MACROECONOMICS: TEST 1 REVIEWDocument4 pagesMACROECONOMICS: TEST 1 REVIEWHenil BhalaniNo ratings yet
- ECO 3108 Tutorial: Supply and Demand AnalysisDocument5 pagesECO 3108 Tutorial: Supply and Demand AnalysisLEE SHXIA YAN MoeNo ratings yet
- BS 110 Assignment 1Document4 pagesBS 110 Assignment 1Mario Rioux JnrNo ratings yet
- Eco 2Document10 pagesEco 2mh2358502No ratings yet
- Microeconomics End Term Exam ReviewDocument7 pagesMicroeconomics End Term Exam ReviewKartik GurmuleNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document6 pagesProblem Set 1Sudisha DasNo ratings yet
- Due: September 24, 2021 Multiple Choice (1 Point Each)Document2 pagesDue: September 24, 2021 Multiple Choice (1 Point Each)A FergNo ratings yet
- SEO-OPTIMIZED TITLE FOR PAPER 1 EXAMDocument5 pagesSEO-OPTIMIZED TITLE FOR PAPER 1 EXAMnisarg_No ratings yet
- MICROECONOMICS PROBLEM SET 2 SOLVEDDocument8 pagesMICROECONOMICS PROBLEM SET 2 SOLVEDThăng Nguyễn BáNo ratings yet
- ECON 205 Chapters 3 & 4 Practice QuestionsDocument4 pagesECON 205 Chapters 3 & 4 Practice Questionskely wilsonNo ratings yet
- Ex 4Document2 pagesEx 4binambissanNo ratings yet
- Imi611s-Intermediate Microeconomics-1st Opp-June 2022Document7 pagesImi611s-Intermediate Microeconomics-1st Opp-June 2022Smart Academic solutionsNo ratings yet
- Ae LM 2ND Quarter FinalDocument6 pagesAe LM 2ND Quarter FinalRhystle Ann BalcitaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document6 pagesAssignment 1Mayank KumarNo ratings yet
- Econ 1b03 Midterm1 2009wDocument11 pagesEcon 1b03 Midterm1 2009wexamkillerNo ratings yet
- ECO101: Introduction To Economics (Summer Semester, 2019) Tutorial Problem Set - 01Document3 pagesECO101: Introduction To Economics (Summer Semester, 2019) Tutorial Problem Set - 01Shubham KumarNo ratings yet
- Version ADocument15 pagesVersion AGrace LeeNo ratings yet
- Microeconomic Principles SPRING 2001 MIDTERM ONE - AnswersDocument13 pagesMicroeconomic Principles SPRING 2001 MIDTERM ONE - AnswersirsaNo ratings yet
- GiẠI Quiz VI MãDocument25 pagesGiẠI Quiz VI MãhaNo ratings yet
- Brandeis Tjniversity Department of EconomicsDocument5 pagesBrandeis Tjniversity Department of EconomicsPeesashizNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics Sample QuestionsDocument10 pagesMicroeconomics Sample QuestionsFarzana Alamgir0% (1)
- Economics G2 Topic2 v3Document16 pagesEconomics G2 Topic2 v3Darshilla Rive ChandramNo ratings yet
- Supply and Demand Problem Sets EconomicsDocument5 pagesSupply and Demand Problem Sets Economicsjesse jamesNo ratings yet
- University of Santo Tomas Elective Eit / PeDocument6 pagesUniversity of Santo Tomas Elective Eit / PeBella AdrianaNo ratings yet
- 2020 Micro Test 3Document5 pages2020 Micro Test 3Bornface WiseNo ratings yet
- Online Assessment For ECO120 Principles of Economics (Oct 2021 To Feb 2022)Document9 pagesOnline Assessment For ECO120 Principles of Economics (Oct 2021 To Feb 2022)AIN ZULLAIKHANo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2Khalid233No ratings yet
- Nama: NPM: Assignment For 2nd Week Meeting (Print Out and Handwrite Your Answer On The Paper)Document3 pagesNama: NPM: Assignment For 2nd Week Meeting (Print Out and Handwrite Your Answer On The Paper)Ameera YasminNo ratings yet
- ECON102 Specimen Exam PaperDocument11 pagesECON102 Specimen Exam PaperEduardoNo ratings yet
- Problem SetDocument6 pagesProblem Setchandel08No ratings yet
- ECO2144 Micro Theory I 2007 Final ExamDocument5 pagesECO2144 Micro Theory I 2007 Final ExamTeachers OnlineNo ratings yet
- University: BotswanaDocument5 pagesUniversity: BotswanaThabo ChuchuNo ratings yet
- Handouts 05 ConsumerDocument2 pagesHandouts 05 Consumergugercin80No ratings yet
- 2022 Lecture Section 2 Systems of Linear EquationsDocument8 pages2022 Lecture Section 2 Systems of Linear EquationsДаша ЗубкоNo ratings yet
- 2023 Classes 1-3 MatricesDocument3 pages2023 Classes 1-3 Matricesgugercin80No ratings yet
- 2023 Lecture Section 1 MatricesDocument12 pages2023 Lecture Section 1 Matricesgugercin80No ratings yet
- Digital Marketing Scope and Career OpportunitiesDocument15 pagesDigital Marketing Scope and Career Opportunitiesarunmittal1985No ratings yet
- SST Holiday Homework 2022Document14 pagesSST Holiday Homework 2022Bunny XingqiuNo ratings yet
- Additional InformationDocument6 pagesAdditional InformationBabylyn NavarroNo ratings yet
- Board MeetingDocument2 pagesBoard MeetingNyamat GuronNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3Document4 pagesQuiz 3ErionNo ratings yet
- CSEC Social Studies January 2012 P2Document6 pagesCSEC Social Studies January 2012 P2Courtney mcintoshNo ratings yet
- Brand Management CH 7 Question AnswerDocument2 pagesBrand Management CH 7 Question AnswerFerdows Abid ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Post Keynesian Monetary Economics PDFDocument185 pagesPost Keynesian Monetary Economics PDFadeelali849714No ratings yet
- Financial ManagementDocument13 pagesFinancial ManagementWajidSyedNo ratings yet
- Chart Pattern Flash CardsDocument10 pagesChart Pattern Flash Cardsmexybaby100% (2)
- Decision Sheet - Aqualisa QuartzDocument1 pageDecision Sheet - Aqualisa QuartzVince Lepcha100% (1)
- Presented By: Group 8 Vaibhav Arora Meghna Das Sanya Sachdeva Achala Mishra Nalin AggarwalDocument28 pagesPresented By: Group 8 Vaibhav Arora Meghna Das Sanya Sachdeva Achala Mishra Nalin AggarwalVaibhav AroraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document2 pagesChapter 3Ashwini PudasainiNo ratings yet
- Compound Financial Instrument ActivityDocument2 pagesCompound Financial Instrument ActivityJeanivyle CarmonaNo ratings yet
- Retail Management Assignment No#1Document6 pagesRetail Management Assignment No#1Rehab ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Business TaxationDocument5 pagesBusiness TaxationMajoy BantocNo ratings yet
- E-Procurement Mind Map Shows Benefits for Natural Shaving Foam BusinessDocument4 pagesE-Procurement Mind Map Shows Benefits for Natural Shaving Foam Businessjuan carlos ruiz molinaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Fair Value Gap FVG-1Document4 pagesLesson 4 Fair Value Gap FVG-1Nguyễn Trường100% (5)
- Intermediate Market LeaderDocument27 pagesIntermediate Market LeaderRichard V100% (1)
- For Each of The Following Scenarios Discuss Whether Profit OpportunitiesDocument1 pageFor Each of The Following Scenarios Discuss Whether Profit Opportunitiestrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- My Project On Big Bazaar FINALDocument101 pagesMy Project On Big Bazaar FINALPramod Kumar BarikNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Yield CurveDocument179 pagesUnderstanding The Yield Curverpcampbell100% (2)
- Financial Viability of Sugar Factories in South GujaratDocument13 pagesFinancial Viability of Sugar Factories in South GujaratRishav DewanNo ratings yet
- Some Problems of Development Planning: Part - ViDocument29 pagesSome Problems of Development Planning: Part - ViKamal SinghNo ratings yet
- B009 Dhruvil Shah Wealth Management WGz0kGfcZbDocument5 pagesB009 Dhruvil Shah Wealth Management WGz0kGfcZbDhruvil ShahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Consolidated Financial Statements and Outside OwnershipDocument25 pagesChapter 4 - Consolidated Financial Statements and Outside OwnershipBLe BerNo ratings yet
- Pas 16-Property, Plant, & Equipment 1. Objective, Scope, and Definition MeasurementDocument4 pagesPas 16-Property, Plant, & Equipment 1. Objective, Scope, and Definition Measurementmarilyn wallaceNo ratings yet
- SFMDocument260 pagesSFMB GANAPATHY100% (1)
- UOSL104 Fundamentals of Accounting final exam questionsDocument3 pagesUOSL104 Fundamentals of Accounting final exam questionsOnurup RahmanNo ratings yet
- Aron Smith: - Head of Marketing - CoursesDocument2 pagesAron Smith: - Head of Marketing - CoursesConstantino Mario PolypathelliNo ratings yet