Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tenants Pathology-Update Uploads 329 SEBASTIAN Roche ePoster+FINAL
Uploaded by
sanderssebastianOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tenants Pathology-Update Uploads 329 SEBASTIAN Roche ePoster+FINAL
Uploaded by
sanderssebastianCopyright:
Available Formats
Hypertonic Saline Dilution: A Simple Technique to Offset Interference of IgM
Paraproteins in Uric Acid Analysis
Sanders Sebastian1, Ashley Teo2, Alan McNeil2, Christina Trambas1
1Department of Biochemistry, St Vincent’s Hospital Melbourne, Victoria, Australia; 2Department of
Biochemistry, Dorevitch Pathology, Victoria, Australia.
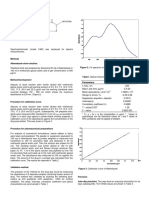
Background Results
The presence of paraproteins, particularly IgM, can cause In all ten samples with falsely low uric acid results, dilution in
interference in many biochemical assays, including uric acid. For hypertonic saline restored the reaction curves to normal
some paraproteins, interference may derive from their propensity appearance (Figure 1B) and increased the uric acid results (Table
to precipitate, depending on the ionic strength of the assay 1). In contrast, dilution of affected samples in isotonic saline or
reaction. Irrespective of the mechanism, the net result of distilled water had no effect on uric acid results or the reaction
interference is an inaccurate result, which may confound clinical curve morphology (not shown).
decision making and lead to adverse events for the patient1-4.
Dilution of control samples with hypertonic saline had no
appreciable effect on reaction curves or uric acid measurement
(Figure 1C-D; Figure 2 and Table 2).
Aim
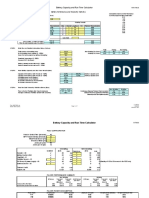
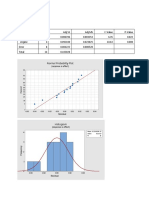
Figure 2 Hypertonic saline has little effect on uric acid
To determine whether increasing the sample ionic strength with measurement in the absence of IgM paraprotein interference
hypertonic saline can overcome IgM paraprotein interference in Method comparison: Neat Results, Post hypertonic dilution v6 .15
the Siemens Atellica uric acid assay. Sheet1 A1:I21
Fi l ter: No fi l ter
La st upda ted 19 Ja nua ry 2023 a t 11:31 by Sa nders Seba stia n
Descriptives
Di fference pl ot
0.01
Post hypertonic dilution -Neat Results (mmol/L)
0.005
Methods 0
-0.005
Mean
(-0.0 113)
-0.01
95% L oA
(-0.0 273 to 0.0047)
-0.015
The Siemens Atellica uric acid assay is based on the Fossati -0.02
-0.025
enzymatic reaction, which uses uricase with a Trinder-like end -0.03
0.15 0.2 0.25 0.3 0.35 0.4 0.45 0.5
point. The absorbance of the coloured complex is measured at (Neat Res ul ts + Pos t hypertoni c di l uti on) / 2 (mmol /L)
545/694 nm5. Paraprotein interference with this assay can cause Table 2 Hypertonic saline has little effect on uric acid
falsely low uric acid results. measurement in the absence of IgM paraprotein interference
Neat Results (mmol/L) Post hypertonic dilution (mmol/L)
Interference in ten suspiciously low uric acid results from patients 0.2 0.18
with IgM paraproteins was confirmed by demonstration of 0.44 0.43
0.25 0.23
abnormal reaction curves (Figure 1A). After 1 in 3 dilution of the 0.19 0.19
samples with 18% saline, uric acid was re-measured and the 0.47 0.45
0.23 0.22
reaction curves re-assessed. Samples with normal uric acid
0.19 0.18
reaction curves were employed as controls. 0.25 0.25
0.36 0.35
0.36 0.35
0.36 0.34
Figure 1 Hypertonic saline restores uric acid reaction curve 0.26 0.25
0.45 0.42
morphology in samples with IgM paraprotein interference 0.3 0.3
A. Abnormal reaction curve in a sample B. Normal reaction curve on dilution of 0.39 0.38
with IgM paraprotein interference affected sample in hypertonic saline 0.28 0.27
0.5 0.49
0.18 0.18
0.42 0.4
0.4 0.39
Discussion
Our data suggests that increasing the ionic strength of a sample
with hypertonic saline can mitigate the effect of IgM paraprotein
C. Normal reaction curve in a sample D. Normal reaction curve on dilution of interference on the Siemens Atellica uric acid assay. This was
without IgM paraprotein interference unaffected sample in hypertonic saline
demonstrated by the “normalisation” of reaction curves upon
dilution of affected samples with hypertonic saline. In tandem
with restored reaction curves, uric acid results also increased.
Further investigation using an interference-resistant reference
method is required to determine whether hypertonic saline
dilution can completely remove IgM paraprotein interference and
restore accurate uric acid measurement. In the interim, our study
suggests that hypertonic saline dilution is a useful technique to
Table 1 Hypertonic saline reverses spuriously low uric acid establish the presence of paraprotein interference in the Siemens
results in samples showing IgM paraprotein interference Atellica uric acid assay. It is also possible that other paraprotein
related interference may be amenable to this technique.
Neat Results (mmol/L) Post Hypertonic dilution (mmol/L)
<0.03 0.25
0.04 0.26
<0.03 0.24
References
0.03 0.26
1. Langman LJ, Allen LC, Romaschin AD. Interference of IgM paraproteins in the Olympus AU800 uric acid assay. Clin
0.03 0.3 Biochem. 1998; 31:517-21
2. Savory DJ, Pearce CJ. Paraprotein interference causing pseudohyperphosphataemia: evaluation of an improved
0.1 0.31 methodology. Ann Clin Biochem. 1995; 32 :498-501
<0.03 0.36 3. Yang Y, Howanitz PJ et al.,. Paraproteins are a common cause of interferences with automated chemistry
methods. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2008; 132:217-23
0.05 0.26 4. Choy KW, Wijeratne N, et al.,. An undetectable prealbumin measurement led to a diagnosis of monoclonal
gammopathy: Two cases of spurious results in the setting of paraproteinaemia. Pathology. 2018; 50: 767-9
<0.03 0.1 5. Uric Acid Advia Chemistry XPT REF 10699686_EN Rev. G, 2016-07. Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics, Erlangen,
Germany. 2016
0.1 0.23
You might also like
- EFIT Int DVD Heron Wilson Islands FINALDocument4 pagesEFIT Int DVD Heron Wilson Islands FINALmaria catalina corrales rojasNo ratings yet
- Facilitating Learning Child and Adolescent Development LectureDocument25 pagesFacilitating Learning Child and Adolescent Development LectureIrish Mendoza Seda100% (4)
- Analysis of Cyclic Voltammetry DataDocument7 pagesAnalysis of Cyclic Voltammetry DataSudip SinhaNo ratings yet
- Este El Correlograma Del Log Pib: 0 10 20 30 40 Lag 0 10 20 30 40 LagDocument1 pageEste El Correlograma Del Log Pib: 0 10 20 30 40 Lag 0 10 20 30 40 Lagjimena pascual vargasNo ratings yet
- Alcohol-Tolerance ChartDocument1 pageAlcohol-Tolerance ChartPrabin ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopic Analysis For Biological Samples: Towards in Situ Sample Analysis of Body FluidsDocument18 pagesSpectroscopic Analysis For Biological Samples: Towards in Situ Sample Analysis of Body Fluidslilong10No ratings yet
- Azithromycin at Low Nanogram LevelsDocument2 pagesAzithromycin at Low Nanogram LevelsDewi WulandhariNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lab - Enzyme Activity (Corpuz, R)Document7 pagesBiochem Lab - Enzyme Activity (Corpuz, R)Reynand MaelNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Behaviour of Tantalum in Sodium Hydroxide SolutionsDocument6 pagesCorrosion Behaviour of Tantalum in Sodium Hydroxide SolutionsRathawit SingpanjanateeNo ratings yet
- Amperometric Biosensor For Oxalate Determination IDocument13 pagesAmperometric Biosensor For Oxalate Determination IEswaramoorthy K VNo ratings yet
- Chem Kinetics NotesDocument24 pagesChem Kinetics NotesMontyNo ratings yet
- CarryoverDocument3 pagesCarryoverRiad ManamanniNo ratings yet
- Explaining Cronbach's AlphaDocument15 pagesExplaining Cronbach's Alphagulshan kumar aroraNo ratings yet
- CVS - Cyclic Voltammetric Stripping With Metrohm: CVS in The Laboratory CVS Atline Systems CVS Online SystemsDocument16 pagesCVS - Cyclic Voltammetric Stripping With Metrohm: CVS in The Laboratory CVS Atline Systems CVS Online SystemsEduardo LimaNo ratings yet
- Book 7Document2 pagesBook 7ppathak2022No ratings yet
- Absorbance Versus Concentration of P-NitrophenolDocument6 pagesAbsorbance Versus Concentration of P-NitrophenolNurul HusnaNo ratings yet
- Páginas Desdecorre17.09cartelessantorini-1Document1 pagePáginas Desdecorre17.09cartelessantorini-1LOLA CORZONo ratings yet
- Analysis of Volatile Toxic Substances Using Headspace GC/MS Part.2 - Cyanide and AzideDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Volatile Toxic Substances Using Headspace GC/MS Part.2 - Cyanide and AzideBilal KilaniNo ratings yet
- Trials Naoh (ML) HCL Normality Naoh (N)Document1 pageTrials Naoh (ML) HCL Normality Naoh (N)AizernerNo ratings yet
- Carryover ReportDocument3 pagesCarryover ReportRiad ManamanniNo ratings yet
- Project Execution Plan VS Actual Progress 24.01Document1 pageProject Execution Plan VS Actual Progress 24.01Mouliska Citra PratamaNo ratings yet
- Chemlab - Module 11Document2 pagesChemlab - Module 11anthanhvuproNo ratings yet
- Nei Characterization of Radioctive Contamination Using Geostatistics Cea GeovariancesDocument3 pagesNei Characterization of Radioctive Contamination Using Geostatistics Cea Geovarianceshassan mohammedNo ratings yet
- Albendazol 3Document1 pageAlbendazol 3Chatgpt goaNo ratings yet
- Gambar RencanaDocument5 pagesGambar RencanarezaNo ratings yet
- Fakulti Kejuruteraan Kimia Chemical Process Control (CPE501) Universiti Teknologi MaraDocument10 pagesFakulti Kejuruteraan Kimia Chemical Process Control (CPE501) Universiti Teknologi MaraSh. Hannan AinaNo ratings yet
- Battery (New) Run Time CalculatorDocument7 pagesBattery (New) Run Time CalculatorJose Mata RamcharanNo ratings yet
- 1 - Tut Quantitative Method of AnalysisDocument5 pages1 - Tut Quantitative Method of AnalysisAyandaNo ratings yet
- Results and DiscussionDocument4 pagesResults and DiscussionEdgar John Pagulayan100% (1)
- The Influence of Thruster Dynamics On Underwater Vehicle Behavior and Their Incorporation Into Control System DesignDocument12 pagesThe Influence of Thruster Dynamics On Underwater Vehicle Behavior and Their Incorporation Into Control System DesignCamila Helena OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Espectro de Diseño Cfe 2015: 0 R Ctor de Importancia R 0Document10 pagesEspectro de Diseño Cfe 2015: 0 R Ctor de Importancia R 0Ernesto Feliciano Basurto GalvezNo ratings yet
- PTH Intrap RUO 2019-12 DxI To DxIDocument2 pagesPTH Intrap RUO 2019-12 DxI To DxIzaid atcNo ratings yet
- JACS Cloruro Terz-Butile SolvolisiDocument8 pagesJACS Cloruro Terz-Butile SolvolisiGiacomo BonomiNo ratings yet
- Industria de Marmore Analise Estatistica de Risco QuimicoDocument1 pageIndustria de Marmore Analise Estatistica de Risco QuimicoGuilherme VimercatiNo ratings yet
- A Good Feature Extractor Is All You Need For Weakly Supervised Learning in HistopathologyDocument25 pagesA Good Feature Extractor Is All You Need For Weakly Supervised Learning in Histopathologymeyina4311No ratings yet
- Carryover ReportDocument3 pagesCarryover ReportRiad ManamanniNo ratings yet
- Static MixerDocument2 pagesStatic Mixerjemakl1568No ratings yet
- Alta Y Gestion de Referencias: Precio Codigo Producto Familia Proveedor IVA +ivaDocument134 pagesAlta Y Gestion de Referencias: Precio Codigo Producto Familia Proveedor IVA +ivaSixto Garcia SerranoNo ratings yet
- Ja 00420 A 034Document3 pagesJa 00420 A 034James TakeNo ratings yet
- Mecklenburg Oslo 2010 PDFDocument73 pagesMecklenburg Oslo 2010 PDFmackerelfish0% (1)
- Expression, Purification, and Testing of His Tag Cleaved Crabp1Document20 pagesExpression, Purification, and Testing of His Tag Cleaved Crabp1api-339904986No ratings yet
- Field Notes GuideDocument12 pagesField Notes GuideRachelleNo ratings yet
- Report TDPP Asi-Florfencol 20%Document23 pagesReport TDPP Asi-Florfencol 20%عارف حسینNo ratings yet
- Analysis of VarianceDocument4 pagesAnalysis of VarianceBablu KumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 10Document4 pagesAssignment 4 10Bablu KumarNo ratings yet
- AOCS - CD - 3d - 63 Acid ValueDocument3 pagesAOCS - CD - 3d - 63 Acid Valueshirley martinez padilla100% (4)
- Effect of Temperature On Enzyme RateDocument3 pagesEffect of Temperature On Enzyme RateJacob TremblayNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Enzyme KineticsDocument5 pagesLab Report Enzyme KineticsABEGAIL JOY MAURICIO LAPITANNo ratings yet
- EN LIH BAOSR6x166 USDocument3 pagesEN LIH BAOSR6x166 USAsma Ben AbdelazizNo ratings yet
- Astm E350 95pdf PDFDocument58 pagesAstm E350 95pdf PDFJuliaBundaMumtazNo ratings yet
- PerspectivaDocument1 pagePerspectivaCarolina HernandezNo ratings yet
- Big Data AssignmentDocument14 pagesBig Data AssignmentAlen AugustineNo ratings yet
- INE-432 Final Project: Faculty of EngineeringDocument10 pagesINE-432 Final Project: Faculty of Engineeringعبدالله سعيدNo ratings yet
- CV LabDocument9 pagesCV LabtworedpartyhatsNo ratings yet
- Report TDPP Asi-Enrofloxacin 100 PDFDocument23 pagesReport TDPP Asi-Enrofloxacin 100 PDFعارف حسینNo ratings yet
- Lkbsis54 Sodium-30335Document2 pagesLkbsis54 Sodium-30335nmakrygNo ratings yet
- Kamar Kerja+Kamar Tidur +3.50 Kamar Kerja+Kamar Tidur +3.50: SMKN 3 JombangDocument1 pageKamar Kerja+Kamar Tidur +3.50 Kamar Kerja+Kamar Tidur +3.50: SMKN 3 JombangBagus SadewoNo ratings yet
- Uji Floating Time Anova + HomogenDocument2 pagesUji Floating Time Anova + HomogenWildan RNo ratings yet
- Fatigue Alcohol and Performance ImpairmentDocument3 pagesFatigue Alcohol and Performance ImpairmentmiloNo ratings yet
- LP Penyakit OktoberDocument12 pagesLP Penyakit OktoberAzis MolaNo ratings yet
- ALTIUS - Unit Test # 2Document11 pagesALTIUS - Unit Test # 2Avrajoty RoyNo ratings yet
- To Err Is Human To Forgive Is Divine EssayDocument4 pagesTo Err Is Human To Forgive Is Divine Essayibnorvbaf100% (2)
- Effect of Bacopamine, A Polyherbal Formulation On Learning and MemoryDocument6 pagesEffect of Bacopamine, A Polyherbal Formulation On Learning and MemorynitishkjhaNo ratings yet
- Final Assesment Agr519 (E-Poster)Document1 pageFinal Assesment Agr519 (E-Poster)Noor Syazwan NasirNo ratings yet
- General Biology: Transport Mechanism That Contributes To The Survival of The CellDocument16 pagesGeneral Biology: Transport Mechanism That Contributes To The Survival of The Cell할에이필No ratings yet
- DNA ExtractionDocument11 pagesDNA ExtractionHoor Ul Ain RounaqNo ratings yet
- # No. Nomor Induk Kependudukan InisialDocument32 pages# No. Nomor Induk Kependudukan Inisiallapak jauhNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Vestibular System and Equilibrium: Dr. Mohommed Moizuddin Khan DR Beenish MukhtarDocument30 pagesPhysiology of Vestibular System and Equilibrium: Dr. Mohommed Moizuddin Khan DR Beenish MukhtarArdiya OktamaNo ratings yet
- Plant Anatomy Three Mark QuestionsDocument6 pagesPlant Anatomy Three Mark QuestionsSriHortpkmNo ratings yet
- Book JewsDocument230 pagesBook JewsFred Duarte CaldeiraNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Comprehensive Perinatal and Pediatric Respiratory Care 4th Edition by Whitaker Isbn 10 1439059438 Isbn 13 9781439059432Document7 pagesTest Bank For Comprehensive Perinatal and Pediatric Respiratory Care 4th Edition by Whitaker Isbn 10 1439059438 Isbn 13 9781439059432trangdatif0No ratings yet
- Cypermethrin: Environmental Health Criteria 82Document159 pagesCypermethrin: Environmental Health Criteria 82AshishNo ratings yet
- CH 18 Endocrine3Document65 pagesCH 18 Endocrine3adamaditya666No ratings yet
- Canine Viral Enteritis: Nipah and Hendra Virus InfectionsDocument9 pagesCanine Viral Enteritis: Nipah and Hendra Virus InfectionsAnnahi BcNo ratings yet
- Application of Artificial Intelligence in Medical FieldDocument8 pagesApplication of Artificial Intelligence in Medical FieldShree krishana ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Ecotourism Is An OxymoronDocument23 pagesEcotourism Is An OxymoronSuzanne NievaartNo ratings yet
- 4-D Printing Technology: Department of Mechanical Engineering K.V.G. College of Engineering Sullia, (D.K.) 574327Document12 pages4-D Printing Technology: Department of Mechanical Engineering K.V.G. College of Engineering Sullia, (D.K.) 574327JECINJOHNNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science A Global Concern 15Th Edition William Cunningham Full ChapterDocument51 pagesEnvironmental Science A Global Concern 15Th Edition William Cunningham Full Chapterpatricia.danner760100% (9)
- Toxic ChemicalsDocument6 pagesToxic ChemicalsSabina Lucia GrapiniNo ratings yet
- COT Presentation Grade 4 Q2 ScienceDocument39 pagesCOT Presentation Grade 4 Q2 ScienceJonathan BernardoNo ratings yet
- Yuca Fermentada de BrasilDocument7 pagesYuca Fermentada de BrasilLuis Enrique Ortega SalinasNo ratings yet
- He ModuleDocument24 pagesHe ModuleFrancisco C. ArianNo ratings yet
- Opening Remarks Thesis DefenseDocument5 pagesOpening Remarks Thesis Defensednr3krf8100% (2)
- Amine Degradation in CO2 Service - HuntsmanDocument16 pagesAmine Degradation in CO2 Service - Huntsmanvictor nuñezNo ratings yet
- 9 Science Sample ApaperDocument3 pages9 Science Sample ApapersameerroushanNo ratings yet
- The Electricity of Touch: Detection and Measurement of Cardiac Energy Exchange Between PeopleDocument14 pagesThe Electricity of Touch: Detection and Measurement of Cardiac Energy Exchange Between PeopleIvan RocaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of AF in CHFDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of AF in CHFBimaIndraNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics, Prosthetic & Orthotics BME 2205: Anatomical MovementDocument33 pagesBiomechanics, Prosthetic & Orthotics BME 2205: Anatomical Movementmorris loguyaNo ratings yet