Professional Documents
Culture Documents
COD 9 November
Uploaded by
rey_doctorOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
COD 9 November
Uploaded by
rey_doctorCopyright:
Available Formats
The patient came with decreased consciousness, had a complex condition where the patient had been short of
breath since 10 days and decreased consciousness, which was due to poor laboratory results, namely procalcitonin,
poor kidney function and electrolytes. Where we have to look for the decrease in consciousness due to what,
whether due to sepsis, uremic encephalopathy or electrolyte imbalance. And you have to know how to handle it
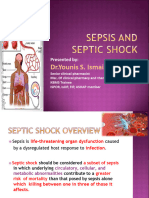
initially -------------------. Sepsis and septic shock are medical emergencies and should be treated immediately.
Resuscitation from sepsis hypoperfusion should be started with 30 ml/kg of IV crystalloid fluid within three hours.
Hemodynamic assessment including cardiac functions should be performed dynamically, and additional fluid use
should be guided by frequent reassessment of hemodynamic status, with the goal of maintaining a mean blood
pressure above 65 mmHg. If hemodynamic stability is not achieved with fluid resuscitation, vasopressor therapy
should be initiated. Norepinephrine is the first-choice vasopressor; vasopressin or epinephrine may be added.
microbiologic cultures should be performed. pathogens that cause pneumonia, including Streptococcus
pneumoniae, atypical bacteria and Gram-negative bacilli. Guidelines suggest the use of a β-lactam plus a macrolide,
β-lactam plus a fluoroquinolone or a fluoroquinolone alone as empirical treatment. Macrolide combinations showed
better outcomes.
Pasien datang dengan kondisi kesadaran menurun, mempunyai kondisi kompleks dimana pasien sesak nafas sejak 10
hari dan penurunan kesadaran, hal ini disebabkan oleh hasil laboratorium yang buruk yaitu prokalsitonin, fungsi
ginjal dan elektrolit yang buruk. Dimana kita harus mencari penurunan kesadaran karena apa, apakah karena sepsis,
uremic encephalopathy atau ketidakseimbangan elektrolit. Dan Anda harus tahu cara menanganinya sejak awal
-------------------. Sepsis dan syok septik merupakan keadaan darurat medis dan harus segera ditangani. Resusitasi dari
hipoperfusi sepsis harus dimulai dengan 30 ml/kg cairan kristaloid IV dalam waktu tiga jam. Penilaian hemodinamik
termasuk fungsi jantung harus dilakukan secara dinamis, dan penggunaan cairan tambahan harus dipandu oleh
penilaian ulang status hemodinamik secara berkala, dengan tujuan mempertahankan tekanan darah rata-rata di atas
65 mmHg. Jika stabilitas hemodinamik tidak tercapai dengan resusitasi cairan, terapi vasopresor harus dimulai.
Norepinefrin adalah vasopresor pilihan pertama; vasopresin atau epinefrin dapat ditambahkan. kultur mikrobiologi
harus dilakukan. patogen penyebab pneumonia, termasuk Streptococcus pneumoniae, bakteri atipikal, dan basil
Gram-negatif. Pedoman menyarankan penggunaan β-laktam ditambah makrolida, β-laktam ditambah fluoroquinolon
atau fluoroquinolone saja sebagai pengobatan empiris. Kombinasi makrolida menunjukkan hasil yang lebih baik.
bagaimana kita tahu pada pasien ini komplek terjadi, bagaimana penanganan yang terbaik bagi pasien ini
How do we know if this patient has a complex, what is the best treatment for this patient?
This patient has been consulted by IPD and why wasn't the suggestion for meropenen given? and what is the initial
management of sepsis?
You might also like
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA: Hypoglycemic StatesDocument41 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA: Hypoglycemic StatesTenzin LhanzeNo ratings yet
- MGT of D KetoacidosisDocument5 pagesMGT of D Ketoacidosisshabatat2002No ratings yet
- Approach To ShockDocument40 pagesApproach To ShockDivesh NaiduNo ratings yet
- Critical Care 123Document66 pagesCritical Care 123Mr.ShazNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument13 pagesAntibioticsVjfsyuiNo ratings yet
- MS Question With Rationales 2Document12 pagesMS Question With Rationales 2Tsuyoshi BangNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis PreeclampsiaDocument13 pagesDiagnosis Preeclampsiabipbip bipNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Emergencies in PicuDocument10 pagesEndocrine Emergencies in PicuDr.MohanNo ratings yet
- Urinary Catheter Placement For Feline ObstructionDocument6 pagesUrinary Catheter Placement For Feline ObstructionWilliam ChandlerNo ratings yet
- Surviving Sepsis GuidelinesDocument17 pagesSurviving Sepsis GuidelinesNabil RohaizatNo ratings yet
- Hyperosmolar Diabetic Non-Ketotic Coma, Hyperkalaemia and An Unusual Near Death ExperienceDocument7 pagesHyperosmolar Diabetic Non-Ketotic Coma, Hyperkalaemia and An Unusual Near Death ExperienceAnonymous nEQNlgbYQCNo ratings yet
- Sepsis Campaign: Oleh: Amalia Devi Pembimbing: Dr. Indri Savitri, SP.PDocument24 pagesSepsis Campaign: Oleh: Amalia Devi Pembimbing: Dr. Indri Savitri, SP.PAmalia DeviNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Fluid Volume Deficit R/T Active Fluid Loss (Increased Urine Output)Document9 pagesNursing Care Plan: Fluid Volume Deficit R/T Active Fluid Loss (Increased Urine Output)Gayu Patel100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan: Fluid Volume Deficit R/T Active Fluid Loss (Increased Urine Output)Document9 pagesNursing Care Plan: Fluid Volume Deficit R/T Active Fluid Loss (Increased Urine Output)ghellersNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Fluid Volume Deficit R/T Active Fluid Loss (Increased Urine Output)Document9 pagesNursing Care Plan: Fluid Volume Deficit R/T Active Fluid Loss (Increased Urine Output)Gayu Patel0% (1)
- Early Symptoms: Insidious Increase in Polydipsia and PolyuriaDocument3 pagesEarly Symptoms: Insidious Increase in Polydipsia and Polyuriabes3rkerNo ratings yet
- Penatalaksanaan StrokeDocument15 pagesPenatalaksanaan StrokerizeviNo ratings yet
- Clinical Evaluation Test Result Trends: DiagnosisDocument3 pagesClinical Evaluation Test Result Trends: DiagnosisStephen CrossNo ratings yet
- 3amali TR 2Document7 pages3amali TR 2Arsh KaiwanNo ratings yet
- Malignant Hyperthermia AlgorithmDocument1 pageMalignant Hyperthermia AlgorithmCesar David CaceresNo ratings yet
- Shock ManagementDocument17 pagesShock ManagementAmare EshetieNo ratings yet
- Case Study Multiple Organ Dysfunction and ShockDocument3 pagesCase Study Multiple Organ Dysfunction and ShockJrBong SemaneroNo ratings yet
- Diabetes EmergenciesDocument7 pagesDiabetes EmergenciesDr.Abdirahman DahirNo ratings yet
- IV FluidDocument28 pagesIV FluidZulfkar Latief QadrieNo ratings yet
- (A) (B) (C) (D) : (A) Primary Polydipsia Is Not The Answer Here Because in Primary PolydipsiaDocument1 page(A) (B) (C) (D) : (A) Primary Polydipsia Is Not The Answer Here Because in Primary PolydipsiaAbdul QuyyumNo ratings yet
- Chapter VDocument15 pagesChapter VJellou MacNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrest Due To Lymphocytic ColitisDocument4 pagesCardiac Arrest Due To Lymphocytic Colitisjhuzt4_facebook_343onlyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument9 pagesNursing Care PlanLura Xstilice B. Galinato100% (1)
- Hypovolemic Shock Case StudyDocument6 pagesHypovolemic Shock Case StudyJenn GallowayNo ratings yet
- Syok - Anzak Akbar Andin PangeDocument34 pagesSyok - Anzak Akbar Andin PangeannisazakirohNo ratings yet
- 10 CaritosDocument3 pages10 CaritosDARREN EDMARK100% (4)
- Adrenal CrisisDocument27 pagesAdrenal CrisissayednourNo ratings yet
- Chapter33Walker2015 PDFDocument12 pagesChapter33Walker2015 PDFMai AngelNo ratings yet
- Renal Emergency RevisiDocument103 pagesRenal Emergency Revisidesy f sarahNo ratings yet
- Sitti Munawarah (F1F1 12 045) Wa Ode Sarmimin (F1F1 12 045)Document6 pagesSitti Munawarah (F1F1 12 045) Wa Ode Sarmimin (F1F1 12 045)ChichiFauziyahNo ratings yet
- Septic ShockDocument35 pagesSeptic Shockphd0780No ratings yet
- MANAGEMENT of DkADocument10 pagesMANAGEMENT of DkAAli SafaaNo ratings yet
- Quizzes NCM116Document10 pagesQuizzes NCM116mendozajanice0601No ratings yet
- Sodium, and 350-500 Meq/L of Chloride. The Combined Effects of Serum Hyperosmolarity, Dehydration, and Acidosis Result in Increased Osmolarity in Brain Cells That ClinicallyDocument5 pagesSodium, and 350-500 Meq/L of Chloride. The Combined Effects of Serum Hyperosmolarity, Dehydration, and Acidosis Result in Increased Osmolarity in Brain Cells That ClinicallyMorgan Mitchell100% (10)
- Surviving Sepsis Campaign - NewDocument21 pagesSurviving Sepsis Campaign - NewIrfan SyakirNo ratings yet
- Joint British Diabetes Societies Inpatient Care Group - The Management of Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Adults - Pathway PosterDocument1 pageJoint British Diabetes Societies Inpatient Care Group - The Management of Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Adults - Pathway PosterAllison Nadine MarchandNo ratings yet
- NCP RiskDocument3 pagesNCP RiskMaricar Azolae MascualNo ratings yet
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument38 pagesDiabetic KetoacidosisEdelrose LapitanNo ratings yet
- CH 39 Anaesthesia and Diabetes MellitusDocument6 pagesCH 39 Anaesthesia and Diabetes MellitusChristian LeepoNo ratings yet
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument10 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosisagar agarNo ratings yet
- Oral Hypoglycemica - AcetoaminophenDocument19 pagesOral Hypoglycemica - Acetoaminophenjoonabil29No ratings yet
- Dka 1Document45 pagesDka 1jomanabuhaniyehNo ratings yet
- HHNSDocument20 pagesHHNSVitis Vinivera KhasanahNo ratings yet
- 04 Diabetic Emergency DKA HHS HypoDocument43 pages04 Diabetic Emergency DKA HHS HypoMoinul Islam MoinNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Laporan 3Document6 pagesJurnal Laporan 3Rutnita NainggolanNo ratings yet
- 11 Peri Operative CareDocument43 pages11 Peri Operative CareAdnan MaqboolNo ratings yet
- Exchange TransfusionDocument35 pagesExchange Transfusionsobinjohnpkl100% (2)
- 10 Management of Patient With Hypoglycemic Coma. Management of Patient With Hyperglycemic (Ketoacidotic) ComaDocument59 pages10 Management of Patient With Hypoglycemic Coma. Management of Patient With Hyperglycemic (Ketoacidotic) ComaMimi ChukwuNo ratings yet
- Fluid GuidelinesDocument8 pagesFluid GuidelinesAya SalahNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Shock c2Document65 pagesSeminar On Shock c2mubarak abdulkadirNo ratings yet
- Guidance For Intravenous Fluid and Electrolyte Prescription in AdultsDocument8 pagesGuidance For Intravenous Fluid and Electrolyte Prescription in AdultsfrakturhepatikaNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Fluid Therapy in Adults in Hospital Algorithm Poster Set 191627821Document5 pagesIntravenous Fluid Therapy in Adults in Hospital Algorithm Poster Set 191627821crsscribdNo ratings yet
- Hypoglycemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHypoglycemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- 一个医学叛逆者的自白 CONFESSION OF A MEDICAL HERETICDocument106 pages一个医学叛逆者的自白 CONFESSION OF A MEDICAL HERETICAllan Zhang100% (1)
- 5.respiratory Distress Dental LectureDocument40 pages5.respiratory Distress Dental LecturehaneeneeNo ratings yet
- 'OET' SAMPLE READING NEW DR TANJIM OVEE 2020Document19 pages'OET' SAMPLE READING NEW DR TANJIM OVEE 2020AHMED TANJIMUL ISLAMNo ratings yet
- 2006 Feb Inpatient Quality IndicatorsDocument1 page2006 Feb Inpatient Quality IndicatorsJPNo ratings yet
- Treatment Dysarthria EfficacyDocument12 pagesTreatment Dysarthria EfficacySwathi GeethaNo ratings yet
- ThyrotoxicosisDocument16 pagesThyrotoxicosisFiorella Peña MoraNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamic Disorders Thromboembolic Disease and ShockDocument13 pagesHemodynamic Disorders Thromboembolic Disease and ShockAbu HuraraNo ratings yet
- Epilepsy Presentation Jo Wykes 2Document27 pagesEpilepsy Presentation Jo Wykes 2Sana SajidNo ratings yet
- AlgorithmACLS Tachycardia 200612Document1 pageAlgorithmACLS Tachycardia 200612YassarNo ratings yet
- Board EamDocument55 pagesBoard Eamjoycevillamor100% (1)
- Fournier's GangreneDocument12 pagesFournier's GangrenepologroNo ratings yet
- BEER CriteriaDocument9 pagesBEER CriteriaKath EstradaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Handbook by Betty J. Ackley MSN EdS RNDocument5 pagesNursing Diagnosis Handbook by Betty J. Ackley MSN EdS RNbowagyzeNo ratings yet
- A Case of Aspartate Aminotransferase MacroenzymeDocument3 pagesA Case of Aspartate Aminotransferase MacroenzymeOlfiany Laurenzia PongohNo ratings yet
- NICU Documentation: Gama Hospital Al Khobar K.S.ADocument8 pagesNICU Documentation: Gama Hospital Al Khobar K.S.ALucian CaelumNo ratings yet
- Safety and Health Issues: Exposure To Cotton DustDocument2 pagesSafety and Health Issues: Exposure To Cotton DustTextile Engineers Association of BholaNo ratings yet
- Benefits of DanceDocument4 pagesBenefits of DancemarroncarcaustoNo ratings yet
- Camh Suicide Prevention HandbookDocument96 pagesCamh Suicide Prevention Handbook873810skah100% (3)
- Bisoprolol Fumarate (Drug Study)Document2 pagesBisoprolol Fumarate (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse688867% (6)
- Article Closed DeglovingDocument2 pagesArticle Closed DeglovingFiki A RisentaNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument6 pagesDiagnosis and TreatmentVadim BulbakNo ratings yet
- Endotoxin CalculationsDocument5 pagesEndotoxin Calculationsjaks2771% (7)
- Da Cryo CystitisDocument34 pagesDa Cryo CystitisAriyanie NurtaniaNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Interventional Pain Management Options For Sacroiliac Joint PainDocument4 pagesDiagnosis and Interventional Pain Management Options For Sacroiliac Joint PainAna Cristina MartinsNo ratings yet
- Meatotomy and Wound CareDocument13 pagesMeatotomy and Wound CareAgung IndraNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Handling Medico Legal CasesDocument5 pagesGuidelines For Handling Medico Legal CasesVaishnavi Jayakumar80% (5)
- Jyane ReubenDocument35 pagesJyane ReubenAmr El-RefaeyNo ratings yet
- Hubungan Self-Efficacy Dengan Tingkat Kepatuhan Minum Obat Pada Penderita HipertensiDocument13 pagesHubungan Self-Efficacy Dengan Tingkat Kepatuhan Minum Obat Pada Penderita HipertensiArista jawamaraNo ratings yet
- Assisting in Intravenous Infusion NewDocument52 pagesAssisting in Intravenous Infusion NewDianne LabisNo ratings yet
- Relief OCD: A Guide For People With Obsessive Compulsive DisorderDocument18 pagesRelief OCD: A Guide For People With Obsessive Compulsive DisorderRadu CzechNo ratings yet