Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study
Drug Study
Uploaded by
gwynethntp0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views4 pagesThe document summarizes information about 6 drugs including their classification, indication, common side effects, and important nursing considerations. Pantoprazole is a proton-pump inhibitor used to treat GERD and stomach ulcers. Side effects include vitamin B12 deficiency, kidney complications, and decreased bone health. Nurses should monitor for signs of deficiencies and fractures. Imdur is a nitrate used to prevent angina but not treat acute episodes. Nurses should assess for heart attack symptoms and check blood pressure. Piptazo is an antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections but can cause severe stomach pain, diarrhea, confusion, and low potassium levels. Nurses should monitor for signs of anaphylaxis and potassium deficiencies.
Original Description:
Original Title
DRUG STUDY
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes information about 6 drugs including their classification, indication, common side effects, and important nursing considerations. Pantoprazole is a proton-pump inhibitor used to treat GERD and stomach ulcers. Side effects include vitamin B12 deficiency, kidney complications, and decreased bone health. Nurses should monitor for signs of deficiencies and fractures. Imdur is a nitrate used to prevent angina but not treat acute episodes. Nurses should assess for heart attack symptoms and check blood pressure. Piptazo is an antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections but can cause severe stomach pain, diarrhea, confusion, and low potassium levels. Nurses should monitor for signs of anaphylaxis and potassium deficiencies.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views4 pagesDrug Study
Drug Study
Uploaded by
gwynethntpThe document summarizes information about 6 drugs including their classification, indication, common side effects, and important nursing considerations. Pantoprazole is a proton-pump inhibitor used to treat GERD and stomach ulcers. Side effects include vitamin B12 deficiency, kidney complications, and decreased bone health. Nurses should monitor for signs of deficiencies and fractures. Imdur is a nitrate used to prevent angina but not treat acute episodes. Nurses should assess for heart attack symptoms and check blood pressure. Piptazo is an antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections but can cause severe stomach pain, diarrhea, confusion, and low potassium levels. Nurses should monitor for signs of anaphylaxis and potassium deficiencies.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
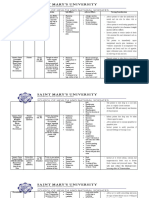
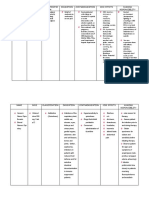
DRUG STUDY
DRUG CLASSIFICATION INDICATION SIDE EFFECTS NURSING
CONSIDERATION
Pantoprazole Proton-pump inhibitor Decreases the amount of Vitamin B-12 1. Instruct not to crush
acid produced in the deficiency or chew the tablet.
stomach, therefore Kidney 2. Observe for signs
indicated for the ff patients: complications of
GERD Diarrhea hypomagnesemia
Acid peptic disease Decreased bone such as dizziness,
Stomach ulcers health (sudden pain tremors, spasms,
or decreased ROM) etc.
Dizziness 3. Monitor bone
Irregular HR fractures or sudden
bone pain.
Tremors/jerking
4. Monitor urine
muscle
output (decrease
movements/spasms
can cause acute
interstitial nephritis)
5. Observe for signs
of vit B-12
deficiency (due to
achlorhydria or
hypochlorhydia)
Imdur Nitrate/Anti-anginal agents Prevention of angina Headache 1. Assess early
pectoris due to coronary Lightheadedness symptoms of heart
artery disease (not for the Irregular HR attack (chest
actual onset) pain/pressure
spreading to jaw or
Works by dilating blood shoulder or general
vessels ill feeling)
2. Instruct to not stop
taking this medicine
suddenly (could
cause severe
anginal attack)
3. Check BP
(contraindicated for
low BP)
Piptazo (Piperacilin- Beta-lactamase inhibitors To treat bacterial infections Severe stomach 1. Watch out for signs
Tazobactam) (such as stomach pain of anaphylaxis.
infections, pneumonia, and Diarrhea (bloody or 2. Monitor bowel
uterine infections) watery) movement.
Confusion 3. Report signs of low
Muscle twitching potassium levels.
Low potassium
level (leg cramps,
constipation,
irregular HR,
numbness, and
muscle weakness)
Seizure
Nausea
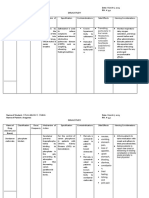
Budesonide Corticosteroids For bronchial asthma Headache 1. Continuously
(nebulization) Rash assess pulmonary
Otitis media function through
Bronchospasm breath sounds and
Abdominal pain RR (to assess for
Oropharyngeal effectiveness).
fungal infections 2. Teach patient on
proper use of
inhalation
techniques.
Memantine N-methyl-D-aspartate To treat moderate to Headache 1. Guard against fall
(NMDA) receptor severe dementia Sleepiness and trauma caused
antagonist (decreases abnormal Dizziness by SEs.
activity in the brain) Hallucinations 2. Help pt and
- May improve the family/caregivers to
ability to think and explore
remember or may nonpharmacologic
slow the loss of methods to reduce
these abilities combative
- Not a CURE episodes and mood
disorders.
3. Report prolonged
headaches or skin
rash to address
symptomatic SEs
to promote comfort.
Combivent (Albuterol Bronchodilator To prevent bronchospasm Infection of ears, 1. Ensure adequate
and Ipratropium) combinations (Anti- (tightening and narrowing nose, and throat hydration to
cholinergic and beta2- of airways) Runny nose prevent
adrenergic agonist) hyperpyrexia.
Cough 2. Use nebulizer
Bronchitis mouthpiece instead
Headache of face mask to
Shortness of breath avoid blurred vision
Paradoxical or aggravation of
bronchospasm narrow-angle
Urinary retention glaucoma.
3. Void before
Palpitations
urination to avoid
Chest pain
urinary retention.
HBP 4. Teach proper use
Tremors of inhaler.
Dry mouth 5. Decrease level of
Narrow-angle activity to prevent
glaucoma risks for fall and
injury.
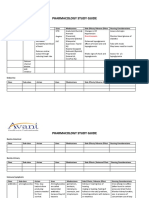
Amlodipine Calcium-channel blocker Angina pectoris and Dizziness 1. Monitor pt closely
hypertension Lightheadedness especially BP
Fatigue/lethargy 2. Take with meals.
Peripheral edema 3. Report irregular
Arrythmias heartbeat,
Nausea shortness of
breath, dizziness,
Abdominal
and swelling of
discomfort
hands and feet.
Trimetazidine Fatty acid oxidation Angina pectoris Dizziness 1. Avoid activities.
inhibitors (piperazine Headache 2. Monitor v/s
derivative) Diarrhea
Indigestion
Extrapyramidal
symptoms
(trembling, shaking
of hands and
fingers, stiffness of
arms and legs)
NAC (Acetylycysteine) Mucolytic Help thin and loosen Dry mouth 1. Assess the quantity
mucus in the airways due Nausea and consistency of
to lung diseases. Vomiting sputum to
Diarrhea determine
Also, for acetaminophen effectiveness of the
overdose. drug.
2. Do back clapping to
loosen secretions.
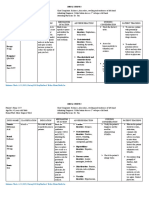
Risperidone Atypical antipsychotics To treat certain Feeling sleepy 1. Maintain seizure
(2nd-generation) mental/mood disorders during the day and precaution.
(schizophrenia, bipolar wide awake at night 2. Instruct not to take
disorder, psychosis, Decreased ROM with tea and cola.
irritability related to autistic Dyskinesia 3. Monitor closely for
disorders, etc.) Headache s/s of DM due to
Changes in appetite insulin resistance
Dementia-related Dizziness and hyperglycemia
psychosis caused by the
Seizure
medication.
Lactulose Osmotic laxative Used as a laxative in the Diarrhea 1. Assess abdominal
treatment of chronic Bloating distention, BM, and
constipation in adults and Burping presence of bowel
geriatric patients Farting sounds.
Stomach rumbling 2. Assess amount and
Most do not need medical consistency of
attention. stool.
3. Increase fluid
intake to avoid
dehydration.
Rosuvastatin HMG-CoA reductase Slows down production of Nausea 1. Encourage simple
inhibitors (statins) cholesterol in the body Constipation meals. Lessen fatty
and spicy foods.
2. Eat a high fiber
diet.
3. Take after a meal
or snack.
You might also like
- Traumatic Brain Injury - TBI Medication ChartDocument5 pagesTraumatic Brain Injury - TBI Medication ChartPNo ratings yet
- GENERIC NAME: Metoprolol Brand Name: CLASSIFICATION: Beta Blockers / Antimigraine Preparations DosageDocument4 pagesGENERIC NAME: Metoprolol Brand Name: CLASSIFICATION: Beta Blockers / Antimigraine Preparations Dosageannice_12No ratings yet
- GENERIC NAME: Metoprolol Brand Name: CLASSIFICATION: Beta Blockers / Antimigraine Preparations DosageDocument4 pagesGENERIC NAME: Metoprolol Brand Name: CLASSIFICATION: Beta Blockers / Antimigraine Preparations Dosageannice_12No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyVanessa Belmonte AzurinNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Omeprazole)Document2 pagesDrug Study (Omeprazole)Baji ۦۦNo ratings yet
- Magnesium Sulfate Doctor'S Order Classifica Tion Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindicat Ions Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationDocument2 pagesMagnesium Sulfate Doctor'S Order Classifica Tion Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindicat Ions Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationLatrell GelacioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document1 pageDrug Study 2Cris Anne AlvarezNo ratings yet
- PrimidoneDocument6 pagesPrimidoneKim SunooNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug Studyjennix_0308100% (1)
- Brand NameDocument7 pagesBrand NameIqra AsimNo ratings yet
- Tramadol - DSDocument2 pagesTramadol - DSThrinNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyNikka Aubrey Tegui-inNo ratings yet
- Drug Classification of AmlodepineDocument5 pagesDrug Classification of Amlodepineshai raNo ratings yet
- Format of Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFormat of Drug StudyNicholas TagleNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Circulatory SystemDocument2 pagesDiseases of The Circulatory SystemJanna Nicole Quening AlcovindasNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Aortic Aneurysmn FINAL WORDDocument16 pagesAbdominal Aortic Aneurysmn FINAL WORDErica P. ManlunasNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyKristine Young100% (1)
- Drug Study MiDocument15 pagesDrug Study MiDorothy AustriacoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyKAROL MARIAE LUZ ERESNo ratings yet
- Drug Therapeutic RecordDocument10 pagesDrug Therapeutic RecordstrawberryNo ratings yet
- DS March 6Document5 pagesDS March 6chessaNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm and Atherosclerosis FINALDocument23 pagesAbdominal Aortic Aneurysm and Atherosclerosis FINALErica P. ManlunasNo ratings yet
- 25 Ethical 24 OTCDocument42 pages25 Ethical 24 OTCBagus KafiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Colleen S. de La Rosa BSN IiiDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Colleen S. de La Rosa BSN IiiColleen De la RosaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyMontero, Ma. Cecilia - BSN 3-BNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Aling MaritesDocument1 pageDrug Study - Aling MaritesAbbyNo ratings yet
- Classification Action Dosage Adverse Reaction Side Effects Nursing ImplicationDocument7 pagesClassification Action Dosage Adverse Reaction Side Effects Nursing ImplicationKate EstradaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Measles)Document7 pagesDrug Study (Measles)Ericka VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Drug 1Document2 pagesDrug 1Nicholas TagleNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyninjmartusNo ratings yet
- AripiprazoleDocument2 pagesAripiprazoleKrisianne Mae Lorenzo FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug Studyunkown userNo ratings yet
- AripiprazoleDocument2 pagesAripiprazoleKrisianne Mae Lorenzo FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesDrug Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing ResponsibilitiesKristinelou Marie ReynaNo ratings yet
- Ari Mfa Important MedicinesDocument1 pageAri Mfa Important MedicinesramudivyNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyOlivia Solomon100% (1)
- Make A Drug Study On The Medications Given To JaneDocument2 pagesMake A Drug Study On The Medications Given To JaneYoko Mae YanoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MethergineDocument2 pagesDrug Study MethergineJahmil DulatreNo ratings yet
- A Case Report of Hydrocephalus S.Y. 2020-2021Document19 pagesA Case Report of Hydrocephalus S.Y. 2020-2021Jewenson SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Avant Pharm Study Guide Set Up With Examples PharmDocument5 pagesAvant Pharm Study Guide Set Up With Examples PharmQwequ Gong AnanseNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - AlfuzosinDocument1 pageDrug Study - AlfuzosinKian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studymarichelle plazaNo ratings yet
- ENT Vertigo FINAL v0.41Document1 pageENT Vertigo FINAL v0.41Farmasi BhamadaNo ratings yet
- Albuterol Drug StudyDocument3 pagesAlbuterol Drug StudyAngelou Joefred CongresoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: CriteriaDocument8 pagesDrug Study: CriteriaJhon eric EscultorNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug Studyunkown userNo ratings yet
- Benztrop, Congentin: Drug StudyDocument4 pagesBenztrop, Congentin: Drug StudyHamimah Bint AliNo ratings yet
- Albuterol Drug StudyDocument1 pageAlbuterol Drug StudyAijeelene NalapoNo ratings yet
- Section and Group Number: BSN2A and Group 2 Estela Isabel Villa RN, MNDocument3 pagesSection and Group Number: BSN2A and Group 2 Estela Isabel Villa RN, MNKristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Heart FailureDocument3 pagesDrug Study Heart FailureAjay SupanNo ratings yet
- Tramadol UltramDocument2 pagesTramadol UltramatchiekNo ratings yet
- General Class and Family Enumerate and Underscore Specific Indication IllustrateDocument5 pagesGeneral Class and Family Enumerate and Underscore Specific Indication IllustrateAlvin DagumbalNo ratings yet
- Drugs 2Document6 pagesDrugs 2Elyse Ann ReyesNo ratings yet
- ClonidineDocument1 pageClonidineYuuki Chitose (tai-kun)No ratings yet
- Pud Drug StudyDocument6 pagesPud Drug StudyLolcoma15 JaymsNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Drug Name Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Consideration Drug NameDocument6 pagesDrug Study Drug Name Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Consideration Drug NameCanny CańasNo ratings yet
- Quetiapine Drug StudyDocument3 pagesQuetiapine Drug StudyEula Angelica Oco100% (1)
- Pharm Drugs ChartsDocument21 pagesPharm Drugs ChartsTris100% (1)
- The Mindful Spine: A Holistic Approach to Healing Back PainFrom EverandThe Mindful Spine: A Holistic Approach to Healing Back PainNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Reviewer: Chapter 27: General and Local Anesthetic AgentsDocument10 pagesPharmacology Reviewer: Chapter 27: General and Local Anesthetic AgentsKyla CastroNo ratings yet
- Pharma NotesDocument38 pagesPharma NotesJose Luis AlmonedaNo ratings yet
- The Child and Adolescent First-Episode Psychosis Study (CAFEPS) : Design and Baseline ResultsDocument12 pagesThe Child and Adolescent First-Episode Psychosis Study (CAFEPS) : Design and Baseline ResultsQwerty QwertyNo ratings yet
- Natural Medicines Comprehensive Database 2010Document26 pagesNatural Medicines Comprehensive Database 2010PsineticNo ratings yet
- Dimethyl MEA (DMAE) : Date of Reporting 05.06.2012Document18 pagesDimethyl MEA (DMAE) : Date of Reporting 05.06.2012郭微No ratings yet
- Brexpiprazole: A Review of A New Treatment Option For Schizophrenia and Major Depressive DisorderDocument6 pagesBrexpiprazole: A Review of A New Treatment Option For Schizophrenia and Major Depressive DisorderLuis Pablo HsNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis in Patient With Undifferentiated SchizophreniaDocument30 pagesCase Analysis in Patient With Undifferentiated SchizophreniaSolsona Natl HS MaanantengNo ratings yet
- KatakatakaDocument1 pageKatakatakaLOUIE BORRALNo ratings yet
- Calamox Tablets SuspensionsDocument4 pagesCalamox Tablets SuspensionsAbdurrahman DarmanNo ratings yet
- Psychiatry Passmedicine & Onexamination Notes 2016 PDFDocument34 pagesPsychiatry Passmedicine & Onexamination Notes 2016 PDFJyothi ReddyNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary Syndromes CaseDocument14 pagesAcute Coronary Syndromes CaseAsep BageurNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension My First Online GP Appointme Reading Comprehension Exercises 127529Document2 pagesReading Comprehension My First Online GP Appointme Reading Comprehension Exercises 127529Jose SanchezNo ratings yet
- Anticholinergic: Classification Generic Name Brand NameDocument6 pagesAnticholinergic: Classification Generic Name Brand NameKarina MadriagaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1. Introduction To Pharmacy InformaticsDocument21 pagesUnit 1. Introduction To Pharmacy InformaticsJenilyn FarnacioNo ratings yet
- Running Head: ACUTE APPENDICITIS 1: Assessment 2: Case Study Essay Name Institutional AffiliationDocument13 pagesRunning Head: ACUTE APPENDICITIS 1: Assessment 2: Case Study Essay Name Institutional Affiliationvrunda patelNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Psychology Mid TermDocument150 pagesAbnormal Psychology Mid TermVincent CawalingNo ratings yet
- Antipsychotic PolypharmacyDocument10 pagesAntipsychotic PolypharmacymarcoNo ratings yet
- Pub - Pediatric Rheumatology in Clinical Practice PDFDocument191 pagesPub - Pediatric Rheumatology in Clinical Practice PDFAna-Mihaela BalanuțaNo ratings yet
- FR 2019 333Document7 pagesFR 2019 333salimabdatNo ratings yet
- Basics of OncologyDocument64 pagesBasics of OncologyCiubotaru Diana -MariaNo ratings yet
- Unitatea de Măsură Cantitate A Preț Unitar, LeiDocument14 pagesUnitatea de Măsură Cantitate A Preț Unitar, LeivictorNo ratings yet
- LIST HARGA Ethical UPDATE 22 NOVEMBER 2023Document11 pagesLIST HARGA Ethical UPDATE 22 NOVEMBER 2023Farmasi sadawiraNo ratings yet
- Anti-Diabetic Activity of Lagenaria Siceraria Pulp and Seed Extract in Normal and Alloxan-Induced Diabetic RatsDocument8 pagesAnti-Diabetic Activity of Lagenaria Siceraria Pulp and Seed Extract in Normal and Alloxan-Induced Diabetic RatsAi RezxxNo ratings yet
- Drug Administration Bangladesh CTD Module 2017 FINALDocument67 pagesDrug Administration Bangladesh CTD Module 2017 FINALChishty Shai NomaniNo ratings yet
- I.V. Drug CalculationsDocument2 pagesI.V. Drug CalculationsIbrahem AlNo ratings yet
- USP 232 MethodDocument5 pagesUSP 232 MethodCindy CarolinaNo ratings yet
- Antiproliferative Potential of Escitalopram in Dimethylhydrazine (DMH) Induced Colon Cancer in Swiss Albino MiceDocument7 pagesAntiproliferative Potential of Escitalopram in Dimethylhydrazine (DMH) Induced Colon Cancer in Swiss Albino MiceIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- 1 PBDocument11 pages1 PBNis RinaNo ratings yet
- Peptic UlcerDocument36 pagesPeptic UlcerZANo ratings yet
- Serialization - Traceability and Big Data in The Pharmaceutical Industry PDFDocument19 pagesSerialization - Traceability and Big Data in The Pharmaceutical Industry PDFBúp CassieNo ratings yet