Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Parts and Function Microscope
Uploaded by
Mikee Cabanlig0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views24 pagesUsing a PowerPoint presentation in teaching the history, parts, and functions of a microscope can be highly beneficial. It allows for a structured and visually engaging exploration of the topic. The historical context can be presented effectively through timelines and images, while detailed slides can break down the components and their functions. Visual aids aid in clarifying complex concepts, making it easier for students to understand the evolution of microscopes and their practical applicati
Original Title
PARTS AND FUNCTION MICROSCOPE
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentUsing a PowerPoint presentation in teaching the history, parts, and functions of a microscope can be highly beneficial. It allows for a structured and visually engaging exploration of the topic. The historical context can be presented effectively through timelines and images, while detailed slides can break down the components and their functions. Visual aids aid in clarifying complex concepts, making it easier for students to understand the evolution of microscopes and their practical applicati
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views24 pagesParts and Function Microscope
Uploaded by
Mikee CabanligUsing a PowerPoint presentation in teaching the history, parts, and functions of a microscope can be highly beneficial. It allows for a structured and visually engaging exploration of the topic. The historical context can be presented effectively through timelines and images, while detailed slides can break down the components and their functions. Visual aids aid in clarifying complex concepts, making it easier for students to understand the evolution of microscopes and their practical applicati
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 24
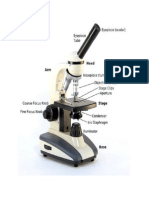
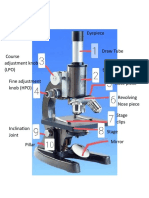
is a device used to see objects that are too
small to be seen by the naked eye.
are made up of several lenses that
magnify an object that cannot usually be
seen with the naked eye.
Contains the magnifying lens
you look through.
also known as
the ocular.
Connects the eyepiece
to the objective lenses.
This is the part of the microscope
that holds two or more objective
lenses and can be rotated to easily
change power (magnification).
a component that magnifies the
images of the specimen to form an
enlarged image.
Usually you will find 1 or 3 objective
lenses on a microscope.
Oil Immersion Objective (OIO)-
used to view bacteria, very
small protists, and fungi. It is
marked 97x or 100x or the word
“oil”.
High Power Objective
(HPO)- is marked 40x, 43x,
or 60x.
Low Power Objective
(LPO)- is marked 10x or
12x.
Low Power Objective
(LPO)- is marked 10x or
12x.
the large knob located on the
arm of the microscope used for
moving the body tube down and up
for bringing the object to be
examined under exact focus.
the small knob used for
focusing finer details of the
specimen being viewed.
the small knob used for
focusing finer details of the
specimen being viewed.
the flat platform where
slides are placed.
hold the slides in
place.
it is used to reflect light from
an external light source up to
the diaphragm, object to be
observed, and lenses
is fastened below the stage.
It regulates the amount of
light passing through the
specimen.
a joint where the arm is fastened
to the base. It is used to tilt the
microscope for more comfortable
viewing.
the bottom of the microscope
used for support. It also
houses the illuminator or
mirror.
the part that supports the
body tube and connects it to
the base of the microscope.
You might also like
- Parasitology Practical HandbookDocument41 pagesParasitology Practical Handbookmaximazarov100% (1)
- Parts and Function of Light MicroscopeDocument34 pagesParts and Function of Light MicroscopeAldous Joaqui IsletaNo ratings yet
- MICROSCOPE NOTES - 2018 by LN PDFDocument7 pagesMICROSCOPE NOTES - 2018 by LN PDFLuyando NzalaNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Compound MicroscopeDocument5 pagesParts of A Compound MicroscopeKim Ashley BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Parts of Microscope and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesParts of Microscope and Their Functionsiammiiie0150% (2)
- A Simple Guide to the Eye and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Eye and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Optigal's Q & A for the NOCE: National Opticianry Certification Exam Questions - Basic CertificationFrom EverandOptigal's Q & A for the NOCE: National Opticianry Certification Exam Questions - Basic CertificationNo ratings yet
- Parts of A MicroscopeDocument5 pagesParts of A MicroscopeShankey Faith BediaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Q2 W1 PPDocument6 pagesGrade 7 Q2 W1 PPKarina GentonNo ratings yet
- Microscope-Parts-and-Functions-Q2-L1 7Document2 pagesMicroscope-Parts-and-Functions-Q2-L1 7kyla nczvcNo ratings yet
- Compound Microscope Definitions For LabelsDocument9 pagesCompound Microscope Definitions For LabelsDURANO, ROSELLE Z.SCINo ratings yet
- Q2 - Living Things and Their EnvironmentDocument69 pagesQ2 - Living Things and Their EnvironmentAURORA () CARIAGANo ratings yet
- Micp211 (Lab) ReviewerDocument2 pagesMicp211 (Lab) ReviewerMAV TAJNo ratings yet
- Compound Microscope Parts: Structural ComponentsDocument3 pagesCompound Microscope Parts: Structural ComponentsJanuary Pentinio AbarentosNo ratings yet
- Background: Biotechnology For Everyone, Bi6Document8 pagesBackground: Biotechnology For Everyone, Bi6Bianchi DyNo ratings yet
- Simple Microscope: Luna, Zyrah Angelic L. BSBA-3 MWF 4:00-5:00pmDocument2 pagesSimple Microscope: Luna, Zyrah Angelic L. BSBA-3 MWF 4:00-5:00pmJerald LunaNo ratings yet
- MicroscopeDocument3 pagesMicroscopeJoun Erica TalinguezNo ratings yet
- CASNS 1a Laboratory - Module 1Document12 pagesCASNS 1a Laboratory - Module 1Maxi VellasNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Microscope and Their Uses (Compilation From Diff. Site.)Document5 pagesParts of The Microscope and Their Uses (Compilation From Diff. Site.)ivoryshin daluroNo ratings yet
- Compound MicroscopeDocument2 pagesCompound MicroscopeditucalanshanmichaelvNo ratings yet
- Microscope G7Document18 pagesMicroscope G7Sheena RacuyaNo ratings yet
- Histology Assignment 1Document3 pagesHistology Assignment 1Kristine Pangahin100% (1)
- Parts of A Microscope and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesParts of A Microscope and Their FunctionsJessica Cordis100% (1)
- Chapter 1 The MicroscopeDocument3 pagesChapter 1 The MicroscopeGela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Study of Compound MicroscopeDocument4 pagesStudy of Compound MicroscopeArman KhanxNo ratings yet
- The Microscope - Parts and FunctionsDocument2 pagesThe Microscope - Parts and FunctionsLhynne Riano Salando100% (1)
- EyepieceDocument2 pagesEyepieceOzner WanijimaNo ratings yet
- Biotech - Microscope (8 - Leeuwenhoek)Document4 pagesBiotech - Microscope (8 - Leeuwenhoek)Leila Nicole FulgencioNo ratings yet
- Parts and Function of The MicroscopeDocument3 pagesParts and Function of The MicroscopeStephen GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Compound Microscope Definitions For LabelsDocument3 pagesCompound Microscope Definitions For LabelsRonalee PeralesNo ratings yet
- Microscope DefinitionsDocument3 pagesMicroscope DefinitionsJessica ThomasNo ratings yet
- 01 Intro To MicroscopesDocument7 pages01 Intro To MicroscopesKarunakarNo ratings yet
- Manual For PrintDocument59 pagesManual For PrintShweta BhutadaNo ratings yet
- Compound Microscope PartsDocument3 pagesCompound Microscope PartsMimi MonteNo ratings yet
- De Guzman, Ryan Gabriel D. - Week 2 Laboratory ActivityDocument2 pagesDe Guzman, Ryan Gabriel D. - Week 2 Laboratory ActivityNuñez, Eliza G.No ratings yet
- MICROSCOPEDocument37 pagesMICROSCOPELeah RualesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-Introduction To MicroscopesDocument26 pagesLecture 2-Introduction To MicroscopesThuto SmithNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 1 Microscopy Part 1Document4 pagesActivity No. 1 Microscopy Part 1Jasmine R. MaturanNo ratings yet
- Laboratory IIDocument9 pagesLaboratory IIDecemei CuaboNo ratings yet
- MicrosDocument7 pagesMicrosJaeyun RuiNo ratings yet
- The Microscope: Dr. S.M. ReyesDocument9 pagesThe Microscope: Dr. S.M. ReyesSheryl Reyes100% (1)
- Head/Body Houses The Optical Parts in The Upper Part of The MicroscopeDocument2 pagesHead/Body Houses The Optical Parts in The Upper Part of The MicroscopeNica Bautista BarsolasoNo ratings yet
- LPO / Low Power ObjectiveDocument2 pagesLPO / Low Power ObjectiveFor AstroNo ratings yet
- MICROSCOPEDocument5 pagesMICROSCOPETeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Compound Microscop EDocument26 pagesCompound Microscop EDixie MerinNo ratings yet
- The MicroscopeDocument8 pagesThe MicroscopeScylla AngcosNo ratings yet
- Lecture MicroscopeDocument3 pagesLecture MicroscopeAlex LimcangcoNo ratings yet
- Prelab Activity MPLDocument5 pagesPrelab Activity MPLAlthea Valenzuela100% (1)
- A. Bonifacio Integrated School Supplemental Activities in Science 7 Second Quarter Week 1Document3 pagesA. Bonifacio Integrated School Supplemental Activities in Science 7 Second Quarter Week 1Rose Ann ChavezNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1 - Mic102Document10 pagesLab Report 1 - Mic102Suhada IdayuNo ratings yet
- The MicroscopeDocument4 pagesThe MicroscopeRyz DoctoraNo ratings yet
- MiriaasdDocument52 pagesMiriaasdCreatia PertokiaNo ratings yet
- PareDocument7 pagesPareEloisa LacanilaoNo ratings yet
- Microscope: B. Type of MicroscopeDocument3 pagesMicroscope: B. Type of MicroscopeFati Andari AlmahdiniNo ratings yet
- Microscope (Science 7)Document26 pagesMicroscope (Science 7)syrine mendozaNo ratings yet
- How To Use A Light MicroscopeDocument4 pagesHow To Use A Light MicroscopebasondesaNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Microscope Microscope Part Function Structural Parts of A MicroscopeDocument6 pagesParts of The Microscope Microscope Part Function Structural Parts of A Microscopelarry machonNo ratings yet
- Lab Prelims ReviewerDocument15 pagesLab Prelims ReviewerAliyaah Nicole SernaNo ratings yet
- MicroscopeDocument40 pagesMicroscopeloopNo ratings yet
- Biological Levels of Organization Part2Document14 pagesBiological Levels of Organization Part2Mikee CabanligNo ratings yet
- Biological Levels of OrganizationDocument15 pagesBiological Levels of OrganizationMikee CabanligNo ratings yet
- History of A MicroscopeDocument11 pagesHistory of A MicroscopeMikee CabanligNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellDocument8 pagesAnimal and Plant CellMikee CabanligNo ratings yet