0% found this document useful (0 votes)
92 views2 pagesTypes of Computer Booting Explained
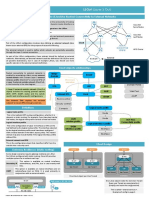
Boot is the process of starting a computer system and initializing its operating system. There are several types of booting that serve different purposes, such as cold booting which occurs on a powered off system and loads the full OS, warm booting which restarts without powering off and skips initial checks, and network booting which loads the OS from a network rather than local storage. Booting types offer flexibility for scenarios like dual booting multiple OSes, booting from remote servers, and safe mode booting for troubleshooting issues.
Uploaded by
abhijitCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
92 views2 pagesTypes of Computer Booting Explained
Boot is the process of starting a computer system and initializing its operating system. There are several types of booting that serve different purposes, such as cold booting which occurs on a powered off system and loads the full OS, warm booting which restarts without powering off and skips initial checks, and network booting which loads the OS from a network rather than local storage. Booting types offer flexibility for scenarios like dual booting multiple OSes, booting from remote servers, and safe mode booting for troubleshooting issues.
Uploaded by
abhijitCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd