Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Topic 1.1 - Environmental Value Systems
Uploaded by
2010130Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic 1.1 - Environmental Value Systems
Uploaded by
2010130Copyright:
Available Formats
06.03.
23
Topic 1.1 : Environmental value systems
Value
- Value = The importance, worth, or usefulness of something
- Types of value:
- Economic: Provides money, strengthens the economy
- Ecological: Provides resources, and services for living things in nature
- Social: Provides services for human societies
- Cultural: Provides symbolic meaning for a society
- Aesthetic: Provides beauty
- Intrinsic value: Something has value “for its own sake” outside of what it can provide you
- Does nature have intrinsic value?
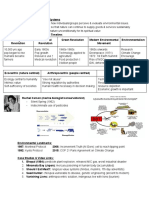
History of the environmental movement
- Post-industrial revolution: Negative impact of human behavior on nature begins to be
examined
- Significant influences on Environmental Movement:
- Literature:
- Walden by H.D Thoreau (1854) - Humans relation to nature
- Nature by R.W Emerson (1836) - Human's relation to nature
- Silent Spring by Rachel Carson (1962) - Dangers of pesticides
- Media:
- An inconvenient truth by Al Gore (2006) - Documentary educating about
global warming
- Twitter of activist like Greta Thunberg
- Major environmental disaster:
- Great London smog (1952)
- Love Canal (1970s) - Site of toxic dumping cause major health effects
- Chernobyl (1986) and Fukushima (2011) - nuclear accidents
- Bhopa (1984) - Chemical accident
- International agreements:
- Rio earth summit (1992) - Climate change
- Kyoto Protocol (1977) - Climate change
- Montreal Protocol (1987) - Ozone layer protection
- Paris Agreement (2015) - Climate change
- Technological advances:
- Green revolution - Increased crop yields and agricultural production
- Climate engineering - Carbon dioxide removal, solar radiation management
Environmental value systems
-
- EVS: Your perspective on how to interact with and use nature
- EVS spectrum:
- Ecocentric (nature-centered)
- Puts nature as central to humanity
- Minimal materialism
- Self-sufficing societies
- Prioritizes bio rights
- Importance of education
- Encouarages self restrain
- Holistic worldview
- Anthropocentric (human-centric)
- Focus on sustainable management of the environment
- Requires regulation by authorities
- Uses taxes, legislation, and incentives
- Debate is encouraged
- Techocentric (technology-centered)
- Tech can provide solutions to environmental problems
- Optimistic view
- Scientific research is encouraged
- Pro-growth agenda demand is necessary for societal improvement
- Extreme ecocentric = Deep ecologist:
- A spiritual revolution is necessary, with nature at the center, equal rights for
all species
- Extreme technocentric = Cornucopian:
- New resources + technologies will solve any environmental problems in the
future
Experimental design
- Variables:
- Independent: Manipulated variable ; cause
- Dependent variable: Measured as a result; effect
- Controlled: All variables kept the same between groups
- Research Question: To what extent does (IV) affect (DV)?
- 5 groups of IV x 5 trials of each group = 25 total trials
You might also like
- Ess - Notes May 24Document59 pagesEss - Notes May 24martipineiro2006No ratings yet
- ESS Unit 1Document5 pagesESS Unit 1Sofia LaereNo ratings yet
- ESS Unit 1Document5 pagesESS Unit 1Sofia LaereNo ratings yet
- ESS Unit 1Document5 pagesESS Unit 1Sofia LaereNo ratings yet
- 1.1.environmental Value Systems 2Document37 pages1.1.environmental Value Systems 2omerr.arass13No ratings yet
- Topic 1.1: Environmental Value SystemDocument38 pagesTopic 1.1: Environmental Value SystemLina ShakarounNo ratings yet
- Ibdp Ess Notes Topic 1Document8 pagesIbdp Ess Notes Topic 1chaitanya anandNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-Introduction To Environmental PolicyDocument107 pagesLecture 1-Introduction To Environmental Policyignacio.garcia11No ratings yet
- Environmental Science Lecture NotesDocument26 pagesEnvironmental Science Lecture Notesjed.berdosNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 ESS 21-23Document110 pagesUnit 1 ESS 21-23Antonio Sesé MartínezNo ratings yet
- PERTEMUAN 3 - 8 Nov 2021Document34 pagesPERTEMUAN 3 - 8 Nov 2021Nurul Ayu Annisa nurulayu.2021No ratings yet
- 1.1 Environmental Value SystemsDocument38 pages1.1 Environmental Value SystemsBhaswati BharNo ratings yet
- Cours Environmental PoliticsDocument23 pagesCours Environmental PoliticsMargotNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 NotesDocument11 pagesTopic 1 NotesRaviNo ratings yet
- ESS - Topic 1 - Foundations To EssDocument36 pagesESS - Topic 1 - Foundations To EssRAGINI RAMACHANDRANNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Environment: Env101 Lecture#1Document29 pagesIntroduction To The Environment: Env101 Lecture#1Raihan RahmanNo ratings yet
- Combinepdf PDFDocument417 pagesCombinepdf PDFmasterindNo ratings yet
- ESS Unit 1Document5 pagesESS Unit 1Nieve JudkinsNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science ReviewDocument9 pagesEnvironmental Science ReviewVictoria ArrudaNo ratings yet
- Barouskaya, I. Anthropocentrism and Ecocentrism Finding Balance For Environmental Protection PurposesDocument19 pagesBarouskaya, I. Anthropocentrism and Ecocentrism Finding Balance For Environmental Protection PurposesEba EbaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Environmental ScienceDocument47 pagesIntroduction To Environmental ScienceEljhon Satsat100% (1)
- Environmental EthicsDocument27 pagesEnvironmental EthicsAroosa Khan0% (1)
- Chapter 1 GEE SummaryDocument5 pagesChapter 1 GEE SummaryKimberly ChivaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Environmental Value Systems For FireflyDocument33 pages1.1 Environmental Value Systems For FireflyareenaNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document10 pagesModule 1anshita jainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Environmental ScienceDocument56 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Environmental ScienceAnne PinoteNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - ScienceDocument2 pagesReviewer - ScienceIvan CaroNo ratings yet
- Tragedy of CommonsDocument5 pagesTragedy of CommonsMd KaziNo ratings yet
- Professional Ethics - Module 3Document122 pagesProfessional Ethics - Module 3VINAYAKUMAR B AEINo ratings yet
- 1.1 Environmental Value SystemsDocument43 pages1.1 Environmental Value SystemsJesús Balmaseda JalvoNo ratings yet
- 3.environmental Trends and The Economic FrameworkDocument40 pages3.environmental Trends and The Economic Frameworksagita fNo ratings yet
- ENVISAFE - (1) IntroductionDocument69 pagesENVISAFE - (1) IntroductionSealtiel1020No ratings yet
- Introduction To Sustainable Development & Corporate SustainabilityDocument31 pagesIntroduction To Sustainable Development & Corporate SustainabilityKiran NsNo ratings yet
- Ess Sstudy GuideDocument60 pagesEss Sstudy GuideDanna AyalaNo ratings yet
- Ecology 9Document17 pagesEcology 9avafinn 13No ratings yet
- Environmental ScienceDocument13 pagesEnvironmental ScienceRhaine EstebanNo ratings yet
- Philosophy, Environemnt and Development The NexusDocument35 pagesPhilosophy, Environemnt and Development The NexusChinwendu peculiarNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science TermsDocument40 pagesEnvironmental Science TermsNasraRealinoNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Environmental ScienceDocument38 pagesAn Introduction To Environmental ScienceAmit AgrawalNo ratings yet
- 1.1 LessonDocument39 pages1.1 LessonViolet XuNo ratings yet
- JSC - ELECT.1 - Introduction To Environmental ScienceDocument4 pagesJSC - ELECT.1 - Introduction To Environmental ScienceGibby ArbiolNo ratings yet
- Define Environmental EthicsDocument13 pagesDefine Environmental EthicsRONALYN PINOTENo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Introduction To E and SDDocument2 pagesLecture 1 Introduction To E and SDDana SatybaldyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 & 2Document46 pagesLecture 1 & 2Dhanuka NadeeraNo ratings yet
- ESS NoteDocument7 pagesESS NoteYi Qi NieNo ratings yet
- Environmental EthicsDocument37 pagesEnvironmental EthicsWanambwa SilagiNo ratings yet
- Green DegrowthDocument27 pagesGreen DegrowthToon BosNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Introduction To Environmental ScienceDocument23 pagesUnit 1: Introduction To Environmental ScienceSaraNo ratings yet
- Bright Green Environmentalism: Ecocentrism andDocument11 pagesBright Green Environmentalism: Ecocentrism andNorma CalderonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-Understanding Our EnvironmentDocument27 pagesLecture 1-Understanding Our Environmentarnienina.niloNo ratings yet
- Environmental Planning & Practice 3671Document79 pagesEnvironmental Planning & Practice 3671M Hammad ManzoorNo ratings yet
- Human Geography 4Document45 pagesHuman Geography 4Rica Anne SembranoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Environmental ScienceDocument39 pagesUnit 1 - Environmental ScienceSaraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Environmental Issues PDFDocument67 pagesLecture 1 Environmental Issues PDFKhánh Huyền TrầnNo ratings yet
- Environment: The Science Behind The Stories, Chapter 2 OutlineDocument5 pagesEnvironment: The Science Behind The Stories, Chapter 2 Outlineevapanda123No ratings yet
- ENV 107 Introduction To Environmental Science: Lecture 2-3: Fundamentals of EnvironmentDocument32 pagesENV 107 Introduction To Environmental Science: Lecture 2-3: Fundamentals of EnvironmentAl-Amin Khan FilmsNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Introduction To Environmental Science-MergedDocument74 pagesLesson 1 - Introduction To Environmental Science-MergedAllyza Delos reyesNo ratings yet
- Development of Envo Law (Nasional & Global)Document26 pagesDevelopment of Envo Law (Nasional & Global)Wahyu Yun SantosoNo ratings yet
- NoNonsense Renewable Energy: Cleaner, fairer ways to power the planetFrom EverandNoNonsense Renewable Energy: Cleaner, fairer ways to power the planetNo ratings yet
- Impact of Technology on Environment: Climate Change and InstrumentationFrom EverandImpact of Technology on Environment: Climate Change and InstrumentationNo ratings yet