Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Beta-Blockers - Pharmacology
Uploaded by
Chona Fontanilla0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesOriginal Title
Beta-blockers - Pharmacology(2)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesBeta-Blockers - Pharmacology
Uploaded by
Chona FontanillaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
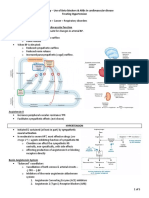
BETA- BLOCKERS
• Beta blockers, also known as beta-adrenergic blocking agents, are medications that reduce blood pressure, it works by blocking the effects of the hormone epinephrine
(adrenaline) and Norepinephrine.
• Beta blockers cause the heart to beat more slowly and with less force, which lowers blood pressure. It helps to widen veins and arteries to improve blood flow.
BETA-RECEPTORS
Receptor Cites
B1 Heart
Kidney (JG cells)
Posterior Pituitary
Adipose tissue
B2 Lungs(Bronchioles)
Blood vessel,
Skeletal muscle
Liver muscle
Adipose tissue
Eye
B3 Fatty/Adipose Tissue
Classification of Beta blockers
Some beta blockers mainly affect the heart, while others affect both the heart and blood vessels.
Your doctor will choose which beta blocker is best for you based on your health conditions.
Non-Selective Blockers Selective Blockers Mixed Blockers
Non-selective, it targets both Beta 1 “selective”, because it only target the The mixed α-/β-
and Beta 2. Beta 1 receptor. blockers, carvedilol and labetalol, block
peripheral α1-receptors and both β1- and β2-
Have cardiac effect and on other Also called CARDIOSELECTIVE. receptors. These agents share the
system pharmacologic properties of nonselective β-
Example drugs here are metoprolol, blockers but have a lower degree of α-
Example drugs are timolol, atenolol and esmolol blockade than pure α-blockers, and their α-
oxprenolol, and nadolol blocking effects become attenuated with
chronic use.
Both Selective and non-selective Beta Blockers can produce cardiac effect because they both target Beta 1 receptors.
Drug Name Pharmacodynamics Pharmacokinetics Adverse Drug Reactions Dosage/Administration Indications/Contraindications
Timolol Mechanism: Nonselective Route: Oral, ophthalmic Bradycardia Oral: start with 10 mg Indications:
beta-blocker Absorption: well- Hypotension once daily, adjust as Hypertension
absorbed orally but for Bronchospasm (caution in needed Glaucoma (ocular use)
Blocks Beta-adrenergic ophthalmic (eye drop) asthma/COPD)
receptors use, the drug is absorbed Fatigue, dizziness Ophthalmic: apply 1 drop Contraindications:
through the eye’s surface Ocular in affected eye(s) twice Bradycardia
Reduces heart rate and bloodstream irritation(opthalmic daily Heart block
contractility Metabolism: primarily Asthma
metabolized in the liver Severe COPD
Lowers intraocular Elimination: through
pressure (IOP) by renal excretion, with a
decreasing aqueous small portion excreted in
humor production the feces.
Drug Name Pharmacodynamics Pharmacokinetics Adverse Drug Reaction Dosage/Administration Indications/Contraindications
Atenolol Mechanism: Selective Route: Oral Bradycardia Oral: in tablet form, the, Indications:
beta1-adrenergic Absorption: Its Hypotension Initial starting dose is at Hypertension
receptor blocker absorption is not Fatigue 20-50 mg qd Angina
significantly affected by Cold extremities Arrythmias
Reduces heart rate and food, so it can be taken Sleep disturbances Maximum dose: 100mg
contractility with or without meals Rare allergic reactions qd Contraindications:
Distribution: Atenolol has Bradycardia
Lowers blood pressure by a relatively short half-life Doctor may adjust the Asthma
decreasing cardiac output of about 6-7 hours. It dosages based on your Severe heart failure
does not extensively bind blood pressure
to plasma proteins which
mean it is mostly found in
the bloodstream rather
than being strongly
bound to proteins.
Metabolism: atenolol
undergoes minimal
hepatic (liver)
metabolism. It is
primarily excreted
unchanged in the urnine.
Elimination: primarily
eliminated through renal
(kidney) excretion. the
dosage of atenolol may
need adjustment in
individuals with impaired
renal kidney function
prevent potential side
effects.
Drug Name Pharmacodynamics Pharmacokinetics Adverse Drug Reaction Dosage Indications/Contraindications
Carvedilol Mechanism: Non- Route: Oral Bradycardia Initial dose: 3.125mg Indications:
selective beta-blocker Absorption: the extent of Hypotension b.i.d. for heart failure Hypertension
and alpha-1 blocker absorption can be Dizziness, fatigue Heart failure
affected by food. It is Potential worsening of Hypertension: usual dose Post MI (myocardial
Reduces heart rate and well-absorbed form the heart failure symtppom 6.25mg to 25 mg b.i.d, infarction)
contractility GI tract after oral
administration. Dosage may be titrated Contraindications:
Dilates blood vessels , Distribution: it can cross based on response and Severe bradycardia
lowering blood pressure the blood brain barrier tolerance Heart block
and enter CNS Asthma/COPD
Used in heart failure to Elimination: Both renal
improve cardiac function and fecal excretion.
You might also like
- Adrenergic Antagonists: An Introduction to Alpha and Beta BlockersDocument64 pagesAdrenergic Antagonists: An Introduction to Alpha and Beta BlockersAneeza AhmadNo ratings yet
- ARBs and Beta Blockers Pharmacology Lecture SummaryDocument14 pagesARBs and Beta Blockers Pharmacology Lecture Summaryبصيص اليقينNo ratings yet
- SympatholyticsDocument46 pagesSympatholyticsHari Kamesh KiranNo ratings yet
- Sympa T Holy TicsDocument47 pagesSympa T Holy Ticsahmad tariqNo ratings yet
- Alpha Blockers PharmacologyDocument23 pagesAlpha Blockers PharmacologyHesbon MomanyiNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument21 pagesPharmacologySophia Kyla AcerNo ratings yet
- Propranolol Introduced in 1963 Was A Therapeutic BreakthroughDocument5 pagesPropranolol Introduced in 1963 Was A Therapeutic BreakthroughOmkar Singh100% (1)
- Abdominal Aortic Aneurysmn FINAL WORDDocument16 pagesAbdominal Aortic Aneurysmn FINAL WORDErica P. ManlunasNo ratings yet
- Adrenolytics Jurusan Pendidikan Dokter Umum Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas SriwijayaDocument33 pagesAdrenolytics Jurusan Pendidikan Dokter Umum Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas SriwijayaagungNo ratings yet
- Beta Adrenergic Blockers: SympatholyticDocument12 pagesBeta Adrenergic Blockers: SympatholyticAbdullah asadNo ratings yet
- Atenolol: Atenolol Is A Beta Blocker MedicationDocument6 pagesAtenolol: Atenolol Is A Beta Blocker MedicationAbdelrhman AboodaNo ratings yet
- CVD and HTNDocument60 pagesCVD and HTNZsazsa100% (1)
- Antiadrenergic DrugsDocument44 pagesAntiadrenergic DrugsHUZAIFA YAMAANNo ratings yet
- 5 SympatholyticsDocument27 pages5 SympatholyticsHussain RazaNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive Agents: Ayman Khdair Ph.D. Pharmaceutical Sciences Wayne State University, Michigan, USADocument15 pagesAntihypertensive Agents: Ayman Khdair Ph.D. Pharmaceutical Sciences Wayne State University, Michigan, USAJalil HaddadinNo ratings yet
- Drug Profiling PHARMACOLOGYDocument71 pagesDrug Profiling PHARMACOLOGYJay MagsaysayNo ratings yet
- Drug studyDocument12 pagesDrug studySocial BaeNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology - Use of Beta-Blockers & Arbs in Cardiovascular Disease Treating HypertensionDocument5 pagesPharmacology - Use of Beta-Blockers & Arbs in Cardiovascular Disease Treating HypertensionDana20SNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic AntagonistDocument30 pagesAdrenergic AntagonistOmar AlaamNo ratings yet
- Antiadrenergic Drugs - II 24.07.018 PDFDocument25 pagesAntiadrenergic Drugs - II 24.07.018 PDFHitesh karnNo ratings yet
- Alpha 1 Blocker: Obstruction and Relieving Effects of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia BPHDocument21 pagesAlpha 1 Blocker: Obstruction and Relieving Effects of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia BPHKaylee LengNo ratings yet
- NebivololDocument2 pagesNebivololSophia MarieNo ratings yet
- Beta Blockers: Dr. Mozna TalpurDocument12 pagesBeta Blockers: Dr. Mozna TalpurShahid HameedNo ratings yet
- 7,8 - Antihypertensive DrugsDocument10 pages7,8 - Antihypertensive DrugsHusniya MehamedNo ratings yet
- Creatin. Creatin. Creatin. Creatin. Creatin. CreatinDocument2 pagesCreatin. Creatin. Creatin. Creatin. Creatin. CreatinEna PaparićNo ratings yet
- ATENOLOLDocument1 pageATENOLOLRPh Krishna Chandra JagritNo ratings yet
- Last Edation Protocol Adan Ade HospitalDocument17 pagesLast Edation Protocol Adan Ade HospitalAxmed MaxamedNo ratings yet
- CARDIOVASCULARDocument2 pagesCARDIOVASCULARAERONH JOHN PURIFICANDONo ratings yet
- 3-11-2018 Beta Blocking DrugsDocument65 pages3-11-2018 Beta Blocking DrugsDharmendra GohilNo ratings yet
- Drug Study GuideDocument2 pagesDrug Study GuideAubrey Sunga100% (1)
- YogeshDocument49 pagesYogeshapi-3741769No ratings yet
- Adrenergic Drugs: ''Sympathomimetics & Sympatholytics"Document17 pagesAdrenergic Drugs: ''Sympathomimetics & Sympatholytics"SimonNo ratings yet
- PharmTest3 StudyGuideDocument9 pagesPharmTest3 StudyGuideTara Bickford ManisNo ratings yet
- 1 DRUGS For HYPERTENSIONDocument4 pages1 DRUGS For HYPERTENSIONEdmon SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensives Summary Katzung PharmacologyDocument8 pagesAntihypertensives Summary Katzung PharmacologyRobin TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Drug StudyDocument6 pagesPharmacology Drug StudyShene Claire VigillaNo ratings yet
- Pharma Unit 1-2 Anti - Adrenergic DrugsDocument21 pagesPharma Unit 1-2 Anti - Adrenergic DrugsMIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Atenolol TenorminDocument3 pagesAtenolol TenorminLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- Beta-Blockers For Cardiovascular Conditions:: One Size Does Not Fit All PatientsDocument7 pagesBeta-Blockers For Cardiovascular Conditions:: One Size Does Not Fit All PatientsspalemaxNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Duty2)Document3 pagesDrug Study (Duty2)Robert َMirandaNo ratings yet
- ANAESTHETICSDocument16 pagesANAESTHETICSAmbroseNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic Effects of AlcoholDocument3 pagesAcute and Chronic Effects of AlcoholGraceNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic Antagonist (2013)Document23 pagesAdrenergic Antagonist (2013)Akmal SafwanNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic AntagonistsDocument6 pagesAdrenergic Antagonistsfiena92100% (2)
- Classification of Sympatholytic DrugsDocument4 pagesClassification of Sympatholytic DrugsHlaSoe WinNo ratings yet
- Understanding How Anti-Adrenergic Drugs Work to Inhibit the Sympathetic Nervous SystemDocument21 pagesUnderstanding How Anti-Adrenergic Drugs Work to Inhibit the Sympathetic Nervous SystemMIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic AntagonistDocument29 pagesAdrenergic AntagonistAreesha ArifNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On The Cardiovascular SystemDocument12 pagesDrugs Acting On The Cardiovascular Systemcleahis cruzNo ratings yet
- Beta BlockersDocument8 pagesBeta BlockersblankNo ratings yet
- LI Case 2 (Pharmacological Properties of Propanolol)Document2 pagesLI Case 2 (Pharmacological Properties of Propanolol)adtyadaviaNo ratings yet
- Heart FailureDocument37 pagesHeart FailureNashita NowshinNo ratings yet
- Ans:1 A. Prolonged ACE Inhibitor Therapy Has Been Found To Prevent or Delay EndDocument6 pagesAns:1 A. Prolonged ACE Inhibitor Therapy Has Been Found To Prevent or Delay EndVijay SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ix. Drug Study: Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesIx. Drug Study: Nursing ResponsibilitiesZhayree R.No ratings yet
- Enalapril, Metropolol, Aspirin, CiticolineDocument8 pagesEnalapril, Metropolol, Aspirin, CiticolineGabriel MatibagNo ratings yet
- 6 SymaptholyticDocument48 pages6 SymaptholyticYoueel IbrahemNo ratings yet
- Drugs Without Positive Inotropic Effect Used in HFDocument12 pagesDrugs Without Positive Inotropic Effect Used in HFDana HamarshehNo ratings yet
- methotrexate-Anti-Asthmatic Drugs Toxicity-1Document9 pagesmethotrexate-Anti-Asthmatic Drugs Toxicity-1joonabil29No ratings yet
- Adrenergic AntagonistsDocument18 pagesAdrenergic AntagonistsKarina MadriagaNo ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrillation A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesFrom EverandAtrial Fibrillation A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Fdar MCHNDocument1 pageFdar MCHNChona FontanillaNo ratings yet
- Deviation AnalysisDocument2 pagesDeviation AnalysisChona FontanillaNo ratings yet
- Thiazide Diuretic - PharmacologyDocument1 pageThiazide Diuretic - PharmacologyChona FontanillaNo ratings yet
- FNCP Priority FamiliesDocument1 pageFNCP Priority FamiliesChona FontanillaNo ratings yet
- HOA4RSW2Document1 pageHOA4RSW2Chona FontanillaNo ratings yet
- Deviation AnalysisDocument2 pagesDeviation AnalysisChona FontanillaNo ratings yet
- Your Paragraph TextDocument1 pageYour Paragraph TextChona FontanillaNo ratings yet
- My Success Map in 10 Years (January 20, 2023 - 2033) PDFDocument1 pageMy Success Map in 10 Years (January 20, 2023 - 2033) PDFChona FontanillaNo ratings yet
- 17th PRESIDENTDocument2 pages17th PRESIDENTChona FontanillaNo ratings yet
- The Senses: Sensory Receptors and PathwaysDocument28 pagesThe Senses: Sensory Receptors and PathwaysChona FontanillaNo ratings yet
- Your Paragraph TextDocument1 pageYour Paragraph TextChona FontanillaNo ratings yet
- Fault ModelingDocument21 pagesFault ModelingRamarao ChNo ratings yet
- SAP ABAP Interview Questions and AnswersDocument8 pagesSAP ABAP Interview Questions and AnswersKarthi ThirumalaisamyNo ratings yet
- PIRA - 2022 - ESTIMATED FMV As of October 2022Document48 pagesPIRA - 2022 - ESTIMATED FMV As of October 2022Aggy ReynadoNo ratings yet
- RD218 Gardan 3110 Ob2226657 NDocument1 pageRD218 Gardan 3110 Ob2226657 Nopen hartigNo ratings yet
- Perlis V. Composer's Voices From Ives To Ellington PDFDocument506 pagesPerlis V. Composer's Voices From Ives To Ellington PDFOleksii Ternovii100% (1)
- Frogkisser! by Garth Nix (Excerpt)Document17 pagesFrogkisser! by Garth Nix (Excerpt)I Read YA0% (1)
- Dear Boy (Acordes para Cancion)Document4 pagesDear Boy (Acordes para Cancion)Rodolfo GuglielmoNo ratings yet
- Student quiz answer sheetsDocument26 pagesStudent quiz answer sheetsSeverus S PotterNo ratings yet
- WEG Low Voltage Motor Control Center ccm03 50044030 Brochure English PDFDocument12 pagesWEG Low Voltage Motor Control Center ccm03 50044030 Brochure English PDFRitaban222No ratings yet
- RJR Nabisco LBODocument14 pagesRJR Nabisco LBONazir Ahmad BahariNo ratings yet
- CEO Corner New Products Powerful Pocket SimulatorDocument23 pagesCEO Corner New Products Powerful Pocket SimulatorMOHAMMA MUSANo ratings yet
- Gray Iron Castings: Standard Specification ForDocument6 pagesGray Iron Castings: Standard Specification Forsafak kahramanNo ratings yet
- XFARDocument14 pagesXFARRIZA SAMPAGANo ratings yet
- SRV210 - 250TC Spare PartsDocument2 pagesSRV210 - 250TC Spare PartsEnzo SovittiNo ratings yet
- Delays in Endoscope Reprocessing and The Biofilms WithinDocument12 pagesDelays in Endoscope Reprocessing and The Biofilms WithinHAITHM MURSHEDNo ratings yet
- Vocabulario Ingles 3 EsoDocument6 pagesVocabulario Ingles 3 EsoPatri ParrasNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Data Analysis 2Document10 pagesQuantitative Data Analysis 2Rhona MaandalNo ratings yet
- 2020会社案内(英語版)Document18 pages2020会社案内(英語版)DAC ORGANIZERNo ratings yet
- Australian Institute For Teaching and School Leadership - AITSLDocument5 pagesAustralian Institute For Teaching and School Leadership - AITSLYu LiNo ratings yet
- Analgesia SystemDocument7 pagesAnalgesia SystemMudassar Roomi100% (1)
- Pilot StudyDocument11 pagesPilot StudySatya Prakash80% (5)
- FS Jack: Information GuideDocument12 pagesFS Jack: Information GuideGemma gladeNo ratings yet
- English Assignment Team:: Devia Annisa E. E44190045 2. TB. Aditia Rizki E44190027 3. Tedi Irfan Jelata E44190028Document3 pagesEnglish Assignment Team:: Devia Annisa E. E44190045 2. TB. Aditia Rizki E44190027 3. Tedi Irfan Jelata E4419002856TB. Aditia RizkiNo ratings yet
- Acoustic Emission InspectionDocument7 pagesAcoustic Emission InspectionAntonio PerezNo ratings yet
- Listening 2 - Log 4 - Answer. SheetDocument3 pagesListening 2 - Log 4 - Answer. SheetNguyen LeeNo ratings yet
- Bartending and Catering: Agenda: Basics of Bartending Bar Tools and EquipmentDocument146 pagesBartending and Catering: Agenda: Basics of Bartending Bar Tools and EquipmentMars Mar100% (1)
- Quickguide Students For CopyrightsDocument2 pagesQuickguide Students For Copyrightslordvorldomort100% (1)
- Crash of Air France ConcordeDocument11 pagesCrash of Air France ConcordeAhmad Aimi SafuanNo ratings yet
- Chen2019 PDFDocument5 pagesChen2019 PDFPriya VeerNo ratings yet
- Meta Hids by eBPFDocument27 pagesMeta Hids by eBPFninggou.yangNo ratings yet