Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Investment Appraisal
Uploaded by
aryananvekar646Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Investment Appraisal
Uploaded by
aryananvekar646Copyright:
Available Formats
Investment appraisal: quantitative and qualitative evaluation of an investment desicion
Working capital: the money available to meet your current short term liabilities
There are three methods:
- Payback period: used to work out the number of years and months it will take for the investment
of a business to pay for itself
- Average rate of return: technique that expresses the annual forecast as a percentage of the initial
capital cost
- Net present value: shows the real value of estimated future net cash flows so that the investment
appraisal is more accurate
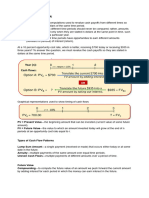
Net present value
Pros:
- considers the change in value of money over time, which provides the business with a more.
accurate understanding of the future value of cash flows for an investment.
- Considers inflation.
- Can handle multiple discount rates or varying cash flows.
- Takes into account time value of money
- Takes into account all future cash flows
Cons:
- Challenging to accurately arrive at a discount rate that represents the investment’s true risk.
- Complicated to calculate in comparison to ARR and payback period.
- Assumptions of the future value of money have to made and this can be inaccurate.
- Discount rate chosen to calculate present value could be inaccurate depending on future economic
conditions.
- Don’t know if the discount rate chosen is the appropriate on to use.
The higher the discount rate the smaller the present value
Project that gives highest net present value, that is the one that you pick/ go for
Present value (single year) = Net cash flow x discount factor
Net present value (NVP) = Sum of all present values of return – original cost
You might also like
- Chapter 12 - Capital Expenditure Decisions: Estimating The Initial Cash PaymentDocument3 pagesChapter 12 - Capital Expenditure Decisions: Estimating The Initial Cash Paymentmaxwell maingiNo ratings yet
- BEC 3 - Financial ManagementDocument11 pagesBEC 3 - Financial ManagementAudreys PageNo ratings yet
- Time Value of MoneyDocument44 pagesTime Value of MoneyJoenna Marie Morales0% (1)
- Powerpoint Presentation On Project EngineeringDocument16 pagesPowerpoint Presentation On Project EngineeringArnab DasNo ratings yet
- Techniques of Investment AnalysisDocument32 pagesTechniques of Investment AnalysisPranjal Verma0% (1)
- Unit VDocument8 pagesUnit VJohn LastonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 Investment AppraisalDocument3 pagesChapter 02 Investment AppraisalMarzuka Akter KhanNo ratings yet
- Applied Corporate Finance. What is a Company worth?From EverandApplied Corporate Finance. What is a Company worth?Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Non Discounted Techniques LectureDocument3 pagesNon Discounted Techniques Lectureamormi2702No ratings yet
- NotesFMF FinalDocument52 pagesNotesFMF FinalKyrelle Mae LozadaNo ratings yet
- Investment Decisions: Decisions Through The Life-Cycle of A Petroleum ProjectDocument6 pagesInvestment Decisions: Decisions Through The Life-Cycle of A Petroleum Projectjhon berez223344No ratings yet
- Engineering Economics COE109 Prelim ReviewerDocument7 pagesEngineering Economics COE109 Prelim Reviewersantoniajhonmark50No ratings yet
- Module in Financial Management - 09Document7 pagesModule in Financial Management - 09Karla Mae GammadNo ratings yet
- EVALUATION OF INVESTMENT PROPOSALS LectDocument6 pagesEVALUATION OF INVESTMENT PROPOSALS LectSimranjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting or InvesmentDocument6 pagesCapital Budgeting or Invesmenttkt ecNo ratings yet
- 09.1 Module in Financial Management 09Document8 pages09.1 Module in Financial Management 09Fire burnNo ratings yet
- Capital BudgetingDocument8 pagesCapital BudgetingYash PatilNo ratings yet
- Prepared By:-Arvind Singh Shivani BabbarDocument36 pagesPrepared By:-Arvind Singh Shivani BabbarArvind SinghNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting Decisions Under Uncertainity - 1 - 09 - 2019Document55 pagesCapital Budgeting Decisions Under Uncertainity - 1 - 09 - 2019Kaushik meridianNo ratings yet
- Annuity Factor Formula NotesDocument2 pagesAnnuity Factor Formula NotesZofigan khawajaNo ratings yet
- Capital BudgetingDocument6 pagesCapital BudgetingKhushbu PriyadarshniNo ratings yet
- Capital BudgetingDocument14 pagesCapital BudgetingD Y Patil Institute of MCA and MBANo ratings yet
- Project Management: The Financial Perspective: Muhammad UmerDocument37 pagesProject Management: The Financial Perspective: Muhammad Umermumer1No ratings yet
- Finman TheoriesDocument4 pagesFinman TheoriesMoguriNo ratings yet
- Financial Modelling and ValuationDocument17 pagesFinancial Modelling and ValuationSHIKHA CHAUHANNo ratings yet
- CH 02 Revised Financial Management by IM PandeyDocument38 pagesCH 02 Revised Financial Management by IM PandeyAnjan Kumar100% (6)
- In Other Words, NPV Is The Additional Value Created in The Investment, So para Di Ka Lugi, NPV Should Always Be PositiveDocument1 pageIn Other Words, NPV Is The Additional Value Created in The Investment, So para Di Ka Lugi, NPV Should Always Be PositiveStevenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document2 pagesChapter 14jhouvanNo ratings yet
- Resumen FinancesDocument11 pagesResumen Financesfranchesca guillenNo ratings yet
- Technic of Cap BudDocument6 pagesTechnic of Cap BudAmar NathNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - MeasurementDocument3 pagesChapter 3 - MeasurementCait PostNo ratings yet
- Capital BudgetingDocument8 pagesCapital BudgetingVarsha KastureNo ratings yet
- Unit - Vi Energy Economic Analysis: Energy Auditing & Demand Side ManagementDocument18 pagesUnit - Vi Energy Economic Analysis: Energy Auditing & Demand Side ManagementDIVYA PRASOONA CNo ratings yet
- CapitDocument8 pagesCapitjanice100% (1)
- Investment Evaluation MethodDocument13 pagesInvestment Evaluation MethodBAo TrAmNo ratings yet
- BF 14Document5 pagesBF 14zhairenaguila22No ratings yet
- Time Value of MoneyDocument16 pagesTime Value of MoneyAnmol Shrestha100% (1)
- CHAPTER 2 - Investment AppraisalDocument19 pagesCHAPTER 2 - Investment AppraisalMaleoaNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Value and ReturnDocument38 pagesConcepts of Value and ReturnVaishnav KumarNo ratings yet
- Capital Investment Analysis and Project Assessment: PurdueDocument12 pagesCapital Investment Analysis and Project Assessment: PurdueFAKHAN88No ratings yet
- Elec 2 HighlightedDocument16 pagesElec 2 HighlightednoelNo ratings yet
- An MBA in a Book: Everything You Need to Know to Master Business - In One Book!From EverandAn MBA in a Book: Everything You Need to Know to Master Business - In One Book!No ratings yet
- Capital BudgetingDocument22 pagesCapital BudgetingRajatNo ratings yet
- Finance 301 Learning Objectives by Chapter Chapter 1: IntroductionDocument7 pagesFinance 301 Learning Objectives by Chapter Chapter 1: Introductionhughng92No ratings yet
- 6 Capital Budgeting TechniquesDocument49 pages6 Capital Budgeting TechniquesAkwasi BoatengNo ratings yet
- Time Value of Money (TVM)Document5 pagesTime Value of Money (TVM)Yesha Jade SaturiusNo ratings yet
- Ital Budgeting: Budgeting Refers To Any Technique Used To Determine The Financial Wisdom of A LongDocument2 pagesItal Budgeting: Budgeting Refers To Any Technique Used To Determine The Financial Wisdom of A LongHazem El SayedNo ratings yet
- Time Value of MoneyDocument24 pagesTime Value of MoneyNitin R GondNo ratings yet
- BEC Notes Chapter 3Document6 pagesBEC Notes Chapter 3cpacfa90% (10)
- Year, Financial Management: Capital BudgetingDocument9 pagesYear, Financial Management: Capital BudgetingPooja KansalNo ratings yet
- Weighted Average Cost of CapitalDocument6 pagesWeighted Average Cost of CapitalStoryKingNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Lecture Slides - Ch02Document39 pagesWeek 2 Lecture Slides - Ch02LuanNo ratings yet
- Energy Audit Notes On Economic Aspects Abd Financial AnalysisDocument11 pagesEnergy Audit Notes On Economic Aspects Abd Financial AnalysisChiru Dana100% (1)
- Time Value of Money: Pooja GuptaDocument24 pagesTime Value of Money: Pooja GuptaRagh KrishhNo ratings yet
- Module Capital BudgetingDocument6 pagesModule Capital BudgetingCeejay RoblesNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting HandoutDocument15 pagesCapital Budgeting HandoutJoshua Cabinas100% (1)
- Engineering EconomicsDocument4 pagesEngineering EconomicstkubvosNo ratings yet
- Common Stock Valuation - Part 1Document35 pagesCommon Stock Valuation - Part 1Mahmoud HassaanNo ratings yet
- Financial Aspects of Project Analysis: ReferencesDocument40 pagesFinancial Aspects of Project Analysis: ReferencesRusty PlacinoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 19 - Complex NumbersDocument2 pagesAssignment 19 - Complex Numbersaryananvekar646No ratings yet
- Chemistry SL - Answers - Second Edition - Pearson 2014Document66 pagesChemistry SL - Answers - Second Edition - Pearson 2014aryananvekar6460% (1)
- Assignment 21 - Matrices II, SOLUTIONSDocument5 pagesAssignment 21 - Matrices II, SOLUTIONSaryananvekar646No ratings yet
- Euler Method, Coupled Differential Equations, LinearDocument13 pagesEuler Method, Coupled Differential Equations, Lineararyananvekar646No ratings yet
- TGG EssayDocument2 pagesTGG Essayaryananvekar646No ratings yet
- Business 124234Document2 pagesBusiness 124234aryananvekar646No ratings yet
- BMDocument1 pageBMaryananvekar646No ratings yet