Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CCM Hypertension
Uploaded by
aba766467Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CCM Hypertension
Uploaded by
aba766467Copyright:
Available Formats
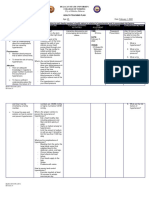
Regularly measure the
older age
patient’s blood pressure
genetics
Screen for secondary causes
CLINICAL CONCEPT MAP HYPERTENSION being overweight
of hypertension
or obese
Review the patient’s
treatment list
not being
smoke. physically active
Risk for Unstable Blood
have a lot of stress. high-salt diet
Pressure related to
Electrolyte imbalances are over 65
do not have proper exercise
Help the patient identify their eat too much salt
personal risk factors
Teach the patient how to monitor Deficient knowledge related
to lack of understanding of severe headaches
blood pressure
Provide positive reinforcement hypertension and its effect chest pain.
on the body as evidenced dizziness.
by the inability to recall
information provided.
Hypertension (high blood
pressure) is when the pressure in
Assist the patient in lifelong change
your blood vessels is too high
Administer beta-blockers or
(140/90 mmHg or higher). It is
calcium-channel blockers as Decrease cardiac output common but can be serious if
prescribed
related to impaired muscle not treated
Monitor and increase activity as
tolerated constriction as evidence
Limit salt intake
by tachycardia
Key: Increase blood pressure
Definition:
Causes: Blood pressure Vasoconstriction
measurement
Risk factors:
Heart
Signs and symptoms: examination Heart attack Endothelial injury
Complications: Eye examination Cerebrovascular
diseases
Diagnostic tests: Ischemia
Nadolol (Corgard) 20mg Renal failure
Medical treatment: Propranolol (Inderal) 10mg Retinopathy
Diagnosis: metoprolol (Toprol) 25-100mg
Target organ damage
carvedilol (Coreg) 3.125-25 mg
Nursing interventions:
Pathophysiology:
You might also like
- Causes of High Blood Pressure: Natural Blood Pressure Solutions and RemediesFrom EverandCauses of High Blood Pressure: Natural Blood Pressure Solutions and RemediesRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- NCP PPHDocument2 pagesNCP PPHMark Joseph Christian100% (1)
- Joval TanDocument2 pagesJoval TanJoval TanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - HYPERTENSIONDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan - HYPERTENSIONJas Slk0% (1)
- NCP-DP NCM112LecDocument4 pagesNCP-DP NCM112LecShane CabucosNo ratings yet
- Preeclampsia Nursing Care PlanDocument8 pagesPreeclampsia Nursing Care PlanElli SuñgaNo ratings yet
- NCP #2Document2 pagesNCP #2Faith CalimlimNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument2 pagesHypertensionBlessie FernandezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan HypertensionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Hypertensionderic98% (124)
- Assessment Diagnosis Interference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Interference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMelDred Cajes BolandoNo ratings yet
- Materi Koas GinjalDocument30 pagesMateri Koas GinjalRichard 151289No ratings yet
- Final Drug Study and Nursing Care For Cs Final Na GidDocument7 pagesFinal Drug Study and Nursing Care For Cs Final Na GidMor Shi DA BalutintikNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan HYPERTENSIONDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan HYPERTENSIONJasmin T. RegaspiNo ratings yet
- DS - DutyDocument19 pagesDS - DutyMarie Kelsey Acena MacaraigNo ratings yet
- HT SampleDocument4 pagesHT SampleElla YuNo ratings yet
- High Blood PressureDocument2 pagesHigh Blood PressureKreisl DizonNo ratings yet
- 01 Cir 39 3 403Document19 pages01 Cir 39 3 403Al FarouqNo ratings yet
- Hypertension GigiDocument10 pagesHypertension GigiAhamefula ChinazaNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Decreased Cardiac OutputDaniel Andre S. SomorayNo ratings yet
- Drug Study StaDocument3 pagesDrug Study StaarjeighNo ratings yet
- NCP 1Document1 pageNCP 1hsiriaNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure NCPDocument6 pagesCongestive Heart Failure NCPShaira Ann Calamba100% (1)
- Data Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesData Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals Intervention Rationale EvaluationmarielfmerlanNo ratings yet
- Case Study of HypertensionDocument37 pagesCase Study of HypertensionAngelo Bellon Bautista75% (4)
- Problem List: Vital SignsDocument13 pagesProblem List: Vital SignsRey Jean GarciaNo ratings yet
- Slide Referensi Natexam 2018Document54 pagesSlide Referensi Natexam 2018Sellyta HasugianNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument1 pageDrugspeppercramNo ratings yet
- NCP 1Document4 pagesNCP 1Jezrale FameNo ratings yet
- Acute GastroenteritisDocument3 pagesAcute Gastroenteritisreejay123No ratings yet
- Risk For Decreased Cardiac Output: Nursing DiagnosisDocument4 pagesRisk For Decreased Cardiac Output: Nursing DiagnosisRiska RamadaniNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching PlanDocument3 pagesHealth Teaching PlanElaine P. RoqueNo ratings yet
- Name: Age/Sex: Medical Diagnosis: Nursing Diagnosis: Short Term Goal: Long Term GoalDocument5 pagesName: Age/Sex: Medical Diagnosis: Nursing Diagnosis: Short Term Goal: Long Term GoalThoLitz AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE)Document5 pagesAngiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE)Isabella SamsonNo ratings yet
- Baber ReqDocument3 pagesBaber ReqRichelle Sandriel C. de CastroNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPNurhaifa MocademaNo ratings yet
- Reversing Chronic Hypertension Naturally : The Healthy way to Prevent the Silent KillerFrom EverandReversing Chronic Hypertension Naturally : The Healthy way to Prevent the Silent KillerNo ratings yet
- Beating High Blood Pressure Naturally: Your Complete Guide to Self-Care, Healthy Eating, and Herbal Remedies: Self Care, #1From EverandBeating High Blood Pressure Naturally: Your Complete Guide to Self-Care, Healthy Eating, and Herbal Remedies: Self Care, #1No ratings yet
- The Complete Guide to Hypertension & High Blood Pressure: Symptoms, Risks, Diagnosis, Treatments & CuresFrom EverandThe Complete Guide to Hypertension & High Blood Pressure: Symptoms, Risks, Diagnosis, Treatments & CuresNo ratings yet
- How to Control High Blood Pressure Without MedicationsFrom EverandHow to Control High Blood Pressure Without MedicationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Reverse Hypertension: Lower Your Blood Pressure With Simple StepsFrom EverandReverse Hypertension: Lower Your Blood Pressure With Simple StepsNo ratings yet
- High Blood Pressure: How to Lower Blood Pressure Naturally and Prevent Heart DiseaseFrom EverandHigh Blood Pressure: How to Lower Blood Pressure Naturally and Prevent Heart DiseaseNo ratings yet
- Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Cure: Powerful Techniques to Stimulate Your Hormones, Improve Metabolism, And Boost Your Energy LevelsFrom EverandChronic Fatigue Syndrome Cure: Powerful Techniques to Stimulate Your Hormones, Improve Metabolism, And Boost Your Energy LevelsNo ratings yet
- Natural High Blood Pressure Solutions: Lower Your Blood Pressure Naturally Using Diet And Natural Remedies Without MedicationFrom EverandNatural High Blood Pressure Solutions: Lower Your Blood Pressure Naturally Using Diet And Natural Remedies Without MedicationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure) - From Causes to Control: Health MattersFrom EverandHypertension (High Blood Pressure) - From Causes to Control: Health MattersNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure Protocol: Lower Your Blood Pressure By 20 Points or More With Fewer MedicationsFrom EverandBlood Pressure Protocol: Lower Your Blood Pressure By 20 Points or More With Fewer MedicationsNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure Protocol: Lower Your Blood Pressure By 20 Points or More with Fewer MedicationsFrom EverandBlood Pressure Protocol: Lower Your Blood Pressure By 20 Points or More with Fewer MedicationsNo ratings yet
- Dash Diet Cookbook: Easy and Healthy Dash Diet Recipes to Lower Your Blood Pressure. 7-Day Meal Plan and 7 Simple Rules for Weight LossFrom EverandDash Diet Cookbook: Easy and Healthy Dash Diet Recipes to Lower Your Blood Pressure. 7-Day Meal Plan and 7 Simple Rules for Weight LossNo ratings yet
- High Blood Pressure: Natural Self-help for Hypertension, including 60 recipesFrom EverandHigh Blood Pressure: Natural Self-help for Hypertension, including 60 recipesNo ratings yet
- Lower Your High Blood Pressure Naturally - How To Control High Blood Pressure Without MedicationFrom EverandLower Your High Blood Pressure Naturally - How To Control High Blood Pressure Without MedicationNo ratings yet
- The Hypertension Mastery Bible: Your Blueprint for Complete Hypertension ManagementFrom EverandThe Hypertension Mastery Bible: Your Blueprint for Complete Hypertension ManagementNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Hypertension and Heart DiseasesFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Hypertension and Heart DiseasesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The High Blood Pressure Diet Natural Foods that will Lower your Blood Pressure within Weeks!From EverandThe High Blood Pressure Diet Natural Foods that will Lower your Blood Pressure within Weeks!No ratings yet
- Blood Pressure Monitoring Journal: A Hypertension Diary and Activity Log Volume IiFrom EverandBlood Pressure Monitoring Journal: A Hypertension Diary and Activity Log Volume IiNo ratings yet
- Rifle May 2015 USADocument72 pagesRifle May 2015 USAhanshcNo ratings yet
- Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion 2marksDocument15 pagesGas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion 2marksAbdul rahumanNo ratings yet
- Activity On Noli Me TangereDocument5 pagesActivity On Noli Me TangereKKKNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of the pulp cavity กย 2562-1Document84 pagesAnatomy of the pulp cavity กย 2562-1IlincaVasilescuNo ratings yet
- QuexBook TutorialDocument14 pagesQuexBook TutorialJeffrey FarillasNo ratings yet
- ELEVATOR DOOR - pdf1Document10 pagesELEVATOR DOOR - pdf1vigneshNo ratings yet
- Application Form InnofundDocument13 pagesApplication Form InnofundharavinthanNo ratings yet
- Final Project Strategic ManagementDocument2 pagesFinal Project Strategic ManagementMahrukh RasheedNo ratings yet
- Disassembly Procedures: 1 DELL U2422HB - U2422HXBDocument6 pagesDisassembly Procedures: 1 DELL U2422HB - U2422HXBIonela CristinaNo ratings yet
- QSP 04bDocument35 pagesQSP 04bakrastogi94843No ratings yet
- Assessment of The Genitourinary System: GeneralDocument2 pagesAssessment of The Genitourinary System: GeneralMaharani UtamiNo ratings yet
- Summary of Bill of Quantities ChurchDocument52 pagesSummary of Bill of Quantities ChurchBiniamNo ratings yet
- My Mother at 66Document6 pagesMy Mother at 66AnjanaNo ratings yet
- Case CapsuleDocument8 pagesCase CapsuleLiza BulsaraNo ratings yet
- Canoe Matlab 001Document58 pagesCanoe Matlab 001Coolboy RoadsterNo ratings yet
- Cummin C1100 Fuel System Flow DiagramDocument8 pagesCummin C1100 Fuel System Flow DiagramDaniel KrismantoroNo ratings yet
- Perancangan Crushing Plant Batu Andesit Di PT Nurmuda Cahaya Desa Batujajar Timur Kecamatan Batujajar Kabupaten Bandung Barat Provinsi Jawa BaratDocument8 pagesPerancangan Crushing Plant Batu Andesit Di PT Nurmuda Cahaya Desa Batujajar Timur Kecamatan Batujajar Kabupaten Bandung Barat Provinsi Jawa BaratSutan AdityaNo ratings yet
- CV Augusto Brasil Ocampo MedinaDocument4 pagesCV Augusto Brasil Ocampo MedinaAugusto Brasil Ocampo MedinaNo ratings yet
- PresentationDocument27 pagesPresentationMenuka WatankachhiNo ratings yet
- MMS - IMCOST (RANJAN) Managing Early Growth of Business and New Venture ExpansionDocument13 pagesMMS - IMCOST (RANJAN) Managing Early Growth of Business and New Venture ExpansionDhananjay Parshuram SawantNo ratings yet
- Durex 'S Marketing Strategy in VietnamDocument45 pagesDurex 'S Marketing Strategy in VietnamPham Nguyen KhoiNo ratings yet
- Produktkatalog SmitsvonkDocument20 pagesProduktkatalog Smitsvonkomar alnasserNo ratings yet
- Acer N300 ManualDocument50 pagesAcer N300 Manualc_formatNo ratings yet
- What Are The Spacer Bars in RC Beams - QuoraDocument3 pagesWhat Are The Spacer Bars in RC Beams - QuoradesignNo ratings yet
- Sandstorm Absorbent SkyscraperDocument4 pagesSandstorm Absorbent SkyscraperPardisNo ratings yet
- Close Enough To Touch by Victoria Dahl - Chapter SamplerDocument23 pagesClose Enough To Touch by Victoria Dahl - Chapter SamplerHarlequinAustraliaNo ratings yet
- Standard Answers For The MSC ProgrammeDocument17 pagesStandard Answers For The MSC ProgrammeTiwiNo ratings yet
- Friction: Ultiple Hoice UestionsDocument5 pagesFriction: Ultiple Hoice Uestionspk2varmaNo ratings yet
- SOL LogicDocument21 pagesSOL LogicJa RiveraNo ratings yet
- Umwd 06516 XD PDFDocument3 pagesUmwd 06516 XD PDFceca89No ratings yet