Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter-3 6
Uploaded by
azazelrallos0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageThis document discusses obligations with a penal clause under Philippine law. It states that a penalty substitutes damages and interest for noncompliance, unless otherwise stipulated. Damages are still due if the obligor refuses to pay the penalty or acts fraudulently. The debtor cannot exempt performance by paying the penalty, unless expressly allowed. The creditor cannot demand both performance and payment of the penalty, unless the right to do so is clearly granted. Proof of actual damages is not needed to demand the penalty. The judge may equitably reduce the penalty if the obligation was partly or irregularly complied with, or if the penalty is iniquitous or unconscionable. Nullity of the penal clause does not nullify the
Original Description:
Original Title
Chapter-3.6
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses obligations with a penal clause under Philippine law. It states that a penalty substitutes damages and interest for noncompliance, unless otherwise stipulated. Damages are still due if the obligor refuses to pay the penalty or acts fraudulently. The debtor cannot exempt performance by paying the penalty, unless expressly allowed. The creditor cannot demand both performance and payment of the penalty, unless the right to do so is clearly granted. Proof of actual damages is not needed to demand the penalty. The judge may equitably reduce the penalty if the obligation was partly or irregularly complied with, or if the penalty is iniquitous or unconscionable. Nullity of the penal clause does not nullify the
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageChapter-3 6
Uploaded by
azazelrallosThis document discusses obligations with a penal clause under Philippine law. It states that a penalty substitutes damages and interest for noncompliance, unless otherwise stipulated. Damages are still due if the obligor refuses to pay the penalty or acts fraudulently. The debtor cannot exempt performance by paying the penalty, unless expressly allowed. The creditor cannot demand both performance and payment of the penalty, unless the right to do so is clearly granted. Proof of actual damages is not needed to demand the penalty. The judge may equitably reduce the penalty if the obligation was partly or irregularly complied with, or if the penalty is iniquitous or unconscionable. Nullity of the penal clause does not nullify the
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
RFBT 1 – Law on Obligations and Contracts 13
TITLE I: OBLIGATIONS (Arts. 1156-1304.) – Chapter 3.6: Obligations with a Penal Clause
CHAPTER 3: DIFFERENT KINDS OF OBLIGATIONS
Obligations with a Penal Clause
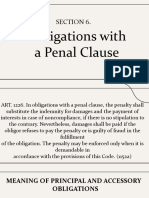
Art. 1226. In obligations with a penal clause, the penalty shall
substitute the indemnity for damages and the payment of
interests in case of noncompliance, if there is no stipulation to
the contrary. Nevertheless, damages shall be paid if the
obligor refuses to pay the penalty or is guilty of fraud in the
fulfilment of the obligation.
General Rule
Penalty serves as substitute to damages and interest
Exceptions
1. Stipulation to contrary
2. Debtor refuses to pay penalty
3. Debtor is guilty of fraud
Art. 1227. The debtor cannot exempt himself from the
performance of the obligation by paying the penalty, save in
the case where this right has been expressly reserved for him.
Neither can the creditor demand the fulfilment of the
obligation and the satisfaction of the penalty at the same time,
unless this right has been clearly granted him. However, if
after the creditor has decided to require the fulfilment of the
obligation, the performance thereof should become
impossible without his fault, the penalty may be enforced.
Art. 1228. Proof of actual damages suffered by the creditor is
not necessary in order that the penalty may be demanded.
Art. 1229. The judge shall equitably reduce the penalty when
the principal obligation has been partly or irregularly complied
with by the debtor. Even if there has been no performance,
the penalty may also be reduced by the courts if it is iniquitous
or unconscionable.
Art. 1230. The nullity of the penal clause does not carry with it
that of the principal obligation.
The nullity of the principal obligation carries with it
that of the penal clause.
Example Scenario:
1. Y is a tenant of X. In their lease contract, there is a
stipulation where should Y fail to pay two (2)
consecutive monthly payments, she will agree to
become X’s mistress.
2. Y agreed to become X’s mistress. If ever Y wanted to
back out from their agreement, Y must pay a penalty
of PHP 10,000.
You might also like
- Orange Black Modern Lawyer PresentationDocument13 pagesOrange Black Modern Lawyer PresentationSherbin PatulotNo ratings yet
- Oblicon Module 7 (Section 6)Document5 pagesOblicon Module 7 (Section 6)Mika MolinaNo ratings yet
- Obligations With A Penal ClauseDocument2 pagesObligations With A Penal ClauseErlene LinsanganNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Section 6Document22 pagesChapter 3 Section 6James ErsandoNo ratings yet
- ObliCon Chapter III Sections 5 6Document4 pagesObliCon Chapter III Sections 5 6Jheza May BañezNo ratings yet
- SECTION 6. - Obligations With A Penal ClauseDocument1 pageSECTION 6. - Obligations With A Penal ClauseGERBGARCIANo ratings yet
- Oblifuckingcon NotesDocument10 pagesOblifuckingcon NotesYfhps LnmNo ratings yet
- Obligations and Contracts11Document5 pagesObligations and Contracts11BenjieRoqueNo ratings yet
- Cabral, Arnold F. 03242022Document2 pagesCabral, Arnold F. 03242022ARNOLD CABRALNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Kinds of Obligations - in - Divisible Obligations and Obligations With PenaltiesDocument3 pagesLecture - Kinds of Obligations - in - Divisible Obligations and Obligations With PenaltiesMickaela Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Article 1233. A Debt Shall Not Be Understood To Have Been Paid Unless The Thing or Service in Which TheDocument3 pagesArticle 1233. A Debt Shall Not Be Understood To Have Been Paid Unless The Thing or Service in Which ThePeytNo ratings yet
- WWW Law Activity 7 & 8Document4 pagesWWW Law Activity 7 & 8Tan ToyNo ratings yet
- Article 1223-1230Document25 pagesArticle 1223-1230viernazanne.viadoNo ratings yet
- Articles 1226-1230 (Obligations With A Penal Clause)Document30 pagesArticles 1226-1230 (Obligations With A Penal Clause)DJAN IHIAZEL DELA CUADRANo ratings yet
- Group 4 - Section6 - Obligations - With - A - Penal - ClauseDocument24 pagesGroup 4 - Section6 - Obligations - With - A - Penal - ClauseJann Marie CalledoNo ratings yet
- Kinds of Division : Obligations Deemed IndivisibleDocument2 pagesKinds of Division : Obligations Deemed IndivisibleFarah Tolentino NamiNo ratings yet
- Article 1227 1235Document2 pagesArticle 1227 1235JANET MARIE MERCADONo ratings yet
- Section 6 - Obligations With A Penal Cause (Arts. 1126-1230)Document11 pagesSection 6 - Obligations With A Penal Cause (Arts. 1126-1230)Patricia DesateNo ratings yet
- Oblicon Reviewer FinalsDocument13 pagesOblicon Reviewer FinalscessyJDNo ratings yet
- Modes-of-Extinguishment Loss To NovationDocument18 pagesModes-of-Extinguishment Loss To NovationRizza Angela MangallenoNo ratings yet
- FT Oblicon ReviewerDocument37 pagesFT Oblicon ReviewerIrine L. LancionNo ratings yet
- Obligations With A Penal ClauseDocument7 pagesObligations With A Penal ClausejustineNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Section 6 On BUSLAWDocument1 pageChapter 3 Section 6 On BUSLAWTherese Chiu83% (6)
- CHAPTER 3, Section 6: Obligations With A Penal ClauseDocument13 pagesCHAPTER 3, Section 6: Obligations With A Penal ClauseSergio ConjugalNo ratings yet
- 01 Civ2 2020 CompilationsDocument218 pages01 Civ2 2020 Compilationsbobbyricky100% (1)
- PAYMENT OR PERFORMANCE Bsa 2aDocument57 pagesPAYMENT OR PERFORMANCE Bsa 2aEJ HipolitoNo ratings yet
- OBLICON 2nd ExamDocument25 pagesOBLICON 2nd ExamXandredg Sumpt LatogNo ratings yet
- Codal CivDocument16 pagesCodal Civmarjbperez7697No ratings yet
- Section 6-Obligations With A Penal CauseDocument3 pagesSection 6-Obligations With A Penal CauseMars TubalinalNo ratings yet
- Arts. 1226 1230Document13 pagesArts. 1226 1230Vj McNo ratings yet
- Assignment #5Document4 pagesAssignment #5Lenmariel GallegoNo ratings yet
- BL ASSIGNMENT (Reden)Document4 pagesBL ASSIGNMENT (Reden)Erlinda LopezNo ratings yet
- OBLIQUIZ V 1 Jan13Document18 pagesOBLIQUIZ V 1 Jan13Roger Montero Jr.No ratings yet
- Kinds of Obligations 2024Document11 pagesKinds of Obligations 2024leighNo ratings yet
- Raytos - Article 1226Document3 pagesRaytos - Article 1226Jonalyn RaytosNo ratings yet
- Oblicon Study Guide (11) Oblicon Study GuideDocument3 pagesOblicon Study Guide (11) Oblicon Study Guiderosalinda ibaleNo ratings yet
- SECTION VI - Study GuideDocument3 pagesSECTION VI - Study GuideLorraine CaliwanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 SEC. 6 Arts. 1226-1230Document6 pagesCHAPTER 3 SEC. 6 Arts. 1226-1230Kelsey De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Payment or Performance Bsa 2aDocument57 pagesPayment or Performance Bsa 2aAikor CarolinoNo ratings yet
- According To The Parties BoundDocument4 pagesAccording To The Parties BoundTin RobisoNo ratings yet
- Oblicon Art 1231 OnwardsDocument7 pagesOblicon Art 1231 OnwardsMajorie ArimadoNo ratings yet
- Study Guide No. 3 (Chapter 3)Document8 pagesStudy Guide No. 3 (Chapter 3)Hannah Marie AliñoNo ratings yet
- Article 1199Document5 pagesArticle 1199JenniferNo ratings yet
- Section 6 - Obligations With A Penal CodeDocument8 pagesSection 6 - Obligations With A Penal Codefer16_nehjNo ratings yet
- BSA 1-3 Meneses Module7Document8 pagesBSA 1-3 Meneses Module7MENESES, GENESIS A.No ratings yet
- Obligations and ContractsDocument19 pagesObligations and ContractskatrinaNo ratings yet
- BL MTDocument50 pagesBL MTSh1njo SantosNo ratings yet
- Extinguishment of ObligationsDocument128 pagesExtinguishment of ObligationsVal Sanchez100% (1)
- Oblicon - Codal (1193-1220)Document3 pagesOblicon - Codal (1193-1220)Joan MaanoNo ratings yet
- LawDocument3 pagesLawLeslie An GarciaNo ratings yet
- Section 4 - Joint and Solidary ObligationsDocument2 pagesSection 4 - Joint and Solidary ObligationsJillian PizarroNo ratings yet
- Philippine Oblicon Articles 1231-1260Document22 pagesPhilippine Oblicon Articles 1231-1260Danielle Alessandra T. Calpo100% (1)
- LAW 20013-Module 8Document11 pagesLAW 20013-Module 8Arago, Kathrina Julien S.No ratings yet
- M 6-B: O M E: Odule Ther Odes OF XtinguishmentDocument20 pagesM 6-B: O M E: Odule Ther Odes OF XtinguishmentDave Lester ApagaNo ratings yet
- GQ 2.3 - PaymentDocument8 pagesGQ 2.3 - PaymentAlvin ValerioNo ratings yet
- Discussion 1Document8 pagesDiscussion 1Elaisha Mae JocdongNo ratings yet
- Oblicon Week 5Document102 pagesOblicon Week 5Ashly MateoNo ratings yet
- Oblicon ReviewerDocument6 pagesOblicon ReviewerFatima Elaine AtienzaNo ratings yet
- 08 - Chapter 4Document33 pages08 - Chapter 4Vinay Kumar KumarNo ratings yet
- Life, Accident and Health Insurance in the United StatesFrom EverandLife, Accident and Health Insurance in the United StatesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Emergency Rescue andDocument4 pagesEmergency Rescue andazazelrallosNo ratings yet
- Fin 101 Midterms 2 - 110710Document1 pageFin 101 Midterms 2 - 110710azazelrallosNo ratings yet
- Vital SignsDocument5 pagesVital SignsazazelrallosNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash Equivalents Bank Reconciliation and Proof of Cash - 043913Document2 pagesCash and Cash Equivalents Bank Reconciliation and Proof of Cash - 043913azazelrallosNo ratings yet
- Bank Reconciliation and Proof of Cash Problems 01 04 - 043916Document2 pagesBank Reconciliation and Proof of Cash Problems 01 04 - 043916azazelrallosNo ratings yet
- AccountingDocument2 pagesAccountingazazelrallosNo ratings yet
- Prin 1Document3 pagesPrin 1azazelrallosNo ratings yet
- Prin 2Document4 pagesPrin 2azazelrallosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document2 pagesChapter 1azazelrallosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document5 pagesChapter 2azazelrallosNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 3Document3 pagesChapter-3 3azazelrallosNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 2Document2 pagesChapter-3 2azazelrallosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3.1Document3 pagesChapter 3.1azazelrallosNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 5Document1 pageChapter-3 5azazelrallosNo ratings yet