Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Abfghx Cfghheat Shfgheet Abx QN
Uploaded by
Răzvan RoșcaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Abfghx Cfghheat Shfgheet Abx QN
Uploaded by
Răzvan RoșcaCopyright:
Available Formats
lOMoARcPSD|27034002
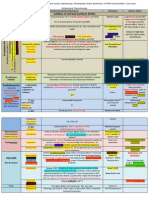
ANTIBIOTICS CHEAT SHEET
Mechanisms of action of antimicrobial agents.
Beta-lactams- penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems, bacitracin, vancomycin, monobactam,
Cell wall synthesis
lipoglycopeptides, lipopeptides
Protein synthesis chloramphenicol, tetracyclines, aminoglycosides, macrolides, lincosamides, oxazolidinones
Cell membrane polymyxins
Nucleic acid function quinolones
Intermediary metabolism sulfonamides, trimethoprim
Inhibitors of Folate Synthesis:
Sulfonamides- alteration of dihydropteroate
synthase
Trimthoprim- inhibition of dihydrofolate
reductase.
Downloaded by Razvan Rosca (rosca.razvan.2011@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|27034002
ANTIBIOTICS CHEAT SHEET
Spectrum of Activity
Broad Spectrum- ex: tetracyclines, carbapenems, 3rd gen quinolones, 2nd/3rd/4th gen cephalosporins, chloramphenicol,
PCN w/beta-lactamase inhibitors
Narrow Spectrum- ex: glycopeptides, bacitracin, aminoglycosides, sulfonamides, penicillin, lincosamides, macrolides,
vancomycin, aztreonam
*Think about what the ABX covers and the more it covers, the broader it is when treating infections.
Atypical Coverage: Pseudomonas Coverage:
Macrolides Ciprofloxacin, Levofloxacin
Tetracyclines Aminoglycosides
Quinolones Some 3rd Gen Cephalosporins
Chloramphenicol Cefepime (4th Gen Cephalosporin)
Ampicillin Broad Spectrum PCN (Ticarcillin,
Piperacillin)
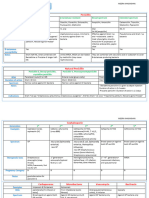
Overview of Antibiotics
PCN Spectrum
Ticarcillin/clavulanate Amoxicillin & Ampicillin Amoxicillin Nafcillin Pen V (Natural)
Piperacillin/tazobactum (w/ beta-lactamase inhibitor) Ampicillin Oxacillin
Cloxacillin *Gm +
*Gm +/-, ESBL, Pseudomonas *Gm +/-, MSSA, Gm- anaerobes *Gm +/- Dicloxacillin
Penicillins *Gm +, MSSA
Time-dependent killing and are bactericidal, except
against Enterococci species. No atypical coverage.
Coverage:
o Natural PCN- Gram +, Enterococcus and anaerobes, Little Gram -
o Aminopenicillins- Adds activity against Gram – (HNPEK) *Haemophilus, Neisseria,
Proteus, E.coli, Klebsiella
Narrow
o Additional of beta lactamase inhibitor- Adds activity against MSSA, more Gram -, Gram – Anaerobes
o Antipseudomonal PCN (extended-spectrum PCN)- very broad coverage with expanded Gram -, Pseudomonas aeruginosa
o Antistaphylococcal PCN- enhanced activity with MSSA, lack Enterococcus activity
DDI:
o Probenecid can ↑ levels of PCN
o Bacteriostatic antibiotics (ex: tetracyclines) can ↓ effectiveness of PCN
o ↑ levels of methotrexate
o ↓ levels of mycophenolate active metabolites
o Nafcillin is a moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor
o Dicloxacillin & nafcillin can ↓ INR through ↑ metabolism of warfarin
Downloaded by Razvan Rosca (rosca.razvan.2011@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|27034002
ANTIBIOTICS CHEAT SHEET
Cephalosporins
Time-dependent killing and are bactericidal. Not active against Enterococcus, atypicals, Listeria, MRSA (except 5th Generation (LAME).
Coverage:
o 1st- Excel against Gram + (preferred cephalosporin against MSSA)
2nd- Split into 2 groups 1) Cefuroxime like agents cover more resistant S.pneumoniae, HNPEK; 2) Cephamycin drugs (Cefotetan,
Cefoxitin) have added anaerobic coverage
o 3rd- Ceftriaxone, Cefotaxime and oral drugs cover more resistant Streptococci and more Gram -; Ceftazidime lacks Gram + and covers
Pseudomonas
o 3rd w/beta lactamase inhibitor combo- added activity against MDR Pseudomonas and Gram -
o 4th- broad Gram -, including Pseudomonas, Gram +
o 5th- only beta-lactam with MRSA activity
DDI:
o Probenecid can ↑ levels of cephalosporins
o Enhance anticoagulant effect of warfarin by inhibiting production of clotting factors
o Drugs that ↓ stomach acid can ↓ bioavailability of some cephalosporins
Carbapenems
Time-dependent killing and are bactericidal. Not active against atypical, MRSA, VRE.
Coverage:
o VERY BROAD COVERAGE “BIG GUN”, generally used for MDR Gram -, most Gram +, Gram – (including ESBL producing bacteria),
anaerobes
o Ertapenem is different and has NO activity against Pseudomonas, Acinetobacter or Enterococcus
DDI:
o Probenecid can ↑ levels of cephalosporins
o ↓ levels of valproic acid leading to a loss of seizure control
o Use in caution in patients at risk for seizures
Monobactam
Aztreonam (similar to ceftazidime); acts like a beta-lactam, but it’s not…like splenda to sugar
Structure makes cross-reactivity with beta-lactam allergy unlikely, primarily used when beta-lactam allergy is present.
Coverage:
o Similar to Ceftazidime lacks Gram +, covers Gram - and covers Pseudomonas
Aminoglycosides
Concertation dependent killing and has post-antibiotic effect. Can use extended dose interval nomograms.
Coverage:
o Gram -, Pseudomonas
DDI:
o Use in caution with patients with impaired renal function
Quinolones
Concertation dependent killing and are bactericidal.
Coverage:
o Broad spectrum (Gram +, Gram -, Atypicals)
Downloaded by Razvan Rosca (rosca.razvan.2011@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|27034002
ANTIBIOTICS CHEAT SHEET
o Gemifloxacin, Levofloxacin, Moxifloxacin (GLM)- respiratory quinolones due to enhanced coverage of S.pneumoniae and atypical
coverage
o Ciprofloxacin, Levofloxacin- enhanced Gram -, including Pseudomonas
o Moxifloxacin- enhanced Gram + and anaerobic
DDI:
o Products contained multivalent cations (ex: antacids, vitamins, calcium rich foods) can chelate and inhibit absorption
o ↑ effects of warfarin, sulfonylureas/insulin and QT-prolonging drugs (moxifloxacin prolongs QT interval the most)
o Probenecid and NSAIDs can ↑ quinolone levels
o Ciprofloxacin is a P-gp substrate, strong 1A2 inhibitor and weak 3A4 inhibitor
Macrolides
Bacteriostatic activity related to total exposure of the drug (AUC/MIC).
Coverage:
o Good Atypical activity
DDI:
o Erythromycin and clarithromycin are 3A4 inhibitors and substrates
o Azithromycin is a substrate for 3A4 and inhibitor of 1A2 and P-gp; it has fewer drug interactions
o ALL MACROLIDES: DO NOT USE WITH AGENTS THAT CAN PROLONG THE QT INTERVAL
Tetracyclines
Bacteriostatic activity related to total exposure of the drug (AUC/MIC).
Coverage:
o Many Gram +, Gram -, including respiratory flora
o Doxy- used in mild MRSA skin infections, VRE in UTI
o Mino- enhanced Gram + and preferred for skin infections (acne)
o Tetra- rarely used, can be used in H.pylori regimens
DDI:
o Absorption is impaired by medications that contain divalent cations
o Tetracycline is a substrate of 3A4 and an inhibitor
o Doxycycline is a weak 3A4 inhibitor
o Enhance the anticoagulant effect with warfarin
Sulfonamides
Individually they are bacteriostatic, but collectively they are bactericidal. Lacks Pseudomonas, Enterococci, atypical or anaerobic coverage.
Coverage:
o Gram +, including Staphylococci/MRSA, many Gram –
DDI:
o Inhibitors of 2C8/9
o Cause ↑ INR with warfarin
o ↑ levels of sulfonylureas, metformin, phenytoin, dofetilide, azathioprine, methotrexate and mercaptopurine
o Levels of SMX/TMP can be ↓ by 2C8/9 inducers
o ↑ in hyperkalemia when used with ACE inhibitors, ARBs, aliskiren, potassium-sparing diuretics, cyclosporine, tacrolimus and more
Glycopeptide
Vancomycin
Coverage:
o Gram +, MRSA, Streptococci, Enterococci (not VRE), C.difficile
DDI:
o ↑ toxicity of other nephrotoxic drugs and ototoxic drugs
Lipoglycopeptide
Concentration-dependent killing and are bactericidal; (similar to Vancomycin, but have extended MOA)
Coverage:
Downloaded by Razvan Rosca (rosca.razvan.2011@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|27034002
ANTIBIOTICS CHEAT SHEET
o Gram +, MRSA, Streptococci, Enterococci (not VRE), C.difficile
DDI:
o Telavancin- cause QT prolongation
Daptomycin (Cubicin)
Concentration-dependent killing and are bactericidal.
Coverage:
o Gram +, MRSA, Streptococci, Enterococci, including VRE, *same coverage as Vancomycin but covers more organisms
DDI:
o Additive risk of muscle toxicity with statins
Oxazolidinones
Bacteriostatic activity.
Coverage:
o Gram +, MRSA, Streptococci, Enterococci, including VRE, *same coverage as Vancomycin but covers more organisms
DDI:
o Weak MAOI (caution in patients taking concurrent serotonergic or adrenergic drugs
o Avoid tyramine-containing foods
o Can exacerbate hypoglycemic episodes
Polymyxins
Concentration-dependent killing and bactericidal. Use in combo with another antibiotic due to the emergence of resistance.
Coverage:
o Gram -, Pseudomonas, used primarily with MDR Gram – pathogens
DDI:
o Other nephrotoxic agents can enhance nephrotoxicity
Chloramphenicol
Bactericidal
Coverage:
o Gram +, Gram -, anaerobes and atypicals
Lincosamides
Bacteriostatic
Coverage:
o Most aerobic and anaerobic Gram +, some MRSA, does not cover Enterococcus
Urinary Agents
Fosfomycin (Monurol)- inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis by inactivating the enzyme pyruval transferase; bactericidal
Coverage:
o E.coli (including ESBLs) and E.faecalis (including VRE)
Nitrofurantoin (Macrodantin, Macrobid, Furadantin)- bacterial cell wall inhibitor; bactericidal
Coverage:
o E.coli, Klebsiella, Enterobacter, S.aureus, Enterococcus (VRE)
Downloaded by Razvan Rosca (rosca.razvan.2011@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|27034002
ANTIBIOTICS CHEAT SHEET
Side Effect Chart (list not all inclusive)
PCN Caution w/ anaphylaxis allergy, GI upset, diarrhea, rash, ↑ LFTs, seizures w/accumulation
Cephalosporins (Pregnancy B)
Carbapenems
Monobactam Similar to PCN (N/V/D, rash and ↑ LFTs) (Pregnancy B)
Aminoglycosides Nephrotoxicity, Ototoxicity (Pregnancy D)
Quinolones GI upset/diarrhea, QT prolongation, peripheral neuropathy, CNS effects,
Hypoglycemia/hyperglycemia, ↑ LFTs, photosensitivity, crystalluria, Boxed warning: tendon
inflammation and/or rupture, muscle weakness (Pregnancy C)
Macrolides QT prolongation, hepatotoxicity, GI upset, taste perversion, ↑ LFTs (Pregnancy B/C)
Tetracyclines Rash, ↑BUN, photosensitivity, N/V/D (Pregnancy D)
Sulfonamides Caution w/G6PD deficiency, N/V/D, anorexia, skin reactions, crystalluria, photosensitivity, ↑K,
hypoglycemia, ↓ folate, ↑LFTs (Pregnancy C/D)
Vancomycin GI upset, infusion reaction (red man syndrome), nephrotoxicity, myelosuppression, fever, ototoxicity
(Pregnancy B-oral/C-IV)
Lipoglycopeptides Metallic taste, N/V, QT prolongation (Pregnancy C)
(Telavancin)
Daptomycin N/V/D, ↑CPK and myopathy (Pregnancy B)
Oxazolidinones Thrombocytopenia, headache, N/D, anemia, myelosuppression (Pregnancy C)
Polymyxins Nephrotoxicity, neurologic disturbances (Pregnancy C)
Chloramphenicol Gray syndrome, myelosuppression, dermatologic (angioedema, rash, Uticaria) *rarely used due to
side effects
Lincosamides C.diff, Severe or fatal skin reactions (SJS), N/V/D, rash, urticaria (Pregnancy B)
Fosfomycin (urinary) Peripheral edema, dizziness, headache, flatulence, nausea, rash (Pregnancy C)
Nitrofurantoin Optic neuritis, hepatoxicity, pulmonary toxicity, anemia, GI upset, headache, rash, brown urine
discoloration (harmless)
Storage
Refrigeration after reconstitution Refrigeration Recommended
Pen VK, Ampicillin, Augmentin, Cephalexin, Cefpodoxime, Amoxicillin (improves taste)
Cefprozil, Cefuroxime, Vancomycin (oral)
*all other do not refrigerate
No Renal Dose Dicloxacillin, oxacillin, nafcillin
Adjustment Ceftriaxone
Moxifloxacin
*not all inclusive Azithromycin, erythromycin
Doxycycline, minocycline, tigecycline
Linezolid
Clindamycin
Chloramphenicol
Downloaded by Razvan Rosca (rosca.razvan.2011@gmail.com)
You might also like
- Group 9 - Bacteriology Reporting (Written Report)Document6 pagesGroup 9 - Bacteriology Reporting (Written Report)DENISE MARA�ANo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Drugs: Laboratory of Microbiology Medical Faculty Brawijaya UniversityDocument38 pagesAntimicrobial Drugs: Laboratory of Microbiology Medical Faculty Brawijaya UniversityYuu Ayu'k LifestarNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics: Classification (Based On Mechanism of Action)Document35 pagesAntibiotics: Classification (Based On Mechanism of Action)Mohol DasNo ratings yet
- Sulfonamides and Their Mechanism of ActionDocument61 pagesSulfonamides and Their Mechanism of ActionYeshaa MiraniNo ratings yet
- Laboratory of Microbiology Medical Faculty UB 2009Document37 pagesLaboratory of Microbiology Medical Faculty UB 2009zianaNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Discovery Mechanisms ResistanceDocument25 pagesAntibiotic Discovery Mechanisms ResistanceMohammed Moutasim AyoubNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy NotesDocument9 pagesChemotherapy Notesnileshkumarhjoshi942No ratings yet
- Antibacterial Agents (1)Document44 pagesAntibacterial Agents (1)belindasithole965No ratings yet
- ChemotherapyDocument66 pagesChemotherapyElias HaimanotNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Chemotherapy IDocument30 pagesAntimicrobial Chemotherapy Inighat khanNo ratings yet
- Pharma AntimicrobialsDocument19 pagesPharma AntimicrobialsYuku BabyNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument23 pagesPharmacologymeher chohanNo ratings yet
- AntibioticDocument84 pagesAntibioticDr. Kalavati PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Inhibitor of Cell Wall Synthesis (ICWS) : Proteus ComboDocument12 pagesInhibitor of Cell Wall Synthesis (ICWS) : Proteus Comboflomax23100% (1)
- AntibioticsDocument10 pagesAntibioticsStevhenson PortacioNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology-Antibiotic 2021Document52 pagesPharmacology-Antibiotic 2021Ngọc VânNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Antimicrobial Chemotherapy: Mechanisms and SpectrumDocument31 pagesIntroduction to Antimicrobial Chemotherapy: Mechanisms and SpectrumPrasad SangishettyNo ratings yet
- Newer Antibiotics: Guide: DR Saroja A ODocument51 pagesNewer Antibiotics: Guide: DR Saroja A OparahulNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics Resistance - 20WDocument24 pagesAntibiotics Resistance - 20WflubbybananaNo ratings yet
- List of AntibioticsDocument10 pagesList of AntibioticsAia JavierNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic resistance in bacteria explainedDocument32 pagesAntibiotic resistance in bacteria explainedاحمد زيد سعيدNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics Classification GuideDocument16 pagesAntibiotics Classification GuideFarida CitraNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Solved Past PapersDocument10 pagesPharmacology Solved Past Papersfatima aghaNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument53 pagesAntibioticsMaheen IdreesNo ratings yet
- Aminoglycoside: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument11 pagesAminoglycoside: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaawajahat100% (3)
- Aminoglycosides (17.07.2017)Document44 pagesAminoglycosides (17.07.2017)Habibul Kowser (Rishat)No ratings yet
- Bacterial Cell Cycle, Morphology, and ClassificationDocument28 pagesBacterial Cell Cycle, Morphology, and ClassificationbellNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology: Fast and Dirty Board ReviewDocument7 pagesPharmacology: Fast and Dirty Board ReviewRochelleth7278No ratings yet
- Essential Antibiotic Guide for Medical StudentsDocument74 pagesEssential Antibiotic Guide for Medical StudentskaelenNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Action, Indications, and Dosing of Common AntimicrobialsDocument90 pagesMechanism of Action, Indications, and Dosing of Common AntimicrobialsJill PardoNo ratings yet
- Lec 7 - AntibioticsDocument46 pagesLec 7 - AntibioticsAiqa QaziNo ratings yet
- Buy The Book PDA DownloadDocument9 pagesBuy The Book PDA Downloadneilbert_jayNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument5 pagesAntibioticsLaureece Salm ApduhanNo ratings yet
- Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Effective: Antibiotics by ClassDocument4 pagesPseudomonas Aeruginosa. Effective: Antibiotics by ClassDocFrankNo ratings yet
- Alternative Second-Line Drugs For TuberculosisDocument42 pagesAlternative Second-Line Drugs For TuberculosisAlvin LaurenceNo ratings yet
- Print Antibiotics ReviewDocument6 pagesPrint Antibiotics ReviewtiuwangNo ratings yet
- Principles of Antimicrobial TherapyDocument19 pagesPrinciples of Antimicrobial TherapyMERVENo ratings yet
- Antimikroba-1Document21 pagesAntimikroba-1Richard MoralesNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy Lect 1Document26 pagesChemotherapy Lect 1kazelio2017No ratings yet
- Antimicrobial ChemotherapyDocument70 pagesAntimicrobial Chemotherapyamanialwerfalli4No ratings yet
- Clinical Pharmacology - Rationale Behind Antibiotics PrescriptionDocument12 pagesClinical Pharmacology - Rationale Behind Antibiotics PrescriptionhalesNo ratings yet
- Anti MicrobialDocument55 pagesAnti MicrobialNdayisaba CorneilleNo ratings yet
- DP On AglDocument12 pagesDP On AglDeepikaNo ratings yet
- Anti TB CologyDocument20 pagesAnti TB CologyManthan ChauhanNo ratings yet
- List of antibiotics: generic names, brands, classes and usesDocument9 pagesList of antibiotics: generic names, brands, classes and usesprince1500100% (1)
- Tri Widyawat & Sit Syarifah: Dep. Farmakologi & TerapeutikDocument52 pagesTri Widyawat & Sit Syarifah: Dep. Farmakologi & TerapeutikAmie Tahir RajagukgukNo ratings yet
- Nejmra1200894 AppendixDocument14 pagesNejmra1200894 AppendixStephan CanoNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Resistance: Dr. Sharifah Shakinah Supervisor: Dr. Eppy SPPD KptiDocument25 pagesAntibiotic Resistance: Dr. Sharifah Shakinah Supervisor: Dr. Eppy SPPD KptiShasha Shakinah100% (1)
- Am and Amr 2020Document46 pagesAm and Amr 2020Mikhael JHNo ratings yet
- Aznan Lelo & Zulkarnain Rangkuty: Dep. Farmakologi & TerapeutikDocument52 pagesAznan Lelo & Zulkarnain Rangkuty: Dep. Farmakologi & TerapeutikPriawanIndraNo ratings yet
- Mark Miguel P. Latras, RPHDocument11 pagesMark Miguel P. Latras, RPHLOLOLONo ratings yet
- List of AntibioticsDocument8 pagesList of AntibioticsMiguel Angel Ortega100% (1)
- Cephalosporins and FriendsDocument4 pagesCephalosporins and FriendsErika De JesusNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial AgentsDocument3 pagesAntimicrobial AgentsErnie G. Bautista II, RN, MD100% (2)
- Fuller AbxDocument78 pagesFuller AbxKe XuNo ratings yet
- Microbial Chemotherapy 2019Document82 pagesMicrobial Chemotherapy 2019salva sambaaNo ratings yet
- Antimikroba Untuk Infeksi Gastrointestinal: Oleh: Evi Sovia Lab. Farmakologi FK UNJANIDocument86 pagesAntimikroba Untuk Infeksi Gastrointestinal: Oleh: Evi Sovia Lab. Farmakologi FK UNJANIKresna Denta ElygioNo ratings yet
- ANTIBIOTICS IN ORAL SURGERYs 123Document43 pagesANTIBIOTICS IN ORAL SURGERYs 123Puneet SinghNo ratings yet
- Adult Infectious Disease Bulletpoints HandbookFrom EverandAdult Infectious Disease Bulletpoints HandbookRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- Molecular and Cellular Biology of Pathogenic TrypanosomatidsFrom EverandMolecular and Cellular Biology of Pathogenic TrypanosomatidsNo ratings yet
- Grofghup 1 Pfghoster PfghfghresentationDocument1 pageGrofghup 1 Pfghoster PfghfghresentationRăzvan RoșcaNo ratings yet
- The Gopro Handbook A Professionals Guide To FilmmakingDocument138 pagesThe Gopro Handbook A Professionals Guide To FilmmakingRăzvan RoșcaNo ratings yet
- GdfgOfgdPRO CdfgdHEAT SdfgHEETDocument3 pagesGdfgOfgdPRO CdfgdHEAT SdfgHEETRăzvan RoșcaNo ratings yet
- Invocation of Lucifer: Lord of Ascending FlameDocument1 pageInvocation of Lucifer: Lord of Ascending FlameAstarte KaliNo ratings yet
- Invocation of Lucifer: Lord of Ascending FlameDocument1 pageInvocation of Lucifer: Lord of Ascending FlameAstarte KaliNo ratings yet
- Thgfhfhe Mysfghtgfhery of FgharfghyDocument108 pagesThgfhfhe Mysfghtgfhery of FgharfghyRăzvan RoșcaNo ratings yet
- Utility Validations - Review: Hvac Explain HVAC QualificationDocument64 pagesUtility Validations - Review: Hvac Explain HVAC Qualifications lavanya100% (1)
- Drugs in Development For Depression/Anxiety, Sleep Disorders, Schizophrenia, Bipolar Disorder, and Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)Document7 pagesDrugs in Development For Depression/Anxiety, Sleep Disorders, Schizophrenia, Bipolar Disorder, and Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)jrbecker100% (3)
- TERM PAPER GlaxoSmithKline Bangladesh LimitedDocument36 pagesTERM PAPER GlaxoSmithKline Bangladesh LimitedTanvirNo ratings yet
- Identifikasi Steroid (Akonitin)Document3 pagesIdentifikasi Steroid (Akonitin)Kurnia MegawatiNo ratings yet
- 9 Nov 23 LKDocument182 pages9 Nov 23 LKaadidilanNo ratings yet
- LSD SeminarskiDocument6 pagesLSD SeminarskiDavor GrljaNo ratings yet
- Best-in-Class Pharma Market Research: Concepts Methods ToolsDocument40 pagesBest-in-Class Pharma Market Research: Concepts Methods ToolsAasNo ratings yet
- Eudragit ReviewDocument16 pagesEudragit ReviewlichenresearchNo ratings yet
- Formulation And Evaluation Of Sustained Release Sodium Alginate Microbeads Of CarvedilolDocument8 pagesFormulation And Evaluation Of Sustained Release Sodium Alginate Microbeads Of CarvedilolDelfina HuangNo ratings yet
- Goodman and Gilman 13th EditionDocument3 pagesGoodman and Gilman 13th EditionStfctayt23% (13)
- AntibioticsDocument9 pagesAntibiotics7aith22No ratings yet
- OPAT WebinarDocument2 pagesOPAT Webinarshafiq0abdullahNo ratings yet
- My Green Patch Overview (Oudtshoorn)Document14 pagesMy Green Patch Overview (Oudtshoorn)Anonymous FPmjI6ENo ratings yet
- Bhai Mohan Singh ProfileDocument2 pagesBhai Mohan Singh ProfileAnonymous aCTfqG9RNo ratings yet
- Moiety (Chemistry)Document2 pagesMoiety (Chemistry)Ja KovNo ratings yet
- Company Profile Ronak Exim-1Document1 pageCompany Profile Ronak Exim-1Youssef KaidNo ratings yet
- Who Guidelines TB Ro 2019 PDFDocument104 pagesWho Guidelines TB Ro 2019 PDFrima melliaNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Magnified Effects With AlcoholDocument1 pageDrug Name Magnified Effects With AlcoholMuhibpi IbrahimNo ratings yet
- A One-Pot Synthesis of 3-Amino-3-Arylpropionic AcidsDocument13 pagesA One-Pot Synthesis of 3-Amino-3-Arylpropionic AcidsTuyenHHCNo ratings yet
- Folfiri Beva Gi Col PDocument12 pagesFolfiri Beva Gi Col Pvera docNo ratings yet
- USPDocument18 pagesUSPAriene NovelliNo ratings yet
- Field Work Report Sher Zada (Role of DOST Foundation)Document37 pagesField Work Report Sher Zada (Role of DOST Foundation)KHAN_EROS100% (2)
- Practice Test Questions Downloaded From FILIPINO NURSES CENTRALDocument4 pagesPractice Test Questions Downloaded From FILIPINO NURSES CENTRALFilipino Nurses CentralNo ratings yet
- Analytical & Bioanalytical TechniquesDocument9 pagesAnalytical & Bioanalytical TechniquesomicspublishinggroupNo ratings yet
- Final European Union Herbal Monograph Echinacea Purpurea L Moench Herba Recens enDocument7 pagesFinal European Union Herbal Monograph Echinacea Purpurea L Moench Herba Recens enMishel Pazmiño100% (1)
- Rheology of Pharmaceutical FormulationsDocument95 pagesRheology of Pharmaceutical FormulationsHuma Hameed Dogar40% (5)
- Investigational New Drug (Ind) : N.Kanaka Durga DeviDocument65 pagesInvestigational New Drug (Ind) : N.Kanaka Durga DeviNaresh Kumar Dhanikonda0% (1)
- Determination of Ambroxol Hydrochloride Using Dithiocarbamic Acid Colorimetric MethodDocument2 pagesDetermination of Ambroxol Hydrochloride Using Dithiocarbamic Acid Colorimetric MethodAlthaf FathanNo ratings yet
- Corporate GovernanceDocument39 pagesCorporate GovernanceNoureen MushtaqNo ratings yet
- 07 EndocrineDocument44 pages07 Endocrineandirio7486No ratings yet