Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CHAPTER1 Quiz - NET202
Uploaded by
Analiza Natividad0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesOriginal Title
CHAPTER1 Quiz_NET202
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesCHAPTER1 Quiz - NET202
Uploaded by
Analiza NatividadCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
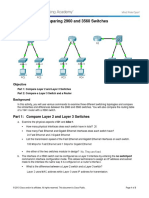
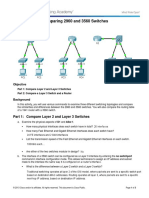
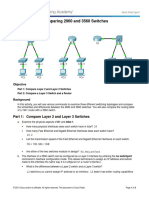
Packet Tracer - Compare 2960 and 3560
Objective
Part 1: Compare Layer 2 and Layer 3 Switches
Part 2: Compare a Layer 3 Switch and a Router
Background
In this activity, you will use various commands to examine three different switching
topologies and compare the similarities and differences between the 2960 and 3560
switches. You will also compare the routing table of a 1941 router with a 3560
switch.
Part 1: Compare Layer 2 and Layer 3 Switches
a. Examine the physical aspects of D1 and ASw-1.
Each individual switch has how many physical interfaces?
How many Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet interfaces does each switch
have?
24 Fast Ethernet and 2 Gigabit Ethernet interfaces
List the transmission speed of the Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet interfaces
on each switch.
Fast Ethernet support speeds of 10/100mb/s, and the Gigabit Ethernet
support speeds up to 1000mb/s.
Are either of the two switches modular in design?
No there are not modular in design
b. The interface of a 3560 switch can be configured as a Layer 3 interface by
entering the no switchport command in interface configuration mode. This
allows technicians to assign an IP address and subnet mask to the interface the
same way it is configured on a router’s interface.
What is the difference between a Layer 2 switch and a Layer 3 switch?
Layer 2 switch makes forwarding decisions based on L2 addresses.
Interfaces on Layer 3 switch can configured with IP addresses. The
switches can also be configured with routing protocols just like a router.
What is the difference between a switch’s physical interface and the VLAN
interface?
The difference between a switch’s physical interface and VLAN interface,
switch‘s physical interface is used to physically connect end devices to the
network. Then the VLAN is used to configure the switch with an IP
address so that it can be managed remotely.
On which layers do 2960 and 3560 switches operate?
The 2960 operates on Layer 2 and the 3560 operates both layer 2 and 3.
Issue the show run command to examine the configurations of the D1 and ASw-
1 switches. Do you notice any differences between them?
Yes, the D1’s G0/1 and G0/2 interfaces are configured with no switchport
command and show an IP address and mask configured on both Gigabit
Ethernet. The D1 has IP routing enabled.
Display the routing table on both switches using the show ip route command.
Why do you think the command does not work on ASW-1, but works on D1?
It works on D1, because it functions on Layer 2 and 3, which allows it to
function as a layer 2 switch but at the same time allows it to route packets
and make forwarding decisions based on layer 3 information that
conventional switches cannot.
Part 2: Compare a Layer 3 Switch and a Router
a. Up until recently, switches and routers have been separate and distinct
devices. The term switch was set aside for hardware devices that function at
Layer 2. Routers, on the other hand, are devices that make forwarding decisions
based on Layer 3 information. They use routing protocols to share routing
information and to communicate with other routers. Layer 3 switches, such as the
3560, can be configured to forward Layer 3 packets. Entering the ip
routing command in global configuration mode allows Layer 3 switches to be
configured with routing protocols, thereby possessing some of the same
capabilities as a router. Although similar in some forms, switches are different
than in many other aspects.
Open the Physical tab on D1 and R1. Do you notice any similarities between the
two? Do you notice any differences between the two?
They both have a console port and both 2 gigabit Ethernet interface. The
R1 is modular and can add various interfaces while D1 has only fixed
interfaces. Also R1 has serial and asynchronous interfaces while D1 only
has Ethernet interfaces. And lastly the D1 use copper cables while R1 can
use various connection types.
Issue the show run command and examine the configurations of R1 and D1.
What differences do you see between the two?
R1 and D1 have the same IP addresses configured on them but on
different interfaced. In order for the switch port to be assigned an Ip
address, technicians will have to issue the no Switchport command.
Which command allows D1 to configure an IP address on one of its physical
interfaces?
The no switchport command
Use the show ip route command on both devices. Do you see any similarities or
differences between the two tables?
The codes are the same except the router has an L code for local. This is
a link that is configured on the physical interface of R1, while the switch
does not have it. Both devices display the same networks in their routing
tables.
Now, analyze the routing table of R2 and D2. What is evident now that was not in
the configuration of R1 and D1?
They both have EIGRP configured and both are learning networks from
one another.
b. Verify that each topology has full connectivity by completing the following tests:
· Ping from PC1 to PC2
· Ping from PC3 to PC4
· Ping from PC5 to PC6
In all three examples, each PC is on a different network. Which device is used to
provide communication between networks?
The device that provide communication between networks is the router.
Why were we able to ping across networks without there being a router?
A multilayer switch can route between networks as long as it is configured
with an IP address and has IP routing enabled. IP routing must also be
enabled if you plan to run routing protocols such as EIGRP on the switch.
The no switchport command must be enabled on the interface in order to
assign an IP address and subnet mask on the switch’s physical interface.
You might also like
- CCNP Swith Case Study 4 AnswersDocument23 pagesCCNP Swith Case Study 4 AnswersPhil Garbett100% (1)
- 11.5.1 Packet Tracer - Compare Layer 2 and Layer 3 Devices AnswerDocument4 pages11.5.1 Packet Tracer - Compare Layer 2 and Layer 3 Devices AnswerVinicio MartinezNo ratings yet
- Packet Tracer ScriptsDocument53 pagesPacket Tracer ScriptsLammetje Lives33% (3)
- 1.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Compare 2960 and 3560 SwitchesDocument7 pages1.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Compare 2960 and 3560 SwitchesJulio Cesar MoralesNo ratings yet
- CCNA Presentation on Networking FundamentalsDocument38 pagesCCNA Presentation on Networking FundamentalsGagan SardanaNo ratings yet
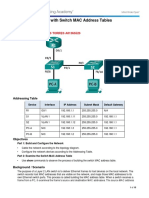
- 5.3.1.10 Lab - Using IOS CLI With Switch MAC Address TablesDocument5 pages5.3.1.10 Lab - Using IOS CLI With Switch MAC Address TablesLaura HampNo ratings yet
- 6.5.1.1 Lab - Securing Layer 2 Switches - InstructorDocument45 pages6.5.1.1 Lab - Securing Layer 2 Switches - InstructorJUAN ISIDRO MENA0% (1)
- 11.5.1 - Packet Tracer - Compare Layer 2 and Layer 3 DevicesDocument3 pages11.5.1 - Packet Tracer - Compare Layer 2 and Layer 3 DevicesMaría ArmijosNo ratings yet
- Compare Layer 2 and Layer 3 Switches and RoutersDocument3 pagesCompare Layer 2 and Layer 3 Switches and RouterscoleparksNo ratings yet
- 1 2 1 7Document2 pages1 2 1 7Francis janeNo ratings yet
- 11.5.1 Packet Tracer - Compare Layer 2 and Layer 3 Devices - ILMDocument4 pages11.5.1 Packet Tracer - Compare Layer 2 and Layer 3 Devices - ILMLizardo Hilario Hinostroza GuillermoNo ratings yet
- 1.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches InstructionsDocument3 pages1.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches InstructionsEdisonJoshuaValistoNo ratings yet
- 1.2.1.7 Packet Tracer Compare 2960 and 3560 SwitchesDocument4 pages1.2.1.7 Packet Tracer Compare 2960 and 3560 SwitchesKurt John MiñozaNo ratings yet
- 1.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches Instructions - Jacob SchwegmanDocument3 pages1.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches Instructions - Jacob Schwegmanberniemonkeyzor20% (5)
- 1.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches InstructionsDocument3 pages1.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches InstructionsJozeph Abod67% (3)
- 1217 Packet Tracer - Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches InstructionsDocument3 pages1217 Packet Tracer - Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches InstructionsDriesNo ratings yet
- Packet Tracer 13Document3 pagesPacket Tracer 13cristhoper espinozaNo ratings yet
- 1.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches InstructionsDocument3 pages1.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches InstructionsRoy Janssen100% (3)
- ACTIVITY 9 - Packet Tracer - Compare 2960 and 3560 (B) : CISC003 - Cisco Networking 3Document2 pagesACTIVITY 9 - Packet Tracer - Compare 2960 and 3560 (B) : CISC003 - Cisco Networking 3Klienze Ashtrid MelencioNo ratings yet
- Docslide - Us 1217 Packet Tracer Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches Instructions 56847ae83fed6Document3 pagesDocslide - Us 1217 Packet Tracer Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches Instructions 56847ae83fed6Christian EspinaNo ratings yet
- Packet Tracer - Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches: TopologyDocument3 pagesPacket Tracer - Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches: TopologyMiguel DragoNo ratings yet
- 1.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Compare 2960 and 3560 SwitchesDocument3 pages1.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Compare 2960 and 3560 SwitchesAnonymous sYXo4KNo ratings yet
- Asd Asd ADocument12 pagesAsd Asd ADarrylJanMontemayorNo ratings yet
- Advanced IP Services-Assignment QuestionsDocument11 pagesAdvanced IP Services-Assignment QuestionsYuvaraj V, Assistant Professor, BCANo ratings yet
- Presentation ON Ccna: TRAINED BY - Kundan Singh (Aptron Solutions PVT LTD)Document36 pagesPresentation ON Ccna: TRAINED BY - Kundan Singh (Aptron Solutions PVT LTD)Akshay Mishra BhardwajNo ratings yet
- 12.9.2-Lab-Configure-Ipv6-Addresses-On-Network (Resuelto)Document5 pages12.9.2-Lab-Configure-Ipv6-Addresses-On-Network (Resuelto)Esteban RcNo ratings yet
- SWITCHINGDocument37 pagesSWITCHINGAbhishrkNo ratings yet
- CCNA3 Practice Final Exam 98.1%Document22 pagesCCNA3 Practice Final Exam 98.1%Iulian StarpituNo ratings yet
- Lab 10.2 - Configure IPv6 Addresses On Network DevicesDocument4 pagesLab 10.2 - Configure IPv6 Addresses On Network DevicesRecky JimmyNo ratings yet
- CCNA Discovery 2 Working at A Small To Medium Business or ISP Practice FinalDocument17 pagesCCNA Discovery 2 Working at A Small To Medium Business or ISP Practice FinalKevin SchultzNo ratings yet
- Configure additional commands needed for remote switch accessDocument28 pagesConfigure additional commands needed for remote switch accessHassoun Ben AissaNo ratings yet
- Ccna TestDocument24 pagesCcna TestArt CamposNo ratings yet
- l2 and l3 Switches EvolutionDocument5 pagesl2 and l3 Switches EvolutionakinengineerNo ratings yet
- 20dit042 CN PDFDocument19 pages20dit042 CN PDFVidhi PitrodaNo ratings yet
- LAN - L3 DesignDocument40 pagesLAN - L3 DesignMehdi LaarifNo ratings yet
- TCP/IP Abc's Layer 3 Layer 2 Switch Web Switch Virtual LANDocument6 pagesTCP/IP Abc's Layer 3 Layer 2 Switch Web Switch Virtual LANapi-26278159No ratings yet
- Find switch IP address and VLAN configuration stepsDocument9 pagesFind switch IP address and VLAN configuration stepshatfied862No ratings yet
- Cómo funcionan los switches y sus principales característicasDocument3 pagesCómo funcionan los switches y sus principales característicasBenjamin Mendoza GonzalesNo ratings yet
- JARKOM11 DaviAdrian - 1803007Document10 pagesJARKOM11 DaviAdrian - 1803007Davi AdrianNo ratings yet
- Final ExamDocument43 pagesFinal ExamMarlena NeștianNo ratings yet
- 6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN - InstructionsDocument5 pages6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN - InstructionsLaura HampNo ratings yet
- Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN: Addressing TableDocument12 pagesPacket Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN: Addressing TableMENDOZA GASPAR PAOLA Ingeniería en Sistemas ComputacionalesNo ratings yet
- CCNA Final D Study GuideDocument108 pagesCCNA Final D Study GuidePhạm TrườngNo ratings yet
- Navdeep Singh Parewa (2030075 - 10.3.4 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANDocument4 pagesNavdeep Singh Parewa (2030075 - 10.3.4 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANNavdeep ParewaNo ratings yet
- L2 AND L3 Switch DifferenceDocument6 pagesL2 AND L3 Switch DifferenceVivek GhateNo ratings yet
- Configuration Cisco Router CCNA Introduction To Networks V7.02Document6 pagesConfiguration Cisco Router CCNA Introduction To Networks V7.02Kim WorldNo ratings yet
- Computer Communication and Networks Lab ManualDocument25 pagesComputer Communication and Networks Lab ManualAnaea OzairNo ratings yet
- Computer Department Cisco Certified Network AssociateDocument38 pagesComputer Department Cisco Certified Network AssociateMuhamed AtefNo ratings yet
- 12.9.2 Lab - Configure Ipv6 Addresses On Network DevicesDocument4 pages12.9.2 Lab - Configure Ipv6 Addresses On Network Devicessouaifi yosraNo ratings yet
- 5.3.3.2 Lab - Troubleshoot LAN Traffic Using SPANDocument6 pages5.3.3.2 Lab - Troubleshoot LAN Traffic Using SPANYaser Samer0% (6)
- Lab - Using IOS CLI With Switch MAC Address Tables: Sergio David Valdes Torres A01365520Document10 pagesLab - Using IOS CLI With Switch MAC Address Tables: Sergio David Valdes Torres A01365520a01365520No ratings yet
- INFO-6078 - Lab 4 - ARP, LAGs & LLDPDocument7 pagesINFO-6078 - Lab 4 - ARP, LAGs & LLDPMinh Phuc LưNo ratings yet
- Ccna 4 Final ExamDocument2 pagesCcna 4 Final Examgy880828No ratings yet
- Configure Admistrative RolesDocument20 pagesConfigure Admistrative RolesestebanNo ratings yet
- Router Vs SwitchDocument2 pagesRouter Vs SwitchKaustubh ParkerNo ratings yet
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingFrom EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingNo ratings yet
- ROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL: RIP DYNAMIC ROUTING LAB CONFIGURATIONFrom EverandROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL: RIP DYNAMIC ROUTING LAB CONFIGURATIONNo ratings yet
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkFrom EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNo ratings yet
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-A: A Beginner's Guide to Next Level of NetworkingFrom EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-A: A Beginner's Guide to Next Level of NetworkingNo ratings yet
- K MapDocument30 pagesK MapAnaliza NatividadNo ratings yet
- Tinkercad Laboratory ExamDocument2 pagesTinkercad Laboratory ExamAnaliza NatividadNo ratings yet
- SimplifytheexpressionsbelowshowingyourworkingoutwhenthereismorethanonestagetothesimplificationDocument1 pageSimplifytheexpressionsbelowshowingyourworkingoutwhenthereismorethanonestagetothesimplificationAnaliza NatividadNo ratings yet
- 03 Alpha Blending ActivityDocument1 page03 Alpha Blending ActivityAnaliza NatividadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Overview of Electronic CommerceDocument16 pagesChapter 1 - Overview of Electronic CommerceAnaliza NatividadNo ratings yet
- TECH301 Midterm Enrichment 1 Casestudy 1Document3 pagesTECH301 Midterm Enrichment 1 Casestudy 1Analiza NatividadNo ratings yet
- Ethics301 Lesson4 ComputerandinternetcrimesquizDocument4 pagesEthics301 Lesson4 ComputerandinternetcrimesquizAnaliza NatividadNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor & Computer Architecture (Μpca) : Unit 4: Usb, Pci, Scsi,Amba And Asb Bus ArchitectureDocument12 pagesMicroprocessor & Computer Architecture (Μpca) : Unit 4: Usb, Pci, Scsi,Amba And Asb Bus ArchitecturePranathi PraveenNo ratings yet
- Kang Wifi-Pisah Trafik RAW-2ISPDocument7 pagesKang Wifi-Pisah Trafik RAW-2ISPAris SetyawanNo ratings yet
- Data Communications Solution Manual PDFDocument5 pagesData Communications Solution Manual PDFshahbazNo ratings yet
- 2023 09 12 17 56 35 HP LogDocument151 pages2023 09 12 17 56 35 HP LogTriust XDNo ratings yet
- Questions Choice A Choice B Choice C Choice D Correct AnswerDocument5 pagesQuestions Choice A Choice B Choice C Choice D Correct AnswerTechno Gaming OfficialNo ratings yet
- Capture ATP NEDocument11 pagesCapture ATP NEPuspa RizkyNo ratings yet
- CES-2CUA ManDocument8 pagesCES-2CUA ManAlexander EscalonaNo ratings yet
- CCNA 4 Chapter 2 V4.0 AnswersDocument9 pagesCCNA 4 Chapter 2 V4.0 AnswersShanta ThapaNo ratings yet
- Hikvision 0904848459 Camera TCMDocument1 pageHikvision 0904848459 Camera TCMKs QuốcNo ratings yet
- FOML ChangedLogsDocument95 pagesFOML ChangedLogsramretNo ratings yet
- Cisco 360 CCIE R&S Exercise Workbook Introduction: 360RSW05-WKB-TA01Document35 pagesCisco 360 CCIE R&S Exercise Workbook Introduction: 360RSW05-WKB-TA01Petko KolevNo ratings yet
- Beckhoff Main Catalog 2018 2 02 EtherCATDocument34 pagesBeckhoff Main Catalog 2018 2 02 EtherCATHarimurti HaryonoNo ratings yet
- Network Visibility: Network Packet Broker Comparison TableDocument9 pagesNetwork Visibility: Network Packet Broker Comparison TableGokhanNo ratings yet
- Configure ASA Connection SettingsDocument16 pagesConfigure ASA Connection SettingsMatthew NawrotNo ratings yet
- What Is CSTA?Document21 pagesWhat Is CSTA?Roberto MontagnanaNo ratings yet
- S1 Vlan 99 S2 Vlan 99 S3 Vlan 99 PC1 NIC PC2 NIC PC3 NIC PC4 NIC PC5 NIC PC6 NICDocument16 pagesS1 Vlan 99 S2 Vlan 99 S3 Vlan 99 PC1 NIC PC2 NIC PC3 NIC PC4 NIC PC5 NIC PC6 NICremonita hufaNo ratings yet
- Hristea Nicolae - ABC Apicol 2Document118 pagesHristea Nicolae - ABC Apicol 2Morosanu LuminitaNo ratings yet
- 11.2.3.10 Packet Tracer - Explore A NetFlow Implementation InstructionsDocument8 pages11.2.3.10 Packet Tracer - Explore A NetFlow Implementation InstructionsNNo ratings yet
- 3.7.10 Lab - Use Wireshark To View Network TrafficDocument6 pages3.7.10 Lab - Use Wireshark To View Network TrafficRazaqNo ratings yet
- Vigor2926 Datasheet 170725Document2 pagesVigor2926 Datasheet 170725GilbertoNo ratings yet
- Real Scenario For Call ArrivalDocument5 pagesReal Scenario For Call ArrivalmandeepmailsNo ratings yet
- TCP Congestion Control and Flow Control ExplainedDocument20 pagesTCP Congestion Control and Flow Control ExplainedAHWSNo ratings yet
- Nport 5110 Users Manual v2Document100 pagesNport 5110 Users Manual v2Liliana SerranoNo ratings yet
- ASAM XCP Part1-Overview V1-1-0Document71 pagesASAM XCP Part1-Overview V1-1-0张敏健No ratings yet
- USB Type-C R2.2 ECN - Remove Vbus Always On From Captive Cable ChargersDocument2 pagesUSB Type-C R2.2 ECN - Remove Vbus Always On From Captive Cable ChargersimtangyuweiNo ratings yet
- Optical EthernetDocument13 pagesOptical Ethernetjsingh19100% (1)
- DCN TrainingDocument52 pagesDCN TrainingkarthiveeraNo ratings yet
- ONVDocument16 pagesONVanh trinhNo ratings yet
- High Speed Networks (HSN)Document10 pagesHigh Speed Networks (HSN)Raja ManickamNo ratings yet