Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Accountability
Uploaded by
Jerymy Dareen Alamares Santos0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageAccountability
Uploaded by
Jerymy Dareen Alamares SantosCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Accountability a set of initiatives others take to monitor the results of our actions, and to penalize or reward us based on the
reward us based on the outcomes.
Accuracy an assessment tool must be accurate. Accuracy is the state of being correct, free from mistakes.
Algorithm are mental procedures that normally do not vary in application once learned.
Alternative Assessment based on students’ abilities to perform meaningful tasks they may have to do in the “real-world”.
Alternative Grading System refers to different ways of evaluating students’ learning and performance, other than the traditional points-based approach.
Analysis The generation of new information not already possessed by the individual.
Analyzing errors Addresses the logic, reasonableness, or accuracy of knowledge.
Analytic Rubric It articulates level of performance of each criterion.
Analytic Rubrics describe on each criterion separately
Assessment the systematic basis for making inferences about the learning and development of students
Assessment or Evaluation Portfolio a collection of student works that are associated with standards you are required to learn.
Assessment tool a systematic and standardized instrument or method used to evaluate and measure specific attributes, skills, competencies, or behaviors of individuals in a
consistent and objective manner.
Asynchronous Student learn at different times
Authentic Assessment refers to non-paper-and-pencil test.
Authentic Assessment a form of direct assessment because it provides direct evidence of application of knowledge, skills and attitudes.
Averaging System Your major average is the average of percentage grades from courses taken toward your major.
Benchmarking Assessment measure a student’s performance against a ‘set point’, say, a national standard, or over a particular time period.
Bite-sized Learning (Microlearning) breaking down e-learning content into digestible chunks, which is easier for learners to work through at a pace that suits them.
Blended Learning an approach to education that combines online educational materials and opportunities for interaction online with traditional place-based classroom
methods.
Blended Learning refers to a learning delivery that combines in-person with any mix of online distance learning, modular learning, and TV/Radio-based instruction
Bodily- Kinesthetic Intelligence ability to control one's body movements and to handle objects is skillfully
Classifying Refers to organizing knowledge into meaningful categories
Classroom Assessment a systematic approach to formative evaluation, used by instructors to determine how much and how well students are learning
Collaborative Assessment learners to support each other’s learning to produce evidence of their learning through discussion, games, group activities and creation of projects.
Competencies the applied skills and knowledge that enable people to successfully perform in professional, educational and life context.
Completion type or Short Answer The examinee needs to supply or create the appropriate word(s), symbol(s) or number(s) to answer the question or complete a statement rather than
Test selecting the answer from the given options. Used for simple recall of knowledge and for computational problems
Comprehension Responsible for translating knowledge into a form appropriate for storage in permanent memory.
Comprehension an assessment tool must include everything or nearly everything that is connected with a particular subject.
Conceptual Knowledge It is knowledge of classifications, principles, generalizations, theories, models or structures pertinent to a particular disciplinary area.
Constructive Alignment knowledge is constructed by the activities of the learner
Continual Assessment based on the day-to-day experience of a teacher observing their student, for instance
Criterion Referenced designed to measure student performance against a fixed set of predetermined criteria or learning standards
Cumulative Grading is calculating a student's grade in a class that counts each new assessment at its assigned weight in a cumulative fashion throughout the year.
Decision Making The process of decision making is used when an individual must select between two or more alternatives.
Deferred Outcome refers to the ability to apply cognitive, psychomotor and affective skills/competencies in various situations many years after completion of a degree program.
Desire Student Learning Outcomes Are statement that describe significant and essential learning that learners have achieved ,and can reliably demonstrate and end pf a course or program.
Development Stage Develop or select items, exercises, tasks, and scoring procedures. Review and critique the overall assessment for quality before use
Diagnostic Assessment Is a type of assessment which examined what a student knows and can do prior to a leaning program being implemented assessment of student’s skill and
knowledge upon entry to program provide a baseline against which to assess progress.
Direct Method a professional makes a decision regarding what a student learned and how well it was learned.
You might also like
- Empowering Growth - Using Proficiency Scales for Equitable and Meaningful Assessment: Quick Reads for Busy EducatorsFrom EverandEmpowering Growth - Using Proficiency Scales for Equitable and Meaningful Assessment: Quick Reads for Busy EducatorsNo ratings yet
- Assessment of LearningDocument23 pagesAssessment of LearningLiezel Montederamos GardeNo ratings yet
- Types of AssessmentDocument4 pagesTypes of AssessmentAegi InfanteNo ratings yet
- Outcomes-Based Learning and Outcomes-Based Assessment Ofelia T. Posecion, PH.DDocument3 pagesOutcomes-Based Learning and Outcomes-Based Assessment Ofelia T. Posecion, PH.DKathlene LeyolaNo ratings yet
- Asessment of Learning Prepared by Ariel Berico ObjectivesDocument7 pagesAsessment of Learning Prepared by Ariel Berico ObjectivesElmera Mae A. DaarolNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 AL2Document5 pagesChapter 1 AL2ABELLANO, SHEENA MAE A.No ratings yet
- Music Curriculum GuidehghuggDocument5 pagesMusic Curriculum GuidehghuggZhaldzCjayBaltazarNo ratings yet
- ReviewernotesDocument15 pagesReviewernotesMark Brian MariñoNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1A Lesson 1 Basic ConceptsDocument7 pagesMODULE 1A Lesson 1 Basic ConceptsVincent Rojo100% (1)
- Assessment Terminology 1Document4 pagesAssessment Terminology 1Julio E RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Types of AssessmentDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Types of AssessmentJA Loayon BeberinoNo ratings yet
- Basics of Assessment and Learning OutcomesDocument8 pagesBasics of Assessment and Learning OutcomesJen EspinaNo ratings yet
- ASSESSMENT IN LEARNING FinalDocument62 pagesASSESSMENT IN LEARNING FinalLance Go LlanesNo ratings yet
- AiL2 Group 2 ReportDocument18 pagesAiL2 Group 2 ReportSharlene Cecil PagoboNo ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument6 pagesAssessmentJulius MatroNo ratings yet
- SEMINAR-WORKSHOP ON TEST CONSTRUCTIONDocument120 pagesSEMINAR-WORKSHOP ON TEST CONSTRUCTIONJonah Faye Suzette FriasNo ratings yet
- Assessment 2 Chapter 2Document10 pagesAssessment 2 Chapter 2Zarah Joyce SegoviaNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument6 pagesReviewerAbegail HernandoNo ratings yet
- Dr. Jagannath K. Dange Department of Education Kuvempu University Shankaraghatta Dist: Shimoga, KarnatakaDocument45 pagesDr. Jagannath K. Dange Department of Education Kuvempu University Shankaraghatta Dist: Shimoga, KarnatakacielNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of 21st Century AssessmentDocument9 pagesCharacteristics of 21st Century AssessmentErnestoNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Assessment TermsDocument4 pagesGlossary of Assessment Termserica de castroNo ratings yet
- Edal 111 Module 1Document10 pagesEdal 111 Module 1Riri PansacalaNo ratings yet
- PCK 6 Assessment of Learning 2 Unit 1Document19 pagesPCK 6 Assessment of Learning 2 Unit 1Maricel RiveraNo ratings yet
- Section 1 Explain The Nature and Roles of A Good Assessment, and Its Relevance To Learners, Teachers, Parents and StakeholdersDocument15 pagesSection 1 Explain The Nature and Roles of A Good Assessment, and Its Relevance To Learners, Teachers, Parents and StakeholdersJeraldine buyserNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document8 pagesModule 6leslieanneokitNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts in Assessment LearningDocument2 pagesBasic Concepts in Assessment LearningKryzel Anne RamiscalNo ratings yet
- Assessing Learning EffectivelyDocument138 pagesAssessing Learning EffectivelyElyka RamosNo ratings yet
- Education Evaluation GuideDocument45 pagesEducation Evaluation GuidemercyNo ratings yet
- Intro To Assessment of LearningDocument13 pagesIntro To Assessment of LearningANGEL REIGN ANTIPORDANo ratings yet
- Defining Curriculum Objective and Intended Learning OutcomesDocument9 pagesDefining Curriculum Objective and Intended Learning OutcomesKrizzle Jane PaguelNo ratings yet
- Cpe Chapter 4 To 6Document8 pagesCpe Chapter 4 To 6Paul John TaguinodNo ratings yet
- Assessing Learning: Basic ConceptsDocument139 pagesAssessing Learning: Basic ConceptsLanaNo ratings yet
- Developing Learner-Centered Assessment Tools and AssignmentsDocument24 pagesDeveloping Learner-Centered Assessment Tools and AssignmentsBrent Joross LibananNo ratings yet
- Development of Values Education Instructional Materials and Assessment ToolsDocument7 pagesDevelopment of Values Education Instructional Materials and Assessment ToolsNgirp Alliv Trebor67% (3)
- Assessment Learning 1 - Quiz ReviewerDocument3 pagesAssessment Learning 1 - Quiz ReviewerAlexander ReyesNo ratings yet
- 8602 Unit 03 Assesment-1Document26 pages8602 Unit 03 Assesment-1Amber AminNo ratings yet
- Module 1 AssessmentDocument19 pagesModule 1 AssessmentDexter BisnarNo ratings yet
- M119-ASSESSMENT-AND-EVALUATION-IN-MATHEMATICS-LECTURE-NOTES (1)Document20 pagesM119-ASSESSMENT-AND-EVALUATION-IN-MATHEMATICS-LECTURE-NOTES (1)Faba, Froi Jastine T.No ratings yet
- Assessing Learning OutcomesDocument36 pagesAssessing Learning OutcomesAllison Yambao CastroNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of MeasurementDocument19 pagesBasic Concept of MeasurementEdwin PerezNo ratings yet
- MICHIGAN ASSESSMENT CONSORTIUM. Glossary.2018Document3 pagesMICHIGAN ASSESSMENT CONSORTIUM. Glossary.2018Janaina RodriguezNo ratings yet
- W8.pentaksiran PembelajaranDocument54 pagesW8.pentaksiran PembelajaranEyka YanaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Activity 1Document7 pagesLesson Activity 1Mariel Suaiso Angeles0% (1)
- Ed107 Module3Document7 pagesEd107 Module3Veronica FiedacanNo ratings yet
- 3 Chapter 2 PDFDocument10 pages3 Chapter 2 PDFBanjo De los Santos0% (1)
- OBE Principles and ProcessDocument8 pagesOBE Principles and Processgladys laguraNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of AssessmentDocument29 pagesBasic Concept of AssessmentDarline Carzon SantelicesNo ratings yet
- Educ 206 Prelim CoverageDocument23 pagesEduc 206 Prelim CoverageJoe Ronnie TorresNo ratings yet
- High Quality AssessmentDocument7 pagesHigh Quality AssessmentCRISTIANDION YBANEZNo ratings yet
- Educational Assessment and EvaluationDocument5 pagesEducational Assessment and EvaluationAnonymous iuPqay100% (1)
- MeasurementDocument3 pagesMeasurementFernan AbusoNo ratings yet
- Gose Educ 105Document19 pagesGose Educ 105api-569343867No ratings yet
- ASSMT 1 Module 2Document9 pagesASSMT 1 Module 2Mikaela AltoNo ratings yet
- 1-2miss Ja, PRELIM ABSTRACTION 1 - TMDocument5 pages1-2miss Ja, PRELIM ABSTRACTION 1 - TMEulogio B. Diaz Jr.No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 and 2Document44 pagesLesson 1 and 2Warda PalisamanNo ratings yet
- Purposes of Classroom AssessmentDocument40 pagesPurposes of Classroom AssessmentANYA NICOLE SEGURANo ratings yet
- Types of Assessment: Lesson 3Document7 pagesTypes of Assessment: Lesson 3saraaahc021No ratings yet
- Ail 2 ReviewerDocument10 pagesAil 2 Reviewerkirbypiloto470No ratings yet
- State The Policy and Guidelines On System Assessment of K-12 Basic Education Program and Give Your CommentDocument8 pagesState The Policy and Guidelines On System Assessment of K-12 Basic Education Program and Give Your CommentFaeona Ferna Joyce MolinesNo ratings yet
- Arts Assessment GlossaryDocument5 pagesArts Assessment GlossaryHANNAN ARSHADNo ratings yet
- NARRATIVEEEEDocument46 pagesNARRATIVEEEEJerymy Dareen Alamares SantosNo ratings yet
- Patul National High SchoolDocument51 pagesPatul National High SchoolJerymy Dareen Alamares SantosNo ratings yet
- 1150 Pcs Ornamental PlantsDocument2 pages1150 Pcs Ornamental PlantsJerymy Dareen Alamares SantosNo ratings yet
- Patul National High SchoolDocument51 pagesPatul National High SchoolJerymy Dareen Alamares SantosNo ratings yet
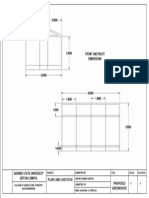
- Front and Right DimensionsDocument1 pageFront and Right DimensionsJerymy Dareen Alamares SantosNo ratings yet
- 1150 Pcs Ornamental PlantsDocument2 pages1150 Pcs Ornamental PlantsJerymy Dareen Alamares SantosNo ratings yet
- Front and Right DimensionsDocument1 pageFront and Right DimensionsJerymy Dareen Alamares SantosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document1 pageChapter 5Jerymy Dareen Alamares SantosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document1 pageChapter 5Jerymy Dareen Alamares SantosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document1 pageChapter 6Jerymy Dareen Alamares SantosNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in HealthDocument7 pagesLesson Plan in HealthApril Grace Genobatin BinayNo ratings yet
- Eng 3 Q1W9Document9 pagesEng 3 Q1W9Herben T. BautistaNo ratings yet
- Effective Reading Techniques for StudentsDocument25 pagesEffective Reading Techniques for Studentsmerii100% (2)
- Learning TheoriesDocument21 pagesLearning Theorieswinwin86No ratings yet
- Developing Teachers To Improve Lessons Using TechnologyDocument11 pagesDeveloping Teachers To Improve Lessons Using Technologyapi-484995893No ratings yet
- Classroom Management Principles for Effective TeachingDocument27 pagesClassroom Management Principles for Effective TeachingAj CapungganNo ratings yet
- Action Plan in Egra 2021Document3 pagesAction Plan in Egra 2021Rose Marie Prietos91% (23)
- HKCC CCN1005 English For Academic Studies (Business) I HKCCDocument4 pagesHKCC CCN1005 English For Academic Studies (Business) I HKCCsiu chau lauNo ratings yet
- Professional Growth TimelineDocument1 pageProfessional Growth Timelineapi-570352037No ratings yet
- Bandura ReviewerDocument5 pagesBandura ReviewerMarjorie VillarosaNo ratings yet
- Business EnglishDocument5 pagesBusiness EnglishDNo ratings yet
- HRM Chapter 8Document15 pagesHRM Chapter 8AilaNo ratings yet
- Three Fluency Exercises for Diverse ClassroomsDocument3 pagesThree Fluency Exercises for Diverse ClassroomsKristin HensleyNo ratings yet
- Student Academic Record As of Spring Semester 2015Document2 pagesStudent Academic Record As of Spring Semester 2015api-270165707No ratings yet
- Individual Learning Monitoring Plan Sample1Document2 pagesIndividual Learning Monitoring Plan Sample1JUDY BUHION100% (1)
- Bilingual Teaching Methods: A Quick Reference Guide For EducatorsDocument35 pagesBilingual Teaching Methods: A Quick Reference Guide For EducatorsSyrile MangudangNo ratings yet
- ForestDocument2 pagesForestapi-225846876No ratings yet
- NSTP2 Peer Evaluation Sheet AY 2019 2020Document2 pagesNSTP2 Peer Evaluation Sheet AY 2019 2020Cj SuperaNo ratings yet
- 20 Circular 2020 PDFDocument5 pages20 Circular 2020 PDFanithaNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Instructional Materials in Math ClassDocument2 pagesEffectiveness of Instructional Materials in Math ClassLIAN JENNON RUBLICONo ratings yet
- Developmental and social factors: Principles of learningDocument19 pagesDevelopmental and social factors: Principles of learningMercy AbaretaNo ratings yet
- Alex Sander Case StudyDocument12 pagesAlex Sander Case StudyAditya Beri100% (1)
- Active Teaching and Learning Approaches Methodologies in FETResource ListDocument21 pagesActive Teaching and Learning Approaches Methodologies in FETResource ListWahyu HidayatNo ratings yet
- Eight Approches To Language TeachingDocument11 pagesEight Approches To Language TeachingNaneth DomenNo ratings yet
- Quality Early Childhood Care and EducatiDocument28 pagesQuality Early Childhood Care and EducatiSai smitaNo ratings yet
- Numeracy and math performanceDocument17 pagesNumeracy and math performanceMARIA CARMELA MALIGAYANo ratings yet
- Effective Goal Setting Planning WorksheetDocument3 pagesEffective Goal Setting Planning WorksheetOdie100% (6)
- FilipinoDocument7 pagesFilipinoLorena NovabosNo ratings yet
- Gifted Children: Team Awesome! Possum!Document14 pagesGifted Children: Team Awesome! Possum!api-1742666067% (3)
- CBT Training PresentationDocument72 pagesCBT Training PresentationJason AsorNo ratings yet