Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Thermo Intermitten Blowdown Valve
Uploaded by
ARIYO ANINDITOCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Thermo Intermitten Blowdown Valve
Uploaded by
ARIYO ANINDITOCopyright:
Available Formats
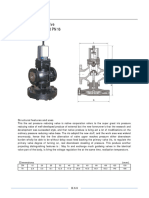
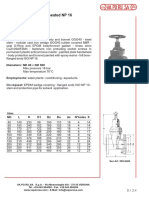
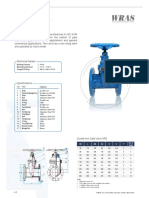
Blow Down Valve
WCB Body, Flanged End PN 40
Materials
PN Pressure Test kg/cm2 Temperature Suitable
Model Materials PN Range (°C) Medium
Seat Shell
Z44H-40 WCB 40 44 60 -10 ~ 350 Steam, Oil
The water in the boiler contains salts, which are built up by the continuous evaporation. If these salts are not eliminated, bubbles and
foam are formed when the density of the water increased.
To prevent these lime deposits forming, the water supply must be suitably treated, with the result that certain salts are
changed producing impurities which form sludge and encrusted deposits which then adhere to the sides or the bottom of the
boiler and to the combustion tubes, together with particles of dirt, remains of electrodes, carbonic acid, oxygen, etc. This leads
to a high level of rust which may:
■ Destroy the metal plate of the boiler, causing high maintenance costs.
■ Produce thermic voltages, causing cracks in the metal plate and soldering cord.
■ Notably slow down thermic transmission, meaning an unnecessary and excessive consumption of fuel.
Nominal pressure: PN-40.
Permitted pressures and temperatures according to DIN-2401. Sheet 2. Flange
connection: DN-25, 32, 40 and 50 (DIN-2545).
Specifications
A the draining section is opened quickly and completely by driving the lever from right to left. The deposits, collected at
the bottom of the boiler, are disturbed and sucked up by the sudden air intake which carries them out.
- Direct emptying passage. meaning a high volume and low level of load loss.
- Rotating the lever from left to right causes instant closing, preventing irrevocable losses of water and pressure.
- Seating’s and stoppers treated and balanced ensuring a level of tightness higher than that required by DIN-3230, Sheet 3.
- Equipped with a screw for the drainage of the sedimentations.
- Simplicity of design ensures good performance.
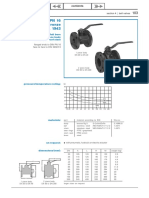
Dimensions (mm)
Size Kg/cm2 L D D1 D2 D3 b H Z-Ød
25 40 160 115 85 65 58 16 180 4-14
32 40 180 135 100 78 66 18 200 4-18
40 40 230 145 110 85 76 18 240 4-18
50 40 250 160 125 100 88 20 260 4-16
65 40 265 180 145 120 110 22 265 8-18
80 40 280 195 160 132 121 24 345 8-16
II.8.6
You might also like
- Practice 6 - Questions - CSWIPDocument12 pagesPractice 6 - Questions - CSWIPravichandran0506No ratings yet
- ASME Standard List of Piping and FittingsDocument7 pagesASME Standard List of Piping and Fittingsjuantamad02No ratings yet
- Din Flange PDFDocument45 pagesDin Flange PDFVineeth MuraleedharanNo ratings yet
- World Bank Rural Water Supply Manual Vol2 Construction Supervision Manual 2012Document168 pagesWorld Bank Rural Water Supply Manual Vol2 Construction Supervision Manual 2012Brilian DwiNo ratings yet
- DIN 2501 PN10 PLATE FLANGE Buyers Suppliers Exporters Dealers Manufacturers in IndiaDocument11 pagesDIN 2501 PN10 PLATE FLANGE Buyers Suppliers Exporters Dealers Manufacturers in IndiataghdirimNo ratings yet
- Kenr5396 04 01 AllDocument76 pagesKenr5396 04 01 AlllunikmirNo ratings yet
- Pipe Sizing V2.3-ASPEDocument56 pagesPipe Sizing V2.3-ASPEAdnan AttishNo ratings yet
- OperatorsManual DC13 PDEDocument73 pagesOperatorsManual DC13 PDEsfe100% (3)
- AUH DataDocument702 pagesAUH DataParag Babar33% (3)
- X-Trail Diagnostic CodesDocument5 pagesX-Trail Diagnostic CodesIndre Ceponiene50% (6)
- Codigos de Falla de DiagnosticoDocument7 pagesCodigos de Falla de Diagnosticocristian faundesNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsFrom EverandSemiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsNo ratings yet
- CuNi Flanges PDFDocument36 pagesCuNi Flanges PDFganeshNo ratings yet
- 5010 Dismatling Joints Edition3 En0607Document3 pages5010 Dismatling Joints Edition3 En0607AhmedRamadan100% (1)
- Q&T Vortex Flow Meter CatalogDocument7 pagesQ&T Vortex Flow Meter CatalogQasimNo ratings yet
- Fas 20 PDFDocument4 pagesFas 20 PDFMohammad HusainNo ratings yet
- Kirloskar Pumps CPHM - 01Document8 pagesKirloskar Pumps CPHM - 01Puguh EbandiNo ratings yet
- Marine ValvesDocument6 pagesMarine ValvesENG PTBBSNo ratings yet
- PRV ARITA PN16 For Steam & GasDocument2 pagesPRV ARITA PN16 For Steam & Gasquality qcNo ratings yet
- WIKA Pressure GaugeDocument4 pagesWIKA Pressure Gaugepaulo maximoNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Pinch Valves of OV SeriesDocument5 pagesMechanical Pinch Valves of OV SeriesDaniel SanNo ratings yet
- Zhejiang Linuo Flow Control Technology Co.,Ltd: Flanged Three-Way Ball ValveDocument5 pagesZhejiang Linuo Flow Control Technology Co.,Ltd: Flanged Three-Way Ball ValvesafirioNo ratings yet
- End Suction Centrifugal PumpDocument7 pagesEnd Suction Centrifugal PumpJosepta SembiringNo ratings yet
- End Suction Centrifugal PumpDocument7 pagesEnd Suction Centrifugal PumpJosepta SembiringNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals For Special Valves: Pressure Reducing Valve V82Document6 pagesFundamentals For Special Valves: Pressure Reducing Valve V82carlosNo ratings yet
- Preheater PDFDocument2 pagesPreheater PDFAhmadi MunibNo ratings yet
- KSB Psa KHG-WDocument4 pagesKSB Psa KHG-WRicardo BarrosNo ratings yet
- Aalborg EH: Versatile Booster, Auxiliary Oil and Water HeaterDocument3 pagesAalborg EH: Versatile Booster, Auxiliary Oil and Water HeaterRafaell SantaNo ratings yet
- Econ Ball Valves PN 16 Bronze Fig. 1943: Full Bore 1 or 2 Piece Body Blow-Out Proof StemDocument1 pageEcon Ball Valves PN 16 Bronze Fig. 1943: Full Bore 1 or 2 Piece Body Blow-Out Proof StemChristianGuerreroNo ratings yet
- Bich Pn10 Pn16 Pn25 Bs4504 Bs4504 FlangesDocument21 pagesBich Pn10 Pn16 Pn25 Bs4504 Bs4504 FlangesDao QuangNo ratings yet
- Vortex Flowmeter User's Manual QTDocument32 pagesVortex Flowmeter User's Manual QTVincent BuensucesoNo ratings yet
- Cast Iron Regulating Globe Valves PN 16Document3 pagesCast Iron Regulating Globe Valves PN 16Mohamed RaafatNo ratings yet
- Vc-90200.01.03-En Ecoline DJDocument6 pagesVc-90200.01.03-En Ecoline DJGary IrawanNo ratings yet
- GOOD JACK UnlockedDocument4 pagesGOOD JACK UnlockeddolensiallaganNo ratings yet
- Gate Cast Steel A216 WCB Class 150 Mod. XXXXX: Pressure Temperature RatingsDocument2 pagesGate Cast Steel A216 WCB Class 150 Mod. XXXXX: Pressure Temperature Ratingsjaponesito01No ratings yet
- BV351E Dismantling JointDocument2 pagesBV351E Dismantling JointFAIYAZ AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Junta de Expansion Tipo Flange: Especificaciones TecnicasDocument1 pageJunta de Expansion Tipo Flange: Especificaciones Tecnicas001dracNo ratings yet
- Technical Data: Globe Valve - AngleDocument1 pageTechnical Data: Globe Valve - Angledona gangulyNo ratings yet
- c93f3c73-ab35-407a-89c1-9982e462e65dDocument4 pagesc93f3c73-ab35-407a-89c1-9982e462e65dKablayialijanNo ratings yet
- DIN 3352 Cast Steel Gate ValveDocument8 pagesDIN 3352 Cast Steel Gate ValveGiancarlo MoiNo ratings yet
- 620102/01 PN16/PN10: DESCRIPTION: Nodular Cast Iron Body Gate Standard & DesignDocument1 page620102/01 PN16/PN10: DESCRIPTION: Nodular Cast Iron Body Gate Standard & Designadvantage025No ratings yet
- Dismantling JointDocument2 pagesDismantling JointFAIYAZ AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Gate Valve: Cast Iron Flat Body Soft Seated NP 16 Art. 085.0400Document1 pageGate Valve: Cast Iron Flat Body Soft Seated NP 16 Art. 085.0400LLNo ratings yet
- BSV-20F Catalog enDocument1 pageBSV-20F Catalog entienNo ratings yet
- DIN 2545 PN40 Plate Flange (Slip On Flange)Document2 pagesDIN 2545 PN40 Plate Flange (Slip On Flange)celiajudalineNo ratings yet
- PPK - Pinch - Hana IkbarDocument17 pagesPPK - Pinch - Hana IkbarHuwaida IkbarNo ratings yet
- IGV-D (Group) (V0418) - RevisedDocument1 pageIGV-D (Group) (V0418) - Revisedismi iqhwan ihsanNo ratings yet
- Strainer EN558 Serie1Document1 pageStrainer EN558 Serie1Jorge FerrerNo ratings yet
- Predpazen KlapanDocument2 pagesPredpazen KlapanКирил АлександровNo ratings yet
- Shield Gate ValveDocument1 pageShield Gate Valvemilton rebelloNo ratings yet
- Check Valve Keystone DualplateDocument2 pagesCheck Valve Keystone DualplateRobi KeiNo ratings yet
- Cast Iron Swing Check Valves With Counter Weight and Lever PN 10 and 16Document2 pagesCast Iron Swing Check Valves With Counter Weight and Lever PN 10 and 16Baskaran RathinamNo ratings yet
- Resilient Seat Gate Valve Pn10/16 Short Pattern Din 3202-F4 CTC EpdmDocument18 pagesResilient Seat Gate Valve Pn10/16 Short Pattern Din 3202-F4 CTC EpdmG DilemaNo ratings yet
- Technical Datasheet Resilient Seat Gate Valve f4 CTC Epdm Acs Flanged pn10-16Document18 pagesTechnical Datasheet Resilient Seat Gate Valve f4 CTC Epdm Acs Flanged pn10-16Benny 37No ratings yet
- Swing Check Valves PN 16Document2 pagesSwing Check Valves PN 16Mohamed RaafatNo ratings yet
- Yoshitake AL-31 - Catalog - en - Luhur SetiabudiDocument2 pagesYoshitake AL-31 - Catalog - en - Luhur SetiabudiikhsanNo ratings yet
- Gate Cast Steel Astm A216 WCB Class 150: Pressure Temperature RatingsDocument2 pagesGate Cast Steel Astm A216 WCB Class 150: Pressure Temperature RatingsJavier Hinojosa Garrido LeccaNo ratings yet
- Diaphragm Valve: G2K Rising HW Type, Flanged EndsDocument1 pageDiaphragm Valve: G2K Rising HW Type, Flanged EndsHARSHANo ratings yet
- Datasheet Type 40104010HD enDocument3 pagesDatasheet Type 40104010HD enTanmoy DuttaNo ratings yet
- Non Return Valve: Type 4010 and 4010HDDocument3 pagesNon Return Valve: Type 4010 and 4010HDTanmoy DuttaNo ratings yet
- Combibloc Tehnicni PDFDocument1 pageCombibloc Tehnicni PDFRyan PatraNo ratings yet
- Combibloc TehnicniDocument1 pageCombibloc TehnicniRyan PatraNo ratings yet
- PVC Butterfly Valve (Worm Gear)Document4 pagesPVC Butterfly Valve (Worm Gear)Elias SusantoNo ratings yet
- En bf880 PDFDocument1 pageEn bf880 PDFshaonaaNo ratings yet
- Jis Series F7410Document1 pageJis Series F7410TripleOffsetNo ratings yet
- CLC 17-12-2L: A 2%mo Containing 18 CR - 10 Ni Austenitic Stainless Steel (316L Grade)Document4 pagesCLC 17-12-2L: A 2%mo Containing 18 CR - 10 Ni Austenitic Stainless Steel (316L Grade)PeterWayNo ratings yet
- F-3061 Jis 5K/Jis 10K: No Part Material CodeDocument1 pageF-3061 Jis 5K/Jis 10K: No Part Material CodeSergio Jesus SanjurjoNo ratings yet
- InstruccionesUso PDFDocument46 pagesInstruccionesUso PDFlaboratorioelectroNo ratings yet
- Marlow Industries Inc. Marlow Industries Inc. Marlow Industries Inc. Marlow Industries IncDocument2 pagesMarlow Industries Inc. Marlow Industries Inc. Marlow Industries Inc. Marlow Industries IncJavad ArabNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Heating, Ventilating, and Air-Conditioning (Hvac) Equipment and ControlsDocument16 pagesChapter 4 Heating, Ventilating, and Air-Conditioning (Hvac) Equipment and Controlssanizan80No ratings yet
- Membrane SeparationDocument9 pagesMembrane SeparationDhananjay Kadam0% (1)
- Dia-Come EngDocument4 pagesDia-Come EngTECNIMETALNo ratings yet
- Extraction of Silica From Paddy HuskDocument16 pagesExtraction of Silica From Paddy HuskShaibaz KudupkarNo ratings yet
- Exotuf-Plus zzb1620Document4 pagesExotuf-Plus zzb1620ethan8888No ratings yet
- Manual Horno HaierDocument20 pagesManual Horno HaierWillman UzcateguiNo ratings yet
- Epoxy-Coated Steel Reinforcing Bars: Standard Specification ForDocument10 pagesEpoxy-Coated Steel Reinforcing Bars: Standard Specification Forayman m.waleedNo ratings yet
- 1409 Experiment 8 Periodic Behavior of MetalsDocument7 pages1409 Experiment 8 Periodic Behavior of MetalsTerra DrakeNo ratings yet
- TFM ProjectDocument22 pagesTFM Projectsai anju100% (1)
- AffanDocument9 pagesAffanAshnab Zahid KhanNo ratings yet
- Training Report 400 KV GSS, RRVPNL Surpura, JodhpurDocument52 pagesTraining Report 400 KV GSS, RRVPNL Surpura, JodhpurManish Bishnoi67% (3)
- PMRDA BOQ Inquiry With ScopeDocument8 pagesPMRDA BOQ Inquiry With ScopeAkd DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Installation Instructions OWSDocument16 pagesInstallation Instructions OWSmarcus100% (1)
- Textile Engineering and Fibre ScienceDocument3 pagesTextile Engineering and Fibre ScienceNikhil TakbhateNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/42Document13 pagesCambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/42Maram MohanNo ratings yet
- BITS Pilani: Module 4: Design of Separation Systems Lecture-15Document24 pagesBITS Pilani: Module 4: Design of Separation Systems Lecture-15sukhmaniNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training On RdsoDocument24 pagesIndustrial Training On RdsoPrakhar AwasthiNo ratings yet
- Pulp - Paper - C3 - Mechanical Pulping PDFDocument61 pagesPulp - Paper - C3 - Mechanical Pulping PDFVũ Đăng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Gas Plant of Ethylene Gas Carrier and A Two Stages Compression Optimization of Ethylene As A Cargo Based On Thermodynamic AnalysisDocument8 pagesGas Plant of Ethylene Gas Carrier and A Two Stages Compression Optimization of Ethylene As A Cargo Based On Thermodynamic AnalysisWendy PramonoNo ratings yet