2.
0 LETTER OF TRANSMITTAL
Group 3
Student of MGT 269,
University Technology Mara,
Kelantan Branch, Machang Campus,
Bukit Ilmu, 18500 Machang,
Kelantan.
9 May 2023
Madam ………….
Lecturer of MGT 269,
University Technology Mara,
Kelantan Branch, Machang Campus,
Bukit Ilmu, 18500 Machang,
Kelantan.
Dear Madam,
SUBMISSION OF BUSINESS COMMUNICATION REPORT (MGT269)
We tried our very best preparing this report. The information of this report is mainly based on
internet information. Some other information was gathered from our respondent which is
undergraduate students. All of us gave our thorough effort to make this report accomplish.
We tried our very best preparing this report. The information of this report is mainly based on
internet information. Some other information was gathered from our respondent which is
undergraduate students. All of us gave our thorough effort to make this report accomplish
It gives us great joy to be able to provide the outcome of the hard work we put into the report
you requested last month.
We are presenting the report, "Increase in Unemployment in Malaysia," which is attached. We
have gathered crucial information for preparation using both primary and secondary sources. We
faced several unusual obstacles relating to Malaysia's rising unemployment rate while
completing this study. We made an effort to address the root causes, ramifications, and viable
solutions to this problem. Most of the information in this article is taken from the internet.
1
�We are grateful for the opportunity to contribute to this project, and we sincerely hope that the
accompanying report meets your expectations. We hope that this report will be able to help deal
with the complicated issues surrounding the unemployment situation in Malaysia.
More importantly, thank you to Madam ………………… for participating in the information-
sharing process and assisting us in completing this project effectively.
Sincerely,
name
3.0 TABLE OF CONTENT
NO. PARTICULAR PAGES
2
� 1.0 Cover Pages 1
2.0 Letter of Transmittal 2-3
3.0 Table of Content 4
4.0 Executive Summary 5
5.0 Introduction
5.1 Background of Problem
5.2 Purpose
5.3 Scope 6-7
5.4 Method of Investigation
5.3 Limitations
6.0 Data Analysis
Figure 1: Total family dependent
Figure 2: Highest level of education
Figure 3: Income that unemployment expects.
Figure 4: How an unemployed person survives in life.
Figure 5: Effect of unemployment 8-17
Figure 6: Average age of unemployment
Figure 7: Factors that can contribute to unemployment.
Figure 8: Obstacles to Finding a Job
Figure 9: Effective ways to find a job.
Figure 10: Unemployment rate in Malaysia from 2015 to
2021
7.0 Conclusion 18
8.0 Recommendations 19-20
9.0 References 21
10.0 Appendix 22-23
4.0 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
Malaysia's unemployment rate dropped from 4.1 percent in March 2022 to 3.5 percent in March
2023. However, as the economy continued to bounce back from the pandemic's disruptions, it
3
�was the lowest number since February 2020. While employment increased by 2.9 percent to
16.22 million, the number of people in the labour force decreased by 12.0 percent to 588.7
thousand. In the meantime, the labour force participation rate increased to 69.9% from 69.2% in
the same period in 2022. The unemployment rate was 3.5 percent in February.
Many students graduate from higher education institutions each year, whether they are public or
private. High unemployment is a result of fierce job competition. Unemployment can also result
from a lack of jobs. Both the public and commercial sectors have fierce rivalries for available
jobs. Because they view them as being more effective and secure for the future, many graduates
are more interested in the public and private sectors than the government. The parties must
therefore take the initiative, which is a special issue in this competition. To tackle
unemployment, parties also need to create several new industries and career fairs. Those who
leave public and private organizations should work in new fields, such as agriculture, small and
medium-sized businesses, and other industries. By diversifying, businesses can lower their
unemployment rate and boost the economy.
If we want to lessen this issue, we should start with the graduates themselves, because it is
pointless for the government to exert significant effort to address this issue while the graduates
themselves are unwilling to take action. The most crucial thing that we should look at are the
graduates' altered attitudes. Graduates themselves must adopt a professional mindset and refrain
from being critical of anything when they are not offered a job with a salary commensurate with
their qualifications.
5.0 INTRODUCTION
5.1 Background of Problem
4
�These days, the employer will pick the candidate with more experience than the one without.
Graduate unemployment is also a result of a lack of experience and abilities. In general,
employers prefer to hire graduates with experience.
Furthermore, because local graduates in Malaysia lack critical abilities like English fluency and
interpersonal skills, the private sector is currently not interested in hiring them. There seems to
be a disconnect between the skills graduates possess and what companies demand. In light of
this, the government has implemented a number of steps to address the issue of graduate
unemployment. One such step is the implementation of various training programmes for recent
graduates.
A review of the tertiary education system is another measure. Soft skill development should be
integrated into the educational curriculum, and students should be able to participate in
extracurricular activities to improve soft skills such as personal traits, interpersonal skills, and
critical and creative thinking.
5.2 Purpose
Identify the issues that have been faced by society.
Do some peer research on how it impacts the economy's growth.
Find a way to prevent further escalation of the problem.
5.3 Scope
In Malaysia including both west and east Malaysia cause by foreign immigration from
another countries.
5.4 Method of Investigation
5
� Our report uses both methods, which are primary data collection and secondary data
collection methods. For primary data, we do some surveys and group discussions. For
secondary data, we use the internet, journals, newspaper articles, and websites to collect
useful data.
5.5 Limitations
To complete the investigation, various limitations of this study were recognized. As a result of
this predicament, steps are being taken to prevent these factors from influencing the findings of
this investigation.
Lack of time
-The time allotted is quite short and constrained. To avoid squandering time, we must carefully
manage our time. As a result, we must devote more time to gathering data and information from
outside sources. Due to time restrictions, the process of developing a solution to this challenge
will be hampered.
Research and Limitations
- The sample framework for this research on the topic of unemployed Malaysians in order to
determine why this occurred in Malaysia. The case sampling procedures used in this study may
be able to access the fall of Malaysia's unemployment problem.
Availability of the secondary data
- We have trouble finding additional material on websites, and there aren't many periodicals that
deal with the unemployment problem in Malaysia. Despite the fact that this issue is available
online, we still need important or in-depth information from other state and university libraries
for more published journals and theses, and we still need to hunt for information in the
newspaper.
Lack of experience
- We have no experience running the thesis other than a lack of expertise. It is tough to conduct
research when we lack appropriate experience and data collection capabilities.
6
�6.0 DATA ANALYSIS
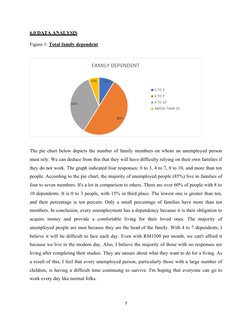
Figure 1: Total family dependent
FAMILY DEPENDENT
10% 15%
0 TO 3
4 TO 7
60% 8 TO 10
ABOVE THAN 10
85%
The pie chart below depicts the number of family members on whom an unemployed person
must rely. We can deduce from this that they will have difficulty relying on their own families if
they do not work. The graph indicated four responses: 0 to 3, 4 to 7, 8 to 10, and more than ten
people. According to the pie chart, the majority of unemployed people (85%) live in families of
four to seven members. It's a lot in comparison to others. There are over 60% of people with 8 to
10 dependents. It is 0 to 3 people, with 15% in third place. The lowest one is greater than ten,
and their percentage is ten percent. Only a small percentage of families have more than ten
members. In conclusion, every unemployment has a dependency because it is their obligation to
acquire money and provide a comfortable living for their loved ones. The majority of
unemployed people are men because they are the head of the family. With 4 to 7 dependents, I
believe it will be difficult to face each day. Even with RM1500 per month, we can't afford it
because we live in the modern day. Also, I believe the majority of those with no responses are
living after completing their studies. They are unsure about what they want to do for a living. As
a result of this, I feel that every unemployed person, particularly those with a large number of
children, is having a difficult time continuing to survive. I'm hoping that everyone can go to
work every day like normal folks.
7
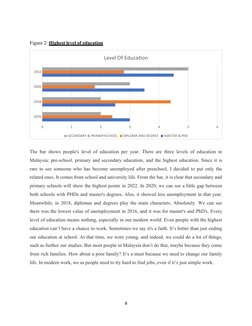
�Figure 2: Highest level of education
Level Of Education
2022
2020
2018
2016
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
SECONDARY & PRIMARYSCHOOL DIPLOMA AND DEGREE MASTER & PHD
The bar shows people's level of education per year. There are three levels of education in
Malaysia: pre-school, primary and secondary education, and the highest education. Since it is
rare to see someone who has become unemployed after preschool, I decided to put only the
related ones. It comes from school and university life. From the bar, it is clear that secondary and
primary schools will show the highest points in 2022. In 2020, we can see a little gap between
both schools with PHDs and master's degrees. Also, it showed less unemployment in that year.
Meanwhile, in 2018, diplomas and degrees play the main characters. Absolutely. We can see
there was the lowest value of unemployment in 2016, and it was for master's and PhD's. Every
level of education means nothing, especially in our modern world. Even people with the highest
education can’t have a chance to work. Sometimes we say it's a faith. It’s better than just ending
our education at school. At that time, we were young, and indeed, we could do a lot of things,
such as further our studies. But most people in Malaysia don’t do that, maybe because they come
from rich families. How about a poor family? It’s a must because we need to change our family
life. In modern work, we as people need to try hard to find jobs, even if it’s just simple work.
8
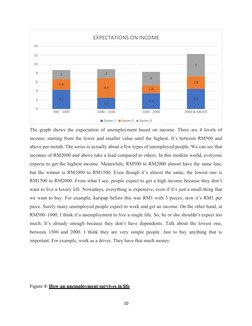
�Figure 3: Income that unemployment expects.
9
� EXPECTATIONS ON INCOME
14
12
10 5
8 2 2
3
6 2.8
2.4
4.4 1.8
4
2 4.3 4.5
3.5
2.5
0
500 - 1000 1000 - 1500 1500 - 2000 2000 & ABOVE
Series 1 Series 2 Series 3
The graph shows the expectation of unemployment based on income. There are 4 levels of
income, starting from the lower and smaller value until the highest. It’s between RM500 and
above per month. The series is actually about a few types of unemployed people. We can see that
incomes of RM2000 and above take a lead compared to others. In this modern world, everyone
expects to get the highest income. Meanwhile, RM500 to RM2000 almost have the same line,
but the winner is RM1000 to RM1500. Even though it’s almost the same, the lowest one is
RM1500 to RM2000. From what I see, people expect to get a high income because they don’t
want to live a luxury life. Nowadays, everything is expensive, even if it’s just a small thing that
we want to buy. For example, karipap before this was RM1 with 3 pieces; now it’s RM1 per
piece. Surely many unemployed people expect to work and get an income. On the other hand, at
RM500–1000, I think it’s unemployment to live a single life. So, he or she shouldn’t expect too
much. It’s already enough because they don’t have dependents. Talk about the lowest one,
between 1500 and 2000. I think they are very simple people. Just to buy anything that is
important. For example, work as a driver. They have that much money.
Figure 4: How an unemployment survives in life
10
� WAY TO RURVIVE
6
0
Category 1 Category 2 Category 3 Category 4
HUMANITARIAN ASSISTENCE OTHERS PART TIME JOB
From the line, it shows how unemployment survives in life. There are three types: humanitarian
assistance, a part-time job, and others. The other is that we also don’t know how to survive in our
own lives. Do a part-time job. Take a lead between three of them with 5 points and start with 2.4
points. Even though it’s not a full-time job, it’s still a job and can earn some money.
Humanitarian assistance has only a little gap with a part-time job, but in the beginning, it has
quite a high point. Others say maybe they can get help from their family or the homeless. Even
the homeless can get help from the country because, in Malaysia, there are so many homeless. In
conclusion, there are a few ways to avoid unemployment. A part-time job will not give you
enough money because you will only have a few hours to work. For example, work packing food
at McDonald's. McDonald's gets a lot of interest from people. There are maybe more than 300
customers every day. So, it will be tiring to work with just a little income. But maybe they can
get free food. At least we can make a little money to survive. Humanitarian aid is substantial, but
it can still outnumber global unemployment. Sometimes, there must be people who do not get
this help, even though they are poor. This is to help with giving some money and a few other
things. But surely it will last quickly. Others are homeless; they live on the street and eat dirty
food. Sometimes, they can also get help from other people.
Figure 5: Effect of unemployment
11
� EFFECTS
EFFECTSOF
OFUNEMPLOYMENT
UNEMPLOYMENT
0.15; 15% MENTAL HEALTH ISSUE
0.15;
0.05; 5% 15% DIFFICULTY FINDING A NEW
JOB MENTAL HEALTH ISSUE
0.05; 5% LESS SATISFACTION
DIFFICULTY FINDING A NEW JOB
0.2; 20% 0.6; 60% POWERLESS
LESS SATISFACTION
0.2; 20% 0.6; 60% POWERLESS
The pie chart above shows us the effect after becoming unemployed. There are 4 total effects of
unemployment. It is a mental health issue, difficulty finding a new job, less satisfaction, and the
last one is powerlessness or limited negotiating power. Let’s see their percentage for each one.
We can see that the highest one is mental health issues, with 60%. It’s already half of the pie
chart. Mental health issues such as depression, stress, and anxiety. The second one is difficulty
finding a new job with 20%. This is because they are not trusted to work and lack confidence.
The third one is powerless with 15%. They are powerless over the direction of their own lives.
The last one has less satisfaction with only a small percentage; it is only 5%. This is because they
compare themselves with people who have jobs. Mental health issues play the main character
because surely those who are unemployed will have a negative mind because they can work like
others. Consider how it will put our mental health at risk. People can feel down and start to think
they are useful. People will also face a problem finding a job because they don’t have work
experience before this. It’s just a lack of trust. For example, working as a cashier is easy work,
but if we do not know how to use the machines, they can’t accept us. Meanwhile, the powerless
are people who will look down on us because they feel great that they have a job. Also, people
with unemployment will not be satisfied with their lives because they can't get enough money to
survive and live a comfortable life like others.
Figure 6: Average age of unemployment
12
� A VER A GE A GE OF UNEPLOYMENT
<23 24-40 >40
5
4.5 4.3 4.4
4
3.5
3
2.4 2.5
2.5
2 2
2
1.5
1
0.5
0
2016 2018
The bar shows the average age of unemployment in Malaysia. The average between people with
ages below 23 is 24, 24 to 40, and the last one is older than 40 years old. The average is between
young people and older people. It doesn’t matter because age means nothing in our modern
world. In 2016, people younger than 23 years old had the highest point compared to others
average age. It’s because people decide to work after the end of the school season. The second is
24–40. Neither high nor low, the lowest one is higher than 40. I believe this many people quit
their jobs at this age. Meanwhile, in 2018, people aged between 24 and 40 should take the lead
because it is hard to find a job every passing year. This age actually differs a lot from university
students. They may not find the right job for themselves. As usual, the lowest one is >40; it has
the same point as in 2016. It doesn’t increase. In conclusion, many of the unemployed are over
the age of 25 and have higher education such as diplomas, degrees, and so on. Even though we
have PHD certificates, we can now easily get work because our world has grown larger with an
increasing number of individuals every day. People who are 23 years old decide not to continue
their studies, such as following SPM. They want to work and create their own business, but it is
difficult, and they eventually become unemployed. Another issue is that they come from a low-
income home. We rarely encounter persons beyond the age of 40 who are unemployed. Also,
there are people who are already retired from jobs at that age. So, that means unemployment
comes from variables of age.
Figure 7: Factors that can contribute to unemployment.
13
� FACTORS THAT CAN CONTRIBUTE TO
UNEMPLOYMENT
ECONOMIC FACTORS
20%
LACK OF SKILLS AND EDUCATION
40%
LIMITED WORK EXPERIENCE
25% DISCRIMINATION AND SOCIAL
EXCLUSION
15%
According to the pie chart above, unemployment has multiple origins and is frequently a
complicated problem influenced by economic, social, and political factors. Here are some of the
reasons behind unemployment. Unemployment is heavily influenced by economic situations.
According to 40% of respondents, the economy is the primary cause of unemployment.
Economic downturns, recessions, or slow development can restrict job possibilities and make it
more difficult for young people to find employment. As many as 25% of those polled believe
that a lack of work experience is the root reason of unemployment. Many entry-level jobs
demand work experience, which can be difficult for young people just starting out in their
careers. A dearth of internships, apprenticeships, or part-time work options can make it difficult
for young people to get valuable work experience and establish a foothold in the job market.
Furthermore, discrimination and social exclusion are variables that contribute to increased
unemployment. Discrimination based on gender, color, ethnicity, or socioeconomic status can
disproportionately affect young people and impede their access to work prospects. The same
factor was mentioned by up to 20% of respondents. Finally, just 15% of respondents felt that a
lack of skills and education were a contributing cause to unemployment. Inadequate education
and skills might make it difficult for young people to find acceptable employment. Inadequate
access to excellent education, restricted vocational training possibilities, and a mismatch between
acquired skills and job market demands can all lead to increased rates of youth unemployment.
Figure 8: Obstacles to finding a job.
14
� OBSTACLES TO FINDING A JOB
16
12
8 17
4
0 0 1 2
s te w es
or a i e ri
tit tifi
c rv la
pe er in
te sa
om n
s b nd
yc tio jo
ns
a
a n
ca ra o
M du fo si ti
e g po
e r rin g
gh pa s in
hi pre o
No t ho
No e rc
ov
Column1
Refer to a graph or piece of data that demonstrates different factors or obstacles people face
when seeking to find work based on the information presented. According to these statistics, the
element that garnered the most public votes (17 votes) is "having a lot of competition." This
implies that many people regard competition from other job seekers as the most difficult
hindrance to getting work. It can be inferred that each task or job opening does not require a
large number of staff, and therefore, there is a need for filtering or selecting the most suitable
candidates. In other words, the number of available job possibilities may not match the number
of people looking for work. Everyone present is seeking work in each area, meaning that
competition for jobs is fierce in each location. When there are a large number of people
searching for jobs in the same location, it becomes difficult for individuals to get work due to
increased competition. Lastly, the lowest percentage of barriers to employment, at 0%, is
associated with not having a higher education credential. This shows that, when compared to the
other reasons or barriers listed in the graph or statistics, a lack of a higher education certification
has the least impact on one's capacity to get work.
Figure 9: Effective ways to find a job.
15
� EFFECTIVE WAYS TO FIND A JOB
JOB FAIRS
ONLINE NETWORKING
GO BEYOND JOB LISTING
COMPANY WEBSITES
0 2 4 6 8 10 12
Through the data above, we can see that company websites only got 2 votes, while going beyond
job listings got 3 votes, online networking got 4 votes, and 11 people agree that job fairs are
effective ways to find a job. Job fairs provide a unique opportunity for job seekers to interact
face-to-face with hiring managers and company representatives. Candidates may stand out from
the competition through this one-on-one encounter by making a good first impression,
showcasing their abilities and credentials, and developing a personal connection. Next, a variety
of businesses and experts from different sectors frequently attend job fairs. By meeting
recruiters, industry leaders, and future coworkers at these events, job seekers may broaden their
professional networks. Networking can result in beneficial connections and recommendations,
giving access to unlisted career chances. The company website has the lowest grade as a resource
for job seekers. Not all businesses currently routinely update their websites with employment
postings. They might also rely on other hiring practices, such employment agencies, job boards,
and social networking sites. As a result, a company's website may not contain all of the available
job possibilities for job seekers. Company websites might not see as much traffic as well-known
online job boards. Dedicated job search engines, social networking sites for professionals, or
online job boards that compile listings from several sources are frequently used by job seekers.
These platforms provide a wider range of employment prospects and increase job seekers'
visibility.
16
�Figure 10: Unemployment rate in Malaysia from 2015 to 2021
UNEMPLOYMENT RATE IN MALAYSIA FROM
2015 TO 2021
6
5.3
5 4.61
4 3.6
3.5 3.4 3.4
3.3 3.3
3
0
2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022
As the country battled the COVID-19 outbreak, unemployment increased by 5.3% in 2020. The
pandemic produced extensive disruption across the economy, resulting in job losses and reduced
employment possibilities. The economic slump is one of the causes contributing to the increase
in unemployment, as firms face falling consumer demand and disrupted supply networks. Many
businesses are experiencing financial difficulties and are being forced to downsize or close,
resulting in job losses. On the other side, the epidemic is posing significant difficulties for many
small enterprises and independent contractors. They frequently do not have the financial
resources to continue running during extended shutdowns, which leads to closures and job
losses. In the end, the pandemic disrupted global supply networks, impacting sectors of the
economy that depend on imports and exports. In the manufacturing and related sectors, reduced
production and distribution operations result in job losses. In 2021, government programmers
aimed at reviving the labor market caused the unemployment rate to start progressively
declining. People looked for employment prospects as a result, both offline and online, in order
to ensure their livelihoods and financial stability.
17
�7.0 CONCLUSION
Unemployment can be defined as a person who is jobless because they quit, got fired, or are
currently searching for a job. We know that an increase in unemployment can reduce the growth
potential of a country. The fact that many graduated people have still been unemployed until now
has had a major impact on society. This can cause resources to arise, but the output of the
production is low because there are no workers that can give their services to the production.
This research has given an overview of the causes, effects, and challenges facing both
individuals and the government with increasing unemployment.
In conclusion, we can see that the increasing rate of unemployment in our country can become a
serious issue for the growth of the economy. It can have a big impact if the issue is left
unaddressed. With this, lots of initiatives and actions have been taken by various parties to
improve the standard of living. Simply put, the reason behind our slow growth in the economy
compared to the devolved country is due to a problem like this.
18
� 8.0 RECOMMENDATIONS
I. Control the number of foreign workers in the local market.
The admission of foreign workers needs to be looked at as one of the threats that affect local
labour especially for the group of young people. One method of overcoming the admission
of foreign workers into the local labour market by strongly opposing memoranda between
ASEAN countries on mass recruitment of foreign workers into the local market. The job
vacancies should be given to Malaysians. University graduates, school leavers, the
unemployed, and poverty groups.
II. Training in language and oral skills
Communication plays an important role for those who are seeking a job. The ability to
speak. More than one language can be a huge advantage for them. In addition to that,
writing skills need to be improvised as the work relies not only on communication. To be
simple, both communication and writing skills are useful in broadening their potential.
III. Improvement in the location of job opportunities based on development action plans and
strategies.
Economic development strategies play a vital role in maximising the economic performance
in one area. Economic development plans must be synchronised at the national level down
to the local level. The location of production and manufacturing should be based on
economic strategies, plans, and directions to produce more job vacancies, especially in the
rural areas. Focus development areas must be precise, especially on the outskirts, to cater to
the needs and demands for local labour indirectly provide more job opportunities to those
who are living in the rural area, as most of them avoid working outside of their living area.
19
�IV. Minimum wage, introduction of skills, and training provided.
The low wage issue is among the concerns that increased the rate of unemployment in
Malaysia. Thus, pertaining to these issues, some of the recommendations could be made by
reducing the working hours of employed people and substitutes with the skills and training
provided by the employers. Skill and training may help workers be more focused and
specialised towards the related field as well as enhance the worker’s abilities. Therefore,
through skills and training, provided, it will increase the possibility of getting a good job
and improve the condition of their production, manufacturing, and services that support
Malaysia's economic performance usually placed in the outskirt’s areas. Existing resources
were identified in those outskirts’ areas and created the job opportunities. The relocation of
manufacturing and services to urban areas require the cost of moving and transportation. In
order to reduce the cost, production needs to run nearby the resource area so as to produce
more productivity rather than face the high cost of moving. This is also in line with the
economic strategy and development plan in order to enhance economic performance in the
outskirts. As potential employees, certainties of having relocated to the outskirts area is
higher due to manufacturing and services spurring a lot in rural areas. One’s mental and
physical should be prepared together willingly to be transferred in order to secure the job
offers.
20
�9.0 REFERENCES
1. Asia Pacific International Conference. (2014)
https://core.ac.uk/
2. Bloomberg. (2023)
https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles
3. Department of statistics Malaysia. (2021)
https://statsdw.dosm.gov.my/
4. The Malaysia deserves. (2023)
https://themalaysianreserve.com/
21
�10.0 APPENDIX
22
�23