Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BCom Financial Accounting Study Material Notes Branch Accounts PDF
Uploaded by
simran32366Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BCom Financial Accounting Study Material Notes Branch Accounts PDF
Uploaded by
simran32366Copyright:
Available Formats
Royalty Accounts ll
l 5.1
L
E
S
S
O
N
6
Branch Accounts
Introduction
As a business grows, it may open branches in different towns and cities within country or
outside country in order to market its product over a large territory and, thus, increase its
profits. A branch may be defined as a section of an enterprise, geographically separated from
the rest of the business, controlled by a Head Office and generally carrying on the same
activities as of the enterprise. For example, Bata Shoe Co. has branches in various cities all
over the country. The same example holds good for a commercial bank also.
Meaning of Branch
The term ‘Branch Accounts’ refer to record of transaction of branches, whether relating
to deal with Head Office or with outsiders or deal between different branches in the books of
Head office. In order to exercise greater control over the branches, it is necessary to ascertain
profit or loss made by such branches separately. For this purpose, a proper accounting system
is to be adopted for recording business transactions between Head Office and Branches. The
accounting system to be adopted for the branch depends upon the size and nature of branch
and the degree of control required by the Head Office. Thus, branches can be broadly
classified into two categories for the purpose of recording transactions in the books of
accounts i.e.
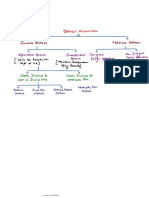
Branches
Home Branches Foreign Branches
Dependent Branches Independent Branches
Home Branches
A. Dependent Branches : Dependent branches are those branches which are bot
keeping their own separate set of books of accounts. The relation between head office and
branch is just like agency, therefore, these are also known as agency branches. The following
are the salient features of such a branch :
(i) These branches generally depend upon the head office for supply of goods. However,
the branch may be allowed to make purchases from the local parties.
(ii) All expenses of the branch are directly paid by the head office.
(iii) In order to meet the petty expenses of the branch, e.g., conveyance expenses,
entertainment expenses etc., may be provided with the petty cash from the head
office.
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
5.2 lll Financial Accounting
(iv) Normally branches receiving goods from head office selling for cash only but also
selling on credit if it is authorised by the head office.
(v) Cash received from branch from its debtors or on account of cash sales is daily
remitted to head office or deposited into a bank account opened in the name of the
head office.
(vi) Such branches maintain certain memorandum records only such as cash book,
debtors account and stock registers.
Accounting procedure : In case of a dependent branch, the head office may keep
accounts of the branch according to the following methods :
1. Debtors or Direct Method
2. Final Accounts Method
3. Stock and Debtors Method
Debtors or Direct Method
Under this method, head office opens one account for one branch. This account is called
Branch Account. The object of this account is to disclose branch profit or loss. This branch
account is a nominal account. The head office maintains this account in its books. Normally
this method is followed in case of branches of small size. On the basis of nature and size of
branch, the dependent branch can be divided into three parts for the purpose of recording
transactions in the books :
(a) Branch receiving goods from head office at cost price and making cash sales
only : These branches receive goods from head office at cost price, sell for cash only and remit
the cash collected to the head office. All expenses of the branch are directly paid by the head
office. These branches do bot make its own set of books. To find out the profit or loss of these
branches, the following accounting entries are passed in the books of the head office :
1. When the opening balances of assets at the branch :
Branch A/c Dr.
To Opening Stock A/c
To Opening Petty Cash A/c
To Opening Balance of Other Assets
(For opening balances at the branch)
2. For opening Creditors and outstanding
Opening Creditors A/c Dr.
Outstanding Liabilities A/c Dr.
To Branch A/c
(Being opening balance of liabilities at the Branch)
3. For goods supplied by the Head office to the branch:
Branch A/c Dr.
To Goods Supplied to Branch A/c
(For goods supplied to branch)
4. For expenses at the branch met by the head office :
Branch A/c Dr.
To Cash or Bank A/c
(For amount sent to branch for expenses)
5. For goods returned by the branch to the Head Office :
Goods Supplied to Branch A/c
To Branch A/c
(For goods returned by Branch)
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
Royalty Accounts ll
l 5.3
6. For amount sent to branch for petty expenses :
Branch A/c Dr.
To Cash A/c
(For amount sent to branch for petty expenses)
7. For remittances received from branch :
Cash A/c Dr.
To Branch A/c
(For cash received from branch)
8. When the closing balances of assets at the branch :
Closing Stock A/c Dr.
Closing Petty Cash A/c Dr.
Closing Balances of Other Assets Dr.
To Branch A/c
(For closing balances at the branch)
9. For loss at the branch (if debit side is bigger)
General Profit & Loss A/c Dr.
To Branch A/c
(For loss transferred to general profit and loss A/c)
10. For transfer of balance in goods to supplied to branch Account :
Goods Supplied to Branch A/c Dr.
To Trading A/c
(For balance in goods supplied to branch A/c transferred to trading A/c)
Branch Account in the books of Head Office
If branch account is to be prepared on the basis of above mentioned entries, it will appear
as follows :
In the books of Head Office
Branch Account
Particular Amount Particular Amount
Dr. Cr.
To Balance b/d ByBalance b/d—
Stock — Creditors —
Petty cash — Outstanding exp. — —
Furniture — ByCash—
Prepaid — Cash sales —
Debtors — — Cash from Debtor — —
To Goods sent to Bank A/c — By Goods Return to H.O. —
To Cash A/c— By Balance c/d
Rent — Stock —
Salaries — Petty Cash —
Other exp. — — Furniture —
To Balance c/d— Prepaid Exp. —
Creditors — Debtors — —
Outstanding exp. — —
To General P&L —
Total Total
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
5.4 lll Financial Accounting
Particular Illustration Questionry
1. Making cash sales only by Branch 1, 2 1, 2, 3
2. Making both cash and credit sales by Branch 3, 4 4, 5, 6
3. When goods are supplied to branch by H.O. at invoice price 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14,
15, 16
4. Memorandum stock account 10, 11 17, 18, 19, 20, 21
5. Final account method 12, 13 22, 23, 24, 25, 26
6. Stock and Debtors method 14, 15, 16, 17 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33,
34
7. Wholesale branch system 18, 19 35, 36, 37
8. Independent Branch 20, 21, 22 38, 39, 40, 41
9. Special entries 23, 24, 25 42, 43, 44, 45
10. Foreign Branch 26, 27 46, 47, 48, 49
Illustration 1.
Hindustan Ltd. has a branch at Bhopal. Branch has to remit daily cash receipts to the
head office and all expenses of the branch are paid by the Head Office directly. Following are
the transactions between Head office and branch for the year ended 31st March, 2016 :
`
Stock at Branch on 1 Aril 2015 6,000
Goods supplied to Branch during the year 1,20,000
Cash sent to Branch for :
Rent 1,100
Salaries 9,000
Insurance 300
Goods returned by branch 3,000
Cash sent to Branch for Petty expenses 500
Cash received from the branch during the year 1,20,000
Cash sent by branch on 29 March 2016 5,000
Stock at Branch on 31st March 2016 10,000
Balance of Petty Cash on 31st March 2016 50
Outstanding Rent on 31st March 2016 100
Give Journal entries and show the Branch Account in the books of Head Office.
Solution. Books of Head Office
Journal
Date Particulars L.F. Amount Amount
Dr. Cr.
` `
Bohpal Branch A/c Dr. 6,000
To Opening Stock at Branch A/c 6,000
(For opening balance of branch stock)
Bhopal Branch A/c Dr. 1,20,000
To Goods Supplied to Branch A/c 1,20,000
(For goods supplied to branch)
Bhopal Branch A/c Dr. 10,400
10,400
To Cash A/c
(For goods purchased for cash)
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
Royalty Accounts ll l 5.5
Goods Supplied to Branch A/c Dr. 3,000
To Bhopal Branch A/c 3,000
(For goods returned by branch)
Bhopal Branch A/c Dr. 500
To Cash A/c 500
(For amount sent to branch for petty expenses)
Cash A/c Dr. 1,20,000
To Bhopal Branch A/c 1,20,000
(For cash received from Branch)
Cash in Transit A/cDr. 5,000
To Bhopal Branch A/c 5,000
(For cash sent by branch still in transit)
Closing Stock at Branch A/c Dr. 10,000
Closing Petty Cash at Branch A/c Dr. 50
To Bhopal Branch A/c 10,050
(For closing balance of branch)
Bhopal Branch A/c Dr. 100
To Outstanding Rent A/c 100
(For rent due to branch)
Bhopal Branch A/c Dr. 1,050
To General Profit & Loss A/c 1,050
(For profit transferred to general profit & loss account)
Goods Supplied to Branch A/c Dr. 1,17,000
To Trading A/c 1,17,000
(For balance of goods supplied to branch A/c transferred to trading A/c
i.e. ` 1,20,000 – ` 3,000)
Bhopal Branch Account
(`) (`)
To Balance b/d ByGoods Supplied to Branch A/c
Stock 6000 (Goods returned by branch) 3,000
To Goods Supplied to Branch A/c 1,20,000 ByCash A/c 1,20,000
To Cash A/c (expenses) 10,400 ByCash in transit A/c 5,000
To Cash A/c (petty expenses) 500 ByBalance c/d
To Outstanding Rent A/c 100 Stock 10,000
To General Profit & Loss A/c 1,050 Petty Cash 50 10,050
(Bal. fig.)
1,38,050 1,38,050
Illustration 2.
Sincere Brothers of Delhi opened a branch at Kanpur on 1 April 2014. From the following
figures, prepare Kanpur Branch Account in the books of Sincere Brothers of the year ending
March. 31, 2015 and 2016.
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
5.6 lll Financial Accounting
2015 2016
` `
Goods sent to Kanpur Branch 1,00,000 1,20,000
Expenses paid by the Head Office–
Rent 1,200 1,200
Salaries 6,000 6,000
Advertisement 600 800
Cash sales at Branch 1,20,000 1,65,000
Remittance received from the branch — 1,60,500
Remittance made on March 30, still in transit — 4,000
Expenses paid by the branch
Cartage 200 250
300 400
Petty Expenses
Stock on March 31 20,000 30,000
Petty cash in hand on March 31 200 —
Solution. Kanpur Branch Account
for the year 2014-15
` `
To Goods sent to Branch A/c 1,00,000 By Bank A/c (Remittances received) 1,19,3001
To Bank A/c : ` By Balance c/d (31-03-2015)
Rent 1,200 Stock 20,000 2
Salaries 6,000 Petty Cash 200 8
Advertisement 600 7,800
To General Profit & Loss A/c 31,700
1,39,500 1,39,500
Kanpur Branch Account
for the year 2015-16
` `
To Balance b/d : (1-4-2015) By Bank A/c (Remittances received) 1,60,500
Stock 20,000 2 By Balance c/d (31-03-2016)
Petty Cash 200 2 Cash in Transit 4,000
To Goods sent to branch A/c 1,20,000 Stock 30,000
To Bank A/c : ` Petty Cash in hand 50 3
Rent 1,200
Salaries 6,000
Advertisement 800 8,000
To General Profit & Loss A/c 46,350
1,94,550 1,94,550
Note : 1. Remittances received from the branch is calculated as follows :
`
Cash sales (2014-15) 1,20,000
Less : (i) Expenses paid by the branch `
(Cartage ` 200 + Petty expenses ` 300) 500
(ii) Petty Cash in hand 200 700
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
Royalty Accounts ll l 5.7
1,19,300
2. Since amounts are closing balances of 2014-15 hence these become the opening
balances of 2015-16.
3. Petty cash in hand is ascertained as follows`:
Cash sales for 2014-15 1,65,000
Less : (i) Cash received 1,60,500
(ii) Cash in Transit 4,000 1,64,500
Balance of Cash with Branch 500
Add : Opening Petty Cash in hand 200
700
Less : Expenses paid by the branch (cartage ` 250
+ Petty exp. ` 400) 650
Petty cash in hand on 31-03-2016 50
4. Petty expenses paid by branch will not be recorded in the debit of branch account.
(B) Branch receiving goods from head office at cost price and making both cash
and credits sales : If branch is authorised to sale goods cash as well as credit, the following
entries are also included in respect of credit sales in addition to the above entries discussed
earlier :
(i) Opening balance of debtors
(ii) Cash received from debtors
(iii) Closing balance of debtors
For the above items, the following journal entries are made by the H.O. :
(i) Branch A/c Dr.
To Branch Debtors A/c
(For opening balance of debtors)
(ii) Cash A/c Dr.
To Branch A/c
(For cash received from debtors)
(iii) Branch Debtors A/cDr.
To Branch A/c
(For closing balance of debtors)
Posting in Branch Account : The posting of above entries in branch account is as
following :
Branch Account
To opening Balance of Debtors .......... By Cash received from Debtors ...........
By Closing Balance of Debtors ...........
The effect of posting of three items in branch account is that net sale are automatically
credited. In other words, sales returns, discount and allowances allowed, bad debts have
already been deducted from sales. Hence no entry is required to be passed by the head office
in branch account in respect of the following :
(i) Goods sold on credit
(ii) Goods returned by debtors
(iii) Discount allowed to debtors
(iv) Bad debts written off
(v) Allowance allowed to debtors
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
5.8 lll Financial Accounting
It is to be remembered that above given five items must be shown in Branch Debtors A/c.
Missing Item
Under direct method, it is necessary to know three items for recording–opening balance
of debtors, cash received form the debtors and closing balance of debtors. If any item of these
is not given in the question, it is a missing figure. This can be calculated by preparing branch
debtors account. The format of branch debtors account is as follows :
Branch Debtors Account
(`) (`)
To Balance b/d (Opening balance of debtors ByCash received from Debtors
either given or balancing figure) … (either given or balancing figure) …
To Credit Sales … ByDiscount Allowed …
ByAllowance Allowed …
ByBad Debts A/c …
BySales Returns A/c …
ByB/R A/c …
ByBalance c/d (Closing balance of debtors,
either given or balancing figure) …
Goods in Transit
Sometimes goods sent by the head office to the branch, though entered in the books of the
head office but might not have reached the branch before the date of closing of the accounts.
It is known as ‘Goods-in-Transit’. The head office will have to make the following entry :
Goods in Transit A/c Dr.
To Branch A/c
(For goods in transit)
It should be remembered that if goods received from head office ` 15,000 is given instead
goods sent by head office and also given goods-in-transit ` 5,000 in the question, it will be
recorded in the branch account as follows :
Branch Account
` `
To Goods Supplied to Branch A/c By Goods in Transit 5,000
(` 15,000 − ` 5,000) 20,000
Illustration 3. (When closing debtors are missing) :
Modern Ltd. has a branch at Agra. All cash received by the branch is daily remitted to
the Head Office and all expenses are paid by the Head Office. Prepare Branch Account in the
books of Head Office from the following particulars as on 31st March 2016 :
`
Opening Stock 10,000
Opening Debtors 5,000
Goods received by Branch from Head Office 50,000
Cash Sales 42,500
Credit Sales 36,300
Cash received from Debtors 30,000
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
Royalty Accounts lll 5.9
Bad Debts 400
Discount Allowed 720
Goods returned by Customers 800
Cheques sent to Branch for :
Salaries 7,500
Other expenses 3,200
Closing Stock 15,000
Goods in Transit as on 31st March 2016 4,000
Agra Branch Account
` `
To Opening Balances : By Cash A/c (Cash received from
branch) :
Stock 10,000 Cash sales 42,500
Debtors 5,000 Amount received from debtors 30,000 72,500
To Goods Supplied to Branch A/c 54,000 By Closing Balances :
To Bank A/c (expenses) 10,700 Stock 15,000
To General Profit & Loss A/c (Bal. fig.) 21,180 By Goods in Transit 4,000
1,00,880 1,00,880
Note : 1. Goods supplied by head office to branch : `
Goods received by Branch 50,000
Add : Goods in Transit 4,000
54,000
Note : 2.
First of all before solving the question, the student should prepare Branch Debtors A/c, to
find out missing figure, (if any) viz :
(`) (`)
To Balance b/d (Opening Debtors) 5,000 ByCash received from Debtors 30,000
To Credit Sales 36,300 ByBad debts 400
By Discount allowed 720
BySales Return 800
By Balance c/d (closing debtors being the 9,380
balancing figure)
41,300 41,300
3. Only 3 items will be shown in Branch Account in repeat a debtors which are as
follows :
(a) Opening balance of debtors : It will be shown on the debit side of branch account.
(b) Cash received from debtors : It will be shown on the credit side of the branch
account.
(c) Closing balance of debtors : It will be shown on the credit side of the branch account
and remaining items i.e. credit sales, bad debts, discount, sales returns will not be
shown in branch account.
If branch is used Imprest System for Petty Expenses
Under this system, a fixed amount is advanced to the branch for petty expenses at the
beginning of the period. The branch submits its accounts at the end of the period and the head
office after auditing its accounts, gives a new advance equivalent to the amount spent by the
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
5.10 lll Financial Accounting
branch during the period. Thus in the beginning of each period, the branch has a same fixed
balance. suppose a branch gets ` 300 from the H.O. to be spent during the specified period. At
the end of the period, its total expenditure amounts to ` 240. According to the imprest system,
branch will be rembursed by ` 240. So his imprest money will again become ` 300. The
amount, so advanced to branch is termed as ‘imprest’ and therefore it is konwn as imprest
system of petty cash.
Illustration 4.
M/s Janta Prakashan invoice goods to their various branches at cost. All the expenses or
petty expenses are paid by the H.O. Petty expenses are paid by the branches, which are
allowed to maintain petty cash balance of ` 500. on imprest system. From the details
regarding Patna branch, prepare Branch Account to calculate profit :
`
Petty Cash on 1st April 2015 500
Debtors on 31st March 2016 4,000
Goods sent to branch during the year 14,000
Goods returned by branch 1,600
Goods returned by the customers 300
Cash sales 8,600
Credit Sales 12,000
Cash remitted to Head Office 22,600
Allowances to Customers 80
Stock on 1st April 2015 4,000
Bad Debts 3,200
Expenses paid by the H.O. 140
Rent from 1st April 2015 to 30th April 2016 2,600
Insurance to 30th June 2016 3,600
Salaries and Wages 5,600
Expenses paid by the Branch 400
Solution. Patna Branch Account
` ` ` `
To Balance b/d : By Bank A/c
Petty Cash 500 Cash Sales 8,600
Stock 4,000 Cash received from Debtors 14,000 22,600
Debtors1 6,520 By Balance c/d :
To Goods sent to Branch A/c 14,000 Petty Cash 500 3
Less : Goods returned by Stock 32,000
Branch 1,600 12,400 Debtors 4,000
To Bank A/c : Rent prepaid (2,600 × 1 / 13 ) 200
Rent 2,600 Insurance prepaid (3,600 × 3 / 12) 900
Insurance 3,600 By General Profit & Loss A/c (Loss) 4,220
Salaries & wages 5,600 11,800
To Bank A/c (petty expenses) 400 3
35,620 35,620
Note : 1. Calculation of opening debtors is as under :
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
Royalty Accounts ll
l 5.11
Branch Debtors Account
` `
To Balance b/d (1-4-2015) By Cash A/c 14,000 2
(Balancing figure) 6,520 By Bad Debts A/c 140
To Credit Sales 12,000 By Allowances A/c 80
By Sales Returns 300
By Balance c/d (31-3-2016) 4,000
18,520 18,520
2. Cash received from debtors is calculated as follows :
`
Total Cash remitted to H.O. 22,600
Less : Cash sales 8,600
balance of cash received from Debtors 14,000
3. Since imprest system is adopted for petty expenses by the branch, hence expenses
made by the Branch ` 400 will be sent by the head office.
4. Normally, insurance is paid for one year. Thus, it will be assumed that insurance
has been paid from 1st July 2015 to 30th June 2016. Therefore prepaid insurance
will be for three months from 1st April 2016 to 30th June 2016.
(C) When goods are supplied to branch by head office at invoice or selling price :
Sometimes goods are sent to branch by the head office at a price higher than cost price.
For example, if cost of goods is ` 8,000 and goods are invoiced at a profit of 20% on cost, the
perform invoice will show the value of goods at ` 9,600. The following are the advantages of
invoicing goods at invoice price :
(i) It is possible to maintain secrecy about the actual cost and profits, from branches
personnel.
(ii) The branch can be directed to sell the goods at the invoice price only or more.
(iii) control over stock with the branch becomes slightly easier.
When goods are invoiced at invoice price, question will be attempted in the same manner
as discussed under cost price method but opening stock, goods supplied to branch, goods
returned by branch and closing stock are to be shown at invoice price and not at cost price.
While calculating the branch profit or loss, adjustment entries are required to be made in
the branch Account for profit included in the above mentioned items so the branch account
shows true profit or loss. Hence, the following adjustment entries are to be passed for inflated
price, i.e., difference between invoice price and cost price :
1. For inflated price in the value of opening stock :
Stock suspense A/c Dr.
To Branch A/c
2. For inflated price in the value of goods sent to branch :
Goods Supplied to Branch A/c Dr.
To Branch A/c
3. Goods returned by branch is to be deducted from goods sent to branch.
Hence, it is not required any adjustment entry.
4. For inflated price in the value of closing stock :
Branch A/c Dr.
To stock Suspense A/c
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
5.12 lll Financial Accounting
The above entries are made in such condition, when head office keeps its account under
direct method. For calculation of inflated price, the following formula is used :
1. If head office includes profit at cost price,
Rate
Profit = Invoice price ×
100
For example if head office includes profit at 10% on cost, inflated price will be calculated
by applying : invoice price × 10/110.
2. If head office includes profit at invoice price,
Rate
Profit = Invoice Price ×
100
For example, if head office includes profit at 20% on invoice price or selling price, inflated
price will be calculated by applying : invoice price × 20/100.
Illustration 5.
National Advertising Co. has a branch at Jaipur. Goods are invoiced to the branch at cost
plus 25%. branch keeps its own sales Ledger and deposits all cash received daily to the Head
Office Account in a local bank. all branch expenses are to be paid by Head Office. Prepare
Branch Account as on 31st March 2015 from the following :
`
Stock on 1st April 2015 5,000
Stock on 31st March 2016 6,000
Goods Supplied to Branch during the year 66,600
Goods returned by Branch 2,600
Total Sales 95,000
Cash Sales 35,000
Debtors on 1st April 2015 7,000
Debtors 31st March 2016 10,000
Discount to Debtors 1,200
Rent & Taxes 5,500
Sundry Expenses 1,400
Goods in transit as on 31st March 2016 3,000
Furniture purchased by H.O. for the branch 10,000
Write off 10% Depreciation on the Furniture.
Solution. Branch Debtors Account
` `
To Balance b/d : By Cash A/c :
Opening Debtors (1-4-2015) 7,000 Received from Debtors (balancing figure) 55,800
To Credit Sales (` 95,000 − ` 35,000) 60,000 By Discount A/c 1,200
By Balance c/d :
Closing Debtors (31-3-16) 10,000
67,000 67,000
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
Royalty Accounts ll
l 5.1
L
E
S
S
O
N
6
Branch Accounts
Introduction
As a business grows, it may open branches in different towns and cities within country or
outside country in order to market its product over a large territory and, thus, increase its
profits. A branch may be defined as a section of an enterprise, geographically separated from
the rest of the business, controlled by a Head Office and generally carrying on the same
activities as of the enterprise. For example, Bata Shoe Co. has branches in various cities all
over the country. The same example holds good for a commercial bank also.
Meaning of Branch
The term ‘Branch Accounts’ refer to record of transaction of branches, whether relating
to deal with Head Office or with outsiders or deal between different branches in the books of
Head office. In order to exercise greater control over the branches, it is necessary to ascertain
profit or loss made by such branches separately. For this purpose, a proper accounting system
is to be adopted for recording business transactions between Head Office and Branches. The
accounting system to be adopted for the branch depends upon the size and nature of branch
and the degree of control required by the Head Office. Thus, branches can be broadly
classified into two categories for the purpose of recording transactions in the books of
accounts i.e.
Branches
Home Branches Foreign Branches
Dependent Branches Independent Branches
Home Branches
A. Dependent Branches : Dependent branches are those branches which are bot
keeping their own separate set of books of accounts. The relation between head office and
branch is just like agency, therefore, these are also known as agency branches. The following
are the salient features of such a branch :
(i) These branches generally depend upon the head office for supply of goods. However,
the branch may be allowed to make purchases from the local parties.
(ii) All expenses of the branch are directly paid by the head office.
(iii) In order to meet the petty expenses of the branch, e.g., conveyance expenses,
entertainment expenses etc., may be provided with the petty cash from the head
office.
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
5.14 lll Financial Accounting
Remittances made to Head Office :
Cash Sales 2,650
Cash collected from Debtors 21,000
Goods returned by branch at invoice price 400
Balances at the end :
Stock at invoice price 13,000
Debtors at the end 2,000
Petty Cash 25
Solution.
(a) When goods are shown at cost price :
Chennai Branch Account
` ` ` `
To Balance b/d : By Cash A/c :
Stock (` 11,000 − ` 1,833) 9,167 Sales 2,650
Debtors 1,700 Debtors 21,000 23,650
Petty Cash 100 By Balance c/d :
To Goods Supplied to Branch 20,000 Stock (` 13,000 − ` 2,167) 10,833
Less : Goods returned by Branch 400 Debtors 2,000
(` 19,600 − ` 3,267) 16,333 Petty Cash 25
To Bank A/c :
Rent 600
Wages 200
Salary, etc 900 1,700
To General Profit & Loss A/c 7,508
36,508 36,508
(b) When goods are shown at invoice price :
Chennai Branch Account
` ` ` `
To Balance b/d : By Cash A/c :
Stock 11,000 Cash Sales 2,650
Debtors 1,700 Collected from Debtors 21,000 23,650
Petty Cash 100 By Balance c/d :
To Goods Supplied to Branch A/c 20,000 Stock 13,000
Less : Returned by Branch 400 19,600 Debtors 2,000
To Bank A/c : Petty Cash 25
Rent 600 By Stock Suspense A/c
Wages 200 (20/120 of ` 11,000) 1,833
Salary, etc 900 By Goods supplied to Branch A/c
To Stock Suspense A/c (20/120 of ` 19,600) 3,267
(20/120 of ` 13,000) 2,167
To General Profit & Loss A/c 7,508
43,775 43,775
Note : Petty expenses made by branch is not shown in the debit side of branch account because
such expenses have already been deducted from the closing balance of petty cash. Thus
opening balance of petty cash ` 100 and closing balance of petty cash ` 25 will be shown
in the debit and credit side of branch account respectively.
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
Royalty Accounts ll
l 5.15
Illustration 7.
Akash Chapal Strores has an old established branch at Lucknow. Goods are invoiced to
the branch at 20% profit on invoice price, the branch having instructed to send all cash daily
to the head office. All expenses are paid by the head office except expenses which are met by
the branch manager. From the following particulars, you are required to draw up the Branch
Account as it would appear in the books of Akash Chappal Stores, Kanpur :
`
Stock on 1st April 2015 at invoice price 15,000
Sundry Debtors on 1st April 2015 9,000
Cash in hand on 1st April 2015 400
Office Furniture on 1st April 2015 1,200
Goods invoiced from the Head Office (Invoice Price) 80,000
Goods returned to Head Office 1,000
Goods returned by Debtors 480
Cash received from Debtors 30,000
Cash Sales 50,000
Credit Sales 30,000
Discount allowed to Debtors 300
Expenses paid by the Head Office :
`
Rent 1,200
Salary 2,400
Stationery & Printing 300
Petty Expenses paid by the Branch Manager 3,900
Stock on 31st March 2016 at invoice price 280
Depreciation to be provided on office furniture at 10% per annum 14,000
Solution.
While attempting a question, first of all debtors account should be prepared to find out
missing figure. i. e. closing debtors.
Branch Debtors Account
` `
To Balance b/d : Debtors (1-4-15) 9,000 By Cash A/c (received from debtors) 30,000
To Credit Sales 30,000 By Sales returns 480
By Discount A/c 300
By Balance c/d : Debtors (31-3-16)
(balancing figure) 8,220
39,000 39,000
Lucknow Branch Account
` ` ` `
To Balance b/d (1-4-15) By Cash A/c :
Stock 15,000 Sales 50,000
Debtors 9,000 Debtors 30,000 80,000
Petty Cash 400 By Goods Supplied to Branch A/c
Furniture 1,200 (20/100 of ` 79,000) 15,800
To Goods Supplied to Branch A/c 80,000 By Stock Suspense A/c
Less : Goods returned by Branch 1,000 79,000 (20/100 of ` 15,000) 3,000
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
5.16 lll Financial Accounting
To Bank A/c : By Balance c/d (31-3-16)
Rent 1,200 Stock 14,000
Salary 2,400 Debtors 8,220
Stationery & Printing 300 3,900 Petty Cash (` 400 − ` 280) 1201
To Stock Suspense A/c Furniture (` 1,200 − ` 120) 1,080
(20/100 of ` 14,000) 2,800
To General Profit & Loss A/c 10,920
1,22,220 1,22,220
Note :
1. If the payment of petty expenses are made by the branch itself, it is not shown on
the debit side of branch account but it should be deducted from petty cash.
2. If goods are invoiced to the branch at 20% profit on invoice price, inflated price will
be found out by applying 20/100.
Accounting Treatment of Liabilities
As opening balances of assets are shown on the debit side of branch account and closing
balances are shown on the credit side of branch account. On the contrary, opening balances of
liabilities are shown on the credit side of branch account and closing balances of liabilities are
shown on the debit side of branch account.
Illustration 8.
U.P. Industries Ltd. have a head office and many retail branches which are supplied
goods from the head office at 20% profit on sale price. Accounts are kept at head office from
which all expenses (except petty expenses) are paid. Such petty expenses are paid by
branches which are allowed to maintain petty cash balance of ` 1,500 on imprest system.
From the following balances, as shown by the books, prepare branch account :
Balances on 1 April, 2015
Petty cash in hand at branch 1,500 Bad-debts written off 200
Stock in hand at branch 30,000 Purchases by branch on permission of H.O. :
Debtors at branch 5,000 Cash purchase 10,800
Creditors at branch 1,000 Credit purchases 10,000
Furniture at branch 9,000 Cash paid to Creditors 8,500
Prepaid Rent (up June 30, 2015) 420 Payment made by H.O. :
Transaction for the year ended 31st March, 2016 Rent for year (paid on 1-7-2015) 1,800
Goods received by the branch from H.O. 1,24,000 Salaries 2,400
Loss in transit at invoice 1,000 Insurance paid for the year ending 30th
Cash sales at branch 1,00,600 June, 2015 440
Credit sale at branch 40,000 Payment of Petey expenses made by branch 200
Allowances to Debtors 400 Balances of Stock at cost on 31st March,
Cash received from Debtors 38,000 2016 35,000
Write off depreciation on furniture at the rate of 10%.
Solution. Branch Account
` ` ` `
To Balance b/d By Balance b/d :
Petty cash 1,500 Creditors 1,000
Stock 30,000 Stock Reserve (30,000 × 20 / 100 ) 6,000 7,000
Debtors 5,000 By Cash A/c :
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
Royalty Accounts ll l 5.17
Furniture 9,000 Cash sales 1,00,600
Prepaid Rent 420 Cash received for debtors 38,000
To Goods sent to Branch (1,24,000 + 1,000 ) 1,25,000 By Balance c/d
To Cash A/c : Petty Cash (1,500 − 200 + 200 ) 1,500 1,500
Rent 1,800 Stock at invoice price 43,750 43,750
(35,000 + 8, 750 )
Salary 2,400 Debtors1 6,400 6,400
Insurance 440 4,640 Furniture (9,000 − 900 ) 8,100 8,100
To Cash A/c (petty exp.) 200 Prepaid Rent 450 450
To Cash A/c : Prepaid Insurance 110 60,310
Cash purchases 10,800 By Goods sent to branch (1,25,000 × 20 / 100 ) 25,000
Payment to creditors 8,500 19,300
To Balance c/d
Creditors 2 2,500
Stock Reserve (43, 750 × 20 / 100 ) 8,750
To General Profit & Loss A/c 24,600
2,30,910 2,30,910
Notes :
1. Branch Debtors Account
` `
To Balance b/d 5,000 By Allowances 400
To Credit Sales 40,000 By Cash A/c 38,000
By Bad Debts 200
By Balance c/d (balancing figure) 6,400
45,000 45,000
2. Branch Creditors Account
` `
To Cash A/c 8,500 By Balance b/d 1,000
To Balance c/d (balancing figure) 2,500 By Purchases 10,000
11,000 11,000
3. As petty cash is maintained on imprest system, amount spent by branch must have
been re-imbursed by head office.
4. Loss of goods in transit will not be recorded in Branch Account under direct method
but goods sent by the Head Office ` 1,25,000 will be shown in branch account.
Purchase of asset by branch
If any asset is purchased by the branch with the permission of head office, it will be
shown on the credit side of branch account because amount paid for the purchase of asset will
be deducted from remittance to head office.
Purchase of asset by head office
If any asset is purchased by head office. Itself, it is debited to the debit side of branch
account and closing balance of asset is shown on the credit side of branch account.
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
5.18 lll Financial Accounting
Illustration 9.
Raghunath Co. had a branch at Lucknow. Goods are invoiced to the branch at cost plus
25%. Branch is instructed to deposit cash every day in the head office account in the bank. All
expenses are paid by cheque by the head office except petty cash expenses which are paid by
the branch manager. From the following particulars, prepare Branch Account in the books of
Head Office :
`
Stock on 1st April 2015 2,500
Stock on 31st March 2016 3,000
Sundry Debtors on 1st April 2015 1,400
Sundry Debtors on 31st March 2016 1,800
Cash Sales for the year 10,800
Credit Sales for the year 7,000
Cash remitted to the Head Office 15,000
Machinery purchased by the branch 1,200
Goods invoiced from the Head Office 18,200
Expenses paid by the branch 120
Expenses paid by the Head Office 1,640
Head Office sent cash to purchases safe for the branch 1,300
Solution. Lucknow Branch Account
` `
To Balance b/d (1-4-15) By Cash A/c (remitted) 15,000
Stock 2,500 By Balance c/d (31-3-16)
Sundry Debtors 1,400 Stock 3,000
To Goods Supplied to branch 18,200 Sundry Debtors 1,800
To Bank A/c (expenses) 1,640 Machinery* 1,200
To Bank A/c (safe) 1,300 Safe* 1,300
To Stock Suspense A/c (3,000 × 25 / 125) 600 Cash in hand 1,080 2
To General Profit & Loss A/c 1,880 By Stock Suspense A/c (2,500 × 25 / 125) 500
By Goods Supplied to Branch A/c 3,640
27,520 27,520
Note : (1) Cash received from debtors is found out as follows :
Branch Debtors Account
` `
To Balance b/d (1-4-2015) 1,400 By Cash received (balancing figure) 6,600
To Credit Sales 7,000 By Balance c/d (31-3-16) 1,800
8,400 8,400
(2) Cash in hand on 31-3-2016 will be calculated by preparing Cash Account :
Cash Account
` `
To Cash Sales 10,800 By Cash sent to H.O. 15,000
To H.O. A/c By Machinery purchased by branch 1,200
(Cash received to purchase safe) 1,300 By Petty Expenses 120
To Debtors A/c By Safe A/c 1,300
(Cash received from Debtors) 6,6001 By Balance c/d on 31-3-16 (Bal. fig.) 1,080
18,700 18,700
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
Royalty Accounts ll
l 5.19
Note : Machinery purchased by branch and petty expenses paid by branch will not appear in the
debit side of branch account, because cash has been reduced to this extent.
Memorandum Branch Stock Account
Memorandum branch stock Account is prepared to find out the missing figure in respect
of closing stock or spoiled goods lost, if any. The word memorandum is used before this
account because the principles of double entry system are not followed. This account is
debited with those items which increase the stock and credited with those items which
decrease the stock and all items are always shown at invoice price. Format of this account is
as follows :
Memorandum Stock Account
` `
To Balance b/d (opening stock) By Sales (cash & credit)
To Goods Supplied to Branch By Goods Returned by Branch
To Sales Returns By Wastage of goods
To Goods received from other Branch By Loss of goods–Pilferage
By Balance c/d (closing stock)
(balancing figure)
If both the sides of this account are equal, it means no missing figure but if debit side
exceeds credit side, difference will represent the figure of closing stock or spoiled goods. If
closing stock is given in the question, the difference will be treated as the value of spoiled
goods otherwise closing stock.
If branch account is prepared, only closing stock will be shown in branch account and not
spoiled goods because the closing stock itself reduces on account of it. In case insurance
company admits claim in respect of spoiled stock and the amount received by the branch, the
amount will be shown on the credit side of the branch account.
Accounting treatment of spoil goods under indirect method : On one hard, it will be shown
on the credit side of branch stock account or branch trading account and on other hand, it will
be shown on the debit side of profit and loss account.
Illustration 10.
Varanasi Traders has a branch at Lucknow. Goods are invoiced to the branch at Cost
1
+33 % . From the following particulars, prepare Lucknow Branch Account in the books of
3
Head Office.
Table
Furniture has to be depreciated 20%. No depreciation is to be charged for new furniture
bought during the period.
Table
Illustration 11.
Snow White Ltd. has one branch at Kanpur and other at Agra. Prepare Agra. Prepare
Agra Branch Account from the following particulars related to Agra Branch :
Table
Goods are supplied to branch at cost plus 20%. All expenses of the branch are met by
Head Office and branch sends all cash received to Head Office. Also prepare a Branch Trading
and Profit and Loss Account.
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
5.20 lll Financial Accounting
Solution :
Before preparing branch account first of all branch debtors account and memorandum
branch stock account are to be prepared to find out closing debtors and closing stock.
Table
Final Accounts Method
Under this method (i) Branch Trading and Profit and Loss Account, and (ii) Branch
Account are prepared. Branch Trading and Profit and Loss Account is prepared as but more
items will be shown which are clear from the following performa :
Table
• If these items are given at invoice price, they are to be shown at cost price. In
other words, inflated price will be deducted from invoice price and
remaining amount is to be shown in Trading Account.
Illustration 12.
Mr. ‘A’ of Mumbai has a branch at Delhi. Goods are invoiced to the Branch at cost plus
20%. The expenses of the Branch are paid from Mumbai and the branch keeps a Sales Journal
and the debtors ledger only. From the information supplied by the Branch, prepare Trading
and Profit & Loss Account of the Branch for the year ending 31st March, 2016 and show the
account of the Branch as it would appear in the books of the Head Office :
Table
Note : (1) Calculation of Opening Debtors
Table
(2) Net profit shown by profit and loss account and by branch account will always be
same.
Illustration 13.
Amar Nath Bros., Chennai has a branch at Kolkata. All goods required for sale at
Kolkata are supplied from Chennai at cost plus 25% and all cash received at branch is banked
daily in head office account opened in a Bank at Kolkata. From the following particulars, give
the Branch Account, Branch Debtor’s Account, Branch Trading & Profit and Loss Account :
Note :
1. Cash received from debtors is ascertained by preparing Debtors Account.
2. Only good debtors are recorded in Branch Account.
3. Reserve for Doubtful Debts has no relation with the Debtors Account. Hence not
taken in Branch Debtors Account.
Table
Stock and Debtors system
When the head office is interested in maintaining a better stock control at the branch,
stock and debtors method is used. Under this method, the head office maintains a number of
accounts for keeping a record of branch transactions in place of one Branch Account. A brief
description of each of these accounts is given below :
1. Branch stock account : This account is maintained at the invoice price. Therefore all
figures relating to opening stock, goods sent to branch, goods returned by customers to branch
are shown on its debit side and all figures relating to cash sales, credit sales, value of spoiled
goods, goods returned to head office and closing stock are shown on its credit side.
Both the sides of the branch account should be equal but, if unequal, it tells about
shortage or surplus of stock or closing stock at the branch. If the debit side is bigger, there is a
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
Royalty Accounts ll
l 5.21
shortage and if the credit side is bigger, there is surplus. The amount of surplus or shortage is
transferred to branch profit and loss account.
It is to be remembered that branch stock account is prepared at invoice price.
2. Branch adjustment account : This account is prepared with a view to ascertain the
gross profit of the branch. all loadings (or inflated price) in the goods are recorded in this
account. Therefore it is credited with the stock reserve on opening stock, loading on goods sent
to branch and it is debited with the loading on shortage in stock, spoilage, pilferage, theft, loss
by fire, loss-in-transit and stock reserve on closing stock. At the end, balance of this account is
transferred to branch profit and loss account. The following adjustment entries is made by the
difference between invoice price and cost price :
Table
The balance of this account will show profit or loss.
3. Branch Expenses Account : Branch expenses account records all branch expenses
in cash. In addition, this account is also debited with the items like bad debts. Discount
allowed, depreciation. Finally, the balance in this account is transferred to branch adjustment
account and, thereby closed :
table
4. Preparation of Branch Account : On the basis of above mentioned accounts, if
branch account has to be prepared, profit or loss shown by this account will be same as shown
by branch profit and loss account.
Illustration 14.
Unity Ltd. Mumbai invoice goods to their Branch at Lucknow at 50% above cost and pays
all branch expenses except petty expenses which are met by the Branch. From the following
particulars prepare all the Branch Accounts on Stock and Debtors system in the Head Office
books :
Table
Illustration 15.
A Company has its branch at Lucknow. All expenses are paid by Head Office and Goods
1
are invoiced to the branch at cost plus 33 %. From the following particulars for the year
3
ended 31st March 2016 ascertain the profit by stock and debtors system :
Table
Credit Side of Branch Stock Account exceeds Debit side
It branch sells goods more than invoice price, in such case credit side of branch stock
account (which is mentioned at invoice price) will be bigger. The difference being gross profit
will be transferred to profit & loss account.
Illustration 16.
Delhi Traders Ltd. sends goods to its Fazabad branch at cost plus 25%. From the
following particulars, you are required to show the Branch Stock Account, Branch
Adjustment Account and Branch Expenses Account in the Head Office books :
Table
Illustration 17.
Kumar Textiles Ltd. with its Head Office at Delhi, invoice goods to its branch at
Amritsar, at 20% less than the list price which is cost plus 100% with instructions that cash
sales were to be made at invoice price and credit sales as catalogue price (i.e. list price).
table
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
5.22 lll Financial Accounting
From the above particulars available from the branch prepare Branch Stock Account,
Branch Adjustment Account, Branch Expenses Account and Branch Debtors Account for the
year ending 31st March 2016.
Table
Note : Excess of list price over invoice price has been shown. This is done to prepare Stock
Account at invoice price so that shortage or surplus may be correctly calculated.
Wholesale Branch system
Meaning
sometimes, head office opens its own retail branches and sells goods through them in
addition to selling goods through wholesalers. The head office invoices the goods to the
wholesalers at wholesale price while branches sell goods to the consumer at retail price. Since
retail price is more than the whole sale price, hence more profit is earned on sales through its
own branch but the entire profit can not be treated as branch’s profit. However, the branch’s
profit will be equal to the difference between wholesale price and retail price and remaining
profit, i. e., wholesale price-cost price will be treated as earned by head office. For example, if
the cost price of an article is ` 100, its wholesale price is ` 120 and consumer price ` 125. In
such case, the branch profit is ` 25 (` 125 – ` 100). However the head office earns only ` 5 (`
125 – ` 120) by opening the branch because the profit of ` 20 can be earned by it directly
selling to the wholesalers.
Accounting treatment
The head office invoices the goods to the branch at wholesale price and not at cost price.
In other words, the wholesale price is the cost price to the branch. A problem arises in such
case, if a portion of the goods supplied to the branch, remains unsold at the end of accounting
year while the profit on these goods is included in the gross profit shown by head office
trading account. This profit is known as unrealized profit and this profit is transferred to
stock reserve account for calculating correct profit. The following entry is made in the books of
H.O.
Tabel
Above entry is reversed in next year because these goods will be sold out in the next year
and profit will be realized.
Illustration 18.
Sulabh Ltd. has a retail branch at Kanpur. Goods are sold to customers at cost plus
100%. The wholesale price is cost plus 80%. Goods are invoiced to Kanpur Branch at
wholesale price. From the following particulars, find out the profit made at Head Office and
Branch for the year 2015-16.
Table
Sales at Head Office are made only on wholesale basis and that at Branch only to
consumers. Stock at Branch is valued at wholesale price.
Solution.
Cost price, say = ` 100; Consumer price = ` 200; Wholesale price = ` 180.
Table
Note : 1. Calculation of unrealised profit :
If wholesale price is ` 180 then actual profit = 80
80
If wholesale price is ` 1 then actual profit =
180
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
Royalty Accounts ll
l 5.23
80
If wholesale price of branch stock is ` 9,000 then actual profit = × 9, 000
180
= ` 4,000
2. It is to be remembered that the wholesale price is the cost price to the branch while
branch sells goods at retail price i.e. more than wholesale price.
Illustration 19.
A head office fixes selling price for its goods at 200% of the cost. Goods are sent to the
branch at 25% less than the selling price and to other dealers at 20% less than the selling
price. Calculate the profit at the head office and at the branch separately from the following
information :
Table
Solution.
Cost price, Say = 100
Selling price = 200
Branch price = 150
Dealer’s price = 160
Table
Note : 1. Calculation of Gross Profit :
Branch :
(i) Gross Profit on goods sold by branch : 92,000 × 50 / 200 = ` 23,000.
(ii) Unrealised profit against opening branch stock = 7,200 × 50 / 150 = ` 2,400.
(iii) Unrealised profit against closing branch stock = 5,700 × 50 / 150 = ` 1,900.
Independent Branches Or Branches Keeping complete Books
Meaning
A branch is said to be independent when it maintains a separate set of books of accounts
and keeps a full system of accounting. In other words, the branch carries on business as an
independent unit, records all the transactions in its own books, extracts its own Trial Balance
and prepares its own Trading and Profit and Loss Account. A copy of the Trial Balance so
prepared will be forwarded to the head office and the head office will incorporate the same in
its books of accounts so that a consolidated Profit and Loss Account and a Balance Sheet can
be prepared for the business as a whole. Independent branches generally do not depend upon
the head office for supplies of goods and for meeting the expenses and they are not required to
remit their collections to the head office daily as in the case of dependent branches. However,
periodical transfer of goods and remittance of money may take place between the head office
and the branch.
Incorporation Entries in the Books of Head Office
The head office maintains a Branch Account in its books to which the goods sent to
branch is debited and cash received from branch is credited. It is like any other personal
account and the balance will show the amount due from/due to branch. At the end of
accounting year, the branch prepares its own Trial Balance and sends a copy of its Trial
Balance to the head office for its incorporation in the head office books. The head office will
incorporate the same in its books of accounts so that a consolidated Trial balance can be
prepared from which the final accounts of whole the business can be prepared easily. Entries
make in the books of head office with the help of Branch Trial Balance is known as
incorporation of branch trial balance and these entries are called ‘Incorporation Entries’. The
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
5.24 lll Financial Accounting
following are the three methods for incorporation of branch trial balance either of which may
be adopted :
(i) First method : Under this method, all items relating to Trading and Profit and loss
Account are incorporated in the head office books besides incorporation of branch assets and
liabilities. for this purpose, the final accounts are prepared in the usual way n the books of the
head office and then the following incorporation entries are passed in the books of head Office.
(a) Incorporation Entries from Branch Trading Account
1. For incorporation items debitable to Branch Trading Account
(except gross profit) :
table
2. For incorporating items creditable to Branch Trading Account
(except gross loss) :
Table
3. For Branch’s Gross Profit :
Table
4. For Branch’s Gross Loss :
Table
(b) Incorporation Entries from Branch Profit & Loss A/c
5. For incorporating items debitable to Branch Profit and Loss Account
(except net profit) :
Table
6. For incorporating items creditable to Branch Profit and Loss Account
(except net loss) :
Table
7. For branch’s net profit :
Table
8. For branch’s net loss :
Table
(c) Incorporation entries from Balance Sheet
9. For incorporation of branch assets :
Table
10. For incorporation of branch liabilities :
table
Note : Before making incorporation entries, branchs trading and profit & loss account and
balance sheet should be prepared from which incorporation entries can be passed easily.
(ii) Second method : Under this method, only one item i.e. net profit or net loss is
incorporated in place of all items of branch trading and profit and loss account in the books of
H.O. whereas incorporation of balance sheet is done in same manner as done in first method.
However, this method is suitable when final accounts are prepared by the branch itself and a
copy of final accounts instead of trial balance is sent to head office. The following
incorporation entries are passed in the books of H.O. :
1. For incorporating branch net profit :
Table
2. For incorporating branch’s net loss :
Table
3. For incorporating branch’s assets :
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
Royalty Accounts ll
l 5.25
Table
4. For incorporating branch’s liabilities :
Table
(iii) Third method : Under this method, on one hand, all debit balances of branch trial
balance and on other hand, all credit balances of trial balance are incorporated and for this
the incorporation entries are passed in the books of H.O. :
Table
Note : Balance of head office account is also mentioned in branch trial balance under above
mentioned three methods but incorporation entries will not be made of this balance
because this balance has already been shown as balance of branch account by H.O.
After posting of the above incorporation entries in branch account, shown in the books of
H.O., branch account will be automatically closed. In other words, both sides of branch
account must be equal.
Table
Stock on 31st March 2016 was ` 2,300. Find out the Surat Branch Profit and draft
journal entries necessary to incorporate the Surat Branch assets and liabilities in the
Mumbai Head Office books. Prepare also the Surat Branch Account in the Mumbai office
ledger. (Agra, Rohilkhand)
Solution.
Table
In Transit Items
When both branch and head office trial balance are given in the question, the balance
shown by the head office account in the branch trial balance and the balance as shown by the
branch account in the head office trial balance normally tally. However, it may not be so, then
the following accounts of branch trial balance must be reconciled with the accounts of head
office trial balance :
Table
1. Goods-in-transit : When the head office may have sent goods to the branches, these
goods may have not been received by the end of the accounting year by the branch. It is called
as goods-in-transit. Thus, goods-in-transit is an asset to the head office.
2. Cash-in-Transit : When the branch may have sent cash to the head office, the
amount may have not been received by the head office by the end of te accounting period. If is
called as cash-in-transit. Thus, cash-in-transit is an asset to the branch.
Adjustment entries are required for reconciliation of the difference on account of above
facts. These entries may either be passed by the head office or the branch but not in both of
them, as follows :
Table
At the end Stock in hand was valued at ` 2,700. The Branch Account in the Head Office
books on 31st March, 1999 stood at `460 (Debit balance). On 28th March, 2016 the Head
Office forwarded goods to the value of ` 2,500 to the Branch where they were received on 3rd
April 2016. similarly a cash remittance of ` 1,200 by Branch on 20th march, 2016 was
received by the Head Office on 1st April 2016.
You are required to submit the Journal entries necessary to incorporate the above figures
and also showing the result of trading at Branch separately in the Head Office Books and to
give the Kolkata Branch Account appearing finally in the Mumbai Head Office Books.
Table
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
5.26 lll Financial Accounting
Illustration 22.
The following are the trial balances of New Delhi Head Office and its Bareilly Branch for
the year ending 31st March 2016.
Table
Fixed assets are to be depreciated at 10%. Stock on 31st March 2016 ` 7,500 and H.O. `
1,500. The difference in Current Accounts is due to goods in transit and cash in transit.
Prepare Branch Final Accounts and incorporate them in the books of Head Office. Also
prepare other accounts and show the consolidated Balance Sheet.
Table
Note : Goods-in-Transit and Cash-in-Transit are calculated as follows :
Table
Special Transactions and Their Entries
As transactions took place between H.O. and Branch during the whole year. Entries of
some important transactions in the books of both are given below :
Table
Inter-Branch Transactions
In case of inter-branch transactions, H.O. is debited or credited in place of each other
branch assuming all the pertainting entries are to be made through H.O. account. If
transactions are took place between branches themselves which are controled by the same
H.O., these transactions are called as inter-branch transactions. These transactions are
recorded as follows :
Table
Special Entries
Illustration 23.
Show what entries would be passed by Head Office and Rangoon Branch to record the
following transactions in their books on 31st March 2016.
(a) Goods amounting to ` 500 transferred from Calcutta branch to Rangoon Branch
under instructions from H.O.
(b) Depreciation of Rangoon Branch Fixed Assets ` 1,000, when such accounts are
opened in the Head Office books.
(c) A remittance of ` 3,000 made by the Rangoon branch to head Office on 26th March
2016 and received by the Head Office on 4th April 2016.
(d) Goods amounting to ` 5,000 sent by Head Office to Rangoon Branch on 20th march
2016 and received by the latter on 15th April 2016.
table
Illustration 24.
Soni Traders Ltd. have their head office at Calcutta and Branches ‘A’ and ‘B’ each
branches keeping a complete set of books for recording daily transactions. All fixed assets
accounts are, however, maintained only in the Head Office books. The branches do not keep
Current Accounts with each other, the entries for any direct transactions between them being
recorded as if affecting the Current Accounts between Head Office and each Branch
concerned. Journalise the following transactions in the books of Head Office as well as in the
books of Branch ‘A’ :
(i) The purchase of a writing desk for ` 500 by Branch ‘A’ paid for by cheque by the
Branch.
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
Royalty Accounts ll
l 5.27
(ii) The transfer at cost of stocks from Head Office to Branch ‘A’; the cost of the goods
being ` 25,000
(iii) The transfer from Branch ‘A’ to Branch ‘B’ of the account of a customer Mr. X
amounting to ` 1,400 on Mr. X shifting his business from ‘A’ to ‘B’.
(iv) ` 10,000 remitted by branch ‘A’ to the Head Office by bank transfer as instructed by
the Head Office.
(v) Branch ‘A’ is charged with ` 2,000 for administrative expenses rendered by H.O.
during the year, as per agreement.
Table
Note : 1. The account relating to the fixed asset is generally maintained by head office. If an asset
is purchased by the branch, an asset account is transferred to the head office books.
Illustration 25. (Special Entries)
A kolkata firm whose accounting year ends on 31st March 2016 has two branches, one at
Agra and other at Varanasi. The branches kept a complete set of books. On 31st march 2016
the Agra and varanasi Branch Accounts in the Kolkata books showed debit balance of `
30,450 and ` 45,000 respectively before taking the following information into account :
1. Goods valued ` 2,000 were transferred from Agra branch to Varanasi branch under
instruction from Head Office.
2. The Agra branch collected ` 2,500 from an Agra customer of the Head Office.
3. The Varanasi Branch paid ` 5,000 for certain goods purchased by the Head Office in
Varanasi.
4. ` 5,000 remitted by the Agra Branch to Calcutta on 29th March 2016 were received
on 3rd April 2016. But the advice of remittance is received on 31st March 2016.
5. The Varanasi Branch received on behalf of the head Office ` 1,500 dividend from
Varanasi Company.
6. For the year 1998, the Agra Branch showed a net loss of ` 1,250 and the Varanasi
Branch a net profit of ` 5,400.
Pass journal entries to record above matters in the Head Office books and then write up
the two Branch Accounts therein.
Table
Note : Entry no. 4 should not be recorded in the books but the advice of remittance received on
March 31, 2016, due that reasen his entry has been recorded.
Table
Foreign Branch
a foreign branch is nothing but an independent branch and located outside country. It
maintains its accounts in a foreign currency because all transactions are made in the currency
of that country. Trial balance is prepared form the foreign branch books and send to the head
office for incorporating in its books. The head office has to convert the trial balance received
into currency of its own currency before incorporating the trial balance in its books of
accounts, because of the facts that the foreign branch trail balance will be in the currencies of
the country in which the branch is operating. After that branch trial balance is incorporated
as usual in the books of the head office to prepare the final accounts.
Conversion of Foreign Branch Trail Balance
The method of conversion depends on whether the exchange rate involved is fixed or
fluctuating, which are discussed as follows :
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
5.28 lll Financial Accounting
1. Fixed rate of exchange : Where the rate of exchange the countries of the head office
and that the branch is fairly constant, a fixed rate may be adopted for conversion of branch
balances. In such a case, all the balances in the branch books are converted at the fixed rate
with the exception of :
(a) Remittance by branch which are converted at the actual rates at which they are
affected; and
(b) The Head Office Account, which is converted at the rupee (or head office currency)
equivalent appearing in the Branch Account in the head office books.
2. Fluctuating rate of exchange : When there is a violent fluctuation in the rate of
exchange, the head office and branch will adopt a standard rate for conversion and all items
in the Trial Balance will be converted at the standard rate which can be one of following three
types :
(a) Opening Rate
(b) Closing Rate
(c) Average Rate
The above rules for conversion in the circumstances may be laid down as follows :
1. Fixed assets : At the rate prevailing when purchased, or at the actual cost of
remittance sent and used for the acquisition. It is known as opening rate. When, however,
capital expenditure is spread over a period, the average rate for that period may be adopted.
These assets are : building, land, machinery, furniture etc.
2. Fixed liabilities : At the rate when incurred, but if there has been a permanent fall
in exchange which will necessitate a large amount of rupee being required when the liabilities
come to be redeemed a reserve should be built up gradually in the head office books to meet
such increased liabilities. These are converted at rate applicable when incurred. Normally
these liabilities are created in the beginning. Thus, it should be converted into opening rate.
For examples, debentures or long term liabilities etc.
3. Current (floating) assets and current liabilities : These are converted at the rete
prevailing on the date of balance sheet. Since balance sheet is prepared at the end of
accounting year, hence these assets and liabilities should be converted at the closing rate.
Current assets includes cash, debtors, B/R investment, closing stock etc. and current
liabilities includes creditors, bills payable, bank overdraft, etc.
4. Opening and closing stock : Which should be converted at the opening and closing
rates respectively.
5. Depreciation : Which should be converted at the rate of conversion of the relevant
assets.
6. Provision for bad and doubtful debts : Which should be converted at the same rate
as that applicable to debtors, i.e., closing rate.
7. revenue items : At the average rate for the period over which they have accrued
except int eh case of opening and closing stocks, depreciation and reserve for bad debts.
Examples of revenue items are : salary, rent, interest, purchases, sales, etc.
8. Remittances by branch : Remittances to and from head office should be converted at
actual proceeds. Therefor no calculation is required for conversion.
9. Head office account : The Head Office account should be converted at the figure
standing in the branch account in the head office books. therefore, no calculation is required
for conversion.
Table
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
Royalty Accounts ll
l 5.29
Difference in Exchange Account : After conversion of foreign branch trial balance,
both sides of converted trail balance may not tally, hence the difference will arise solely by
reason of variation in exchange rates adopted for converting various balances. The difference
is called as difference in exchange or exchange suspense. For recalculation of converted trial
balance, the difference is transferred to difference in exchange account or exchange suspense
account, Normally, this account is shown in balance sheet. On the assets side, if it shows debit
balance or on the liabilities side if it shows a credit balance.
Note : Thus, first of all, the head office has to convert the branch trial balance into currency of its
own country before incorporation work and after that branch final accounts are prepared.
Illustration 26.
On 31st March 2016 the following balances appeared in the books of Delhi Branch of an
English firm having its Head Office in London.
Table
Stock on 31st March 2016 was ` 32,500. Branch Account in the London Books showed a
debit balance of £ 2,680 on 31st March 2016 and furniture appeared in the Head Office books
at £ 350.
The rate of exchange on 31-3-2015 was ` 14 and on 31-3-2016 ` 13. The average rate for
the year 2015-16 was ` 12.
Prepare in the H.O. books the Profit and Loss Account and the Balance Sheet of the
Branch.
Table
Illustration 27.
M/s Hinderson & Co. London has a branch in Calcutta. The following was the Head
Office trial balance as on 31 March, 2016.
Table
The assets and liabilities of the Calcutta Branch on 31st March, 2016 were as follows :
Table
The authorised share capital of the company is £ 1,50,000 in £ 1 share. On 31st March,
2016 there was cash in transit from Calcutta to London amounting to ` 24,000.
Prepare the combined Balance Sheet of company as on 31st March, 2016 taking the
rupee at 0.075 £.
Table
Note : 1. Adjustment of cash-in-transit will be made by branch, therefore, this will be the capital of
branch and H.O. A/c balance will increase by ` 5,37,520 to ` 5,61,520. In the books of
H.O. ` 5,61,520 has been changed in £ 41,520.
Table
2. The Aligarh Wax Ltd. invoices goods to its various branches at cost and the branches
sell on credit as well as for cash. From the following details relating to Meerut
Branch, show the Branch Debtors’ Account and Branch Account in the Head Office
books :
table
Objective Type Questions
(a) Select best alternate :
1. Branch account under debtors system is :
(a) Real Accounts (b) Personal Account
(c) Nominal Accounts (d) All these
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
5.30 lll Financial Accounting
2. Total Sales ` 3,00,000, Cash Sales ` 2,00,000, Cash received from debtors `
12,000, Bad Debts ` 3,000, Sales Return ` 20,000. Debtors will be :
(a) ` 1,00,000 (b) ` 80,000
(c) ` 65,000 (d) ` 85,000
3. The Head Office sent ` 10,000 to its branch for the purchase of furniture. The
Branch purchased the furniture. How these items are to be dealt with in the
Branch Account ?
(a) Debit side (b) Credit side
(c) Not in any side (d) In debit and credit sides
4. Branch Adjustment Account is in the nature of :
(a) Real A/c (b) Nominal A/c
(c) Personal A/c
5. By what rate the balance of head office account is converted in foreign
branch :
(a) Opening Rate (b) Closing Rate
(c) Average Rate (d) None of these
6. In case of foreign branch, the amount of creditors is convered :
(a) at closing rate (b) at average rate
(c) at opening rate (d) None of the above
7. Branch Adjustment Account is prepared :
(a) By Dependent Branch (b) By head office of dependent branch
(c) By head office of independent branch
8. Goods have been transferred from Agra Branch to Bareilly Branch under
instructions from Head Office. What shall be the entry for this transaction
in the books of head office :
(a) Dr. Bareilly Branch; Cr. goods Sent to Branch A/c
(b) Dr. Goods received from Agra branch; Cr. Agra Branch A/c
(c) Dr. Bareilly Branch A/c; Cr. Agra Branch A/c
(d) None of these
9. Agra branch collected some amount from a customer of H.O. at Agra. What
shall be the entry for this transaction in the books of Agra Branch ?
(a) Dr. Cash A/c; Cr. customer’s A/c (b) Dr. Cash A/c; Cr. H.O. A/c
(c) Dr. H.O. A/c; Cr. Customers A/c (d) Dr. Customer’s A/c; Cr. H.O. A/c
10. Agra Branch sent ` 1,000 to H.O. on 29-12-2000 which was received by H.O.
on 3-1-2001 but the intimation received on 31-12-2000. What shall be the
entry in the books of H.O. on 31st December) :
(a) Dr. Cash A/c; Cr. Agra Branch A/c
(b) Dr. Agra Branch A/c; Cr. Cash A/c
(c) Dr. Cash in Transit A/c; Cr. Agra Branch
(d) None of these
11. When branch ‘A’ sends goods to branch ‘B’, in the books of branch ‘A’ debit is
given to :
(a) Head office account (b) Branch ‘B’ account
(c) Sales return account (d) Purchase return account
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
Royalty Accounts ll
l 5.31
12. The cash and credit sales of a branch are ` 5,000 and ` 10,000 respectively.
The amount collected from debtors is ` 10,000. Under debtors system the
amount credited to branch account will be :
(a) ` 20,000 (b) ` 15,000 (c) ` 25,000 (d) ` 10,000
13. Goods are sent to the branch at 20% margin on selling price, when branch
stock discloses a surplus of ` 2,000 the amount to be credited to branch
adjustment account will be :
(a) ` 2,000 (b) `400 (c) `333 (d) 1,600
14. Goods sent by the head office to the branch but not received by the branch
before the close of financial year are credited by head office to :
(a) Branch Account (b) Trading account
(c) Goods sent to branch account (d) Goods in transit account
15. Depreciation on branch assets under debtors system is :
(a) Not shown separately in branch account
(b) Shown in branch account
(c) Not accounted
(d) Shown in the profit and loss account of H.O.
16. Stock reserve in relation to closing stock appears :
(a) On the debit side of branch account
(b) On the credit side of branch account
(c) On the debit side of profit and loss account
(d) On the credit side of the profit and loss account
17. In foreign branch fixed assets shall be converted at :
(a) Opening rate
(b) Average rate
(c) Rate at the date of purchase
(d) Closing rate or that shows likely realisation
18. Provision for bad debts of a foreign branch is converted at :
(a) Opening rate of exchange (b) Closing rate of exchange
(c) Average rate of exchange (d) Rate applicable to debtors
Ans. : 1. (c) 2. (c) 3. (a) 4. (b) 5. (d) 6. (a) 7. (b) 8. (c) 9. (b) 10. (c) 11. (a) 12. (b) 13.
(b) 14. (a) 15. (a) 16. (a) 17. (d) 18. (d).
(b) Fill in the Blanks :
1. Head office sent goods to branch for ` 2,40,000. These goods were sent at cost
plus 20%. The amount of adjustment will be .................... .
2. Under stock and debtors system branch profit is ascertain by opening
.................... account.
3. Under debtors system branch account is a .................... account.
4. When an assets account of the branch is maintained in the head office, the
entry for depreciation is made by debiting branch account and crediting
.................... account.
5. The balance in the ‘goods sent to branch’ account is transferred to the credit
of .................... account.
6. When goods are sent by X branch to Y branch, y branch debits ....................
and credits .................... .
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
5.32 lll Financial Accounting
7.
In case of foreign branch, difference in convert trial balance is transferred to
.................... .
8. The exchange rate that exists at the balance sheet date is known as
.................... .
9. While converting the trial balance of a foreign branch, opening stock is
converted at the .................... rate.
10. Under branch account method, items related to debtors are written in
.................... .
11. Under branch account method, items related to debtors are written in
.................... .
1
12. If profit on goods supplied to Branch is 33 % of cost. It will be .................... %
3
of sales.
13. Bad debts and discount allowed to debtors are .................... shown in the
branch A/c.
Ans. 1. ` 40,000, 2. Branch adjustment 3. Nominal 4. Branch assets 5. Trading
6. goods from H.O. A/c.; Head office A/c 7. Exchange Suspense A/c 8. Closing rate 9. Opening
10. Branch Stock 11. Branch Account 12. 25 13. Not.
(c) Write True or False :
1. Under debtors system branch account is a real account.
2. Under debtors system branch account is debited with losses like bad debts,
discount allowed and depreciation.
3. When the branch manager is allowed petty cash on imprest system, the
amount remitted by H.O. to reimburse the actual expenses will be debited to
the branch account.
4. Under the stock and debtors system, branch stock account is a real account.
5. Branch stock account is always prepared at cost price.
6. Under stock and debtors system, branch adjustment account discloses the
profit.
7. In the case of independent branch, the head office account in the books of the
branch is analogous to capital account.
8. The items goods-in-transit and remittances-in-transit normally figure in
the balance sheet of branch and head office respectively.
9. In the case branch assets account are maintained in H.O. books,
depreication is to be debited to the profit and loss account of head office.
10. The balances shown by head office account and the branch account are
always equal although the nature of balance differs.
11. if the goods sent by the head office to the branch is destroyed in transit, the
relevant amount is shown in the debit side of the branch A/c.
12. Cash and credit sales are shown in credit side of Branch Account.
13. discount allowed to debtors is shown in the credit side of Branch Account.
Ans. 1. False, 2. False, 3. True, 4. False, 5. False, 6. True, 7. True, 8. False, 9.
False, 10. False, 11. True, 12. False, 13. False.
Short Answer Type Questions
(a) Theoretical Questions
1. What do you understand by branch accounts?
2. Give any three objectives of branch accounting.
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
Royalty Accounts ll
l 5.33
3. Give salient features of branch account method.
4. Discuss the relationship between Head Office and Branch.
5. Give the methods of calculating profit or loss of branch.
6. What are features of dependent branch.
7. Which account is prepared by the Head Office to calculate the profit of
branch under debtor system?
8. Discuss the ‘stock and debtors system’ of branch accounts.
9. Give parformate of Branch Stock Account and Branch Adjustment Account.
(Kanpur)
10. What are the features of independent branch?
11. What is the difference between a dependent branch and an independent
Branch from accounting point of view? (Avadh)
12. What is meant by goods in transit?
13. Give an example of cash-in-transit.
14. What journal entries are made in the books of Head office to incorporate
assets and liabilities f an independent branch? (Gorakhpur)
15. Define inter-branch transactions. How are they recorded in books of
accounts?
16. Give inter-branch transactions.
17. In which account the stock reserve in case of inter-branch transactions is
shown?
18. What is foreign branch?
19. Describe the rules conversion of foreign branch amount into home currency.
(Meerut; Gorakhpur 2001; Agra)
20. Do not write in not more than 60 words the rules of converting trial balance
of foreign branch in the books of head office in home currency.
21. Which items are converted on the basis of opening exchange rate and closing
exchange rate?
Long Answer Type Questions
(a) Theoretical Questions
1. What are different types of branches? What is the difference in accounting
method of various branches? (Meerut)
2. Why are the accounts of branches maintained? What are rules regarding
accounting treatment of it.
3. What is meant by dependent branch? In this regard what journal entries are
passed in the books of Head Office?
4. What journal entries are made in the books of Head office to incorporate the
trial balance of an independent branch?
(Rohikhand, Agra, Kanpur, Gorakhpur, Avadh, Garhwal)
5. How are the accounts of an independent branch situated in the same
country incorporated in head office? Give necessary journal entries for the
same.
6. What is foreign branch? What are the important rules for converting the
figures of a foreign branch trial balance into home currency? (Kanpur)
7. Prepare trail balance of a foreign branch situated at Washington by using
imaginary figures and convert it is the currency of head office situated at
Delhi.
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
5.34 lll Financial Accounting
Making Cash Sales Only
(b) Practical Questions
1. X Ltd. has a branch at Chandausi. Branch remits all cash received daily to the Head
Office and all expenses of the branch are paid by the Head Office directly. From the
following particulars as on 31st March, 2016 prepare Journal entries and a Branch
Account in the books of the Head Office :
Table
2. Yadav Sales Ltd. had a branch at Mathura. From the following particulars, prepare
Mathura Branch Account for the years ending 31st March, 2015 and 2016)
Table
Charge 10% p.a. depreciation on furniture by diminisuing balance method.
Ans. Branch’s Profit for the year 2015 ` 3,350 and for the year 2016 ` 24,390.
Hints : (1) Cash received from branch in 2015 ` 77,400 (500 + 78,000 - 850 - 250)
(2) Petty cash on 31-3-2016 ` 400 (250 + 1,15,000 - 2,500 - 350)
3. From the following particulars relating to Gazhiabad branch for the year ending
31st March, 2016, prepare Branch Account in the books of Head office :
Table
Provide depreciation on furniture at 10% p.a.
Ans. Branch Profit ` 77,950, Closing Debtors 4,900,
Hint : Cash received from Debtors ` 37,000 (35,000 + 2,000)
Making Both Cash and Credit Sales by Branch
4. The Aligarh Wax Ltd. invoices goods to its various branches at cost and the branches
sell on credit as well as for cash. From the following details relating to Meerut
Branch, show the Branch Debtors Account and Branch Account in the Head Office
books :
Table
Ans. Balance of Debtors as on 31-3-2016 ` 33,100; Branch Profit ` 29,300.
Hint : Goods sent to branch will be ` 50,800 plus ` 2,000 in transit = 52,800.
Goods in Transit will be shown in the Cr. side of Branch A/c as well.
5. Ram Kumar Furniture House with its head Office at Delhi has a Branch at
Ghaziabad. You are given the following particulars relating to Ghaziabad Branch
for the year ended 31st March, 2016 :
Table
Prepare Ghaziabad Branch Account in the books of Head Office). (Meerut)
Ans. Closing debtors 36,600 Branch profit ` 32,560.
6. M/s Jawahar Bros. invoice goods to their various branches at cost. From the
following details regarding South Branch, prepare Branch Account to calculate
profit :
Table
Ans. Opening Debtors ` 65,200, Branch Loss ` 38,200.
Hint : (i) Prepaid rent for one month ` 2,000, (ii) Prepaid insurance for three
month ` 9,000.
When Goods are Supplied to Branch by Ho. At Invoice Price
7. Srinagar head office has its branch at Dehradun. Goods invoiced to branch at cost
plus 25 percent thereon. Both cash and credit sales are affected by the branch.
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
Royalty Accounts ll
l 5.35
Branch expenses are paid by the head office. all cash received by the branch being
sent to head office. From the following particulars, prepare barnch Account in the
books of Head Office for the year ending 31st March, 2016 :
Table
Ans. Branch Debtors at the end ` 25,000; Branch Profit ` 56,500
Hint : Loading profit will be adjusted @ 25/125 in opening stock, goods supplies
less return and closing stock.
8. R Ltd. has a branch at Delhi. Goods are sent to the branch at 20 percent profit on
invoice price. The branch has to remit daily cash receipts to the Head Office and all
branch expenses except petty expenses which are paid by the branch manager, are
paid from the Head Office. From the following, prepare branch account :
Table
Ans. Closing Debtors ` 16,980; branch’s Profit ` 22,380.
Hint : O/s salary ` 400 (4400 ÷ 11), Prepaid Insurance ` (800 × 3/12)
1
9. A Head Office supplies goods to its Gorkhpur Branch at cost plus 33 %. Branch
3
remits all Cash daily and Head Office pays all expenses of the branch, except petty
expenses which are paid by the branch itself. Branch adopts imprest system of petty
cash.
Table
Prepare Gorkhpur Branch Account for the year ending 31st March, 2016 from the above
particulars.
Ans. Branch Profit ` 45,900, Closing Debtors ` 8,000.
Hint : (1) Cash received from Debtors will be ` 1,60,000 - `85,000 = ` 75,000.
(2) Under imprest system petty expenses ` 860 will be shown in the debit side
of Branch A/c as these must have been reimbursed by H.O. Opening and Closing balance of
Petty Cash will be ` 1,000.
1
10. A Company invoices goods to its Branch at cost plus 33 %. All the cash collected by
3
the branch is banked on the same day to the credit of the Head Office. All expenses
are paid by the Head Office except petty expenses which are paid by the branch
manager. Prepare Branch Account from the following :
Table
Ans. Cash received from Debtors ` 38,000; Cash remitted to H.O. ` 88,300,
(2,000 + 55,000 + 38,000 - 4,000 - 200 - 2,500) Profit ` 25,050.
11. Jaunpur head office has a branch in Mirzapur to which goods are invoiced by the
head office at cost plus 25%. All expenses are paid by H.O. Following ar the
particulars of branch for the year 2015-16.
Table
Provide depreciation @ 10% on furniture
Prepare Branch Account and Debtors Account in the books of Head office.
(Poorvanchal)
Ans. Branch profit ` 51,240, Closing debtors ` 24,400
Hints : Goods by theft will not be shown in branch account under direct method.
12. Goods are invoiced by H.O. to its Branch at Lucknow at 20% on invoice price. All the
expense of the branch are paid by H.O. Branch keeps only a Debtors Ledger.
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
5.36 lll Financial Accounting
Prepare Lucknow Branch Account for the year ended at 31st March, 2016 from the
following particulars :
Table
13. The Bharat Stores Ltd., Agra have a Branch at Indore. Goods are invoiced to the
branch at selling price being cost plus 25%. The branch keeps its own Sales Ledger
and deposits all cash received daily to the credit of the Head Office Account opened
at State Bank of India, Indore. All expenses are paid by cheque form Agra. From the
following details, prepare a Branch Account in the Head Office Books, Nd make
necessary adjustments therein to arrive at the actual Branch Profit or Loss during
the year 2015-16.
Table
Ans. Branch profit ` 5,500; Cash received from debtors ` 19,800
Hint : Prepaid rent at end ` 600 (3,000/15 × 3)
14. The General merchants Ltd. Kanpur has a sales Branch in Allahabad and charges
1
all goods sent to the Branch at cost price plus 33 %. It is arranged that all cash
3
received by the Branch is to be paid daily to the Head Office. The Branch is to effect
very little credit sales. From the following particulars prepare the Branch Account
for 2014-15 under cost price method and Branch Account for 2014-15 under invoice
price method only :
Table
Ans. Branch profit : 2014-15 – ` 58,200 and 2015-16 – ` 49,550.
15. A head office in Pali has a branch at jalore to which goods are invoiced by the Head
Office at cost plus 25%. All cash received by the branch is daily remitted to Head
Office. All expenses are paid from Pali. From the following particulars, show as to
how the branch account will appear in the Head Office books when entries are made
at invoice price.
Table
Other information is available as follows :
(i) Branch furniture is to be depreciated at 10% per annum, and
(ii) The branch spent ` 1,875 as petty expenses during the half year ending 31st march
2016.
Ans. Branch profit ` 10,750, cash received from debtors ` 51,700, Closing
balance of petty cash ` 125 i.e. 200 + 1,800 - 1875 and furniture ` 1,425 i.e. ` 1,500 - ` 75.
16. Indu Ltd. Ludhiana started a branch at Barnala on 1st April, 2015 to which goods
were sent at 20% above Cost. The branch makes both credit and cash sales. Branch
expenses are met from branch cash and balance money remitted to head Office. The
branch does not maintain double entry books of accounts and necessary accounts
relating to branch are maintained in Head Office books. Following further details
are given for the year ended 31st march, 2016.
Table
Ans. Cash received from Debtors ` 37,000; Cash Sales ` 17,000; Net Profit `
22,800.
Hints : (1) Prepare Branch Debtors A/c and Branch Cash A/c. (2) Goods sent to
Branch (120/100) × 50,000 = ` 60,000. (3) Goods in Transit = Goods sent to Branch - Goods
received by Branch i.e. ` 6,000 (` 60,000 - ` 54,000)
Memorandum stock Account
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
Royalty Accounts ll
l 5.37
17. Dun Co. Dehrahun has its branch in Delhi. Goods are invoiced to this branch at 20%
profit on invoice price (or cost plus 25%). From the following details, prepare Banch
Account in the books of H.O. showing branch profit :
Table
Provide 10% depreciation on furniture (Meerut; Agra; Garhwal; Rohilkhand)
Ans. Furniture purchased by H.O. for branch.
18. Khanna Ltd. has one Brnah at Mumbai and other at Kolkata. Prepare Mumbai
Branch Account in the books of Head office from the following particulars which are
related to Mumbai branch :
Table
Goods are supplied to Branches by Head Office at cost + 25%. All expenses of the
Branch are met by the Head Office and Branch sends all cash received to Head
Office.
Also prepare a Branch Trading and Profit & Loss Account.
Ans. Branch Profit ` 1,350; Closing Stock ` 113. Closing Debtors ` 1,215.
19. Vasan of Chennai has a branch at Kolkata. Goods are invoiced from the Head Office
1
at cost plus 33 %. Branch is allowed to make sales at invoice price only. Expenses
3
of the Branch except petty expenses are paid directly by the Head Office. From the
following particulars, you are required to prepare the Branch Account to ascertain
the net profit at the Branch :
Table
Ans. Cash received from debtors ` 20,500, Closing debtors ` 24,650; Closing
Stock ` 7,800, Profit ` 13,820.
Hints : (1) Closing stock will be calculated by preparing memorandum stock
account.
(2) Goods damaged will not be taken to Branch A/c but amount received from
insurance Co. will be taken to the Cr. side of branch A/c.
20. Vishal Ltd. has one Branch at Kanpur and the other as Gorakhpur. Goods are
supplied to Branch by Head Office at cost + 25%. All expenses of the branch are met
by Head Office and branch sends all cash received to Head Office. Prepare Kanpur
Branch Account in the books of Vishal Ltd. from the following particulars :
Table
Ans. Closing debtors ` 5,400; Closing stock ` 500; Branch profit ` 6,000
21. Swastik Vanaspati Ltd. sends goods to branch at sale price, which is made up of cost
plus 25%. You are given the following particulars :
Table
Prepare Branch Account in the books of Head Office (Gorakhpur)
Ans. Closing stock ` 7,250; Branch Loss ` 5,200.
Final Account Method
Final Accounts Method
22. Mira & Co. opened a branch at Meerut. Following are the transactions between the
Head Office and the branch for the year ended 31st March 2016 :
Table
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
5.38 lll Financial Accounting
Prepare Meerut Branch Account and Trading and Profit & Loss A/c in the
books of the Head Office.
Ans. Branch’s Profit ` 1,310.
23. A Delhi merchant has a branch at Chennai to which he supplies goods at cost plus
5%. The branch keeps its own sales ledger and transmits all cash received to the
Head Office every day. all expenses are paid from the Head Office. for the year
ended 31st March 2016 the transactions of the branch were as follows :
Table
Prepare the Branch Trading and Profit and Loss Account and Branch
Account for the year ended 31st March 2016.
Ans. Gross Profit ` 10,220; Net Profit ` 8,195.
24. Shkti Traders of Gorakhpur has a branch at Jaunpur to which goods are supplied at
a profit of 20% on sale price. All expenses of branch except petty expenses are paid
by the head office. From the following particulars of the branch, prepare Trading &
Profit and Loss Account and Branch Account for the year ended 31st March 2016 :
Table
Ans. Gross Profit ` 16,000; Net Profit ` 10,750; Closing Debtors ` 6,000.
25. Sharad Ltd. supplied goods to its Deoria Branch at 20% less than list price which is
cost + 50%, with the instruction that the credit sales are to be made at list price less
discount at 10% on prompt payment and cash sales to be made at invoice price.
Prepare branch Trading and Profit and Loss Account for the year ended 31 March
2016 from the following particulars of Deoria Branch in the books of Head Office
showing actual profit or loss of the branch :
Table
Some sotock at the branch was burnt bu fire during the year whose value is
to be found out; it was not insured.
Ans. Loss of goods by fire ` 1,200 (invoice price), Gross profit ` 20,500, Net
profit ` 13,500.
26. A Head Office sent goods to the branch invoiced at 9,200 which was at a profit of
25% on cost. From the following particulars, prepare Branch Trading Profit & Loss
Account and Branch Account in H.O. books :
Table
Ans. Gross profit ` 1,740; Net profit ` 1,260
Hints : Cash in hand with branch ` 300.
Stock and Debtors Method
27. Edible Oils Ltd. opened a branch at Jamsehdpur on 1st April 2015. Goods are
1
invoiced at cost + 33 %. From the following particulars, calculate the profit or less
3
by Stock and Debtors System :
Table
Closing Stock at Branch on 31st March 2016 at Invoice Price
Ans. Shortage of Stock ` 300; Branch Profit ` 3,100.
Stock and Debtor System
28. A Chandigrah H.O. has a branch at New Delhi. All Goods are supplied by H.O. to
Branch at cost plus 25%. All expenses are paid by H.O. From the following
particulars you ar required to show Branch Debtors Account, Branch Stock Account,
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
Royalty Accounts ll
l 5.39
Stock Adjustment Account and Branch Profit & Loss Account in the Head Office
books :
Table
Ans. Credit Sales ` 97,200; Closing Stock 19,600 at invoice price, Gross Profit `
39,440; Net Profit ` 14,720.
29. An Agra H.O. has a Branch in New Delhi. All goods are supplied by H.O. to Branch
at cost plus 25%. All expenses are paid by H.O. The following are the particulars of
the Branch for the year 2015-16.
Table
Prepare Branch Stock A/c, Branch Adjustment A/c and Branch Expenses
Account in the books of Head Office. Also prepare a Branch A/c.
Ans. Surplus in Branch Stock A/c ` 55,600, Profit in Branch adjustment A/c `
8,600, Net Profit ` 51,840, Closing Debtors ` 25,000.
30. Raja Ltd. with its Head Office at Mumbai invoiced goods to its branch at Delhi at
20% less than the list price which is cost plus 100% with instructions that cash sales
were to be made at invoice price and credit sales at catalogue price (i.e. list price).
Some Stock of the branch is destroyed by fire and it was uninsured.
Table
From the above particulars, prepare the necessary accounts of the branch for the
year 1998.
Ans. Gross Profit in Branch Stock A/c ` 11,000; Loss of Stock by Fire ` 5,000 at
invoice price; G.P. in Branch Adjustment A/c ` 24,000; Net Profit ` 22,875, Closing Debtors `
19,000.
31. X Ltd. send goods to its branch at Saharanpur at cost plus 20%. From the following
particulars you are required to prepare Branch Stock A/c, Branch Adjustment A/c
and Branch Expenses A/c in the Head Office books :
Table
Ans. Gross profit in Branch stock account ` 1,19,000; Gross profit in branch
adjustment ` 13,500; Net profit ` 1,14,500. Actual loss in transit transferred to branch P/L A/c
` 5,000. (18,000 - 3,000 - 10,000)
32. M.R. & Co. operates a retail branch at Ajmer. all the goods are invoiced to the
branch at selling price which is 125% of the cost price to the Head office. From the
following particulars of the Branch, prepare Branch Stock. Goods sent to Branch,
Branch Debtors, Branch Expenses, Branch Adjustment Accounts in the books of
Head office :
Table
Ans. Goods sent to branch ` 1,50,000 at invoice price; Credit sales ` 72,000,
Net profit ` 9,200.
Hint : Balance of Goods Sent to Branch A/c ` 1,16,000.
33. The head office of ta company sends goods to branch at cost price. All the cash
collected by branch is deposited in the head office account in a local bank. All branch
expenses are directly paid by the head office by cheque. From the following
particulars prepare necessary ledger accounts of branch in the books of head office
under stock and debtors method :
Table
Ans. Gross profit ` 73,000, Net profit ` 43,000
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
5.40 lll Financial Accounting
Hint : Branch Stock Account will be prepared at cost price instead of invoice
price.
Therefore Branch Adjustment Account is not required.
34. Ved Prakash opened a branch in Modi Nagar on April 2014. Goods were sent to the
Branch at selling price which was fixed by adding 25% to the cost. From the
following particulars find out Branch Profit by the Stock and Debtors System :
Table
Ans. 2014-15—Closing stock ` 22,200, Gross profit ` 23,600; Net profit `
13,840; Closing debtors ` 4,000. 2015-16—Spoilage in stock ` 1,100, Gross profit ` 47,700; Net
profit ` 33,720; Closing debtors ` 8,500.
Wholesale Branch System
35. Hira Lal started business on Ist April, 2015. His head office is in Saharanpur and
branch office at Panipat. Goods are sent to the branch at a price 10% below selling
price. Goods are sold to customers at 50% profit to cost. All branch expenses are paid
by Head office. As per agreement branch manager is paid commission at 10% on
branch gross profit from the following information, prepare. Trading and Profit &
Loss Account of Head office and the Branch in head office books :
Table
Ans. Gross Profit : H.O. ` 1,03,800, Branch ` 7,400; Branch Manager’s
Commission ` 740 i.e. (74,000 × 10/100); stock Reserve ` 10,500 (40,000 × 35/135), Net Profit :
H.O. ` 81,000 and Branch ` 2,960.
36. A Head Office sends goods to its branch at 20% below the list price. Goods are sold to
customers after adding 100% to cost price. From the following particulars, ascertain
the profit of Head Office and the branch by the wholesale system :
Table
Head Office is selling goods to customers at list price.
(Rohilkhand, Purvanchal, Meerut)
Ans. Gross profit : H.O. ` 2,30,000, Branch ` 32,000; Closing stock — H.O. `
1,30,000, branch ` 32,000; Net profit H.O. ` 2,18,000, Branch ` 32,000; Stock reserve ` 12,000
i.e. 32,000 × 60/160.
37. Rahim and Co. has a branch at Chandausi. They supply goods to the branch at 20%
below selling price. The Head Office and the branch both sell goods to customers at
100% profit on cost. Rahim and Co. sells goods to approved stockists also at the same
price at which they supply to the branch. From the following particulars calculate
the net profit of Head Office and the branch :
Table
Ans. Gross Profit : H.O. ` 97,500, Branch ` 7,200, Closing Stock : H.O. `
1,63,500; Branch ` 12,800; Net Profit : H.O. 93,300; Branch ` 7,200; Stock Reserve of Opening
Stock ` 600; Closing Stock ` 4,800; i.e. 12,800 × 60/160.
Independent Branches
Independent Branch
38. The Ludhiana Branch sent the following Trial Balance to its Head Office at
Amritsar as on 31st March 2016.
Table
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
Royalty Accounts ll
l 5.41
The Stock on 31st March 2016 was ` 5,800. Prepare Branch Trading and Profit &
Loss Account. Pass Journal entries to incorporate th above figures in the H.O. books
and also show Branch Account.
Ans. Gross Profit ` 14,250; Net profit ` 9,400 and Balance Sheet total ` 26,150.
Total of Branch Account ` 1,39,800 if incorporation entries as per first method.
39. Delux Furnitures Delhi, have a branch at Agra which maintains independent sets of
books of accounts but intimates the net result of the trading activity of the Branch
for the year to the Head Office for incorporation in its accounts. Show the journal
entries to be made for closing the books and transferring the balance to the Head
Office Books. The Trial Balance of the Branch as on 31st March 2016 was :
Table
The Closing Stock on 31st March 2016 was ` 520. Show also the Head Office Account
as it would appear in the books of the Branch and the Branch account in the books of
the Head Office. The balance of the Head Office Account on 1st April 2015 was `
2,300 and during the year the cash remitted to the Head Office (by branch) was `
6,600.
Ans. Branch Gross Profit ` 1,380; Net Profit ` 330.
Hint : The closing balance of Branch (` 2,500) in the H.O. books will come after
transferring the cash received from Branch and goods sent to branch i.e. ` 2,300 + ` 6,800 − `
6,600 :
Table
40. A company with its Head Office at Delhi has a branch office in Kanpur which
obtains supplies partly from Head Office at cost and partly from outside suppliers.
The Branch keeps a separate set of books. On 31st march, 2016 the following Trial
Balances were extracted :
Table
The difference between currents accounts of H.O. and Branch is due to goods in
transit and cash in transit. Fixed assets are to be depreciated at 10%, Stock on 31st
March, 1999, Head Office ` 10,000 and branch ` 2,100. Prepare the company’s Profit
and Loss Account for the year ended 31st March 2016 and Balance Sheet on the
same date.
Ans. Gross Profit : H.O. ` 28,000; Branch ` 4,450; Net Profit : H.O. ` 11,400,
Branch ` 1,400; General P/L A/c ` 16,800, Consolidated Balance Sheet Total ` 58,850.
Hint : Cash in Transit will be calculated as follows :
Table
41. The Kanpur Branch send the following trial balance to the Head Office on 31st,
March 2016 :
Table
The stock on 31st, Dec was ` 10,000. Pass necessary Journal entries to incorporate
the branch assets and liabilities in the H.O. books and prepare branch Trading and
Profit & Loss Account for the year ended 31st, March 2016. (Kanpur 1996)
Ans. Branch gross profit ` 23,100, Net profit ` 12,600, B/S total ` 50,000,
Branch A/c total ` 2,77,000.
Special Entries
42. Show what entries would be passed by the Head Office and Branches to record the
following transactions in their books :
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
5.42 lll Financial Accounting
1. Goods amounting to ` 500 transferred from Calcutta Branch to Allahabad Branch,
under instructions from Head Office.
2. Depreciation amounting to ` 1,000 on Branch Fixed Assets, when such accounts are
opened in the Head Office Books.
3. A remittance of ` 3,000 made by te Calcutta Branch to Head Office on 28th, March
2016 and received by the Head Office on 4th April 2016.
4. Goods of ` 5,000 sent by the Head Office to the Allahabad Branch on 26th March
2016 and received by the latter on 10th April 2016.
5. The Calcutta Branch collected ` 2,000 from a Calcutta customer of the Head Office.
6. The Allahabad Branch paid ` 12,000 for machinery purchased by the Head Office at
Allahabad.
Ans. (A) In the books of : H.O. : (i) Dr. Allahabad Branch; Cr. Kolkata
Branch (ii) Dr. branch; Cr. Fixed Assets (iii) No Entry (iv) Dr. Goods in Transit; Cr. Allahabad
Branch (v) Dr. Kolkata Branch; Cr. Debtors (vi) Dr. Machine; Cr. Allahabad Branch. (B)
Allahabad Branch : (i) Dr. Goods received from H.O. Cr. H.O. (ii) Dr. Depreciation A/c, Cr.
H.O. (iii) (iv) (v) No Entry; (vi) Dr. H.O.; Cr. Cash. (C) Kolkata Branch : (i) Dr. H.O., Cr.
Goods received from H.O. (ii) No Entry (iii) Dr. Cash in Transit, Cr. H.O. (iv) No Entry (v) Dr.
Cash; Cr. H.O. (vi) No Entry.
43. A firm of engineers in Delhi, whose accounting year ends on 31st March 9, has two
branches one at Agra and the other at Lucknow at which a complete set of books is
maintained.
On 31st March 2016 the Agra and Lucknow Branch Account in the Delhi Books
showed debit balance of ` 27,500 and ` 35,300 respectively, before giving effect to the
following transactions :
(a) Goods valued to ` 2,500 were transferred from Lucknow to the Agra branch under
instructions from the Head Office.
(b) A remittance of ` 3,500 made the Agra Branch to the Head Office on 30th March
2016 was received by H.O. on 2nd April following.
(c) The Agra Branch collected ` 1,500 from an Agra customer of the Head Office.
(d) The Lucknow Branch paid ` 6,500 for some machinery purchased by the Head
Office in Lucknow.
(e) For the year 2015-16, the Agra Branch showed a net loss of ` 2,500 and Lucknow
Branch a net profit of ` 4,500.
Make journal entries to record these matters in the Head Office Books, and then
write up the two Branch Accounts therein.
Ans. (a) Dr. Agra Branch; Cr. Lucknow Branch (b) No entry (c) Dr. Agra
Branch; Cr. Debtors (d) Dr. Machine; Cr. Lucknow Branch (e) (i) Dr. General P/L A/C, Cr.
Agra Branch (ii) Dr. Lucknow Branch; Cr. General P/L A/c. Balance due : Agra Branch `
29,000 : Lucknow Branch ` 30,800.
44. The H.O. books shows the balance of Branch Account as ` 2,000 (Cr.) and branch
books show H.O. Account ` 22,000 (Dr.) on 31-3-2016. The reasons of difference are
revealed following :
(i) The H.O. sent goods worth ` 15,000 to branch but the branch not received it up to
31-3-2016.
(ii) The branch remitted cash ` 5,000 to H.O. H.O. received the same on 3-4-2016.
(iii) Branch received interest ` 3,000 on behalf of H.O.
(iv) H.O. received ` 40,000 payment from branch debtor.
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
Royalty Accounts ll
l 5.43
(v) Branch received ` 7,000 from H.O. debtor.
(vi) H.O. charged depreciation on branch assets ` 3,000 kept in H.O.
Journalise the above transactions and prepare H.O. A/c and branch A/c in the books
of branch and H.O. (Kanpur)
Ans. ` 44,000.
45. Kolkata head office has two branches, one at Kanpur and the other at Delhi. The
head office closes its books of accounts on 31st March every year. Give adjustment
entries for the following in the books of accounts on 31st March every year. Give
adjustment entries for th following in the books of head office :
(i) Dividend paid by Kanpur branch on behalf of head office ` 250.
(ii) Depreciation is provided @ 20% on Delhi branch assets costing ` 20,000 whose
accounts are kept in head office books.
(iii) Kanpur Branch has remitted ` 2,040 to head office on 23rd March 2016 was
received by H.O. on 4th April 2016.
(iv) Goods amounting to ` 6,500 sent by H.O. to Delhi branch on 23rd March 2016 was
received in Delhi on 6th April 2016.
(v) A typewriter of ` 8,000 was purchased by Kanpur branch. The payment was made
by Kanpur branch by cheque.
(vi) A sum of ` 1,200, being arrears of call money was received by Delhi branch from
shareholder in January 2016 but was not communicated to H.O. till 5th April 2016.
(vii) The Kanpur branch collected ` 2,000 from Kanpur customer of the head office.
(viii) The head office paid ` 5,000 for goods purchased by Delhi Branch in Delhi.
(Poorvanchal)
Ans. (i) Dr. Dividend Cr. Kanpur branch (ii) Dr. Delhi branch, Cr. Machine by
` 4,000 (iii) No Entry (iv) Dr. Goods in transit, Cr. Delhi branch (v) No entry (vi) No Entry (vii)
Dr. Kanpur branch, Cr. debtors (viii) Dr. Purchases; Cr. Delhi Branch A/c.
Foreign Branch
Foreign Branch
46. Convert the following Trail Balance as on 31st March 2016 of the London Branch
which has got its Head Office in Kolkata, Prepare Branch Trading and Profit & Loss
A/c and Balance Sheet :
Table
Stock on 31st March 2016 was £ 1,200 London Branch account (Dr. Balance) in
Calcutta books stood as debit ` 37,000 and Furniture appeared in Calcutta books at
` 10,000. The rate of exchange was as follows :
On 1st April 2015 ` 19 per pound, On 31st March 2016 ` 17 per pound, Average
Rate for the year year ` 18 per pound.
Ans. Exchange Suspense (Cr) ` 10,675 Total of converted Trial Balance
2,06,625; Gross Profit of 66,850, Net Profit 50,650, Balance Sheet total of 1,13,275.
Hint : Exchange Suspense A/c will be shown on liabilities side in the balance
sheet.
47. A Trading Company has its Head Office in London and Branch in Mumbai. The
following is the Trial Balance of both the houses on 31st March 2016.
Table
The rate of exchange between Mumbai and London may be taken at ` 15 to £ 1.
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
5.44 lll Financial Accounting
Prepare Trading and Profit & Loss Account and the Balance Sheet to the Company
as at 31st March, 2016 in Sterling. The Closing Stock were : London £ 12,500,
Mumbai ` 1,41,150.
Ans. Exchange Suspense A/c (Cr.) £ 1,574; Converted Trial Balance Total £
67,524; Gross Profit–H.O. £ 8,500, Branch £ 9,470; Net Profit H.O. £ 2,500, Branch £ 2,450;
consolidated Balance Sheet total £ 61,354.
48. Trial Balance on 31 March 2016 is as under :
Table
On 31st March 2016 Stock was Frances 91,683.
The above is a trial balance sent from the Paris Branch of a London Co. In the
London books, the Paris Branch balance on 1st Oct. 2015 was £ 5,218 and on 30th
March 2016 the remittance Account balance was £ 2,641. There was no cash in
transit.
1 1
The Rates of Exchange were as follows–1st October 86 , 31st March 2016 91 . At
2 2
the time of the purchases of the fixtures the rate was 124.
How would you deal with the above details in order to show the Paris result of the
trading and incorporate them in the London Books? What percentage of gross profit
to sales do the Paris results show? Write difference in exchange in P & L A/c.
Ans. Exchange suspense ` £ 248, Gross profit £ 933. Percentage of Gross profit
with sales 30.67% (933/3042 × 100) Net loss £ 83, Balance sheet total ` 5,767.
49. An Indian company has a branch in London. On March 31, 2016 the trail balance of
the branch was as below :
Table
On March 31, 2016 the Stock was £ 2,600. The Balance of Branch A/c in Head Office
books was ` 1,32,500 and Building was ` 6,000. Rate of exchange on 1-4-2015 ` 12,
on 31-3-2016 `. 11, and average rate of ` 10. Prepare Branch Profit & Loss Account
and the Balance Sheet.
Ans. Difference in Exchange ` 4,500; Gross Profit ` 54,800; Net Profit ` 51,800;
Total Balance Sheet ` 7,77,200.
Short Questions
(b) Numerical Questions
1. Following are the particulars of Indore branch. Its head office is in Gwalior. Prepare
Indore Branch Account in the head office books :
Table
Ans. Branch profit ` 675.
Hint : Prepaid Insurance ` 400, Prepaid Rent ` 300 and Prepaid wages ` 700.
2. Prepare Branch Account from the following particulars. Branch makes only cash
sales :
Table
Closing stock has not been ascertained. Manager gets commission @ 10% on net
profit before charging such commission. Branch sells goods at cost + 25%.
Ans. Closing ` 7,000, Commission ` 800, Profit ` 7,200.
3. All goods are supplied by the Head Office at invoice price on cost + 20%. From the
following particulars, prepare Branch Account in the Head Office books :
Table
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
Royalty Accounts ll
l 5.45
Ans. Branch profit 17,320, Closing debtors ` 26,000.
4. Prepare Stock Reserve Account under Stock and Debtors system from the following
data :
Table
Ans. (i) Dr. Stock Reserve Cr. Branch Adjustment A/c (ii) Dr. Branch
Adjustment A/c, Cr. Stock Reserve A/c.
5. From the following information, prepare Branch Debtors A/c in the books of H.O. to
ascertain closing balance of debtors as on 31st March, 2016 :
Debtors (1-4-2015) ` 3,260; Total Sales ` 10,300; Cash Sales ` 4,300; Collection from
debtors ` 7,000. Sales returns ` 150; Bad debts ` 70; Discount on purchases ` 120.
Ans. Closing Debtors ` 2,040
Hint : Discount on purchases will not be shown in debtors A/c.
6. If goods worth ` 20,000 sent by H.O. to its branch were in transit, then how will you
record in the books of Head Office or in the books of Branch?
Ans. Dr. Goods in Transit Cr. Branch A/c or No Entry.
7. H.O. sent goods to its branches at an invoice price of ` 2,20,000. These were charged
to branch at 10% above cost. Calculate profit charged by H.O.
Ans. Profit ` 20,000.
8. From the following information compute closing stock of Branch by making
Memorandum Stock A/c :
Table
Ans. Closing stock ` 8,800 at invoice price.
9. A company has a branch in Agra. Goods are invoiced to branch at cost plus 50%.
Accounts are maintained on Stock and Debtors System. From the following
information, prepare Branch Debtors Account :
Table
Ans. Closing debtors ` 6,000.
10. Give adjustment entries in the books of Head Office and Branch, of the following
cases. Branch is an independent branch :
(i) A remittance of ` 3,500 made by Branch to Head office on 30th March 2016 was
received by Head office on 2nd April 2016.
(ii) Branch collected ` 1,500 from the customers of Head Office. (Purvanchal)
Ans. In the books H.O. (i) No. Entry (ii) Dr. Branch Cr. Debtors A/c. In the
books of Branch (i) Dr. Cash in Transit, Cr. H.O. (ii) Dr. Cash, Cr. H.O.
11. Show what entries would be passed by H.O. and Gorakhpur branch to record the
following transactions in their books on 31st March 2016.
(i) Goods amounting to ` 800 transferred from Basti branch to Gorakhpur branch
under instruction from H.O.
(ii) Depreciation of Gorakhpur Branch Fixed Assets ` 1,500 when accounts are opened
in the head office books. (Gorakhpur)
Ans. H.O. (i) Dr. Gorakhpur Branch; Cr. Basti Branch. (ii) Dr. Gorakhpur
Branch, Cr. Fixed Assets. In the books of Branch : (i) Dr. Goods, Cr. H.O. (ii) Dr.
Depreciation, Cr. H.O.
Practical Questions
Tables
PDF Created with deskPDF PDF Writer - Trial :: http://www.docudesk.com
You might also like
- Theory and PracticeDocument27 pagesTheory and PracticeJulynna Victoria Sodsod Belleza83% (6)
- Compiler CAP II Cost AccountingDocument187 pagesCompiler CAP II Cost AccountingEdtech NepalNo ratings yet
- Customer Satisfaction Towards Mobile Service ProvidersDocument52 pagesCustomer Satisfaction Towards Mobile Service ProvidersSaloni AnandNo ratings yet
- Bir 2306Document2 pagesBir 2306Caroline Sanchez90% (10)
- Role of Education in Social ChangeDocument10 pagesRole of Education in Social Changelaljoel100% (1)
- 37 19 Branch Accounts Theory ProblemsDocument19 pages37 19 Branch Accounts Theory Problemsemmanuel Johny100% (2)
- Accounting For BranchesDocument54 pagesAccounting For BranchesabbyNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Text Book Exercises: Non-Trading ConcernsDocument12 pagesSolutions To Text Book Exercises: Non-Trading ConcernsM JEEVARATHNAM NAIDUNo ratings yet
- CA IPCC Accounting Guideline Answers May 2015Document24 pagesCA IPCC Accounting Guideline Answers May 2015Prashant PandeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter # 6 Departmental AccountDocument36 pagesChapter # 6 Departmental AccountRooh Ullah KhanNo ratings yet
- NON INTEGRATED TheoryDocument26 pagesNON INTEGRATED TheorySushant MaskeyNo ratings yet
- CAP III - Suggested Answer Papers - All Subjects - June 2019 PDFDocument133 pagesCAP III - Suggested Answer Papers - All Subjects - June 2019 PDFsantosh thapa chhetriNo ratings yet
- 4 Branch AccountsDocument18 pages4 Branch AccountsBAZINGANo ratings yet
- Sectional and Self Balancing SystemDocument7 pagesSectional and Self Balancing SystemBhupender Singh Kaushal78% (9)
- Practice Accounts Prime PDFDocument56 pagesPractice Accounts Prime PDFShraddha NepalNo ratings yet
- Accounting for Business Combinations and Internal ReconstructionsDocument27 pagesAccounting for Business Combinations and Internal ReconstructionsbinuNo ratings yet
- Non-Integrated, Integrated & Reconciliation of Cost and Financial AccountsDocument107 pagesNon-Integrated, Integrated & Reconciliation of Cost and Financial Accountsanon_67206536267% (3)
- Problem 5: XY LTDDocument4 pagesProblem 5: XY LTDAF 1 Tejasri PamujulaNo ratings yet
- Branch BestDocument46 pagesBranch Bestsamuel debebeNo ratings yet
- CA Inter Cost Important Questions For CA Nov'22Document93 pagesCA Inter Cost Important Questions For CA Nov'2202 Tapasvee ShahNo ratings yet
- Adv Accounts - AmalgamationDocument31 pagesAdv Accounts - Amalgamationmd samser50% (2)
- Cash ManagementDocument14 pagesCash ManagementSushant MaskeyNo ratings yet
- MTP1 May2022 - Paper 5 Advanced AccountingDocument24 pagesMTP1 May2022 - Paper 5 Advanced AccountingYash YashwantNo ratings yet
- Merged RTP - CA Foundation AccountsDocument124 pagesMerged RTP - CA Foundation AccountsAkash AjayNo ratings yet
- 13 17227rtp Ipcc Nov09 Paper3aDocument24 pages13 17227rtp Ipcc Nov09 Paper3aemmanuel JohnyNo ratings yet
- Group - I Paper - 1 Accounting V2 Chapter 13 PDFDocument13 pagesGroup - I Paper - 1 Accounting V2 Chapter 13 PDFjashveer rekhiNo ratings yet
- Revision Test Paper CAP II Dec 2017Document163 pagesRevision Test Paper CAP II Dec 2017Dipen AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Departmenatal AccountsDocument4 pagesDepartmenatal Accountsmanjunatha TKNo ratings yet
- WN - 1 Resource Test WN-2 Shares Outstanding TestDocument8 pagesWN - 1 Resource Test WN-2 Shares Outstanding TestSimran KhandujaNo ratings yet
- Selling Goods Through Agents: Consignment Accounts ExplainedDocument43 pagesSelling Goods Through Agents: Consignment Accounts ExplainedSWAPNA IS FUNNYNo ratings yet
- Chap 6Document27 pagesChap 6Basant OjhaNo ratings yet
- 35 Resource 11Document16 pages35 Resource 11Anonymous bf1cFDuepPNo ratings yet
- Investment Accounts: Attempt Wise AnalysisDocument54 pagesInvestment Accounts: Attempt Wise AnalysisJaveedNo ratings yet
- ACW366 - Tutorial Exercises 4 PDFDocument6 pagesACW366 - Tutorial Exercises 4 PDFMERINANo ratings yet
- Ravi's Trading and Profit & Loss AccountDocument6 pagesRavi's Trading and Profit & Loss AccountBlaze MysticNo ratings yet
- Revision Test Paper: Cap-Ii: Advanced Accounting: QuestionsDocument158 pagesRevision Test Paper: Cap-Ii: Advanced Accounting: Questionsshankar k.c.No ratings yet
- CS Exec - Prog - Paper-2 Company AC Cost & Management AccountingDocument25 pagesCS Exec - Prog - Paper-2 Company AC Cost & Management AccountingGautam SinghNo ratings yet
- Accounts Ques Nov06Document48 pagesAccounts Ques Nov06api-3825774No ratings yet
- Cost Accs Reconciliation Extra SumsDocument7 pagesCost Accs Reconciliation Extra Sumspurvi doshiNo ratings yet
- Banking CompaniesDocument34 pagesBanking CompaniesLodaNo ratings yet
- OG1 9 Branch AccountingDocument25 pagesOG1 9 Branch AccountingsridhartksNo ratings yet
- Job CostingDocument18 pagesJob CostingBiswajeet DashNo ratings yet
- Partnership PDFDocument28 pagesPartnership PDFBasant OjhaNo ratings yet
- Risk-Coverage Risks: Chapter - 9 Insurance ClaimsDocument24 pagesRisk-Coverage Risks: Chapter - 9 Insurance Claimss2sNo ratings yet
- Operating CostingDocument13 pagesOperating CostingJoydip DasguptaNo ratings yet
- TYBAF UnderwritingDocument49 pagesTYBAF UnderwritingJaimin VasaniNo ratings yet
- Profit Prior to Incorporation AccountsDocument7 pagesProfit Prior to Incorporation AccountsParul Bhardwaj VaidyaNo ratings yet
- 11 CaipccaccountsDocument19 pages11 Caipccaccountsapi-206947225No ratings yet
- Branch Accounting Examination BankDocument71 pagesBranch Accounting Examination BankNicole TaylorNo ratings yet
- Revision - Test - Paper - CAP - II - June - 2017 9Document181 pagesRevision - Test - Paper - CAP - II - June - 2017 9Dipen AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Autonomous Branches.Document7 pagesAutonomous Branches.Axam Ndawula100% (1)
- Assets.: (Vi) Due To Lack of Information, Depreciation Has Not Been Provided On FixedDocument6 pagesAssets.: (Vi) Due To Lack of Information, Depreciation Has Not Been Provided On FixedMehul Gupta100% (1)
- Coc Departmental Accounting Ca/Cma Santosh KumarDocument11 pagesCoc Departmental Accounting Ca/Cma Santosh KumarAyush AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Paper - 1: Principles & Practice of Accounting Questions True and FalseDocument29 pagesPaper - 1: Principles & Practice of Accounting Questions True and FalsePiyush GoyalNo ratings yet
- Purchase ConsiderationDocument5 pagesPurchase ConsiderationAR Ananth Rohith BhatNo ratings yet
- CA Ipcc Costing Suggested Answers For Nov 20161Document12 pagesCA Ipcc Costing Suggested Answers For Nov 20161Sai Kumar SandralaNo ratings yet
- Trial Balance Adjustments Income Statement Balance SheetDocument3 pagesTrial Balance Adjustments Income Statement Balance SheetREEMA MATHIASNo ratings yet
- Home Work Section Working CapitalDocument10 pagesHome Work Section Working CapitalSaloni AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Brs Practise SheetDocument1 pageBrs Practise Sheetapi-252642432No ratings yet
- Branch AccountingDocument38 pagesBranch AccountingUmra khatoonNo ratings yet
- Manage branch accounting with the Debtors methodDocument49 pagesManage branch accounting with the Debtors methodSunnyNo ratings yet
- FA - II Ch. 3 - Branch Accounting - 1643714338Document46 pagesFA - II Ch. 3 - Branch Accounting - 1643714338SWAPNA IS FUNNYNo ratings yet
- Branch AccountingDocument64 pagesBranch Accountingudaywal.nandiniNo ratings yet
- Accounting For BranchesDocument11 pagesAccounting For BranchesShrinidhi.k.joisNo ratings yet
- Indirect Taxes: Income TaxDocument9 pagesIndirect Taxes: Income TaxDanial ShadNo ratings yet
- SST Versus Solvency II - Comparison AnalysisDocument7 pagesSST Versus Solvency II - Comparison AnalysisXena WarriorNo ratings yet
- Premium CH 18 Saving, Investment, and The Financial SystemDocument37 pagesPremium CH 18 Saving, Investment, and The Financial SystemSuraj OVNo ratings yet
- Q CH 9Document7 pagesQ CH 9Jhon F SinagaNo ratings yet
- Expanding The Public System of Household Assistance: A Pilot Experiment in SloveniaDocument15 pagesExpanding The Public System of Household Assistance: A Pilot Experiment in SloveniaMala PlavaNo ratings yet
- A Study of Inventory Management at Ark EnterprisesDocument48 pagesA Study of Inventory Management at Ark Enterprisesshrikrushna javanjalNo ratings yet
- 5708 RadhakrishnanDocument2 pages5708 RadhakrishnanAvishek GhosalNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Income Statement AnalysisDocument29 pagesComprehensive Income Statement AnalysisAlphan SofyanNo ratings yet
- Marciczak2013 Et Al Bucharest Urban Geographies of Hesitant TransitionDocument19 pagesMarciczak2013 Et Al Bucharest Urban Geographies of Hesitant TransitionDomnProfessorNo ratings yet
- CTM REOI EA-RDIP Somalia-004Document2 pagesCTM REOI EA-RDIP Somalia-004Daud SuleimanNo ratings yet
- InvoiceDocument1 pageInvoiceKrishNo ratings yet
- Aryan Sirohi - STPR - 2100290700038Document115 pagesAryan Sirohi - STPR - 2100290700038Bharti KatyanNo ratings yet
- Investor Perceptions of Mutual FundsDocument81 pagesInvestor Perceptions of Mutual FundsHanu DonNo ratings yet
- Cost Estimates at Green Global BookDocument3 pagesCost Estimates at Green Global BookraaNo ratings yet
- Ball and Brown RelatedDocument5 pagesBall and Brown RelatedLin XinNo ratings yet
- API COD DS2 en Excel v2 1622388Document454 pagesAPI COD DS2 en Excel v2 1622388jo joNo ratings yet
- Annual Report TB 2018Document370 pagesAnnual Report TB 2018Laura Desi SitumorangNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Full Final Computation Jun'21 - EZ1281Document5 pages2.0 Full Final Computation Jun'21 - EZ1281Rohit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Aggregation of Income Set Off and Carry Forward of Losses 2Document21 pagesAggregation of Income Set Off and Carry Forward of Losses 2qazxswNo ratings yet
- Strategic Cost Management - Management ConsultancyDocument7 pagesStrategic Cost Management - Management ConsultancyVanna AsensiNo ratings yet
- ATH Technologies (E) : New Management: 2016-2017Document2 pagesATH Technologies (E) : New Management: 2016-2017Siti Nurul Asyiqin Binti Mohd Nor H20A1810No ratings yet
- Letter of CreditDocument12 pagesLetter of CreditNovi DiantoroNo ratings yet
- Corporate Governance Disclosure Practices in IndiaDocument29 pagesCorporate Governance Disclosure Practices in IndiasabyavgsomNo ratings yet
- Weekly Accomplishment Report On-The-Job Training/Field PracticeDocument2 pagesWeekly Accomplishment Report On-The-Job Training/Field PracticeJomari Tobes SatorreNo ratings yet
- Bcsbi Pictorial BookDocument24 pagesBcsbi Pictorial BookMALAYADRI DUARINo ratings yet
- Assignment #3 Financial Distress and RestructuringDocument6 pagesAssignment #3 Financial Distress and Restructuringcharlie simo100% (2)