Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Laws of Motion Worksheet
Uploaded by
Sajjan BalasubramanyanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Laws of Motion Worksheet
Uploaded by
Sajjan BalasubramanyanCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER-5
LAWS OF MOTION
2 MARK
1. State third law of motion. Action and reaction are equal and opposite. Why do they not
balance each other?
2. What do you mean by equilibrium of forces?
3. Friction is a self adjusting force comment?
4. Proper inflation of tyres of vehicles saves fuel. Why?
5. Give some methods to reduce friction.
6. What happens when the surfaces in contact are over polished?
7. Calculate the impulse due to the force 𝐹 = 4𝑖̂ + 2𝑗̂ 𝑁. If this force acts from ti=0 to
tf=0.33.
8. The body of mass ‘m’ strikes on a surface with a speed ‘v’ and it rebounds with the same
speed. Find the change in momentum of the body.
9. Why wheels are made circular in automobiles.
10. Explain why does a cyclist bend inward while riding along a curved road?
11. State Impulse momentum theorem.
12. Is friction a necessary evil? Justify.
13. To what extent a cyclist has top bend to negotiate a curved path? Derive an expression.
3 MARK
1. State second law of motion. Derive the expression for force from Newton’s second law?
2. Why is second law of motion considered to be the real law of motion among the three?
3. Why is it easier to pull lawn-roller than to push it?
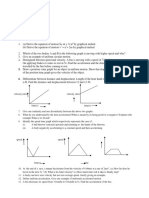
4. The figure shows the force versus time graph for a particle.
100 N
0.2 s 0.4 s
(i) Find the change in momentum of the particle
(ii) Find the average force on the particle.
5. Define force of friction. How does the use of ball bearing reduce friction?
6. Distinguish between static friction, limiting friction and kinetic friction. How do they
vary with the applied force, explain by diagram.
CLASS XI (PHYSICS WORKSHEET)Page 1
7. Define impulse. A cricket ball of mass 150 g moving with speed of 12 m/s is hit by a bat
so that the ball is turned back with a velocity of 20 m/s. Calculate the impulse received
by the ball.
8. State law of conservation of momentum and prove it using third law of motion.
9. Two masses m1 and m2 are connected to the ends of a string passing over a pulley. Find
the tension and acceleration associated.
10. A block of wood of mass 3 kg is resting on the surface of a rough inclined surface,
inclined at an angle ϴ as shown in the figure .
(i) Name the forces (1,2,3)
(ii) If the coefficient of static friction is 0.2, calculate the value of all the three forces
(g=10 m/s2).
30˚
5 MARKS
1. (i) Define friction
(ii)Show that the kinetic friction is less than the static friction.
(iii)Establish that static friction is a self-adjustable force
(iv)Write the basic laws of limiting friction.
2. Derive an expression for velocity of a car on a banked circular road having coefficient of
friction. Hence write the expression for optimum velocity.
3. Consider a mass ‘m’ attached to a string of length ‘l’ performing vertical circle. Find an
expression for the (i) velocity at any point (ii) tension at any point (iii) velocity minimum
at the lower most point for a vertical circle.
4. (i)A curved road of diameter 1.8 km is banked so that no friction is required at a speed
of 30
ms-1. What is the banking angle?
(ii)Two masses 8 kg and 12 kg are connected at the two ends of a light inextensible string
that goes over a frictionless pulley. Find the acceleration of the masses and the tension
in the string when the masses are released.
CLASS XI (PHYSICS WORKSHEET)Page 2
5. Explain (i) why does a horse have to apply more force to start a cart than to keep it
moving?
(ii)What is the need for banking the tracks? (iii) State two advantages and two
disadvantages of friction. (iv) Derive an expression for the safe speed of a vehicle to be
in a banked road.
CLASS XI (PHYSICS WORKSHEET)Page 3
You might also like
- Junior-Physics Imp QsDocument12 pagesJunior-Physics Imp QsVenu Gopal100% (1)
- Conceptual QuestionsDocument4 pagesConceptual QuestionssmrutirekhaNo ratings yet
- I Year Physics List of QuestionsDocument5 pagesI Year Physics List of QuestionspachikollasrinivasaraoNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Physics Sample Paper Set 5Document3 pagesCBSE Class 11 Physics Sample Paper Set 5Prajin MuruganNo ratings yet
- 11th Physics Worksheet (CH 2 To 6)Document3 pages11th Physics Worksheet (CH 2 To 6)Aadil ShakulNo ratings yet
- Acfrogcotthiaaw5ijplyyv4xwwtz7k8a6rjmi5tglxbnapq Kvubt p69mzhkhpnx7gbztj8xixdcvnehh0m2tay9zo5-Bx5eslder28mpvqp-Kwj5ajqsdgi7xbnzi6axuvuyibu5uvdpporzDocument6 pagesAcfrogcotthiaaw5ijplyyv4xwwtz7k8a6rjmi5tglxbnapq Kvubt p69mzhkhpnx7gbztj8xixdcvnehh0m2tay9zo5-Bx5eslder28mpvqp-Kwj5ajqsdgi7xbnzi6axuvuyibu5uvdpporzFalak SetaNo ratings yet
- Practice Test-1 Class: Xi Subject: Physics Physical World (Chapter-1) Units & Measurement (Chapter-2)Document21 pagesPractice Test-1 Class: Xi Subject: Physics Physical World (Chapter-1) Units & Measurement (Chapter-2)Sunil KumarNo ratings yet
- Laws of MotionDocument3 pagesLaws of Motionmili groupNo ratings yet
- MechanicsDocument27 pagesMechanicsJ T MNo ratings yet
- 11th PT-1Document6 pages11th PT-1ABHISHEK PANDANo ratings yet
- TS - JR - Phy - Imp Questions - 05-02-2024Document4 pagesTS - JR - Phy - Imp Questions - 05-02-2024Aarav JalanNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Uniform Circular MotionDocument12 pages1.0 Uniform Circular Motiongeofry lutondoNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument17 pagesPhysicsShubham VermaNo ratings yet
- REV12020 PhysicsDocument4 pagesREV12020 Physicshari kroviNo ratings yet
- List of DerivationsDocument7 pagesList of DerivationsJaruNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1 Class 9 Physics1566297629634Document5 pagesWorksheet 1 Class 9 Physics1566297629634Manoj PawarNo ratings yet
- Dakshana Class 11th Unit Test 3 - Laws of MotionDocument2 pagesDakshana Class 11th Unit Test 3 - Laws of MotionullasagwNo ratings yet
- 5.laws of MotionDocument16 pages5.laws of Motionmonu991No ratings yet
- Gravitation UnlockedDocument3 pagesGravitation UnlockedHarmeet SinghNo ratings yet
- TS - JR - Physics Imp - Questions 2023-24Document4 pagesTS - JR - Physics Imp - Questions 2023-24Vishvag ReddyNo ratings yet
- Imp. Question Vol 1 XI 2017 18Document5 pagesImp. Question Vol 1 XI 2017 18akash kalraNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IGCSE Physics: Chapter-4 Momentum Study QuestionDocument2 pagesEdexcel IGCSE Physics: Chapter-4 Momentum Study QuestionMahbub KhanNo ratings yet
- Ch.5lawsofmotionDocument4 pagesCh.5lawsofmotionsamahadadilkhanNo ratings yet
- 1st Yr Hy 09Document4 pages1st Yr Hy 09Grezzju CauchiNo ratings yet
- Laws of Motion QuestionDocument4 pagesLaws of Motion QuestionJoyabrata SarkarNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS-Ist YEAR (Board List)Document2 pagesPHYSICS-Ist YEAR (Board List)vaseem22772No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Physics Sample Paper Set 4Document4 pagesCBSE Class 11 Physics Sample Paper Set 4yatinchaudhary0571No ratings yet
- Physics - 11Document11 pagesPhysics - 11Ishika GuptaNo ratings yet
- Section A Physics Paper 1 Mechanics Revision Questions For A LevelDocument29 pagesSection A Physics Paper 1 Mechanics Revision Questions For A Levelalemorgan418No ratings yet
- Revision Worksheet 1 Jan 2023Document1 pageRevision Worksheet 1 Jan 2023Mohammed BasilNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Lakhmir SinghDocument4 pagesCH 2 Lakhmir SinghYashika SinghNo ratings yet
- Dom AssigimentDocument2 pagesDom AssigimentRoop LalNo ratings yet
- 11 Physics Laws of Motion Test 04Document1 page11 Physics Laws of Motion Test 04Gopal VenkatramanNo ratings yet
- Kovilpapakudi, Madurai. Slip Test - 2 Class: IX Physics Max - Marks: 50 Time: 1.30 Hrs I. Choose The Correct Answer: (10 X 1 10)Document4 pagesKovilpapakudi, Madurai. Slip Test - 2 Class: IX Physics Max - Marks: 50 Time: 1.30 Hrs I. Choose The Correct Answer: (10 X 1 10)THANIGAINATHAN.G.D 10A3No ratings yet
- Physics short answer and numerical questionsDocument3 pagesPhysics short answer and numerical questionsMani Chandra X CNo ratings yet
- Uka Tarsadia UniversityDocument4 pagesUka Tarsadia UniversityRishit ShahNo ratings yet
- Class-XI IMP Questions 2023-24Document3 pagesClass-XI IMP Questions 2023-24AbhishekNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Physics Term 1 Most Imp QuestionsDocument7 pagesClass 11 Physics Term 1 Most Imp QuestionsSANJAY PARMARNo ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.co - In: Illustrate Your Answer With NEAT Sketches Wherever NecessaryDocument3 pagesWWW - Manaresults.co - In: Illustrate Your Answer With NEAT Sketches Wherever NecessaryrajuNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 11 Annual Exam Model Question Paper 2 - PHYSICSDocument3 pagesICSE Class 11 Annual Exam Model Question Paper 2 - PHYSICSArindam SardarNo ratings yet
- Solving Friction ProblemsDocument6 pagesSolving Friction ProblemsSurya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Forces & Laws of MotionDocument2 pagesClass 9 Forces & Laws of MotionAmita RanaNo ratings yet
- Dehradun Public School Physics AssignmentDocument6 pagesDehradun Public School Physics AssignmentlembdaNo ratings yet
- Met304 ADocument5 pagesMet304 AVenkitaraj K PNo ratings yet
- Section A and B MechanicsDocument7 pagesSection A and B MechanicsJerrord ThomasNo ratings yet
- PH Handout QnsDocument31 pagesPH Handout QnsAZORYNo ratings yet
- Model Questiones For Engineering Mechanics 1 Year All BranchesDocument10 pagesModel Questiones For Engineering Mechanics 1 Year All BranchesFeolo Riel TarayNo ratings yet
- QuestionDocument8 pagesQuestionHimanshuTripathiNo ratings yet
- Momentum NpteDocument30 pagesMomentum NptediliniNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Practice: (86 Marks)Document18 pagesTopic 2 Practice: (86 Marks)terrygohNo ratings yet
- University of Zambia PHY1015 Tutorial Sheet 4 2021/2022 Newton’s Laws of MotionDocument2 pagesUniversity of Zambia PHY1015 Tutorial Sheet 4 2021/2022 Newton’s Laws of MotionAngel JereNo ratings yet
- Islamabad Academy MZD: Section-I 2. Write Answers of Any EIGHT Questions. (8x2 16)Document3 pagesIslamabad Academy MZD: Section-I 2. Write Answers of Any EIGHT Questions. (8x2 16)Prince ArsalNo ratings yet
- Junior Physics Quarterly Exam Important QuestionsDocument3 pagesJunior Physics Quarterly Exam Important Questionswahajk504No ratings yet
- Phys11 c04 4 3Document6 pagesPhys11 c04 4 3api-237070241No ratings yet
- MotionDocument17 pagesMotionJohnNo ratings yet
- 11 Physics Chapter 5 Test 2 PDFDocument2 pages11 Physics Chapter 5 Test 2 PDFMohd UvaisNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE-9-LAS-April-11-122024 (2)Document4 pagesSCIENCE-9-LAS-April-11-122024 (2)signejohnrickkuNo ratings yet
- Physics Winter Vaction WorkDocument2 pagesPhysics Winter Vaction WorkRana ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 5.continuity and Differentiability Class - Xii: Chennai Public School-AnnanagarDocument4 pages5.continuity and Differentiability Class - Xii: Chennai Public School-AnnanagarSajjan BalasubramanyanNo ratings yet
- Units and Dimentions WorksheetDocument3 pagesUnits and Dimentions WorksheetSajjan BalasubramanyanNo ratings yet
- Waves WorksheetDocument4 pagesWaves WorksheetSajjan BalasubramanyanNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of Gases WorksheetDocument5 pagesKinetic Theory of Gases WorksheetSajjan BalasubramanyanNo ratings yet
- Simple Harmonic Motion: AllenDocument9 pagesSimple Harmonic Motion: AllenSajjan BalasubramanyanNo ratings yet
- Thermal Properties of Matter WorksheetDocument1 pageThermal Properties of Matter WorksheetSajjan BalasubramanyanNo ratings yet
- Scope and Sequence StudyForgeDocument5 pagesScope and Sequence StudyForgeJeffrey VuongNo ratings yet
- Concepts and Developments in Physics - Module I - Sem 1Document49 pagesConcepts and Developments in Physics - Module I - Sem 1an.radhakrishnan1452No ratings yet
- Science 8 Curriculum Guide PDFDocument29 pagesScience 8 Curriculum Guide PDFZerleighDream Villorente PagalNo ratings yet
- Newton'sLaws Inertia LectDocument30 pagesNewton'sLaws Inertia LectYomiko Danise P. EloresNo ratings yet
- Definitions - Topic 4 Mechanics and Materials - AQA Physics A-LevelDocument3 pagesDefinitions - Topic 4 Mechanics and Materials - AQA Physics A-LevelLaud FumhandaNo ratings yet
- Force and Laws of Motion: B.Ed Iind Year (Third Semester)Document30 pagesForce and Laws of Motion: B.Ed Iind Year (Third Semester)BeastNo ratings yet
- Law of Acceleration: Sir Isaac NewtonDocument3 pagesLaw of Acceleration: Sir Isaac NewtonEricka HuseñaNo ratings yet
- PPT1Document5 pagesPPT1Jianna Francesca GayodNo ratings yet
- Physical Science FET PDFDocument148 pagesPhysical Science FET PDFSimlindile NgobelaNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Science quiz resultsDocument1 pageGrade 8 Science quiz resultsJaaziel Malunes Declaro-FerrerNo ratings yet
- Flexible Instruction Delivery Plan Template 1 Newtons LawDocument3 pagesFlexible Instruction Delivery Plan Template 1 Newtons LawSamson Meim80% (5)
- Fundamentals of BiomechanicsDocument11 pagesFundamentals of BiomechanicsMonwarul AzizNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Momentum, Energy and Simple SystemsDocument32 pagesChapter 6 Momentum, Energy and Simple SystemslachlanNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of A Particle Moving in A Straight LineDocument84 pagesDynamics of A Particle Moving in A Straight LineisamalhassanNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics Sports GuideDocument13 pagesBiomechanics Sports GuideAyushiNo ratings yet
- Forces NotesDocument13 pagesForces NotesAthena HuynhNo ratings yet
- JEE SPRINT PHYSICS QUESTION BANKDocument517 pagesJEE SPRINT PHYSICS QUESTION BANKParth ShahNo ratings yet
- Demonstration Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesDemonstration Lesson PlanVirgie Lizza B. Sino CruzNo ratings yet
- CP12eFMCA PDFDocument19 pagesCP12eFMCA PDFRaihan AsyifaNo ratings yet
- Rocket PropulsionDocument16 pagesRocket PropulsionAditya DashNo ratings yet
- CS. Physics NotesDocument141 pagesCS. Physics NotesOmarNo ratings yet
- MIT8 01SC Problems08 SolutionDocument31 pagesMIT8 01SC Problems08 SolutionJackie Peccadillo Lim67% (3)
- Biomechancal Principles in Orthodontics / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDocument84 pagesBiomechancal Principles in Orthodontics / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academyNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument4 pagesPhysicsAkash Kumar BeheraNo ratings yet
- Physics Booster Dose For EteaaDocument36 pagesPhysics Booster Dose For EteaaUmar FarooqNo ratings yet
- Mousetrap Cars ModuleDocument12 pagesMousetrap Cars ModulePradeep WalaweNo ratings yet
- Third Law of MotionDocument24 pagesThird Law of Motiongamms upNo ratings yet
- Newton's Third Law of MotionDocument27 pagesNewton's Third Law of MotionJayhia Malaga JarlegaNo ratings yet
- GP1 - Q1 - Week 5Document10 pagesGP1 - Q1 - Week 5Sathya Cruz100% (2)
- Newton's 2nd Law LectureDocument15 pagesNewton's 2nd Law LectureKhalid AlqahtaniNo ratings yet