Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Report of BroadBand (107and 127)
Uploaded by
fa20-bee-107Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Report of BroadBand (107and 127)
Uploaded by
fa20-bee-107Copyright:
Available Formats
COMSATS University Islamabad, Lahore Campus
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Report Of Broad Band
Project Title Modern Wireless Broadband Technology(5G)
Project Supervisor Main Ahmad Yasir
Group Name Reg. ID Email Address
Members M.Fasih Afzal FA20-BEE-107 Fa20-bee-107@cuilahore.edu.pk
M.Ahsan Shahid FA20-BEE-127 Fa20-bee-127@cuilahore.edu.pk
Comments about the Group and the Project Scope:
M.Fasih Afzal
First Person
(Member’s Signature)
M.Ahsan Shahid Supervisor Name
Second Person (Checked and Signed by the Supervisor)
(Member’s Signature)
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
COMSATS University Islamabad
LAHORE Campus – PAKISTAN
Table of Contents
Abstract
1) Introduction
2) Objectives
3) Key features
4) Applications and uses
5)Benefits
6)Challenges
7)Comparison Diagram
8) Working
9) Conclusion
Abstract :-5G, the fifth generation of wireless communication technology, represents
a paradigm shift in connectivity. With unprecedented data speeds, minimal latency, and
the capacity to support a massive number of devices simultaneously, 5G is set to
revolutionize industries and redefine user experiences. This abstract provides a brief
overview of 5G's key features, applications, and the challenges it poses. As 5G
deployment accelerates globally, understanding its potential and addressing associated
issues becomes paramount for stakeholders in technology, telecommunications, and
beyond."
1) Introduction:-5G builds upon the foundation laid by its predecessors (2G, 3G,
and 4G) and aims to provide faster data rates, lower latency, increased device
connectivity, and enhanced network reliability.The advent of the fifth generation of
wireless technology, commonly referred to as 5G, heralds a transformative era in
telecommunications. Building upon the foundations laid by its predecessors, 5G
introduces unparalleled speed, ultra-low latency, and the ability to connect a vast
multitude of devices simultaneously. This evolution in connectivity promises not only to
enhance our daily communication but also to revolutionize industries, ranging from
healthcare to manufacturing. In this introduction, we delve into the key features and
potential applications of 5G, exploring the profound impact it is poised to have on our
interconnected world.
2) Objectives:-
1) Understand the fundamental principles of 5G technology.
2) Explore the potential applications and use cases.
3) Analyze the benefits and challenges associated with 5G deployment.
3) Key Features of 5G:-
A) Enhanced Data Rates:-5G promises significantly faster data speeds compared
to its predecessors, with the potential to reach gigabit-per-second speeds.
B) Low Latency:-Reduced latency is a crucial aspect of 5G, enabling near-real-time
communication, which is essential for applications like augmented reality (AR), virtual
reality (VR), and autonomous vehicles.
C) Massive Device Connectivity:-5G is designed to support a massive number of
connected devices simultaneously, making it suitable for the Internet of Things (IoT) and
smart city applications.
D) Network Slicing:-This feature allows network operators to create virtual
networks tailored to specific applications, optimizing resources and improving overall
efficiency.
4) Applications and Use Cases:
A) Internet of Things (IoT):-5G facilitates the seamless connectivity of IoT
devices, enabling smart homes, industrial automation, and efficient energy management.
B) Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB):-Improved data rates make 5G ideal
for delivering high-quality multimedia content, supporting applications like 4K streaming
and virtual reality.
C) Critical Communications:-The low latency of 5G makes it suitable for critical
communications, such as emergency services and mission-critical applications.
5) Benefits:-
A) Faster Speeds:-5G offers significantly faster data speeds, enhancing the user
experience and enabling new applications and services.
B) Economic Growth:-The deployment of 5G infrastructure is expected to
stimulate economic growth by fostering innovation and supporting new
business models.
C) Improved Efficiency:-Network slicing and other features contribute to improved
network efficiency, allowing operators to optimize resource allocation.
6) Challenges:-
A) Infrastructure Investment:-The rollout of 5G requires substantial investment
in new infrastructure, including the deployment of small cells and the upgrade of existing
networks.
B) Spectrum Allocation:-Effective spectrum allocation is crucial for the success of
5G, and regulatory challenges may arise as demand for spectrum increases.
C) Security Concerns:-As with any new technology, 5G introduces security
challenges that need to be addressed, particularly given the increased connectivity and
potential attack vectors.
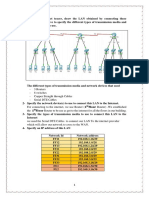
7) Comparision Diagram with 4G,3G:-
8) Working :-At its core, 5G technology operates by utilizing higher-frequency
radio waves, enabling data transmission at speeds and capacities far beyond its
predecessors. The key innovation lies in its ability to harness millimeter-wave spectrum,
providing faster data rates and significantly reducing latency. The deployment of a dense
network of small cells, coupled with advanced beamforming techniques, enhances
coverage and connectivity. This revolutionary advancement not only translates into
lightning-fast download and upload speeds for mobile users but also opens the door to a
plethora of transformative applications, from augmented reality and virtual reality
experiences to the seamless integration of an exponentially growing number of Internet of
Things (IoT) devices. The implications of 5G extend far beyond mere speed, promising
to reshape industries, facilitate the proliferation of smart technologies, and propel us into
a new era of interconnected innovation.
9) Conclusion:-
5G broadband technology represents a transformative shift in wireless communications,
offering unprecedented speed, low latency, and massive device connectivity. While the
technology holds immense promise, addressing challenges such as infrastructure
investment, spectrum allocation, and security will be critical for its successful
deployment and widespread adoption.
You might also like
- Open Radio Access Network (O-RAN) Systems Architecture and DesignFrom EverandOpen Radio Access Network (O-RAN) Systems Architecture and DesignNo ratings yet
- Project Charter - Team Fine CrewDocument3 pagesProject Charter - Team Fine CrewGAME BUSTERNo ratings yet
- OBIEE 11g Assessment Datasheet PDFDocument2 pagesOBIEE 11g Assessment Datasheet PDFSrikanth RoddaNo ratings yet
- Practical MLOPSDocument52 pagesPractical MLOPSCarlos Alberto Portela BrásNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Review On The Feasibility and Challenges of Millimeter Wave in Emerging 5G Mobile CommunicationDocument7 pagesA Comprehensive Review On The Feasibility and Challenges of Millimeter Wave in Emerging 5G Mobile CommunicationAnant SinhaNo ratings yet
- Enabling Process Bus Communication For Digital Substations Using 5G Wireless SystemDocument8 pagesEnabling Process Bus Communication For Digital Substations Using 5G Wireless SystemMarques SilvaNo ratings yet
- Next Generation 5 G Wireless NetworkDocument16 pagesNext Generation 5 G Wireless NetworkaslNo ratings yet
- Technologies For Move Towards 5GDocument9 pagesTechnologies For Move Towards 5GAnonymous izrFWiQNo ratings yet
- A Literature Survey On Applications of 5G Technologies For Water Resource ManagementDocument8 pagesA Literature Survey On Applications of 5G Technologies For Water Resource ManagementIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Overview On 5G and 6G Wireless Communication With Iot TechnologyDocument11 pagesOverview On 5G and 6G Wireless Communication With Iot TechnologyGokarala Triveni9119No ratings yet
- A Survey On Hybrid Beamforming Techniques in 5G: Architecture and System Model PerspectivesDocument38 pagesA Survey On Hybrid Beamforming Techniques in 5G: Architecture and System Model Perspectivesيسرى بوشوشةNo ratings yet
- 5g Architicture PDFDocument12 pages5g Architicture PDFOsman AlbahiNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Future 5G-Iot Millimeter-Wave Network Performance at 38 GHZ For Urban Microcell Outdoor EnvironmentDocument26 pagesInvestigation of Future 5G-Iot Millimeter-Wave Network Performance at 38 GHZ For Urban Microcell Outdoor EnvironmentNhat Tran XuanNo ratings yet
- Microwavejournal IEEEformatDocument8 pagesMicrowavejournal IEEEformatrhinestone gamerNo ratings yet
- A Survey On Channel Estimation and Practical Passive Beamforming Design For Intelligent Reflecting Surface Aided Wireless CommunicationsDocument37 pagesA Survey On Channel Estimation and Practical Passive Beamforming Design For Intelligent Reflecting Surface Aided Wireless CommunicationsSam SonNo ratings yet
- Topological Planningand Designof Heterogeneous Mobile Networksin Dense AreasDocument7 pagesTopological Planningand Designof Heterogeneous Mobile Networksin Dense Areasfelix NizeyimanaNo ratings yet
- 5G TechnologyDocument3 pages5G TechnologyJoseph GathuaNo ratings yet
- Zigbee Technology: A Seminar Report ONDocument68 pagesZigbee Technology: A Seminar Report ONarchanasingh88100% (3)
- Recent Advancements in User Effect Mitigation For Mobile Terminal Antennas: A ReviewDocument11 pagesRecent Advancements in User Effect Mitigation For Mobile Terminal Antennas: A ReviewAdriana PostaruNo ratings yet
- 5G Survey REPORT PDFDocument15 pages5G Survey REPORT PDFShyam GuptaNo ratings yet
- Towards The 5th Generation of Wireless Communication SystemsDocument15 pagesTowards The 5th Generation of Wireless Communication SystemsrajibuleceNo ratings yet
- The Potential Short-And Long-Term Disruptions and Transformative Impacts of 5G and Beyond Wireless Networks: Lessons Learnt From The Development of A 5G Testbed EnvironmentDocument28 pagesThe Potential Short-And Long-Term Disruptions and Transformative Impacts of 5G and Beyond Wireless Networks: Lessons Learnt From The Development of A 5G Testbed EnvironmentMarcus LimNo ratings yet
- Prediction 5GDocument15 pagesPrediction 5GKátherin Huarhuachi EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Your Project Report (5G Standards)Document6 pagesPreparation of Your Project Report (5G Standards)AneelaMalikNo ratings yet
- Key Challenges Drivers and Solutions For Mobility Management in 5G Networks A SurveyDocument19 pagesKey Challenges Drivers and Solutions For Mobility Management in 5G Networks A SurveyaliNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Higher Order Sectorisation On The Performance of Millimetre Wave 5G NetworkDocument6 pagesThe Impact of Higher Order Sectorisation On The Performance of Millimetre Wave 5G NetworkSara CherfiNo ratings yet
- 5GW C S: P C: Ireless Ommunication Ystems Rospects and HallengesDocument3 pages5GW C S: P C: Ireless Ommunication Ystems Rospects and HallengesPauline AdamsNo ratings yet
- Micro ProjectDocument15 pagesMicro ProjectBhumika BarseNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study On 4G and 5G Technology For Wireless ApplicationsDocument6 pagesA Comparative Study On 4G and 5G Technology For Wireless ApplicationsIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- Ref 17-Des Of5g PDFDocument5 pagesRef 17-Des Of5g PDFsssNo ratings yet
- Seminar 1Document24 pagesSeminar 1Sameer KapoorNo ratings yet
- 5G Mobile Technology: A Survey: SciencedirectDocument6 pages5G Mobile Technology: A Survey: Sciencedirectmesfin DemiseNo ratings yet
- Research Article Sixth Generation (6G) Cognitive Radio Network (CRN) Application, Requirements, Security Issues, and Key ChallengesDocument18 pagesResearch Article Sixth Generation (6G) Cognitive Radio Network (CRN) Application, Requirements, Security Issues, and Key ChallengesswathiNo ratings yet
- Architectural Performance of WiMAX Over WiFi WithDocument9 pagesArchitectural Performance of WiMAX Over WiFi WithKartik MuppirisettyNo ratings yet
- Fifth Generation (5G) Wireless Technology "Revolution in Telecommunication"Document7 pagesFifth Generation (5G) Wireless Technology "Revolution in Telecommunication"Angelo RubiaNo ratings yet
- 5g CommunicationsDocument59 pages5g CommunicationsDarknielzNo ratings yet
- 5G An Operators Perspective Eric Hardouin LTEWS 250613Document10 pages5G An Operators Perspective Eric Hardouin LTEWS 250613Enio LaguardiaNo ratings yet
- 5G Mobile Technologies: A Technical Seminar Report OnDocument22 pages5G Mobile Technologies: A Technical Seminar Report OnAshok SharmaNo ratings yet
- Fifth Generation (5G) Wireless Technology "Revolution in Telecommunication"Document6 pagesFifth Generation (5G) Wireless Technology "Revolution in Telecommunication"Harsha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Multilevel Service-Provisioning-Based Autonomous Vehicle ApplicationsDocument16 pagesMultilevel Service-Provisioning-Based Autonomous Vehicle ApplicationsSMITH CAMILO QUEVEDONo ratings yet
- Network Architecture of 5g Mobile TechnoDocument22 pagesNetwork Architecture of 5g Mobile TechnoChooKae JyeNo ratings yet
- Emerging Fields in 4G Technology, Its Applications & Beyond-An OverviewDocument10 pagesEmerging Fields in 4G Technology, Its Applications & Beyond-An Overviewo positifNo ratings yet
- "4G (4 Generation) Wireless System": Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirement For The Award of The Degree ofDocument32 pages"4G (4 Generation) Wireless System": Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirement For The Award of The Degree ofprabhakar58No ratings yet
- 4G Technology: January 2016Document5 pages4G Technology: January 2016Abhishek SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report-5G Tech - MangeshDDocument43 pagesSeminar Report-5G Tech - MangeshDmangesh deshmukhNo ratings yet
- Ijece 2023Document10 pagesIjece 2023Beulah JacksonNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument39 pagesPDFThalyson LuizNo ratings yet
- Performance Enhancement in 5G Mobile Network Processing: Conference PaperDocument7 pagesPerformance Enhancement in 5G Mobile Network Processing: Conference PaperandrianNo ratings yet
- Network Architecture of 5G Mobile TechnoDocument22 pagesNetwork Architecture of 5G Mobile TechnoWarood ALHadhramiNo ratings yet
- A Systematic Review On 5G Mass-IRO-Journals-4 2 3Document12 pagesA Systematic Review On 5G Mass-IRO-Journals-4 2 3Harish MahoreNo ratings yet
- Ayush Saxena Ccna Internship ReportDocument32 pagesAyush Saxena Ccna Internship ReportAmber GuptaNo ratings yet
- Performance Enhancement in 5G Mobile Network Processing: Lecture Notes On Information Theory May 2015Document7 pagesPerformance Enhancement in 5G Mobile Network Processing: Lecture Notes On Information Theory May 2015Naeem IslamNo ratings yet
- Roll No 36 Shivani Pandey 5G NetworkDocument5 pagesRoll No 36 Shivani Pandey 5G Networktapasya2097No ratings yet
- The Evolution of 5G Mobile Communication Standard Technology and Its ImplementationDocument11 pagesThe Evolution of 5G Mobile Communication Standard Technology and Its ImplementationMuhammad HussainNo ratings yet
- 5 G Communication NetworksDocument9 pages5 G Communication NetworksselfwayserviceproviderNo ratings yet
- Prasad V. Potluri Siddhardha Institute of Technology: Ifreak 09Document7 pagesPrasad V. Potluri Siddhardha Institute of Technology: Ifreak 09ksgtejaNo ratings yet
- Thesis On 3g NetworkDocument7 pagesThesis On 3g Networkgbww46x7100% (2)
- Ejaet 9 12 1 10Document11 pagesEjaet 9 12 1 10ARJUN BALA MURALINo ratings yet
- 5g Technology Research PapersDocument8 pages5g Technology Research Papersphqfgyvkg100% (1)
- Exploring Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces For 6G State of TheDocument14 pagesExploring Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces For 6G State of TheTaher El-AllousNo ratings yet
- Introduction Technical Sem Srinidhi inDocument9 pagesIntroduction Technical Sem Srinidhi inSahana GNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument18 pagesReportshubham8gargNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Operating System by B Lokesh JoelDocument61 pagesUnit 1 Operating System by B Lokesh JoeltowNo ratings yet
- Software Asset ManagementDocument37 pagesSoftware Asset ManagementPrashant UnnyNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Hacking and CrackingDocument15 pagesPresentation On Hacking and CrackingsrinivasNo ratings yet
- DPDK With KNI Pushing The Performance of An SDWAN Gateway To Highway LimitsDocument24 pagesDPDK With KNI Pushing The Performance of An SDWAN Gateway To Highway LimitsManoj SamarakoonNo ratings yet
- Change Data CaptureDocument4 pagesChange Data Capturekatherine976No ratings yet
- Research Methodology Project On Social Networking Sites (6) - RemovedDocument53 pagesResearch Methodology Project On Social Networking Sites (6) - RemovedShakshi YadavNo ratings yet
- Sap-Abap BasicDocument44 pagesSap-Abap BasicjaiNo ratings yet
- Tspu: Russia'S Decentralized Censorship System: Diwen Xue Benjamin Mixon-Baca ValdikssDocument16 pagesTspu: Russia'S Decentralized Censorship System: Diwen Xue Benjamin Mixon-Baca ValdikssAbraxasOssuaryNo ratings yet
- Java Programming PaperDocument2 pagesJava Programming Papermixipe3375No ratings yet
- GNSS H68G-2Document3 pagesGNSS H68G-2femin49249No ratings yet
- Ferramentas para Home OfficeDocument37 pagesFerramentas para Home OfficeTreinamentos Conlog S.A.No ratings yet
- Sudheerj - Reactjs-Interview-Questions - List of Top 500 ReactJS Interview Questions & Answers.... Coding Exercise Questions Are Coming Soon!!Document107 pagesSudheerj - Reactjs-Interview-Questions - List of Top 500 ReactJS Interview Questions & Answers.... Coding Exercise Questions Are Coming Soon!!smaryalaNo ratings yet
- Ramdump Wcss Msa0 2023-09-19 18-11-34 PropsDocument14 pagesRamdump Wcss Msa0 2023-09-19 18-11-34 PropsJose CanoNo ratings yet
- Content Manager Backup Recovery and High Availability Strategies Options and Procedures IBM Redbooks PDFDocument280 pagesContent Manager Backup Recovery and High Availability Strategies Options and Procedures IBM Redbooks PDFBruno Rafael Santos LopesNo ratings yet
- Electronic Banking Has Many Names Like e BankingDocument4 pagesElectronic Banking Has Many Names Like e BankingFalansh JainNo ratings yet
- CompTIA Solutions Catalog - Sept2023Document58 pagesCompTIA Solutions Catalog - Sept2023Ilham Rizkia MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Final Term Exam Datesheet Spring 2023Document3 pagesFinal Term Exam Datesheet Spring 2023Hamza khalidNo ratings yet
- Enabling Keycloak Metrics - KeycloakDocument3 pagesEnabling Keycloak Metrics - Keycloakhisyam darwisNo ratings yet
- Sales Order Header Test ScriptDocument13 pagesSales Order Header Test ScriptSunil ursNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Existing Threat Modeling Approaches (COMPLETE)Document68 pagesModule 2 Existing Threat Modeling Approaches (COMPLETE)KESTREL KELLNER CERVANTESNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 - Lecture 1 & 2Document74 pagesChapter - 1 - Lecture 1 & 2Junaid SarwarNo ratings yet
- Timothy Budd - Understanding Object-Oriented Programming With JavaDocument373 pagesTimothy Budd - Understanding Object-Oriented Programming With JavaMarcos Antônio B. de SouzaNo ratings yet
- Explore Business Add-Ins (BAdIs) For SAP S4HANA Cloud On SAP API Business HubDocument7 pagesExplore Business Add-Ins (BAdIs) For SAP S4HANA Cloud On SAP API Business Hubkoizak3No ratings yet
- شبكDocument5 pagesشبكعمر عبد العزيز النقيبNo ratings yet
- GL300A @track Air Interface Protocol R200Document95 pagesGL300A @track Air Interface Protocol R200Yosef GUEVARA SALAMANCANo ratings yet
- Huntel MTK NV Restore Tool User Guide - 20080709Document10 pagesHuntel MTK NV Restore Tool User Guide - 20080709Fuad Al-AzaniNo ratings yet
- Industrial Cybersecurity 4.0: Preparing The Operational Technicians For Industry 4.0Document6 pagesIndustrial Cybersecurity 4.0: Preparing The Operational Technicians For Industry 4.0L.A FloresNo ratings yet