Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SDG GOAL NO 5 AND ITS CONNECTIVITY WITH OTHER SDGs OF THE UNITED NATION
Uploaded by
agatha linusOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SDG GOAL NO 5 AND ITS CONNECTIVITY WITH OTHER SDGs OF THE UNITED NATION
Uploaded by
agatha linusCopyright:
Available Formats
SDG GOAL NO 5 AND ITS CONNECTIVITY WITH OTHER SDGs OF THE UNITED
NATION
A PATH TO GENDER EQUALITY
Gender equality is not only a basic human right, but its achievement has enormous socio-
economic ramifications. Empowering women fuels thriving economies, spurning productivity
and growth. Gender equality lies at the heart of the 2030 Sustainable Development Goals,
accelerating it leads to a more rapid increase in progress towards achieving the 2030 agenda.
Gender equality is a goal in its own right enshrined in SDG 5 but it cuts across all 17 SDGs
within the Agenda, which contains 45 targets and 54 indicators related to gender equality. It
is found to have positive effects on promoting economic growth and labour productivity
(SDG 8) and enhancing human capital through health (SDG 3) and education (SDG 4), which
has important implications for poverty reduction (SDG 1).
Gender equality is also critical for attaining food security (SDG 2) and addressing climate
change (SDG 13), while also strengthening resilience to climate-related disasters and
managing natural resources. Furthermore, providing equal opportunities for women’s
participation in decision-making processes is beneficial for ensuring more peaceful and
inclusive communities (SDG 16) which asserts gender equality as both a fundamental human
right and a necessary foundation for a peaceful prosperous and a sustainable world.
Gender equality is crucial to achieve a wide range of objectives pertaining to sustainable
development. These include promoting economic growth and labour productivity, reducing
poverty, enhancing human capital through health and education attaining food security,
addressing climate change impacts and strengthening resilience to disasters and ensuring
more peaceful and inclusive communities.
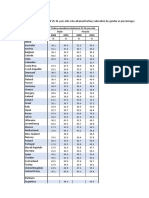
The World's 20 Nations with the Highest Number of Children Out of School
Out of School Male Female
1. Somalia 71.5 69.0 74.5
2. South Sudan 67.0 64.0 71.0
3. Niger 60.0 56.0 63.5
4. Burka Fasco 52.5 51.0 53.0
5. Mali 50.0 47.0 53.5
6. Afghistan 49.0 39.0 60.5
7. Syria 47.5 47.0 47.5
8. Chad 46.5 41.0 53.0
9. Guinea 43.0 36.0 50.0
10. Sengal 39.0 39.5 38.0
11. Liberia 38.5 39.5 38.0
12. Gambia 36.0 37.0 36.0
13. Czech Republic 35.0 29.0 40.5
14. Ethiopita 34.0 36.0 31.5
15. Pakistan 32.5 28.5 37.0
16. Guinea-Bissauu 32.5 29.5 35.5
17. Uited Rep of Tanaiza 32.5 31.5 34.0
18. Nigeria 29.5 27.5 32.0
19. Benin 29.5 26.5 33.0
20. Central African Republic 28.5 20.0 37.0
You might also like
- 2018 Amfori BSCI CRC V2020Document15 pages2018 Amfori BSCI CRC V2020S P Suganthi GaneshNo ratings yet
- Huiles D'Olive - Olive Oils: Tableau 1: PRODUCTION (1.000 TM) - Table 1: PRODUCTION (1,000 Tonnes)Document1 pageHuiles D'Olive - Olive Oils: Tableau 1: PRODUCTION (1.000 TM) - Table 1: PRODUCTION (1,000 Tonnes)Rodrigo Alejandro Romo MuñozNo ratings yet
- 2016 Amfori BSCI CRC V2018Document16 pages2016 Amfori BSCI CRC V2018S P Suganthi GaneshNo ratings yet
- Consommation1 AngDocument1 pageConsommation1 AngEMS Metalworking MachineryNo ratings yet
- Africa PrintableDocument6 pagesAfrica PrintableKatya KateNo ratings yet
- Statistiques de 1994 À 2000Document47 pagesStatistiques de 1994 À 2000Khadija KamousNo ratings yet
- Situatie Infectii Coronavirus (COVID-19) - 21.03.2020 PDFDocument7 pagesSituatie Infectii Coronavirus (COVID-19) - 21.03.2020 PDFElena GadinaNo ratings yet
- Situatie Infectii Coronavirus (COVID-19) - 21.03.2020Document7 pagesSituatie Infectii Coronavirus (COVID-19) - 21.03.2020PAUL GoreanuNo ratings yet
- 100 KKKDocument25 pages100 KKKSotuco ultraNo ratings yet
- Toys-Hobby Toys-Games Toys-For-Toddlers-Kids Pakistan USD enDocument14 pagesToys-Hobby Toys-Games Toys-For-Toddlers-Kids Pakistan USD enhira baigNo ratings yet
- Table 04 Corn Area, Yield, and ProductionDocument1 pageTable 04 Corn Area, Yield, and ProductionSubdivisi Analisis PermintaanNo ratings yet
- BlueDocument1 pageBlueSimon FloodNo ratings yet
- Africa Countries Numbered Labeled PDFDocument1 pageAfrica Countries Numbered Labeled PDFListerine WhitehouseNo ratings yet
- Gold Mining Production Volumes DataDocument6 pagesGold Mining Production Volumes DataM Rallupy MeyraldoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2A Good Times Good FeelingsDocument30 pagesUnit 2A Good Times Good FeelingsMi PhạmNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen-Dissociated Ammonia RelationDocument3 pagesHydrogen-Dissociated Ammonia RelationSatyendra PandeyNo ratings yet
- TABLE 1.2 Distribution of Overseas Filipino Workers by Age Group, Sex and Area 2017Document1 pageTABLE 1.2 Distribution of Overseas Filipino Workers by Age Group, Sex and Area 2017Sheryl BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Situatie Infectii Coronavirus (COVID-19) - 19.03.2020Document7 pagesSituatie Infectii Coronavirus (COVID-19) - 19.03.2020Alina IancuNo ratings yet
- Name: Sanju Priya V Roll No: 1811142 Section: BDocument13 pagesName: Sanju Priya V Roll No: 1811142 Section: BSanju VisuNo ratings yet
- Gender Equality in The Wake of COVID 19 Annexes enDocument89 pagesGender Equality in The Wake of COVID 19 Annexes enAbid RidoNo ratings yet
- Male Female 2009 2019 2009 2019 % % % %: Tertiary Educational Attainment 25-34 Year-OldsDocument7 pagesMale Female 2009 2019 2009 2019 % % % %: Tertiary Educational Attainment 25-34 Year-OldsAhmed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Aging Population (Assgt)Document27 pagesAging Population (Assgt)Thessa Lonica GarciaNo ratings yet
- Guillen Book 2030 - Feb 1, 2021Document32 pagesGuillen Book 2030 - Feb 1, 2021Praveen undruNo ratings yet
- Strictly No Erasure Final Examination Strictly No ErasureDocument1 pageStrictly No Erasure Final Examination Strictly No ErasureKhrisAngelPeñamanteNo ratings yet
- Analytics - Middle East and AfricaDocument1 pageAnalytics - Middle East and Africasadi raniaNo ratings yet
- Situatie Infectii Coronavirus (COVID-19) - 23.03.2020 PDFDocument7 pagesSituatie Infectii Coronavirus (COVID-19) - 23.03.2020 PDFTudor ManisNo ratings yet
- Güvender M1 Testleri 80 SoruDocument10 pagesGüvender M1 Testleri 80 SoruMehmet ÖzdemirNo ratings yet
- Life Expectancy YearsDocument160 pagesLife Expectancy YearsMarcko Condezo GonzalesNo ratings yet
- AFRICADocument1 pageAFRICAdipeshudwadiaNo ratings yet
- Mayk BernardoDocument21 pagesMayk BernardoMayk Allan BernardoNo ratings yet
- Where Is Rice in The World Economy?: Dennis DelaughterDocument56 pagesWhere Is Rice in The World Economy?: Dennis DelaughterPivaralNo ratings yet
- Internal Assesment Maths 22 AppendixDocument8 pagesInternal Assesment Maths 22 Appendixa.magjedrzejewskaNo ratings yet
- Puj General Fare Guide: Effective: February 8, 2017Document1 pagePuj General Fare Guide: Effective: February 8, 2017ALYSSA ANNE TADEONo ratings yet
- 2 - Corruption CPI2019Document41 pages2 - Corruption CPI2019Trung TạNo ratings yet
- Has I Lases Men Talents MappingDocument26 pagesHas I Lases Men Talents Mappingdee.aira2955No ratings yet
- DSS Urbanization ConceptDocument10 pagesDSS Urbanization Conceptolusanyadaniel01No ratings yet
- Departamento: "Chuquisaca" Fecha Y Hora de Impresión: 16/06/2019 16:23Document2 pagesDepartamento: "Chuquisaca" Fecha Y Hora de Impresión: 16/06/2019 16:23Ariel Joffré MedinacelliNo ratings yet
- Jadual5 Agihan Pendapatan Kumpulan Isi Rumah Mengikut Kumpulan Etnik Ketua Isi Rumah Dan Strata Malaysia 1970 2022Document1 pageJadual5 Agihan Pendapatan Kumpulan Isi Rumah Mengikut Kumpulan Etnik Ketua Isi Rumah Dan Strata Malaysia 1970 2022Syed IskandarNo ratings yet
- In Thousand 60kg Bags: Monthly Export Statistics (Members & Non-Members) - December 2020Document1 pageIn Thousand 60kg Bags: Monthly Export Statistics (Members & Non-Members) - December 2020Gemechis BidoNo ratings yet
- The Global Competitiveness Index 2009-2010 Rankings and 2008-2009 Comparisons GCI 2008-2009Document4 pagesThe Global Competitiveness Index 2009-2010 Rankings and 2008-2009 Comparisons GCI 2008-2009sumanth1437No ratings yet
- As LastDocument3 pagesAs LastJhon Chiem OdtojanNo ratings yet
- Import Index - Trademap.2010 2020Document740 pagesImport Index - Trademap.2010 2020Nguyễn Linh TrangNo ratings yet
- Situatie Infectii Coronavirus (COVID-19) - 20.03.2020 PDFDocument7 pagesSituatie Infectii Coronavirus (COVID-19) - 20.03.2020 PDFMaria PaicuNo ratings yet
- Situatie Infectii Coronavirus (COVID-19) - 20.03.2020Document7 pagesSituatie Infectii Coronavirus (COVID-19) - 20.03.2020georgeiliescuNo ratings yet
- Situatie Infectii Coronavirus (COVID-19) - 20.03.2020Document7 pagesSituatie Infectii Coronavirus (COVID-19) - 20.03.2020PAUL GoreanuNo ratings yet
- Situatie Infectii Coronavirus (COVID-19) - 20.03.2020Document7 pagesSituatie Infectii Coronavirus (COVID-19) - 20.03.2020PAUL GoreanuNo ratings yet
- Situatie Infectii Coronavirus (COVID-19) - 20.03.2020 PDFDocument7 pagesSituatie Infectii Coronavirus (COVID-19) - 20.03.2020 PDFCatalin FidelNo ratings yet
- Regional Sofi 2021 Asiapacific Fig10Document5 pagesRegional Sofi 2021 Asiapacific Fig10kaysbookishNo ratings yet
- табл самстійнаDocument10 pagesтабл самстійнаYana ReuNo ratings yet
- Table 4. Public Finances, 2015-18 (Percentage of GDP)Document2 pagesTable 4. Public Finances, 2015-18 (Percentage of GDP)Zainal WafaNo ratings yet
- GVDocument4 pagesGV謇醟鞝No ratings yet
- Arango - Et Al. - Symbol Digit Modalities Test. Normative Data For Spanish Speaking Pediatric Population (Appendix)Document13 pagesArango - Et Al. - Symbol Digit Modalities Test. Normative Data For Spanish Speaking Pediatric Population (Appendix)RICARDO MANUEL LAJO ALVAREZNo ratings yet
- Power Generation EfficiencyDocument5 pagesPower Generation Efficiencydjamel eddine GhersiNo ratings yet
- Samoa External Debt by Tarun Das Part 2 TablesDocument8 pagesSamoa External Debt by Tarun Das Part 2 TablesProfessor Tarun DasNo ratings yet
- Tramo Ad1 X y 0 0.00 0.5 - 1.51 1 - 2.73 1.5 - 3.68 2 - 4.38 2.5 - 4.83 3 - 5.08 3.5 - 5.13 4 - 5.00 4.5 - 4.72 5 - 4.30Document16 pagesTramo Ad1 X y 0 0.00 0.5 - 1.51 1 - 2.73 1.5 - 3.68 2 - 4.38 2.5 - 4.83 3 - 5.08 3.5 - 5.13 4 - 5.00 4.5 - 4.72 5 - 4.30Kevvin FrancisNo ratings yet
- Deagel Analysis UpdatedDocument7 pagesDeagel Analysis UpdatedAll News PipelineNo ratings yet
- Civil Socity Manifesto On EducationDocument14 pagesCivil Socity Manifesto On EducationFemi AderibigbeNo ratings yet
- DCPT Slava ProjectDocument1 pageDCPT Slava Projectadit Saka AdityaNo ratings yet
- Countryid Country Name Region: Brunei Burma Cambodia Indonesia Laos Malaysia Philippines Singapore Thailand VietnamDocument9 pagesCountryid Country Name Region: Brunei Burma Cambodia Indonesia Laos Malaysia Philippines Singapore Thailand VietnamLion HunterNo ratings yet
- Kirby Forest Industries, Inc., Petitioner v. United StatesDocument16 pagesKirby Forest Industries, Inc., Petitioner v. United StatesScribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Magna Carta RightsDocument2 pagesMagna Carta RightsLeanne MorenoNo ratings yet
- Capital Punishment Essay Final VersionDocument4 pagesCapital Punishment Essay Final Versionapi-221979538No ratings yet
- How To Apply For Visa D - Manual - Under 18 - 9months - April2021Document5 pagesHow To Apply For Visa D - Manual - Under 18 - 9months - April2021Kristina ArtskhanovaNo ratings yet
- 6-2021 - Automatic Advancement SchemeDocument8 pages6-2021 - Automatic Advancement SchemePradeep ReddyNo ratings yet
- International Health Organizations and Nursing OrganizationsDocument35 pagesInternational Health Organizations and Nursing OrganizationsMuhammad SajjadNo ratings yet
- Investigation Finds Driver in Fatal Bronx Bus Crash Exploited Flaws in Licensing ProcessDocument7 pagesInvestigation Finds Driver in Fatal Bronx Bus Crash Exploited Flaws in Licensing ProcessNick ReismanNo ratings yet
- SS 5 Aralin 1 PDFDocument26 pagesSS 5 Aralin 1 PDFChris Micah EugenioNo ratings yet
- Murray's QFRsDocument62 pagesMurray's QFRsValerie Strauss100% (3)
- Rwandan Genocide EssayDocument5 pagesRwandan Genocide Essayapi-318662800No ratings yet
- Report To The MayorDocument3 pagesReport To The MayorTommy D. SoledadNo ratings yet
- Post Reform PeriodDocument26 pagesPost Reform PeriodIshu ChopraNo ratings yet
- Nigeria Stability and Reconciliation Programme Volume 1Document99 pagesNigeria Stability and Reconciliation Programme Volume 1Muhammad NaseerNo ratings yet
- DD Form 4Document4 pagesDD Form 4Arthur BarieNo ratings yet
- Misc SignalDocument74 pagesMisc SignalAnonymous wbhG5IdmFNo ratings yet
- King Charles' Coronation TVDocument2 pagesKing Charles' Coronation TV9LO JadziaNo ratings yet
- SSRN Id2566126Document152 pagesSSRN Id2566126Tauseef AhmadNo ratings yet
- Treasury FOIA Response 6-8-11Document60 pagesTreasury FOIA Response 6-8-11CREWNo ratings yet
- Law Thesis MaltaDocument4 pagesLaw Thesis MaltaEssayHelperWashington100% (2)
- Ang Mga Kilalang Propagandista at Ang Mga Kababaihang Lumaban Sa RebolusyonDocument3 pagesAng Mga Kilalang Propagandista at Ang Mga Kababaihang Lumaban Sa Rebolusyonshiela fernandezNo ratings yet
- Glossary SociologyDocument10 pagesGlossary SociologydigitalfaniNo ratings yet
- The Jats of Northern India: Their Traditional Political SystemDocument4 pagesThe Jats of Northern India: Their Traditional Political SystemSandeep BadoniNo ratings yet
- Federalism in The PhilippinesDocument43 pagesFederalism in The PhilippinesAgustinVillareal100% (3)
- The Geopolitical Economy of Resource WarsDocument23 pagesThe Geopolitical Economy of Resource WarsLucivânia Nascimento dos Santos FuserNo ratings yet
- Updated Learning Modules in GeccomDocument83 pagesUpdated Learning Modules in GeccomArielle AlontagaNo ratings yet
- Ambassador's Interview With The Jewish NewsDocument1 pageAmbassador's Interview With The Jewish NewsKaren Saul KaufmanNo ratings yet
- DMG ShanghiDocument3 pagesDMG ShanghiMax Jerry Horowitz50% (2)
- Digest Imbong V ComelecDocument2 pagesDigest Imbong V ComelecManila Loststudent100% (2)
- Doe v. Clenchy DecisionDocument23 pagesDoe v. Clenchy Decisionjsnow489No ratings yet
- Attacks by Erwin Rommel Book ReportDocument2 pagesAttacks by Erwin Rommel Book ReportRichNo ratings yet