Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Epi Reportable Practitioners
Uploaded by
pauloantoniolima450Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Epi Reportable Practitioners
Uploaded by
pauloantoniolima450Copyright:
Available Formats
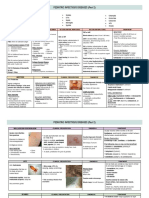
Reportable Diseases/Conditions in Florida
Practitioner List (Laboratory Requirements Differ)
Per Rule 64D-3.029, Florida Administrative Code, promulgated October 20, 2016 Florida Department of Health
! Report immediately 24/7 by phone upon
initial suspicion or laboratory test order
The Florida Department of Health in Orange County Reporting Numbers: Report immediately 24/7 by phone
AIDS/HIV: 407-858-1437 STD: 407-858-1445 or FAX 407-836-7101 Report next business day
Tuberculosis: 407-858-1446 or FAX 407-836-2639 + Other reporting timeframe
All Others: 407-858-1420 or FAX 407-858-5517
Birth Defects 850-617-1440 ! Arboviral diseases not otherwise listed ! Meningococcal disease
+ Congenital anomalies Babesiosis Mercury poisoning
+ Neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS) ! Botulism, foodborne, wound, and Mumps
unspecified Neurotoxic shellfish poisoning
Cancer 305-240-4600 Botulism, infant Paratyphoid fever (Salmonella serotypes
+ Cancer, excluding non-melanoma ! Brucellosis Paratyphi A, Paratyphi B, and Paratyphi C)
skin cancer and including benign and
borderline intracranial and CNS California serogroup virus disease Pertussis
tumors Campylobacteriosis Pesticide-related illness and injury, acute
HIV/AIDS 407-858-1437 Carbon monoxide poisoning ! Plague
+ Acquired immune Chikungunya fever ! Poliomyelitis
deficiency syndrome (AIDS) Chikungunya fever, locally acquired Psittacosis (ornithosis)
+ Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
infection ! Cholera (Vibrio cholerae type O1) Q Fever
• HIV-exposed infants <18 months old born Ciguatera fish poisoning Rabies, animal or human
to an HIV-infected woman Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) ! Rabies, possible exposure
STDs 407-858-1445 Cryptosporidiosis ! Ricin toxin poisoning
• Chancroid Cyclosporiasis Rocky Mountain spotted fever and other
spotted fever rickettsioses
• Chlamydia ! Dengue fever
! Rubella
• Conjunctivitis in neonates <14 days old ! Diphtheria
St. Louis encephalitis
• Gonorrhea Eastern equine encephalitis
Salmonellosis
Ehrlichiosis/anaplasmosis
• Granuloma inguinale Saxitoxin poisoning (paralytic shellfish
Escherichia coli infection, Shiga toxin-
• Herpes simplex virus (HSV) in infants <60
producing
poisoning)
days old with disseminated infection and ! Severe acute respiratory disease
liver involvement; encephalitis; and Giardiasis, acute syndrome associated with coronavirus
infections limited to skin, eyes, and ! Glanders infection
mouth; anogenital HSV in children <12 ! Haemophilus influenzae invasive disease Shigellosis
years old in children <5 years old ! Smallpox
• Human papillomavirus (HPV)-associated Hansen’s disease (leprosy)
Staphylococcal enterotoxin B poisoning
laryngeal papillomas or recurrent
respiratory papillomatosis in children <6 Hantavirus infection Staphylococcus aureus infection,
years old; anogenital papillomas in Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) intermediate or full resistance to
children ≤12 years old Hepatitis A vancomycin (VISA, VRSA)
• Lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV) Streptococcus pneumoniae invasive
Hepatitis B, C, D, E, and G
disease in children <6 years old
• Syphilis Hepatitis B surface antigen in pregnant Tetanus
Syphilis in pregnant women and neonates women and children <2 years old
Trichinellosis (trichinosis)
Herpes B virus, possible exposure
Tuberculosis 407-858-1446 ! Tularemia
! Influenza A, novel or pandemic strains
Tuberculosis (TB) Influenza-associated pediatric mortality in Typhoid fever (Salmonella serotype Typhi)
All Others 407-858-1420 children <18 years old ! Typhus fever, epidemic
! Outbreaks of any disease, any case, Lead poisoning (blood lead level ! Vaccinia disease
cluster of cases, or exposure to an ≥5 µg/dL)
Varicella (chickenpox)
infectious or non-infectious disease, Legionellosis
condition, or agent found in the general Leptospirosis
! Venezuelan equine encephalitis
community or any defined setting (e.g., Vibriosis (infections of Vibrio species and
Listeriosis closely related organisms, excluding
hospital, school, other institution) not
listed that is of urgent public health Lyme disease Vibrio cholerae type O1)
significance Malaria ! Viral hemorrhagic fevers
Amebic encephalitis ! Measles (rubeola) West Nile virus disease
! Anthrax ! Melioidosis ! Yellow fever
Arsenic poisoning Meningitis, bacterial or mycotic ! Zika fever
*Subsection 381.0031(2), Florida Statutes, provides that “Any practitioner licensed in this state to practice medicine, osteopathic medicine, chiropractic medicine, naturopathy, or
veterinary medicine; any hospital licensed under part I of chapter 395; or any laboratory licensed under chapter 483 that diagnoses or suspects the existence of a disease of public
health significance shall immediately report the fact to the Department of Health.” Florida’s county health departments serve as the Department’s representative in this reporting
requirement. Furthermore, subsection 381.0031(4), Florida Statutes, provides that “The Department shall periodically issue a list of infectious or noninfectious diseases determined by
it to be a threat to public health and therefore of significance to public health and shall furnish a copy of the list to the practitioners…”
You might also like
- Thyroid Function TestDocument28 pagesThyroid Function TestDhinesh Muthusamy100% (1)
- Polyarteritis NodosaDocument36 pagesPolyarteritis NodosaAbigaleNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Infectious Disease PT 2Document7 pagesPediatric Infectious Disease PT 2Erin Whisenand100% (1)
- LIST OF PHOBIAS (Assignment in Psycho)Document70 pagesLIST OF PHOBIAS (Assignment in Psycho)Eli Joshua EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- All Pediatric Seminars - AsemDocument356 pagesAll Pediatric Seminars - AsemAsem Shadid100% (1)
- Infection in NeonateDocument28 pagesInfection in Neonateamel015No ratings yet
- Transfusion of Blood & Blood Components1Document45 pagesTransfusion of Blood & Blood Components1Chamika Huruggamuwa100% (1)
- AntibioticsDocument7 pagesAntibioticsCeleste Largo Arayan-LedesmaNo ratings yet
- Curs 12 Hiv Amg 2020Document43 pagesCurs 12 Hiv Amg 2020denisa100% (1)
- Chinese Medicine Gu ParasitesDocument8 pagesChinese Medicine Gu Parasitesnepretip100% (2)
- Infectious Disease in PregnancyDocument21 pagesInfectious Disease in PregnancyLauren McrobertsNo ratings yet
- Congenital Infections - Dr. R. Adhi Teguh SpA (K)Document65 pagesCongenital Infections - Dr. R. Adhi Teguh SpA (K)syak turNo ratings yet
- VirologyDocument24 pagesVirologyRohama Qubra 279No ratings yet
- Krizia Joy Borromeo-Galve, MD: Bulacan Medical Center, Department of PediatricsDocument84 pagesKrizia Joy Borromeo-Galve, MD: Bulacan Medical Center, Department of PediatricsTara Oliveros Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal ToothbrushDocument6 pagesProject Proposal ToothbrushARLENE AQUINONo ratings yet
- Investigatory Project 2014Document27 pagesInvestigatory Project 2014nerkerlNo ratings yet
- BlobdloadDocument1 pageBlobdloadapi-378214922No ratings yet
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)Document29 pagesHuman Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)Stiffany GlenNo ratings yet
- San Francisco Department of Public HealthDocument2 pagesSan Francisco Department of Public Healthjon elleNo ratings yet
- Notifiable Diseases and Conditions List: Telephone: 1-800-821-5821 Fax: 1-800-293-7534Document1 pageNotifiable Diseases and Conditions List: Telephone: 1-800-821-5821 Fax: 1-800-293-7534muhammad hamzaNo ratings yet
- Penyakit Virus: - Virus Dna Rna - Virus DNADocument23 pagesPenyakit Virus: - Virus Dna Rna - Virus DNAKelas BNo ratings yet
- Viral and Prion Pathogens - Hand Out 2023Document1 pageViral and Prion Pathogens - Hand Out 2023Hasan ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Common Viral Infec - Part 2Document13 pagesCommon Viral Infec - Part 2d99452727No ratings yet
- Pediatric Infectious Diseases. Vaccination ProgramsDocument44 pagesPediatric Infectious Diseases. Vaccination ProgramsShubhra PaulNo ratings yet
- TORCHDocument42 pagesTORCHKarla RosadoNo ratings yet
- Virology: Herpesviruses II: Herpes SimplexDocument4 pagesVirology: Herpesviruses II: Herpes SimplexJaz CNo ratings yet
- Infections in PregnancyDocument124 pagesInfections in Pregnancyxzfdf2mwvxNo ratings yet
- Fever With Rash 1Document52 pagesFever With Rash 1victor vampNo ratings yet
- Comm Disease Assignment 5 Handout - INFECTIOUS-DISEASE-REPORTABLE-FLYERDocument6 pagesComm Disease Assignment 5 Handout - INFECTIOUS-DISEASE-REPORTABLE-FLYERUgochi 'Gucci' NdubuisiNo ratings yet
- Fever and Rash Apcp 260818 FinalDocument69 pagesFever and Rash Apcp 260818 FinalPriscilla Putri HarmanyNo ratings yet
- Viral Skin RashesDocument26 pagesViral Skin RashesGeoffreyNo ratings yet
- Block 4B 2023 Viral Exanthems Part 2Document29 pagesBlock 4B 2023 Viral Exanthems Part 2Sabelo VictorNo ratings yet
- Measles-Rubella CRS Disease Epidemiology and Measles Case ManagementDocument26 pagesMeasles-Rubella CRS Disease Epidemiology and Measles Case Managementnavneet singhNo ratings yet
- S & T ClassDocument97 pagesS & T ClassAnish AldrinNo ratings yet
- 2.4.1-Infectious and Non-Infectious DiseasesDocument2 pages2.4.1-Infectious and Non-Infectious DiseasesCHIA YIN MEINo ratings yet
- Fever and Rash Mar 2016Document30 pagesFever and Rash Mar 2016almiraerickaiNo ratings yet
- Viral Infection Skin Diseases May - 13Document91 pagesViral Infection Skin Diseases May - 13ade setiawatiNo ratings yet
- Myco Viro Hand Out Batch2 UpdatedDocument10 pagesMyco Viro Hand Out Batch2 UpdatedMark jay LlanoNo ratings yet
- San Laz High Yield ReviewerDocument5 pagesSan Laz High Yield ReviewerKen Edward ZataNo ratings yet
- Peds - FeverDocument20 pagesPeds - FeverdryogeshrNo ratings yet
- Enterovirus: Virologi Klinik KDM 726 Pembimbing: Dr. Abu Rohiman, MS, SPMK (K)Document12 pagesEnterovirus: Virologi Klinik KDM 726 Pembimbing: Dr. Abu Rohiman, MS, SPMK (K)Daniel EdbertNo ratings yet
- Double-Stranded DNA Viruses: 1. HerpesviridaeDocument3 pagesDouble-Stranded DNA Viruses: 1. HerpesviridaeGerald John PazNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Condition Description Signs/symptoms DDX Viral InfectionsDocument40 pagesDermatology Condition Description Signs/symptoms DDX Viral InfectionsWaseem Ullah100% (1)
- Infeksi Virus Pada KehamilanDocument43 pagesInfeksi Virus Pada KehamilanAgungwiraNo ratings yet
- ParvoviridaeDocument22 pagesParvoviridaeSadam IrshadNo ratings yet
- MEASLESDocument68 pagesMEASLESMonysyha AtriNo ratings yet
- Varicella/Herpes Zoster: Communicable Disease Management ProtocolDocument5 pagesVaricella/Herpes Zoster: Communicable Disease Management Protocolyuliyanto.efendiNo ratings yet
- Tugas Mikrobiologiku Mendekati SeleseDocument5 pagesTugas Mikrobiologiku Mendekati SelesealdaNo ratings yet
- Infections of The Fetus and NewbornDocument55 pagesInfections of The Fetus and Newbornlordoftheweb100% (4)
- Viral InfectionsDocument59 pagesViral InfectionsSajin AlexanderNo ratings yet
- VirologyDocument5 pagesVirologyAmnah ✨No ratings yet
- Acute Flaccid Myelitis (AFM) PoliomyelitisDocument25 pagesAcute Flaccid Myelitis (AFM) PoliomyelitisluisNo ratings yet
- Rna Viruses: EnterovirusDocument4 pagesRna Viruses: EnterovirusYeshaa MiraniNo ratings yet
- Large Single Ulcer of The Prepuce: Ulkus Durum DG Ulkus Di KGB InguinalDocument43 pagesLarge Single Ulcer of The Prepuce: Ulkus Durum DG Ulkus Di KGB InguinalAyen AlingNo ratings yet
- Meningitis Clinical Presentation - History, Physical Examination, ComplicationsDocument11 pagesMeningitis Clinical Presentation - History, Physical Examination, ComplicationsdilaNo ratings yet
- Meningitis Clinical Presentation - History, Physical Examination, ComplicationsDocument11 pagesMeningitis Clinical Presentation - History, Physical Examination, ComplicationsdilaNo ratings yet
- Herpes Viruses LectureDocument46 pagesHerpes Viruses Lectureapi-19969058100% (1)
- Salivary Gland InfectionsDocument12 pagesSalivary Gland InfectionsRabina PantaNo ratings yet
- Bovine Viral Diarrhoea: BVD Is A Sub Acute, Acute or INAPPARENT Contagious Disease Characterized byDocument27 pagesBovine Viral Diarrhoea: BVD Is A Sub Acute, Acute or INAPPARENT Contagious Disease Characterized byhari krishnaa athotaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Presentation and ManagementDocument60 pagesClinical Presentation and Managementar_thikaNo ratings yet
- Inrauterine InfectionsDocument83 pagesInrauterine Infectionsahmad aminNo ratings yet
- Reportable DiseasesDocument4 pagesReportable Diseasesadityarajawat720No ratings yet
- CYRUSSDocument13 pagesCYRUSSRienna Marie HentoloroNo ratings yet
- Oportunistic InfectionDocument20 pagesOportunistic InfectionIsman SandiraNo ratings yet
- Pir 37-12 Enterovirus PPT Final PDFDocument10 pagesPir 37-12 Enterovirus PPT Final PDFbentoeNo ratings yet
- Pir 37-12 Enterovirus PPT Final PDFDocument10 pagesPir 37-12 Enterovirus PPT Final PDFbentoeNo ratings yet
- Feline Immunodeficiency Virus: From Diagnosis to Well-being for Cats with FIVFrom EverandFeline Immunodeficiency Virus: From Diagnosis to Well-being for Cats with FIVNo ratings yet
- The Complete Guide To HIV / AIDs: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Risks, Treatments & SupportFrom EverandThe Complete Guide To HIV / AIDs: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Risks, Treatments & SupportNo ratings yet
- Kenyan Medical CertificateDocument3 pagesKenyan Medical CertificateIsrael JacksonNo ratings yet
- Common Injuries Sports Pe Q1 Day 3Document20 pagesCommon Injuries Sports Pe Q1 Day 3Jerry Jeroum RegudoNo ratings yet
- NURS 6512 Advanced Health Assessment FInal ExamDocument19 pagesNURS 6512 Advanced Health Assessment FInal ExamtroillerdrippyNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Infertility ProjectDocument6 pagesBIOLOGY Infertility ProjectSOUMYADEEP BHUINYA100% (1)
- Research 2Document14 pagesResearch 2annaliza cabañogNo ratings yet
- MANIFESTASI KLINIK Penyakit Jantung KoronerDocument4 pagesMANIFESTASI KLINIK Penyakit Jantung KoronerDwitya NoviariNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 5Document9 pagesJurnal 5Nuzulia KhoirilliqoNo ratings yet
- Maryville NURS 623 ExamDocument14 pagesMaryville NURS 623 ExamWizzardNo ratings yet
- GR Courseagenda Vs4Document6 pagesGR Courseagenda Vs4Βασίλης ΦραγκιαδάκηςNo ratings yet
- (2192021123313 PM) Sasolmed Member Guide 2021 - Updated 15 FebDocument82 pages(2192021123313 PM) Sasolmed Member Guide 2021 - Updated 15 FebLenox D LengauNo ratings yet
- Sistematika ParasitDocument30 pagesSistematika ParasitFatmawati NadhyaNo ratings yet
- E-Circular: Staff:: Award Policies Regarding Transfer/PostingDocument22 pagesE-Circular: Staff:: Award Policies Regarding Transfer/Postingrahulthapa403No ratings yet
- STS - MODULE1 - Answer SheetsDocument8 pagesSTS - MODULE1 - Answer SheetsRamil VillacarlosNo ratings yet
- Study Guide of Medical Parasitology, Part 1. ProtozoologyDocument50 pagesStudy Guide of Medical Parasitology, Part 1. Protozoologymicrobehunter007No ratings yet
- Stretch Mark PowerpointDocument14 pagesStretch Mark Powerpointdhaval88No ratings yet
- Study On Urbanization People Mobility Inclusive Development FINALDocument182 pagesStudy On Urbanization People Mobility Inclusive Development FINALBrenda Shania LombuNo ratings yet
- 10 Tips To Prevent Spreading Impetigo, and Avoid Getting It AgainDocument2 pages10 Tips To Prevent Spreading Impetigo, and Avoid Getting It Againputri aisheNo ratings yet
- (BS en 16616) - Chemical Disinfectants and Antiseptics. Chemical-Thermal Textile Disinfection. Test Method and Requirements (Phase 2, Step 2)Document35 pages(BS en 16616) - Chemical Disinfectants and Antiseptics. Chemical-Thermal Textile Disinfection. Test Method and Requirements (Phase 2, Step 2)Muhamad Zaky100% (1)
- MCQ 1Document5 pagesMCQ 1DrPreeti Thakur ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Physiology and Injuries in Sports: Unit - 7Document33 pagesPhysiology and Injuries in Sports: Unit - 7Vansh GoyalNo ratings yet
- Washed Red Cells: Theory and Practice: Review ArticleDocument11 pagesWashed Red Cells: Theory and Practice: Review Articlemy accountNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Interventio N Rationale Evaluatio N SubjectiveDocument58 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Interventio N Rationale Evaluatio N SubjectiveJemina Rafanan RacadioNo ratings yet