ME18703 – ASSIGNMENT II
Last Date to submit : 20-09-2023
1. Given two single-pole switches, write a program that will turn on an output when both
switch A and switch B are closed.
2. Given two single-pole switches, write a program that will turn on an output when either
switch A or switch B is closed.
3. Given four NO (Normally Open) pushbuttons (A,B,C and D), write a program that will turn a
lamp on if pushbuttons A and B or C and D are closed.
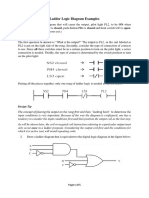
4. Write a program for the relay ladder diagram shown in Figure
5. A personal computer is to be used to program several different PLCs from different
manufacturers. What would be required?
6. Express the decimal number 18 in each of the following number codes:
a. Binary
b. Octal
c. Hexadecimal
d. BCD
7. Express each of the following equations as a ladder logic program:
8. Write the ladder logic program, draw the logic gate circuit, and state the Boolean equation
for the two relay ladder diagrams in Figure
9. State the logic instruction you would use when you want to:
a. Know when one or both matching bits in two different words are 1.
b. Reverse the state of bits in a word.
c. Know when matching bits in two different words are both 1.
� d. Know when one or the other bit of matching bits, but not both, in two different
words is 1.
10. For the logic gate circuit shown in Figure:
a. Determine the Boolean equation.
b. Draw an equivalent ladder logic program for the gate circuit.
11. For the logic gate circuit shown in Figure:
a. Determine the Boolean equation.
b. Draw an equivalent ladder logic program for the gate circuit
12. It is required to have a pilot light come on when all of the following circuit requirements
are met:
• All four circuit pressure switches must be closed.
• At least two out of three circuit limit switches must be closed.
• The reset switch must not be closed.
Using AND, OR, and NOT gates, design a logic circuit that will solve this hypothetical
problem.
13. Write the Boolean equation for the logic gate circuit shown in Figure
14. Write the Boolean equation for the logic gate circuit shown in Figure
15. Write the Boolean equation for the logic gate circuit shown in Figure
�16. Write the Boolean equation for the logic gate circuit shown in Figure
17. Write the Boolean equation for the logic gate circuit shown in Figure
18. Write the Boolean equation for the logic gate circuit shown in Figure
19. The logic circuit of Figure is used to activate an alarm when its output Y is logic HIGH or 1.
Draw a truth table for the circuit showing the resulting output for all 16 of the possible
input conditions.
� 20. What will be the data stored in the destination address of Figure 4-33 for each of the
following logical operations?
a. AND operation
b. OR operation
c. XOR operation
21. Write the Boolean expression and draw the gate logic diagram and typical PLC ladder logic
diagram for a control system wherein a fan is to run only when all of the following
conditions are met:
• Input A is OFF
• Input B is ON or input C is ON, or both B and C are ON
• Inputs D and E are both ON
• One or more of inputs F, G, or H are ON
22. List the five standard PLC languages as defined by the International Standard for
Programmable Controllers, and give a brief description of each.
23. Outline the sequence of events involved in a PLC scan cycle.
24. Draw the symbol and state the equivalent instruction for each of the following: NO contact,
NC contact, and coil.
25. Answer the following with regard to the Examine If Closed instruction:
a. What is another common name for this instruction?
b. What is this instruction asking the processor to examine?
c. Under what condition is the status bit associated with this instruction 0?
d. Under what condition is the status bit associated with this instruction 1?
e. Under what condition is this instruction logically true?
f. What state does this instruction assume when it is false?
26. Answer the following with regard to the Examine If Open instruction:
a. What is another common name for this instruction?
b. What is this instruction asking the processor to examine?
c. Under what condition is the status bit associated with this instruction 0?
d. Under what condition is the status bit associated with this instruction 1?
e. Under what condition is this instruction logically true?
� f. What state does this instruction assume when it is false?
27. Answer the following with regard to the Output Energize instruction:
a. What part of an electromagnetic relay does this instruction look and act like?
b. What is this instruction asking the processor to do?
c. Under what condition is the status bit associated with this instruction 0?
d. Under what condition is the status bit associated with this instruction 1?
28. A normally closed pushbutton is connected to a PLC discrete input. Does this mean it must be
represented by a normally closed contact in the ladder logic program? Explain why or why
not.
29. Answer the following with regard to a ladder logic rung:
a. Describe the basic makeup of a ladder logic rung.
b. How are the contacts and coil of a rung identified?
c. When is the ladder rung considered as having logic continuity?
30. What does the address assigned to an instruction indicate?
31. When are input branch instructions used as part of a ladder logic program?
32. A normally open limit switch is to be programmed to control a solenoid. What determines
whether an Examine-on or Examine-off contact instruction is used?
33. Electrical devices and signals can be divided into two categories: analog and digital. What is
the major difference between these two categories?
34. Compare the way memory space is assigned and referenced in rack-based and tag-based
PLCs.
35. Figure shows the sketch of a continuous filling operation. This process requires that boxes
moving on a conveyor be automatically positioned and filled. The sequence of operation for
the continuous filling operation is as follows:
a. Start the conveyor when the start button is momentarily pressed.
b. Stop the conveyor when the stop button is momentarily pressed.
c. Energize the run status light when the process is operating.
d. Energize the standby status light when the process is stopped.
e. Stop the conveyor when the right edge of the box is first sensed by the
photosensor.
f. With the box in position and the conveyor stopped, open the solenoid valve and
allow the box to fill. Filling should stop when the level sensor goes true.
g. Energize the full light when the box is full. The full light should remain energized
until the box is moved clear of the photosensor.
�36. Explain the basic operating principle of an electromagnetic control relay.
37. What is the operating difference between a normally open and a normally closed relay
contact?
38. Draw the electrical symbol used to represent each of the following switches:
a. NO pushbutton switch
b. NC pushbutton switch
c. Break-make pushbutton switch
d. Three-position selector switch
e. NO limit switch
f. NC temperature switch
g. NO pressure switch
h. NC level switch
i. NO proximity switch
39. Explain the function of each of the following actuators: a. Solenoid and b. Solenoid valve.
40. Design and draw the schematic for a conventional hardwired relay circuit that will perform
each of the following circuit functions when a normally closed pushbutton is pressed:
a. Switch a pilot light on
b. De-energize a solenoid
c. Start a motor running
d. Sound a horn
41. Design and draw the schematic for a conventional hardwired circuit that will perform the
following circuit functions using two break-make pushbuttons:
a. Turn on light L1 when pushbutton PB1 is pressed.
b. Turn on light L2 when pushbutton PB2 is pressed.
c. Electrically interlock the pushbuttons so that L1 and L2 cannot both be turned
on at the same time.
42. Study the ladder logic program in Figure, and answer the questions that follow:
a. Under what condition will the latch rung 1 be true?
b. Under what conditions will the unlatch rung 2 be true?
c. Under what condition will rung 3 be true?
d. When PL1 is on, the relay is in what state (latched or unlatched)?
e. When PL2 is on, the relay is in what state (latched or unlatched)?
f. If AC power is removed and then restored to the circuit, what pilot light will
automatically come on when the power is restored?
g. Assume the relay is in its latched state and all three inputs are false. What input
change(s) must occur for the relay to switch into its unlatched state?
h. If the examine if closed instructions at addresses I/1, I/2, and I/3 are all true,
what state will the relay remain in (latched or unlatched)?
i.
�43. Explain the difference between the timed and instantaneous contacts of a mechanical
timing relay.
44. Draw the symbol and explain the operation of each of the following timed contacts of a
mechanical timing relay:
a. On-delay timer—NOTC contact
b. On-delay timer—NCTO contact
c. Off-delay timer—NOTO contact
d. Off-delay timer—NCTC contact
45. Name five pieces of information usually associated with a PLC timer instruction.
46. When is the output of a programmed timer energized?
47. a. What are the two methods commonly used to represent a timer instruction within a
PLC’s ladder logic program?
b. Which method is preferred? Why?
48. Explain the difference between the operation of a nonretentive timer and that of a retentive
timer.
49. State three advantages of using programmed PLC timers over mechanical timing relays.
50. For a TON timer:
a. When is the enable bit of a timer instruction true?
b. When is the timer-timing bit of a timer instruction true?
c. When does the done bit of a timer change state?
51. For a TOF timer:
a. When is the enable bit of a timer instruction true?
b. When is the timer-timing bit of a timer instruction true?
c. When does the done bit of a timer change state?
52. Explain what each of the following quantities associated with a PLC timer instruction
represents:
a. Preset time
b. Accumulated time
c. Time base
53. State the method used to reset the accumulated time of each of the following:
a. a. TON timer
b. b. TOF timer
c. c. RTO timer
54. With reference to the relay schematic diagram in Figure, state the status of each light (on or
off) after each of the following sequential events: Also draw the equivalent ladder.
a. Power is first applied and switch S1 is open.
b. Switch S1 has just closed.
c. Switch S1 has been closed for 5 s.
d. Switch S1 has just opened.
e. Switch S1 has been opened for 5 s.
�55. Design a PLC program and prepare a typical I/O connection diagram and ladder logic
program that will execute this hardwired control circuit correctly.
56. Design a PLC program and prepare a typical I/O connection diagram and ladder logic
program that will correctly execute the hardwired relay control circuit shown in Figure
57. Study the ladder logic program in Figure 7-40 and answer the questions that follow:
a. What type of timer has been programmed?
b. What is the length of the time-delay period?
c. What is the value of the accumulated time when power is first applied?
d. When does the timer start timing?
e. When does the timer stop timing and reset itself?
f. When input LS1 is first closed, which rungs are true and which are false?
� g. When input LS1 is first closed, state the status (on or off) of each output.
h. When the timer’s accumulated value equals the preset value, which rungs are
true and which are false?
i. When the timer’s accumulated value equals the preset value, state the status (on
or off) of each output.
j. Suppose that rung 1 is true for 5 s and then power is lost. What will the
accumulated value of the counter be when power is restored?
58. Study the ladder logic program in Figure and answer the questions that follow:
a. What type of timer has been programmed?
b. What is the length of the time-delay period?
c. What is the value of the accumulated time when power is first applied?
d. When does the timer start timing?
e. When does the timer stop timing and reset itself?
f. When input LS1 is first closed, which rungs are true and which are false?
g. When input LS1 is first closed, state the status (on or off) of each output.
h. When the timer’s accumulated value equals the preset value, which rungs are
true and which are false?
i. When the timer’s accumulated value equals the preset value, state the status (on
or off) of each output.
j. Suppose that rung 1 is true for 5 s and then power is lost. What will the
accumulated value of the counter be when power is restored?
�59. Study the ladder logic program in Figure, and answer the questions that follow:
a. What type of timer has been programmed?
b. What is the length of the time-delay period?
c. When does the timer start timing?
d. When is the timer reset?
e. When will rung 3 be true?
f. When will rung 5 be true?
g. When will output PL4 be energized?
h. Assume that your accumulated time value is upto 020 and power to your system
is lost. What will your accumulated time value be when power is restored?
i. What happens if inputs PB1 and PB2 are both true at the same time?
�60. Study the ladder logic program in Figure and answer the questions that follow:
a. What is the purpose of interconnecting the two timers?
b. How much time must elapse before output PL is energized?
c. What two conditions must be satisfied for timer T4:2 to start timing?
d. Assume that output PL is on and power to the system is lost. When power is
restored, what will the status of this output be?
e. When input PB2 is on, what will happen?
f. When input PB1 is on, how much accumulated time must elapse before rung 3
will be true?
�61. Study the on-delay timer ladder logic program in Figure, and from each of the conditions
stated, determine whether the timer is reset, timing, or timed out or if the conditions stated
are not possible.
a. The input is true, and EN is 1, TT is 1, and DN is 0.
b. The input is true, and EN is 1, TT is 1, and DN is 1.
c. The input is false, and EN is 0, TT is 0, and DN is 0.
d. The input is true, and EN is 1, TT is 0, and DN is 1.
62. Study the off-delay timer ladder logic program in Figure, and from each of the conditions
stated, determine whether the timer is reset, timing, or timed out or if the conditions stated
are not possible.
a. The input is true, and EN is 0, TT is 0, and DN is 1.
b. The input is true, and EN is 1, TT is 1, and DN is 1.
c. The input is true, and EN is 1, TT is 0, and DN is 1.
d. The input is false, and EN is 0, TT is 1, and DN is 1.
e. The input is false, and EN is 0, TT is 0, and DN is 0.
63. Write a program to implement the process illustrated in Figure. The sequence of operation
is to be as follows:
a. Normally open start and normally closed stop pushbuttons are used to start and
stop the process.
b. When the start button is pressed, solenoid A energizes to start filling the tank.
� c. As the tank fills, the empty level sensor switch closes.
d. When the tank is full, the full level sensor switch closes.
e. Solenoid A is de-energized.
f. The agitate motor starts automatically and runs for 3 min to mix the liquid.
g. When the agitate motor stops, solenoid B is energized to empty the tank.
h. When the tank is completely empty, the empty sensor switch opens to de-
energize solenoid B.
i. The start button is pressed to repeat the sequence.
64. When the lights are turned off in a building, an exit door light is to remain on for an
additional 2 min, and the parking lot lights are to remain on for an additional 3 min after
the door light goes out. Write a program to implement this process.
65. Write a program to simulate the operation of a sequential taillight system. The light system
consists of three separate lights on each side of the car. Each set of lights will be activated
separately, by either the left or right turn signal switch. There is to be a 1-s delay between
the activation of each light, and a 1-s period when all the lights are off. Ensure that when
both switches are on, the system will not operate. Use the least number of timers possible.
The sequence of operation should be as follows:
a. The switch is operated.
b. Light 1 is illuminated.
c. Light 2 is illuminated 1 s later.
d. Light 3 is illuminated 1 s later.
e. Light 3 is illuminated for 1 s.
f. All lights are off for 1 s.
g. The system repeats while the switch is on.
66. Name the three forms of PLC counter instructions, and explain the basic operation of each.
67. State four pieces of information usually associated with a PLC counter instruction.
68. In a PLC counter instruction, what rule applies to the addressing of the counter and reset
instructions?
69. When is the output of a PLC counter energized?
70. When does the PLC counter instruction increment or decrement its current count?
�71. The counter instructions of PLCs are normally retentive. Explain what this means.
72. a. Compare the operation of a standard Examine on contact instruction with that of an off-
to-on transitional contact.
b. What is the normal function of a transitional contact used in conjunction with a counter?
73. Identify the type of counter you would choose for each of the following situations:
a. Count the total number of parts made during each shift.
b. Keep track of the current number of parts in a stage of a process as they enter
and exit.
c. There are 10 parts in a full hopper. As parts leave, keep track of the number of
parts remaining in the hopper
74. Describe the basic programming process involved in the cascading of two counters.
75. a. When is the overflow bit of an up-counter set?
b. When is the underflow bit of a down-counter set?
76. Describe two common applications for counters.
77. What determines the maximum speed of transitions that a PLC counter can count? Why?
78. Two MCR output instructions are to be programmed to control a section of a program.
Explain the programming procedure to be followed.
79. State how the status of the output devices within the fenced zone will be affected when the
MCR instruction makes a false-to-true transition.
80. State how the status of the output devices within the fenced zone will be affected when the
MCR instruction makes a true-to-false transition.
81. What is the main advantage of the jump instruction?
82. In general, what do data manipulation instructions allow the PLC to do?
83. Why are PLCs installed within an enclosure?
84. Compare continuous and batch processes.
85. State the basic function of each of the following as part of a process control system:
a. Sensors
b. Human-machine interface
c. Signal conditioning
d. Actuators
e. Controller
86. Draw a ladder diagram for 3 motor operation for following condition:
a. Start push button starts motor M1. After 15 seconds M2 and M3 starts
b. Stop push button stops M3 and after 15 seconds motor M2 and M1
87. Explain the working of PLC based Traffic light control with the help of ladder diagram.
88. Develop a ladder program explaining the use of Latching Relay.
89. Explain the ladder program of water level controller
90. Explain the working of PLC based bottle filling system with the help of ladder Diagram.
91. Develop a ladder diagram for ON/OFF temperature control.
92. Develop the ladder diagram for stepper motor control.
93. Write the ladder program for 24 hour clock.
94. Draw a PLC wiring diagram for control of a lamp from 2 switches.
95. Draw the off delay timer instruction with waveforms.
96. Draw the symbols of following relay type instructions. i) IF-OPEN ii) IF –CLOSE
97. Draw the ladder program for verifying the XOR logic.
98. Draw and explain ladder diagram for AND operation.
99. What are the logic functions used for switches (a) in series, (b) in parallel?
�100. Draw the ladder rungs to represent:
a. two switches are normally open and both have to be closed for a motor to
operate;
b. either of two, normally open, switches have to be closed for a coil to be
energised and operate an actuator;
c. a motor is switched on by pressing a spring-return push-button start switch, and
the motor remains on until another spring-return push-button stop switch is
pressed.
101. Write the program instructions corresponding to the latch program shown in Figure.
102. Write the program instructions for the program in Figure and state how the output varies
with time.
103. Write the program instructions corresponding to the program in Figure and state the
results of inputs to the PLC.
104. Devise a timing circuit that will switch on an output for 1 s then off for 20 s, then on for 1
s, then off for 20 s, and so on.
105. Devise a timing circuit that will switch on an output for 10 s then switch it off.
106. Devise a circuit that can be used to start a motor and then after a delay of 100 s start a
pump. When the motor is switched off there should be a delay of 10 s before the pump is
switched off.
107. Devise a circuit that could be used with a domestic washing machine to switch on a pump
to pump water for 100 s into the machine, then switch off and switch on a heater for 50 s
to heat the water. The heater is then switched off and another pump is to empty the water
from the machine for 100 s.
108. Devise a circuit that could be used with a conveyor belt which is used to move an item to a
work station. The presence of the item at the work station is detected by means of
breaking a contact activated by a beam of light to a photosensor. There the item stops for
100 s for an operation to be carried out before moving on and off the conveyor. The motor
� for the belt is started by a normally open start switch and stopped by a normally closed
switch.
109. Explain how a PLC can be used to handle an analogue input.
110. Devise a system, using a PLC, which can be used to control the movement of a piston in a
cylinder so that when a switch is momentarily pressed, the piston moves in one direction
and when a second switch is momentarily pressed, the piston moves in the other
direction. Hint: you might consider using a 42 solenoid-controlled valve.
111. Devise a system, using a PLC, which can be used to control the movement of a piston in a
cylinder using a 42 solenoid-operated pilot valve. The piston is to move in one direction
when a proximity sensor at one end of the stroke closes contacts and in the other
direction when a proximity sensor at the other end of the stroke indicates its arrival there.