Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Duel Nature
Duel Nature
Uploaded by
nanditha lejeeshOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Duel Nature
Duel Nature
Uploaded by
nanditha lejeeshCopyright:
Available Formats
DUEL NATURE OF MATTER AND WAVE
Photoelectric effect Einstein's photoelectric equation
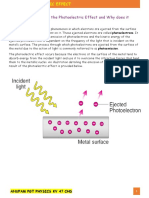
• The phenomena of emission of electrons
from a metal surface, when radiations of
suitable frequency is incident on it, is called
photoelectric effect.
• Work Function(φ) The minimum amount of
energy required to eject one electron from
a metal surface, is called its work function.
• Threshold Frequency The minimum
frequency of light which can eject photo
electron from a metal surface is called
threshold frequency of that metal.
• Threshold Wavelength (λmax) The
maximum wavelength of light which can
eject photo electron from a metal surface is
called threshold wavelength of that metal.
Photoelectric Effect
• For a given metal and frequency of incident
light, the photo electric current (the rate of
emission of photoelectrons) is directly Matter wave
proportional to the intensity of incident
light.
• For a given metal. there is a certain
minimum frequency, called threshold
frequency, below which there is no
emission of photo electrons takes place.
• Above threshold frequency the maximum Davisson and Germer experiment
kinetic energy of photo electrons depends
upon the frequency of incident light.
• The photoelectric emission is an
instantaneous process.
Stopping Potential
• The minimum negative potential given to
anode plate at which photoelectric current
becomes zero is called stopping potential (Vo).
• (Ek)max = 1 / 2 mv2max = eVo
www.anglebelearn.com +91 8594000416,+91 8594000417
You might also like
- The Photo Electric Effects: Nikhil MerothiyaDocument15 pagesThe Photo Electric Effects: Nikhil Merothiyapradeep bijarniaNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of Radiation and MatterDocument3 pagesDual Nature of Radiation and MatterMijazuddin MansooriNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of Matter and RadiationDocument14 pagesDual Nature of Matter and RadiationSRISHTI SRIVASTAVANo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of Radiation: in 1 ShotDocument64 pagesDual Nature of Radiation: in 1 ShotDisney DoreamonNo ratings yet
- Nikhil MerothiyaDocument15 pagesNikhil MerothiyaGururaj KjNo ratings yet
- Notes DualDocument13 pagesNotes DualAdarsh DhawanNo ratings yet
- Dual Nauure of Radiation and MatterDocument6 pagesDual Nauure of Radiation and Matterreet.patidar18No ratings yet
- 1.2 Photoelectric EffectDocument1 page1.2 Photoelectric EffectMd Noor HabibNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric Effect and Limitations of Classic PhysicsDocument5 pagesPhotoelectric Effect and Limitations of Classic Physics8hhznfvp2sNo ratings yet
- 4-Photoelectric EffectDocument15 pages4-Photoelectric EffectKush GuptaNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric Effect PDFDocument26 pagesPhotoelectric Effect PDFSabbirNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric EffectDocument15 pagesPhotoelectric EffectHimanshu YadavNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric Effect: Engy DiabDocument34 pagesPhotoelectric Effect: Engy DiabHazem DiabNo ratings yet
- Dr. Shilpi Banerjee (Photo Electric Effect)Document15 pagesDr. Shilpi Banerjee (Photo Electric Effect)shashank mishraNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric EffectDocument9 pagesPhotoelectric Effecthandy moseyNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS CLASS 12 Module 54Document19 pagesPHYSICS CLASS 12 Module 54Mahi SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Dualisme Cahaya Sebagai Gelombang Dan Partikel: Wave Properties Light IntensityDocument31 pagesDualisme Cahaya Sebagai Gelombang Dan Partikel: Wave Properties Light IntensityTitis AndriawanNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric EffectDocument15 pagesPhotoelectric EffectAjlaNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric EffectDocument5 pagesPhotoelectric EffectUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument14 pagesPhysicssindhupraveen78No ratings yet
- Photoelectric EffectDocument7 pagesPhotoelectric EffectSuleiman MkuluNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Photoelectric EffectDocument13 pagesLecture 2 Photoelectric Effecttoobazufiqar81No ratings yet
- Photo Electric Effect NotesDocument11 pagesPhoto Electric Effect NotesChitransh AwasthiNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter: Max ArgDocument7 pagesDual Nature of Radiation and Matter: Max ArgPrerna AroraNo ratings yet
- 11 Dual NatureDocument14 pages11 Dual NatureRavindar PurohitNo ratings yet
- Physics-Dualnatureofradiationandmatte 97611Document10 pagesPhysics-Dualnatureofradiationandmatte 97611user 003No ratings yet
- PPPPPPeDocument13 pagesPPPPPPeAyushNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of Radiation (PDF - Io)Document8 pagesDual Nature of Radiation (PDF - Io)kingbossff16No ratings yet
- Photoelectric EffectDocument7 pagesPhotoelectric EffectAnushka Jaiswal100% (1)
- Hsslive - Plus Two Chapter 11 - 2024Document11 pagesHsslive - Plus Two Chapter 11 - 2024aniesbegumNo ratings yet
- Dual MatterDocument3 pagesDual Matteraadiv2012006No ratings yet
- Dual Nature of Radiation and MatterDocument35 pagesDual Nature of Radiation and MattersomarshidubeyNo ratings yet
- QPhysics-Lab 1 - Photoelectric EffectDocument2 pagesQPhysics-Lab 1 - Photoelectric EffectEvariste MigaboNo ratings yet
- Dual NatureDocument87 pagesDual Naturemeow meowNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric EffectDocument9 pagesPhotoelectric Effectnapnom22No ratings yet
- PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT yDocument17 pagesPHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT ynidhikoshaliaNo ratings yet
- Physics Project: Photoelectric EffectDocument20 pagesPhysics Project: Photoelectric EffectAnonymous 3CivXAHALiNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation-1Document10 pagesDual Nature of Matter and Radiation-1Aaditya Divyam100% (1)
- Photoelectric EffectDocument14 pagesPhotoelectric EffectTamilselvan BaskaranNo ratings yet
- Intro, Electron Emission and Photoelectric EffectDocument12 pagesIntro, Electron Emission and Photoelectric EffectSattiki DasNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 Einstein Theory of Photoelectric EffectDocument12 pagesLec 3 Einstein Theory of Photoelectric EffectThis Is Me.No ratings yet
- 1515015-Dual Nature of Matter and RadiationDocument12 pages1515015-Dual Nature of Matter and RadiationMohit SahuNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument30 pagesNotessureshmohanty.sailNo ratings yet
- UNIT - 7 Photo Electric Effect and Dual NatureDocument12 pagesUNIT - 7 Photo Electric Effect and Dual NatureSahil ChawlaNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric EffectDocument10 pagesPhotoelectric EffectSalman ArshadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Photoelectric Effect2Document40 pagesChapter 3 Photoelectric Effect2moxsueNo ratings yet
- 11.dual Nature of Radiation and Matter13Document11 pages11.dual Nature of Radiation and Matter13ROHANNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature, Radiation and Matter. Byju'sDocument83 pagesDual Nature, Radiation and Matter. Byju'sGaurav BhandariNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Wave FunctionDocument32 pagesLecture 2 - Wave FunctionTYSON PETRO JONATHANNo ratings yet
- G482 Mod 5 2.5.2 The Photoelectric EffectDocument8 pagesG482 Mod 5 2.5.2 The Photoelectric EffectAmberNo ratings yet
- Photo Electric EffectDocument8 pagesPhoto Electric EffectRahul SoodNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of Radiation and MatterDocument6 pagesDual Nature of Radiation and Mattersub100% (1)
- Manan Vyas - XII A2Document14 pagesManan Vyas - XII A2samplghNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 PhotocellDocument6 pagesExperiment 1 Photocellalbara83% (6)
- The Photoelectric Effect (Notes)Document10 pagesThe Photoelectric Effect (Notes)Chathumi LelwalaNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation: Most Important Questions & MindmapDocument484 pagesDual Nature of Matter and Radiation: Most Important Questions & Mindmaprajeshgandla68No ratings yet
- Dual Nature of Matter and RadiationDocument12 pagesDual Nature of Matter and RadiationGaurvi AroraNo ratings yet
- Optical Sources, Detectors, and Systems: Fundamentals and ApplicationsFrom EverandOptical Sources, Detectors, and Systems: Fundamentals and ApplicationsNo ratings yet