Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Geosynthetics
Uploaded by
Angelika DuszyńskaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Geosynthetics
Uploaded by
Angelika DuszyńskaCopyright:
Available Formats
E1-12 GEOSYNTHETICS
Environmental aspects
Geosynthetics are applied in solving hydrotechnical and geomechanical tasks in construction.
Geosynthetics include synthetic polymeric materials: HDPE, LDPE, polypropylenic and
polyesther fibres, sometimes impregnated with bitumen or betonite, and in this latter case they
are called geocomposits.
Geosynthetics are products in the field of construction and they can be said to «protect the
environment, as they reduce soil erosion, reduce the consumption of natural resources (stone,
clay, gravel) and protect groundwaters from consequences of improper waste disposal. In terms
of these special criteria geosynthetics include also plastic-coated wire-grids, if they are used to
protect from erosion, e.g. hydrocrops (specially prepared autonomous nutritive layers sown
with special food crops) and gabion structures (specially reinforced wire gabions combined
with horizontal meshes, e.g. the Terramesh System), that are filled with stone material, while it
is environmentally especially advantageous if material directly from the building site, e.g.
sandstone, can be used.
With regard to environmental impact, erosion protection systems have been assessed very
favourably, particularly when they are applied in road cuttings on karst ground, and in some
slopes (examples in Italy – ecological «green» construction measures in nature).
Landfill insulation represent a rather complex hydrotechnical application of geosynthetics:
usually at least three geomembranes are utilised, geotextiles in the mechanically protected layer
and in the filter and drainage layer as well as in the drainage layer.
In view of general environmental commitments, as well as within the framework of preserving
potable water reserves, application of geosynthetics will be relevant in the remediation of
«temporary» waste disposal sites.
Requirements
When using geosynthetics, regular/common building practices in line with the General
technical requirements for road works, Zagreb, 1989, have to be applied, while for the
development and remediation of solid waste landfills the Technical requirements with regard to
geomembranes, geotextile and the detection system for Jakuševac landfill, ZGOS, IGH, Golder
Ass., Zagreb, 2000, as well as all standards and working procedures therein indicated.
If the previous basic requirements have been met, the procedure of applying for the
Environmentally Friendly label for Geosynthetics may be initiated by the manufacturer,
supplier (importer), designer-consultant-building supervisor and contractor, if their products or
services were included in the technical execution of structures, through the integration of
- a minimum of 2.0 mill. m2 of geotextiles,
- a minimum of 0.2 mill. m2 of geomeshes, or
- a minimum of 0.2 mill. m2 of geomembranes,
provided that
- the durability of Geosynthetics under the prescribed application requirements corresponds
to a minimum of 40 years,
provided that
- at solid waste landfill sealing by geomembrane application a minimum of 0.3 m3 less clay
per m2 landfill surface area was utilised as compared to sealing with clay layers only,
provided that
- by application of geotextile and geomeshes at embankment construction under
unsatisfactory base soil conditions (e.g. excessive humidity) a minimum of 0.2 m2 of stone
and gravel material per section m2 can be saved,
provided that
- at embankment construction under unsatisfactory base soil conditions removal of a
minimum of 0.3 m3 of earth material per m2 can be avoided.
If the application for the environmental label is submitted by the manufacturer or supplier of
Geosynthetics, the applicant is required to be IGS member (International Geosynthetics
Society) and certified in line with ISO 9000 or ISO 14000 standard.
Geosynthetics production has to be coordinated with all environmental regulations (protection
of water, soil, air; waste management; working environment) and other specific regulations
including individual provisions related to the environment.
You might also like
- Eco-efficient Rendering Mortars: Use of Recycled MaterialsFrom EverandEco-efficient Rendering Mortars: Use of Recycled MaterialsNo ratings yet
- Geo SyntheticsDocument32 pagesGeo SyntheticsI_am_Pallavi100% (1)
- GeoTextiles PDFDocument6 pagesGeoTextiles PDFAsım DavulcuNo ratings yet
- Geosynthetic S:-Its Recent Advancement S& Application: by Karamjeet ChahalDocument12 pagesGeosynthetic S:-Its Recent Advancement S& Application: by Karamjeet ChahalSudip GhimireNo ratings yet
- Dreno Tex PDFDocument10 pagesDreno Tex PDFvranceanu.ovidiu-1No ratings yet
- Prepared By: Saurabh Shah Code: 1710Document58 pagesPrepared By: Saurabh Shah Code: 1710Openheart Janardan KumarNo ratings yet
- J. K. Gupta, Scientist D', Bureau of Indian Standards: Standardization in The Field of GeotechDocument27 pagesJ. K. Gupta, Scientist D', Bureau of Indian Standards: Standardization in The Field of GeotechBiren ShethNo ratings yet
- Geo-Syntherics - Asheka C K and Sharmah C VDocument44 pagesGeo-Syntherics - Asheka C K and Sharmah C VC.V. SHARMAHNo ratings yet
- Unit 1BDocument107 pagesUnit 1BNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Geosynthetics: Prepared By: Saurabh Shah Code: 1710Document58 pagesGeosynthetics: Prepared By: Saurabh Shah Code: 1710Govendan GopalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Geo in HighwayDocument13 pagesGeo in HighwayPradeepBansalNo ratings yet
- Geo-Syntherics - Asheka C K and Sharmah C VDocument44 pagesGeo-Syntherics - Asheka C K and Sharmah C VC.V. SHARMAHNo ratings yet
- 7sec.700 (Geosynthetics)Document10 pages7sec.700 (Geosynthetics)e_manpreetNo ratings yet
- Building Materials From Waste: Karin Weimann, Lutz B. Giese, Gu Nter Mellmann and Franz-Georg SimonDocument4 pagesBuilding Materials From Waste: Karin Weimann, Lutz B. Giese, Gu Nter Mellmann and Franz-Georg Simonhasnath kpNo ratings yet
- What Are Geosynthetics?Document23 pagesWhat Are Geosynthetics?Kapil SoniNo ratings yet
- Bentofix Case StudiesDocument6 pagesBentofix Case StudiesDhananjay ShahNo ratings yet
- Geo Textiles: Kavitha Rajan, Lecturer in Textile and Apparel Fashion Technology, Ethiopian Technical University EthiopiaDocument35 pagesGeo Textiles: Kavitha Rajan, Lecturer in Textile and Apparel Fashion Technology, Ethiopian Technical University EthiopiaBebi WakaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5BDocument28 pagesUnit 5BNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Geosynthetics: Prepared By: Bishal Chakrabort Roll No: 1701604Document21 pagesGeosynthetics: Prepared By: Bishal Chakrabort Roll No: 1701604kalpa vrikshaNo ratings yet
- AGGE ClassroomDocument71 pagesAGGE ClassroomShashank VayfalNo ratings yet
- The Use of Geosynthetics in Road ConstructionDocument47 pagesThe Use of Geosynthetics in Road ConstructionPaulo Nascimento100% (2)
- InTech-Landscape Engineering Protecting Soil and Runoff StormwaterDocument26 pagesInTech-Landscape Engineering Protecting Soil and Runoff Stormwaterm.aminNo ratings yet
- Reinforced SoilDocument26 pagesReinforced SoilArun VenugopalanNo ratings yet
- A Review On Jute Geotextile - Part 1Document9 pagesA Review On Jute Geotextile - Part 1esatjournalsNo ratings yet
- Presentation Outline: IntoductionDocument30 pagesPresentation Outline: IntoductionssdssNo ratings yet
- Textiles 02 00011 v2Document20 pagesTextiles 02 00011 v2Alejandro MerinoNo ratings yet
- IGS - Geosynthetics Functions PDFDocument2 pagesIGS - Geosynthetics Functions PDFMauricio De Stefani100% (1)
- Mejor ProjectDocument11 pagesMejor ProjectPavani MaliNo ratings yet
- A Material Which Started A New Era in Geotechnical Engineering GeosyntheticsDocument21 pagesA Material Which Started A New Era in Geotechnical Engineering GeosyntheticsApoorva AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Types of GeosyntheticsDocument8 pagesTypes of Geosyntheticsvadlamani7No ratings yet
- Geosynthetics PGDocument51 pagesGeosynthetics PGRonald KahoraNo ratings yet
- Role of GeotextDocument13 pagesRole of GeotextSougata DasNo ratings yet
- The Useof Geosyntheticsin RoadconstructionDocument47 pagesThe Useof Geosyntheticsin RoadconstructionJohn Francis PedrosoNo ratings yet
- Ingenieria HidraulicaDocument24 pagesIngenieria HidraulicaEiber Guarachi SilvaNo ratings yet
- Geotextiles PDFDocument1 pageGeotextiles PDFvaradsalkeNo ratings yet
- Geosynthetic Lining System For Modern Waste Facilities - Experiences in Developing AsiaDocument8 pagesGeosynthetic Lining System For Modern Waste Facilities - Experiences in Developing AsiaSweetyy KumariNo ratings yet
- Geomembrane - WikipediaDocument5 pagesGeomembrane - WikipediaMrutyunjaya BeheraNo ratings yet
- Geosynthetics: Geosynthetics Are Synthetic Products Used To Stabilize Terrain. TheyDocument7 pagesGeosynthetics: Geosynthetics Are Synthetic Products Used To Stabilize Terrain. TheyJakka hitheshiniNo ratings yet
- Welded Geogrids Triaxial Geogrids Biaxial Geogrids Uniaxial GeogridsDocument5 pagesWelded Geogrids Triaxial Geogrids Biaxial Geogrids Uniaxial Geogridsaira babehisNo ratings yet
- Processes 11 00125 v2 PDFDocument20 pagesProcesses 11 00125 v2 PDFhamiss tsumaNo ratings yet
- Polymer Materials From Recycled Plastic in Road ConstructionDocument7 pagesPolymer Materials From Recycled Plastic in Road ConstructionYuv RajNo ratings yet
- Geosynthetics: Presented By: G.MahendranathDocument20 pagesGeosynthetics: Presented By: G.MahendranathMahendra108No ratings yet
- Recycled Plastic Used in Concrete Paver BlockDocument3 pagesRecycled Plastic Used in Concrete Paver BlockInternational Journal of Research in Engineering and TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Geo SyntheticsDocument20 pagesGeo SyntheticsPradeepBansalNo ratings yet
- Recycled Plastic Aggregates in Manufacturing of Insulating MortarsDocument7 pagesRecycled Plastic Aggregates in Manufacturing of Insulating MortarsBasil Baby-PisharathuNo ratings yet
- TN-DT-019 - ENG - Carbon Footprint of DT Products - Rev. 4 PDFDocument11 pagesTN-DT-019 - ENG - Carbon Footprint of DT Products - Rev. 4 PDFszemianNo ratings yet
- Daño Inducido Por Áridos Reciclados en El Comportamiento A La Tracción A Corto Plazo de Un Geotextil de Alta ResistenciaDocument8 pagesDaño Inducido Por Áridos Reciclados en El Comportamiento A La Tracción A Corto Plazo de Un Geotextil de Alta Resistenciamanuel velasquez camposNo ratings yet
- KHRI-Webinar (16-05-2020) - Intro-geosynthetics-Prof - Rajagopal (IITM) - Sankar V AD, KHRIDocument68 pagesKHRI-Webinar (16-05-2020) - Intro-geosynthetics-Prof - Rajagopal (IITM) - Sankar V AD, KHRIAmit Rajendra Phadatare100% (1)
- Geo Textiles in TransportationDocument26 pagesGeo Textiles in Transportationvasanth patelNo ratings yet
- Green ConcreteDocument17 pagesGreen Concreteapi-3766593100% (2)
- Eg4 326Document99 pagesEg4 326niharika meena100% (1)
- 2069 Mapelastic Foundation GB NoRestrictionDocument4 pages2069 Mapelastic Foundation GB NoRestrictionFloorkitNo ratings yet
- Handbook of GeosyntheticsDocument76 pagesHandbook of GeosyntheticsRavindra Subramaniam KashyapNo ratings yet
- Geomembranes Concept 2-3 ExportDocument8 pagesGeomembranes Concept 2-3 ExportJoel CristobalNo ratings yet
- Define GeosyntheticsDocument3 pagesDefine GeosyntheticsRalph Lauren RodriguezNo ratings yet
- J Conbuildmat 2017 02 107Document7 pagesJ Conbuildmat 2017 02 107Jerson SotoNo ratings yet
- Nano Technology Asphalt PavementDocument13 pagesNano Technology Asphalt PavementwillypraviantoNo ratings yet
- Geotessili IngDocument15 pagesGeotessili IngSathiya SeelanNo ratings yet
- 2608 Planitop Fast 330 Uk NoRestrictionDocument4 pages2608 Planitop Fast 330 Uk NoRestrictionFloorkitNo ratings yet
- Soil Stabilization Using Plastic FiberDocument4 pagesSoil Stabilization Using Plastic FiberIJSTENo ratings yet
- National Anthems of Selected Countries: Country: United States of America Country: CanadaDocument6 pagesNational Anthems of Selected Countries: Country: United States of America Country: CanadaHappyNo ratings yet
- SLA in PEGA How To Configue Service Level Agreement - HKRDocument7 pagesSLA in PEGA How To Configue Service Level Agreement - HKRsridhar varmaNo ratings yet
- Amount of Casien in Diff Samples of Milk (U)Document15 pagesAmount of Casien in Diff Samples of Milk (U)VijayNo ratings yet
- Delonghi Esam Series Service Info ItalyDocument10 pagesDelonghi Esam Series Service Info ItalyBrko BrkoskiNo ratings yet
- Teaching Profession - Educational PhilosophyDocument23 pagesTeaching Profession - Educational PhilosophyRon louise PereyraNo ratings yet
- Wner'S Anual: Led TVDocument32 pagesWner'S Anual: Led TVErmand WindNo ratings yet
- Activity Title: Learning Targets: Reference (S)Document5 pagesActivity Title: Learning Targets: Reference (S)Jhev LeopandoNo ratings yet
- Sandstorm Absorbent SkyscraperDocument4 pagesSandstorm Absorbent SkyscraperPardisNo ratings yet
- SSP 237 d1Document32 pagesSSP 237 d1leullNo ratings yet
- Delusion in SocietyDocument2 pagesDelusion in SocietyGasimovskyNo ratings yet
- Performance Task 1Document3 pagesPerformance Task 1Jellie May RomeroNo ratings yet
- Clockwork Dragon's Expanded ArmoryDocument13 pagesClockwork Dragon's Expanded Armoryabel chabanNo ratings yet
- Oxford EAP B1 Pre-Intermediate Student - S Book 2Document167 pagesOxford EAP B1 Pre-Intermediate Student - S Book 2Thư Dương Thị AnhNo ratings yet
- Toeic: Check Your English Vocabulary ForDocument41 pagesToeic: Check Your English Vocabulary ForEva Ibáñez RamosNo ratings yet
- ML Ass 2Document6 pagesML Ass 2Santhosh Kumar PNo ratings yet
- Catify To Satisfy - Simple Solutions For Creating A Cat-Friendly Home (PDFDrive)Document315 pagesCatify To Satisfy - Simple Solutions For Creating A Cat-Friendly Home (PDFDrive)Paz Libros100% (2)
- Quarter 1-Week 2 - Day 2.revisedDocument4 pagesQuarter 1-Week 2 - Day 2.revisedJigz FamulaganNo ratings yet
- Cyber Briefing Series - Paper 2 - FinalDocument24 pagesCyber Briefing Series - Paper 2 - FinalMapacheYorkNo ratings yet
- 50114a Isolemfi 50114a MonoDocument2 pages50114a Isolemfi 50114a MonoUsama AwadNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Public Health ManagementDocument3 pagesFundamentals of Public Health ManagementHPMA globalNo ratings yet
- Meno's Paradox of Inquiry and Socrates' Theory of RecollectionDocument10 pagesMeno's Paradox of Inquiry and Socrates' Theory of RecollectionPhilip DarbyNo ratings yet
- Week-3-Q1-Gen Chem-Sep-11-15-DllDocument12 pagesWeek-3-Q1-Gen Chem-Sep-11-15-DllJennette BelliotNo ratings yet
- 20-Admission of PatientDocument3 pages20-Admission of Patientakositabon100% (1)
- DBMS Lab ManualDocument57 pagesDBMS Lab ManualNarendh SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Economic Review English 17-18Document239 pagesEconomic Review English 17-18Shashank SinghNo ratings yet
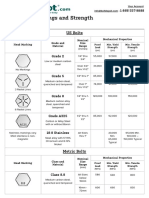
- Bolt Grade Markings and Strength ChartDocument2 pagesBolt Grade Markings and Strength ChartGregory GaschteffNo ratings yet
- Durex 'S Marketing Strategy in VietnamDocument45 pagesDurex 'S Marketing Strategy in VietnamPham Nguyen KhoiNo ratings yet
- Evolution Army 3 R DadDocument341 pagesEvolution Army 3 R DadStanisław DisęNo ratings yet
- 01 托福基础课程Document57 pages01 托福基础课程ZhaoNo ratings yet
- PC Model Answer Paper Winter 2016Document27 pagesPC Model Answer Paper Winter 2016Deepak VermaNo ratings yet
- 2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersFrom Everand2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Digital Filmmaking: The Ultimate Guide to Web Video Production for Beginners and Non-Professionals, Learn Useful Tips and Advice on How You Can Create, Film and Edit Your VideosFrom EverandDigital Filmmaking: The Ultimate Guide to Web Video Production for Beginners and Non-Professionals, Learn Useful Tips and Advice on How You Can Create, Film and Edit Your VideosRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionFrom EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (543)
- Electrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tFrom EverandElectrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (27)
- Programming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonFrom EverandProgramming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- INCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and ActivitiesFrom EverandINCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and ActivitiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Multiplexed Networks for Embedded Systems: CAN, LIN, FlexRay, Safe-by-Wire...From EverandMultiplexed Networks for Embedded Systems: CAN, LIN, FlexRay, Safe-by-Wire...No ratings yet
- Teach Yourself Electricity and Electronics, 6th EditionFrom EverandTeach Yourself Electricity and Electronics, 6th EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (15)
- Retro Gaming with Raspberry Pi: Nearly 200 Pages of Video Game ProjectsFrom EverandRetro Gaming with Raspberry Pi: Nearly 200 Pages of Video Game ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Analog Design and Simulation Using OrCAD Capture and PSpiceFrom EverandAnalog Design and Simulation Using OrCAD Capture and PSpiceNo ratings yet
- Conquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeFrom EverandConquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- Practical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialFrom EverandPractical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Hacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsFrom EverandHacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Current Interruption Transients CalculationFrom EverandCurrent Interruption Transients CalculationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Wearable Sensors: Fundamentals, Implementation and ApplicationsFrom EverandWearable Sensors: Fundamentals, Implementation and ApplicationsEdward SazonovNo ratings yet
- A Mind at Play: How Claude Shannon Invented the Information AgeFrom EverandA Mind at Play: How Claude Shannon Invented the Information AgeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (53)
- Empires of Light: Edison, Tesla, Westinghouse, and the Race to Electrify the WorldFrom EverandEmpires of Light: Edison, Tesla, Westinghouse, and the Race to Electrify the WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (87)